Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences) ›› 2023, Vol. 55 ›› Issue (3): 537-542. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2023.03.021
Previous Articles Next Articles
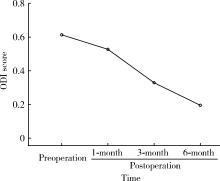
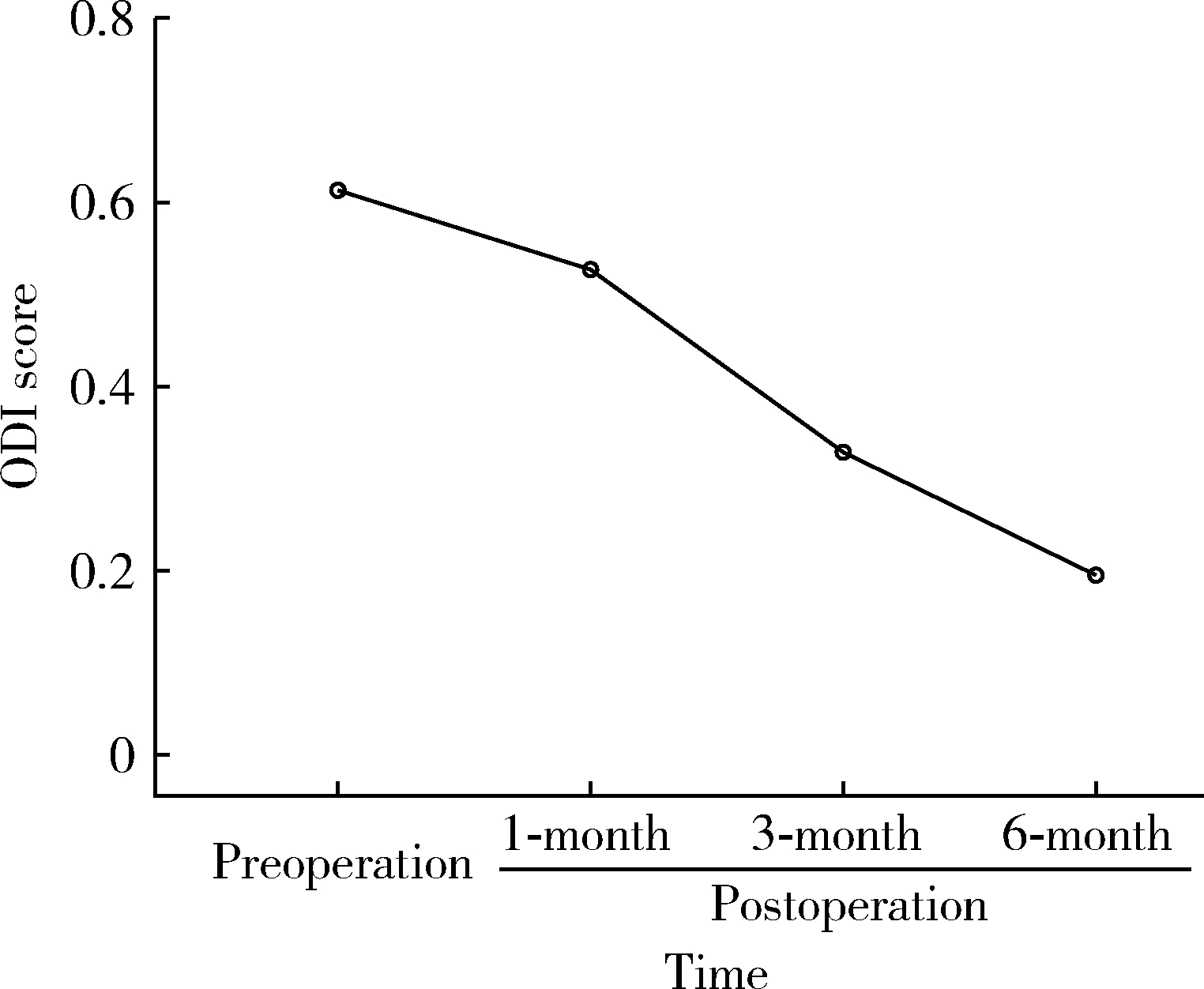
Influential factors related to functional status after full-endoscopic lumbar discectomy
Wei ZHU1,Bin ZHU1,2,*( ),Xiao-guang LIU1
),Xiao-guang LIU1
- 1. Department of Pain Medicine, Peking University Third Hospital, Beijing 100191, China
2. Department of Orthopedic, Beijing Friendship Hospital, Capital Medical University, Beijing 100050, China
CLC Number:
- R681.53
| 1 | 王琦, 倪家骧. 慢性疼痛的评估与治疗策略[J]. 中国医刊, 2005, 40 (4): 201- 203. |
| 2 |
Bair M , Wu J , Damush T , et al. Association of depression and anxiety alone and in combination with chronic musculoskeletal pain in primary care patients[J]. Psychosom Med, 2008, 70 (8): 890- 897.
doi: 10.1097/PSY.0b013e318185c510 |
| 3 | 刘丽丽, 王维宁. 疼痛日记对腰椎间盘突出症患者恐动症和恐惧回避信念的影响[J]. 护理学杂志, 2015, 30 (10): 25- 28. |
| 4 |
Shi R , Wang F , Hong X , et al. Comparison of percutaneous endoscopic lumbar discectomy versus microendoscopic discectomy for the treatment of lumbar disc herniation: A meta-analysis[J]. Int Orthop, 2019, 43 (4): 923- 937.
doi: 10.1007/s00264-018-4253-8 |
| 5 | 祝斌, 刘晓光, 李水清, 等. 内镜下无血管间隙减压技术治疗腰椎间盘突出症[J]. 中国疼痛医学杂志, 2017, 23 (2): 117- 121. |
| 6 | 符祖昶, 王清铿, 尤瑞金, 等. 经皮椎间孔镜治疗腰椎间盘突出症的临床效果[J]. 中国医药导报, 2017, 14 (18): 80- 83. |
| 7 | Watson J , Ryan C , Cooper L , et al. Pain neuroscience education for adults with chronic musculoskeletal pain: A mixed-methods systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. J Pain, 2019, 20 (10): 1140. e1- 1140. e22. |
| 8 | Louw A , Zimney K , Puentedura E , et al. The efficacy of pain neuroscience education on musculoskeletal pain: A systematic review of the literature[J]. Physiother Theory Pract, 2016, 32 (5): 332- 355. |
| 9 | Nijs J , Clark J , Malfliet A , et al. In the spine or in the brain? Recent advances in pain neuroscience applied in the intervention for low back pain[J]. Clin Exp Rheumatol, 2017, 107 (5): 108- 115. |
| 10 | Steenstra I , Munhall C , Irvin E , et al. Systematic review of prognostic factors for return to work in workers with sub-acute and chronic low back pain[J]. J Occup Rehabil, 2017, 27 (3): 369- 381. |
| [1] | Zhicun LI, Tianyu WU, Lei LIANG, Yu FAN, Yisen MENG, Qian ZHANG. Risk factors analysis and nomogram model construction of postoperative pathological upgrade of prostate cancer patients with single core positive biopsy [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(5): 896-901. |
| [2] | Ye YAN,Xiaolong LI,Haizhui XIA,Xuehua ZHU,Yuting ZHANG,Fan ZHANG,Ke LIU,Cheng LIU,Lulin MA. Analysis of risk factors for long-term overactive bladder after radical prostatectomy [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(4): 589-593. |
| [3] | Yan CHEN,Kuangmeng LI,Kai HONG,Shudong ZHANG,Jianxing CHENG,Zhongjie ZHENG,Wenhao TANG,Lianming ZHAO,Haitao ZHANG,Hui JIANG,Haocheng LIN. Retrospective study on the impact of penile corpus cavernosum injection test on penile vascular function [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(4): 680-686. |
| [4] | Bo PANG,Tongjun GUO,Xi CHEN,Huaqi GUO,Jiazhang SHI,Juan CHEN,Xinmei WANG,Yaoyan LI,Anqi SHAN,Hengyi YU,Jing HUANG,Naijun TANG,Yan WANG,Xinbiao GUO,Guoxing LI,Shaowei WU. Personal nitrogen oxides exposure levels and related influencing factors in adults over 35 years old in Tianjin and Shanghai [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(4): 700-707. |
| [5] | Jing HE,Zhongze FANG,Ying YANG,Jing LIU,Wenyao MA,Yong HUO,Wei GAO,Yangfeng WU,Gaoqiang XIE. Relationship between lipid metabolism molecules in plasma and carotid atheroscle-rotic plaques, traditional cardiovascular risk factors, and dietary factors [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(4): 722-728. |
| [6] | Shan CAI,Yihang ZHANG,Ziyue CHEN,Yunfe LIU,Jiajia DANG,Di SHI,Jiaxin LI,Tianyu HUANG,Jun MA,Yi SONG. Status and pathways of factors influencing physical activity time among elementary and junior high school students in Beijing [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(3): 403-410. |
| [7] | Zuhong ZHANG,Tianjiao CHEN,Jun MA. Associations between puberty timing and cardiovascular metabolic risk factors among primary and secondary students [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(3): 418-423. |
| [8] | Yuting LIN,Huali WANG,Yu TIAN,Litong GONG,Chun CHANG. Factors influencing cognitive function among the older adults in Beijing [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(3): 456-461. |
| [9] | Jinrong ZHU,Yana ZHAO,Wei HUANG,Weiwei ZHAO,Yue WANG,Song WANG,Chunyan SU. Clinical characteristics of COVID-19 infection in patients undergoing hemodialysis [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(2): 267-272. |
| [10] | Zhanhong LAI,Jiachen LI,Zelin YUN,Yonggang ZHANG,Hao ZHANG,Xiaoyan XING,Miao SHAO,Yuebo JIN,Naidi WANG,Yimin LI,Yuhui LI,Zhanguo LI. A unicenter real-world study of the correlation factors for complete clinical response in idiopathic inflammatory myopathies [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(2): 284-292. |
| [11] | Xiaoqian SI,Xiujuan ZHAO,Fengxue ZHU,Tianbing WANG. Risk factors for acute respiratory distress syndrome in patients with traumatic hemorrhagic shock [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(2): 307-312. |
| [12] | Yangyang LI,Lin HOU,Zijun MA,Shanyamei HUANG,Jie LIU,Chaomei ZENG,Jiong QIN. Association of pregnancy factors with cow's milk protein allergy in infants [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(1): 144-149. |
| [13] | Xiaoqiang LIU,Yin ZHOU. Risk factors of perioperative hypertension in dental implant surgeries with bone augmentation [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(1): 93-98. |
| [14] | Liang LUO,Yun LI,Hong-yan WANG,Xiao-hong XIANG,Jing ZHAO,Feng SUN,Xiao-ying ZHANG,Ru-lin JIA,Chun LI. Anti-endothelial cell antibodies in predicting early miscarriage [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(6): 1039-1044. |
| [15] | Yu-fei LI,Ya-ni YAN,Jia-yang JIN,Chun LI,Qiu-yan PEI. Clinical characteristics of fetal cardiac disease in patients with anti-SSA antibody positive [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(6): 1053-1057. |
|
||