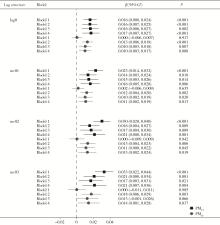
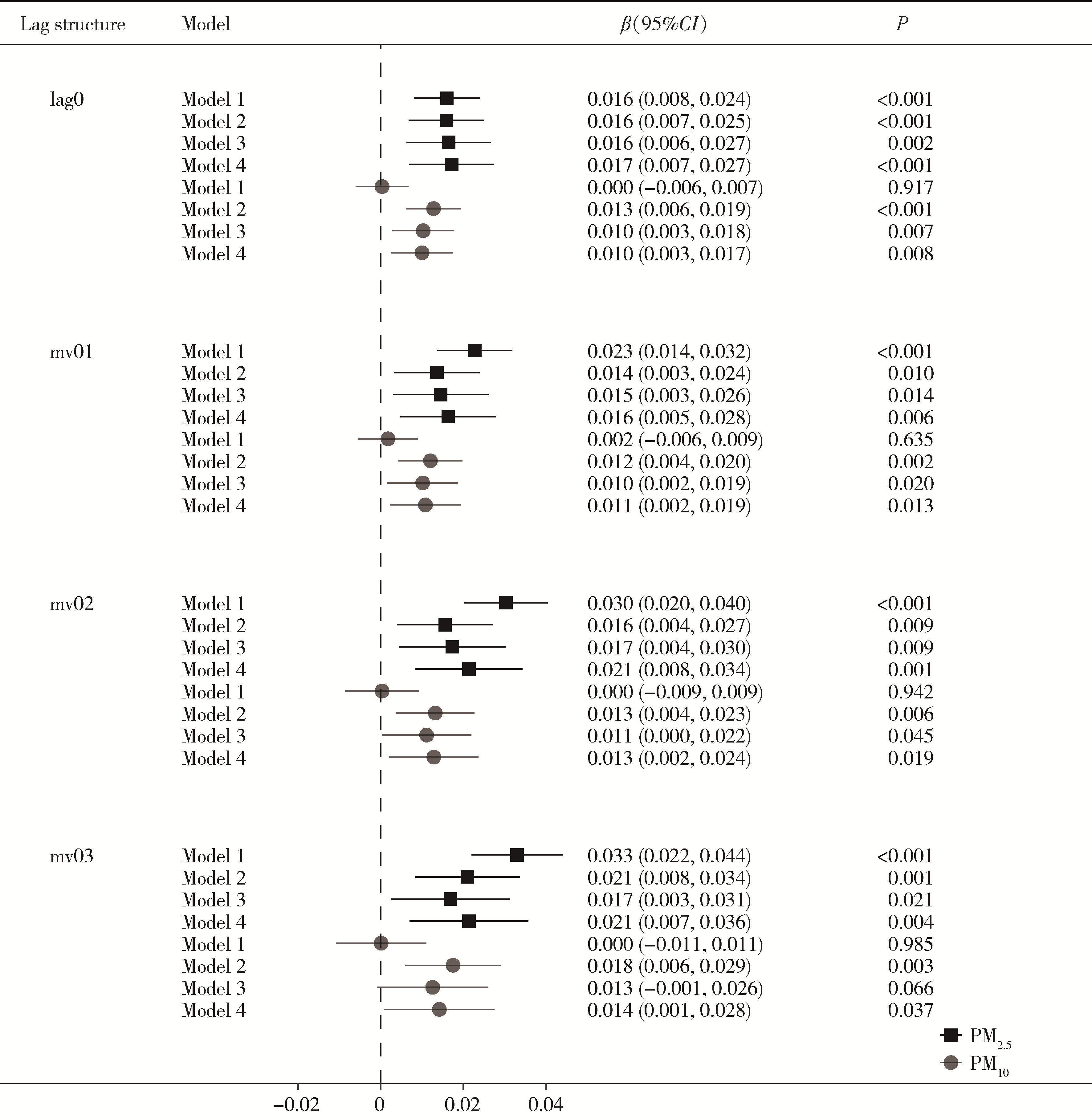
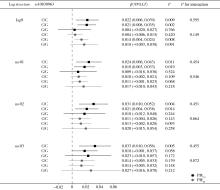
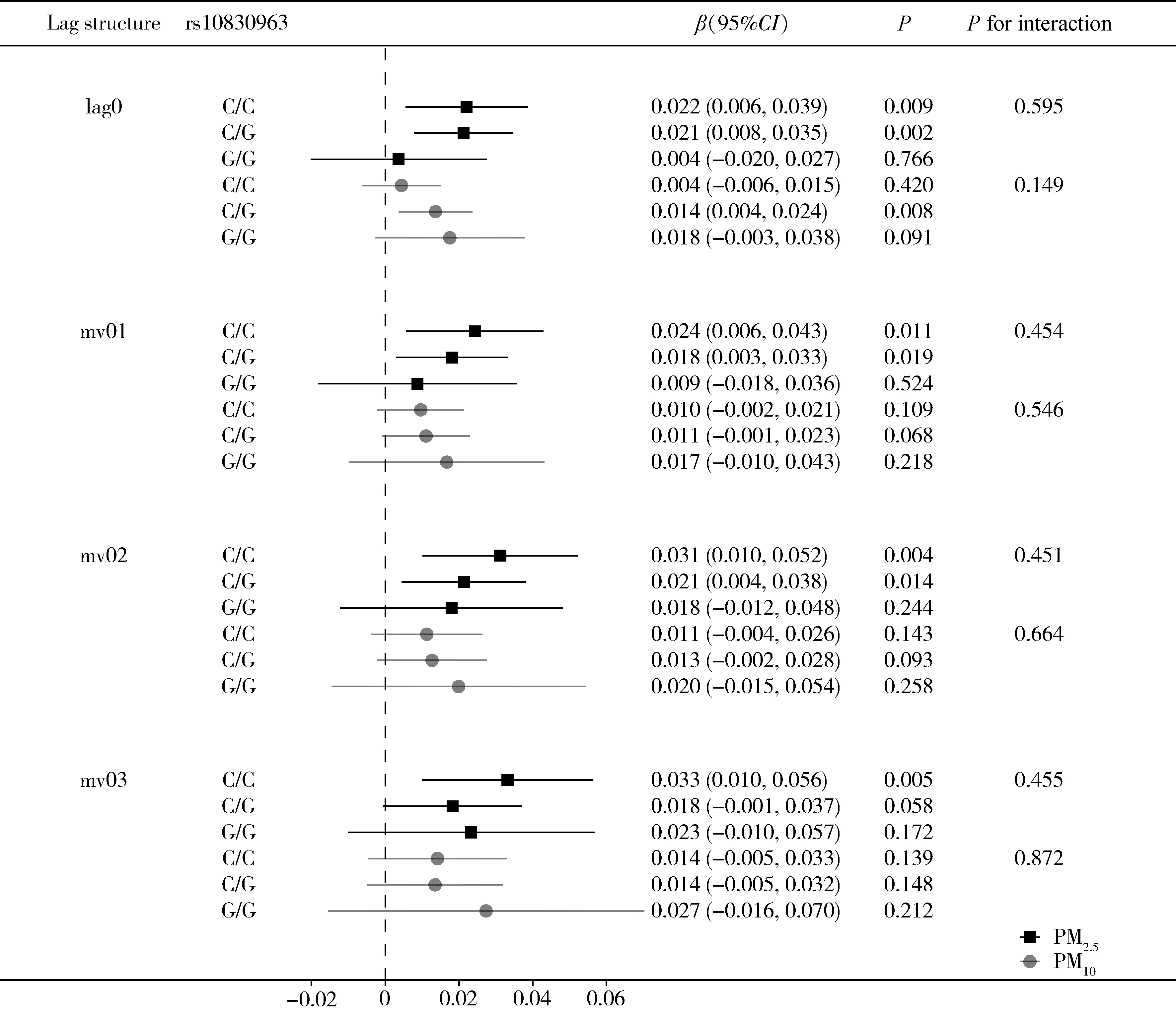
Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences) ›› 2024, Vol. 56 ›› Issue (3): 375-383. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2024.03.001
A ssociations of short-term ambient particulate matter exposure and MTNR1B gene with triglyceride-glucose index: A family-based study
Huangda GUO1,Hexiang PENG1,Siyue WANG1,Tianjiao HOU1,Yixin LI1,Hanyu ZHANG1,Mengying WANG2,3,Yiqun WU1,3,Xueying QIN1,3,Xun TANG1,3,Jing LI1,3,Dafang CHEN1,3,Yonghua HU1,3,Tao WU1,3,*( )
)
- 1. Department of Epidemiology and Biostatistics, Peking University School of Public Health, Beijing 100191, China
2. Department of Nutrition and Food Hygiene, Peking University School of Public Health, Beijing, 100191, China
3. Key Laboratory of Epidemiology of Major Diseases(Peking University), Ministry of Education, Beijing 100191, China
CLC Number:
- R122.2
| 1 |
Xiao D , Sun H , Chen L , et al. Assessment of six surrogate insulin resistance indexes for predicting cardiometabolic multimorbidity incidence in Chinese middle-aged and older populations: Insights from the China health and retirement longitudinal study[J]. Diabetes Metab Res Rev, 2024, 40 (1): e3764.
doi: 10.1002/dmrr.3764 |
| 2 |
Guerrero-Romero F , Simental-Mendía LE , González-Ortiz M , et al. The product of triglycerides and glucose, a simple measure of insulin sensitivity. Comparison with the euglycemic-hyperinsulinemic clamp[J]. J Clin Endocrinol Metab, 2010, 95 (7): 3347- 3351.
doi: 10.1210/jc.2010-0288 |
| 3 |
Zhang J , Yin B , Xi Y , et al. Triglyceride-glucose index is a risk factor for breast cancer in China: A cross-sectional study[J]. Lipids Health Dis, 2024, 23 (1): 29.
doi: 10.1186/s12944-024-02008-0 |
| 4 |
Hao B , Lyu L , Xu J , et al. The relationship between triglyceride-glucose index and prospective key clinical outcomes in patients hospitalised for coronary artery disease[J]. Cardiovasc Diabetol, 2024, 23 (1): 40.
doi: 10.1186/s12933-024-02132-2 |
| 5 |
Su W , Wang J , Chen K , et al. A higher TyG index level is more likely to have enhanced incidence of T2DM and HTN comorbidity in elderly Chinese people: A prospective observational study from the reaction study[J]. Diabetol Metab Syndr, 2024, 16 (1): 29.
doi: 10.1186/s13098-024-01258-3 |
| 6 | Dong W , Gong Y , Zhao J , et al. A combined analysis of TyG index, SII index, and SIRI index: Positive association with CHD risk and coronary atherosclerosis severity in patients with NAFLD[J]. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne), 2023, 14, 1281839. |
| 7 |
Peng H , Wang M , Wang S , et al. KCNQ1 rs2237892 polymorphism modify the association between short-term ambient particulate matter exposure and fasting blood glucose: A family-based study[J]. Sci Total Environ, 2023, 876, 162820.
doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2023.162820 |
| 8 |
Wu Y , Tian Y , Wang M , et al. Short-term exposure to air pollution and its interaction effects with two ABO SNPs on blood lipid levels in northern China: A family-based study[J]. Chemosphere, 2020, 249, 126120.
doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.126120 |
| 9 | Wang S , Wang M , Peng H , et al. Synergism of cell adhesion re-gulatory genes and instant air pollutants on blood pressure elevation[J]. Chemosphere, 2023, 312 (Pt 1): 136992. |
| 10 | Guo H , Wang M , Ye Y , et al. Short-term exposure to nitrogen dioxide modifies genetic predisposition in blood lipid and fasting plasma glucose: A pedigree-based study[J]. Biology (Basel), 2023, 12 (12): 1470. |
| 11 |
Pan M , Liu F , Zhang K , et al. Independent and interactive associations between greenness and ambient pollutants on novel glycolipid metabolism biomarkers: A national repeated measurement study[J]. Environ Res, 2023, 233, 116393.
doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2023.116393 |
| 12 | Liu F , Chen G , Huo W , et al. Associations between long-term exposure to ambient air pollution and risk of type 2 diabetes mellitus: A systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Environ Pollut, 2019, 252 (Pt B): 1235- 1245. |
| 13 |
Prokopenko I , Langenberg C , Florez JC , et al. Variants in MTNR1B influence fasting glucose levels[J]. Nat Genet, 2009, 41 (1): 77- 81.
doi: 10.1038/ng.290 |
| 14 |
Lyssenko V , Nagorny CL , Erdos MR , et al. Common variant in MTNR1B associated with increased risk of type 2 diabetes and impaired early insulin secretion[J]. Nat Genet, 2009, 41 (1): 82- 88.
doi: 10.1038/ng.288 |
| 15 |
Prokopenko I , Poon W , Mägi R , et al. A central role for GRB10 in regulation of islet function in man[J]. PLoS Genet, 2014, 10 (4): e1004235.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1004235 |
| 16 |
Garaulet M , Lopez-Minguez J , Dashti HS , et al. Interplay of dinner timing and MTNR1B type 2 diabetes risk variant on glucose tolerance and insulin secretion: A randomized crossover trial[J]. Diabetes Care, 2022, 45 (3): 512- 519.
doi: 10.2337/dc21-1314 |
| 17 | Xu XH , Kou LC , Wang HM , et al. Genetic polymorphisms of melatonin receptors 1A and 1B may result in disordered lipid metabolism in obese patients with polycystic ovary syndrome[J]. Mol Med Rep, 2019, 19 (3): 2220- 2230. |
| 18 |
Wang M , Wang S , Wang X , et al. Carotid intima-media thickness, genetic risk, and ischemic stroke: A family-based study in rural China[J]. Int J Environ Res Public Health, 2020, 18 (1): 119.
doi: 10.3390/ijerph18010119 |
| 19 |
Tian Y , Liu H , Zhao Z , et al. Association between ambient air pollution and daily hospital admissions for ischemic stroke: A nationwide time-series analysis[J]. PLoS Med, 2018, 15 (10): e1002668.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1002668 |
| 20 |
Zhan M , Li Z , Li X , et al. Effect of short-term ambient PM2.5 exposure on fasting blood glucose levels: A longitudinal study among 47 471 people in eastern China[J]. Environ Pollut, 2021, 290, 117983.
doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2021.117983 |
| 21 |
Chen L , Zhou Y , Li S , et al. Air pollution and fasting blood glucose: A longitudinal study in China[J]. Sci Total Environ, 2016, 541, 750- 755.
doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.09.132 |
| 22 |
Chen J , Wu L , Yang G , et al. The influence of PM2.5 exposure on non-alcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. Life Sci, 2021, 270, 119135.
doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2021.119135 |
| 23 |
Glencross DA , Ho TR , Camiña N , et al. Air pollution and its effects on the immune system[J]. Free Radic Biol Med, 2020, 151, 56- 68.
doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2020.01.179 |
| 24 |
Peng C , Bind MC , Colicino E , et al. Particulate air pollution and fasting blood glucose in nondiabetic individuals: Associations and epigenetic mediation in the normative aging study, 2000-2011[J]. Environ Health Perspect, 2016, 124 (11): 1715- 1721.
doi: 10.1289/EHP183 |
| 25 |
Ning R , Li Y , Du Z , et al. The mitochondria-targeted antioxidant MitoQ attenuated PM2.5-induced vascular fibrosis via regulating mitophagy[J]. Redox Biol, 2021, 46, 102113.
doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2021.102113 |
| 26 |
Sabatti C , Service SK , Hartikainen AL , et al. Genome-wide association analysis of metabolic traits in a birth cohort from a founder population[J]. Nat Genet, 2009, 41 (1): 35- 46.
doi: 10.1038/ng.271 |
| 27 |
Tuomi T , Nagorny CLF , Singh P , et al. Increased melatonin signaling is a risk factor for type 2 diabetes[J]. Cell Metab, 2016, 23 (6): 1067- 1077.
doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2016.04.009 |
| 28 |
Li C , Zhou Y , Qiao B , et al. Association between a melatonin receptor 1b genetic polymorphism and its protein expression in gestational diabetes mellitus[J]. Reprod Sci, 2019, 26 (10): 1382- 1388.
doi: 10.1177/1933719118765983 |
| 29 |
Garaulet M , Gómez-Abellán P , Rubio-Sastre P , et al. Common type 2 diabetes risk variant in MTNR1B worsens the deleterious effect of melatonin on glucose tolerance in humans[J]. Metabolism, 2015, 64 (12): 1650- 1657.
doi: 10.1016/j.metabol.2015.08.003 |
| 30 |
Xia AY , Zhu H , Zhao ZJ , et al. Molecular mechanisms of the melatonin receptor pathway linking circadian rhythm to type 2 diabetes mellitus[J]. Nutrients, 2023, 15 (6): 1406.
doi: 10.3390/nu15061406 |
| 31 |
Dubocovich ML , Delagrange P , Krause DN , et al. International union of basic and clinical pharmacology. LXXV. Nomenclature, classification, and pharmacology of G protein-coupled melatonin receptors[J]. Pharmacol Rev, 2010, 62 (3): 343- 380.
doi: 10.1124/pr.110.002832 |
| 32 | Mühlbauer E , Albrecht E , Bazwinsky-Wutschke I , et al. Melatonin influences insulin secretion primarily via MT(1) receptors in rat insulinoma cells (INS-1) and mouse pancreatic islets[J]. J Pineal Res, 2012, 52 (4): 446- 459. |
| 33 |
Stumpf I , Mühlbauer E , Peschke E . Involvement of the cGMP pathway in mediating the insulin-inhibitory effect of melatonin in pancreatic beta-cells[J]. J Pineal Res, 2008, 45 (3): 318- 327.
doi: 10.1111/j.1600-079X.2008.00593.x |
| [1] | Shengqi ZHENG,Tianchi HUA,Guicao YIN,Wei ZHANG,Ye YAO,Yifan LI. Association between the triglyceride-glucose index and the incidence of nephrolithiasis in male individuals [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(4): 610-616. |
| [2] | CHU Meng-tian, DONG Wei, CHI Rui, PAN Lu, LI Hong-yu, HU Da-yu, YANG Xuan, DENG Fu-rong, GUO Xin-biao. Effects of high-efficiency particulate air purifiers on indoor fine particulate matter and its constituents in a district of Beijing during winter [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2018, 50(3): 482-487. |
| [3] | WU Xiao-yin, LI Guo-xing, WANG Xu-ying, LIANG Feng-chao, PAN Xiao-chuan. Correlation study between respiratory death and airborne particles in Beijing: Spa-tiotemporal analysis based on satellite remote sensing data [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2017, 49(3): 409-417. |
| [4] | ZHANG Yi1, SONG Xiao-ming1, ZHAO Qian, WANG Tong, Li Li-juan, CHEN Jie, XU Hong-bing, LIU Bei-bei, SUN Xiao-yan, HE Bei, HUANG Wei. Effects of exposure to ambient particulate matter and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons on oxidative stress biomarkers in the patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2017, 49(3): 394-402. |
| [5] | FAN Ai-qin, FENG Jin-qiu, LIU Wei, ZHANG Min-jia, LIU Tan, ZHOU Ya-lin, XU Ya-jun. Antagonistic effect of quercetin on PM2.5 toxicity in the rat’s embryonic development in vitro [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2017, 49(3): 388-393. |
| [6] | YI Tie-Ci, LI Jian-Ping. Adverse effects of ultrafine particles on the cardiovascular system and its mechanisms [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2014, 46(6): 996-1000. |
| [7] | NI Yang, TU Xing-Ying, ZHU Yi-Dan, GUO Xin-Biao, DENG Fu-Rong. Concentrations of fine particulate matters and ultrafine particles and influenced actors during winter in an area of Beijing [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2014, 46(3): 389-394. |
|
||