Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences) ›› 2024, Vol. 56 ›› Issue (5): 809-814. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2024.05.009
Previous Articles Next Articles
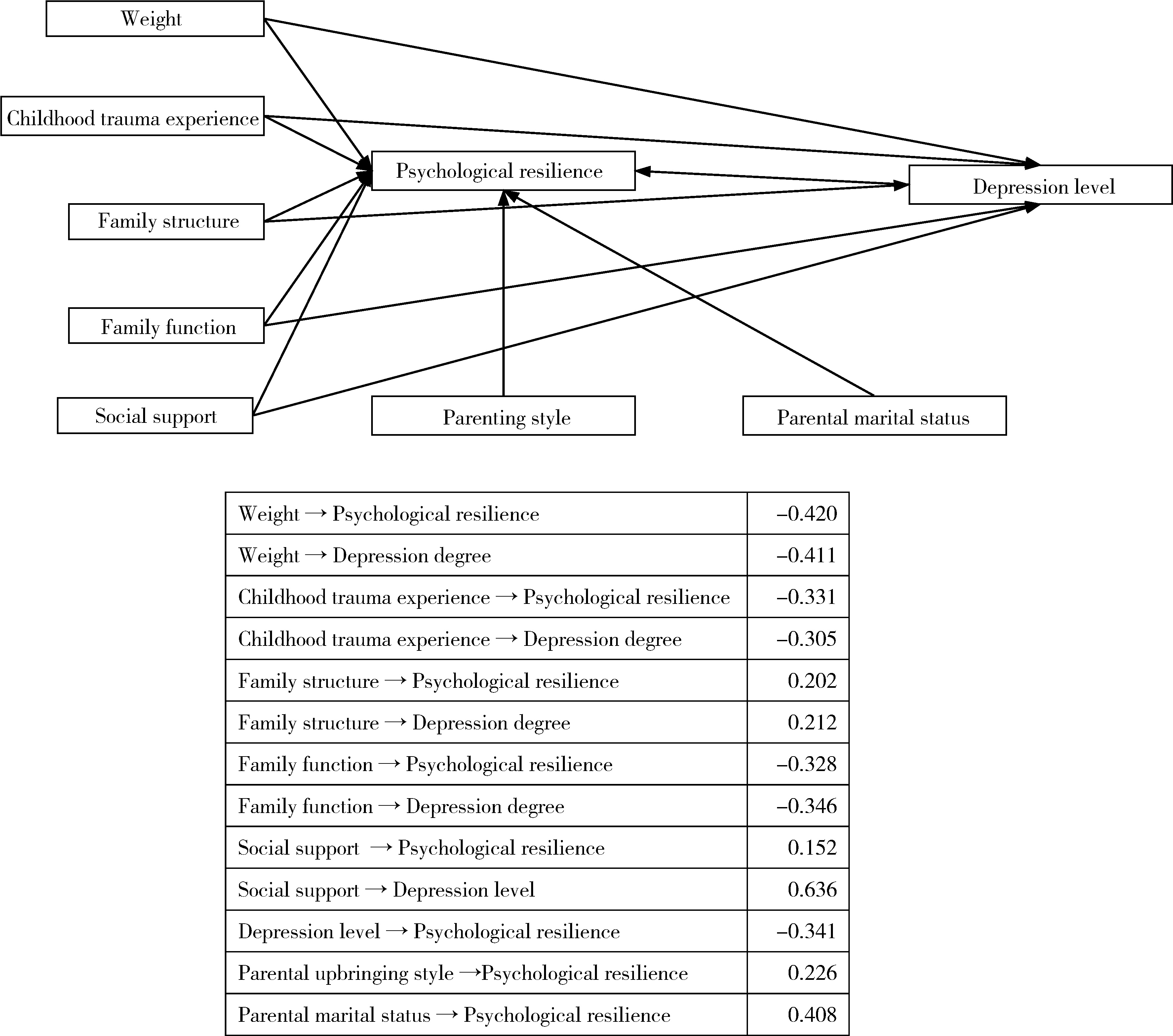
Path analysis of influencing factors of mental resilience in adolescents with depression
- Department of Psychology, Jiaozuo Fourth People ' s Hospital, Jiaozuo 454000, Henan, China
CLC Number:
- R749.4
| 1 |
Shorey S , Ng ED , Wong CHJ , et al. Global prevalence of depression and elevated depressive symptoms among adolescents: A systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Br J Clin Psychol, 2022, 61 (2): 287- 305.
doi: 10.1111/bjc.12333 |
| 2 |
Dwyer JB , Landeros-Weisenberger A , Johnson JA , et al. Efficacy of intravenous ketamine in adolescent treatment-resistant depression: A randomized midazolam-controlled trial[J]. Am J Psychiatry, 2021, 178 (4): 352- 362.
doi: 10.1176/appi.ajp.2020.20010018 |
| 3 | 徐莉, 赵锦涵, 金于雄, 等. 青少年抑郁症患者非自杀性自伤的相关因素[J]. 昆明医科大学学报, 2022, 43 (5): 58- 64. |
| 4 |
Wang MF , Lu X , Liu MH , et al. The mediating effect of psychological resilience on the level of mindfulness and general well-being in patients with inflammatory bowel disease[J]. Ann Palliat Med, 2021, 10 (8): 9215- 9222.
doi: 10.21037/apm-21-2053 |
| 5 | 周晓璇, 叶海森. 青少年抑郁症患者心理弹性与父母养育方式, 自我接纳程度相关性分析[J]. 精神医学杂志, 2021, 34 (4): 304- 307. |
| 6 | 抑郁障碍中西医整合诊治专家共识组, 中国民族医药学会神志病分会. 抑郁障碍中西医整合专家共识[J]. 中国医药导报, 2021, 18 (6): 4- 12. |
| 7 |
刘莉莉, 孔凡贞, 季彩芳, 等. 反刍思维对首发抑郁症患者1年结局的影响: 家庭功能的中介作用[J]. 中华行为医学与脑科学杂志, 2022, 31 (10): 887- 892.
doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn371468-20220402-00157 |
| 8 | 吴秋彦, 邱丹, 肖水源. 新冠肺炎防控常态化期间医务人员睡眠质量与社会支持的关系[J]. 中国心理卫生杂志, 2023, 37 (5): 442- 448. |
| 9 | 郑春叶, 蔡巧娣, 陈信捷, 等. 柴甘解忧汤联合重复经颅磁刺激对帕金森病合并轻中度抑郁的随机对照研究[J]. 中国中西医结合杂志, 2022, 42 (11): 1312- 1317. |
| 10 | 李健, 祁娜. 慢性前列腺炎/慢性盆腔疼痛综合征患者的心理弹性及其影响因素分析[J]. 中国性科学, 2022, 31 (12): 60- 63. |
| 11 | 李文俊, 布龙华, 郑竻云, 等. 抑郁症患者心理弹性与自尊水平及自我病耻感相关性分析[J]. 临床心身疾病杂志, 2023, 28 (3): 95- 97. |
| 12 | Chen N , Xi JZ , Fan XW , et al. Correlations among psychological resilience, cognitive fusion, and depressed emotions in patients with depression[J]. Behav Sci (Basel), 2023, 13 (2): 100. |
| 13 | 黄欣欣, 李雨婷, 陈剑华, 等. 家庭结构对青少年抑郁和焦虑症状的影响: 情感忽视的中介作用[J]. 中国当代儿科杂志, 2023, 25 (1): 80- 85. |
| 14 | Martinez AB , Co M , Lau J , et al. Filipino help-seeking for mental health problems and associated barriers and facilitators: A syste-matic review[J]. Soc Psychiatry Psychiatr Epidemiol, 2020, 55 (11): 1397- 1413. |
| 15 | Huang JG , Xu LL , Xu Z , et al. The relationship among pregnancy-related anxiety, perceived social support, family function and resilience in Chinese pregnant women: A structural equation modeling analysis[J]. BMC Womens Health, 2022, 22 (1): 546. |
| 16 | Peleg O , Tzischinsky O , Spivak-Lavi Z , et al. Depression and social anxiety mediate the relationship between parenting styles and risk of eating disorders: A study among Arab adolescents[J]. Int J Psychol, 2021, 56 (6): 853- 864. |
| 17 | Forbes EE , Eckstrand KL , Rofey DL , et al. A social affective neuroscience model of risk and resilience in adolescent depression: Preliminary evidence and application to sexual and gender minority adolescents[J]. Biol Psychiatry Cogn Neurosci Neuroimaging, 2021, 6 (2): 188- 199. |
| 18 | Dong CQ , Xu R , Xu LQ , et al. Relationship of childhood trauma, psychological resilience, and family resilience among undergraduate nursing students: A cross-sectional study[J]. Perspect Psychiatr Care, 2021, 57 (2): 852- 859. |
| 19 | 马冰, 黄求进, 王晓春. 黑龙江省男护士心理弹性在社会支持和简单应对方式间的中介作用[J]. 中国实用护理杂志, 2021, 37 (32): 2500- 2505. |
| 20 | Moradi M , Mozaffari H , Askari M , et al. Association between overweight/obesity with depression, anxiety, low self-esteem, and body dissatisfaction in children and adolescents: A systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies[J]. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr, 2022, 62 (2): 555- 570. |
| [1] | Yuanyuan ZENG,Yun XIE,Daonan CHEN,Ruilan WANG. Related factors of euthyroid sick syndrome in patients with sepsis [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(3): 526-532. |
| [2] | Huameng TANG,Dianqi YUAN,Mingxing WANG,Hanbing YANG,Chao GUO. Sequential mediating role of digital participation and health lifestyle in the relationship between socioeconomic status and depression of older adults [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(2): 230-238. |
| [3] | Xiaohan LIU,Fan YANG,Xindi WANG,Ning HUANG,Taozhu CHENG,Jing GUO. Related factors and equity of health status among floating population in China based on geographic information system analysis [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(2): 223-229. |
| [4] | Silan AN,Qunyi ZHENG,Kai WANG,Shan GAO. Characteristics and influencing factors of early pain in patients after total knee arthroplasty [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(1): 167-173. |
| [5] | Jin-hui LAI,Qi WANG,Jia-xiang JI,Ming-rui WANG,Xin-wei TANG,Ke-xin XU,Tao XU,Hao HU. Effects of delayed ureteral stents removal during the COVID-19 pandemic on the quality of life and psychological status of postoperative patients with urinary calculi [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(5): 857-864. |
| [6] | Wen YUAN,Yi ZHANG,Li CHEN,Jia-nuo JIANG,Man-man CHEN,Jie-yu LIU,Tao MA,Qi MA,Meng-jie CUI,Tong-jun GUO,Xin-xin WANG,Yan-hui DONG,Jun MA. Association of body fat distribution with depression and social anxiety in children and adolescents: A cross-sectional study based on dual-energy X-ray detection [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(3): 429-435. |
| [7] | FAN Li-shi,GAO Min,Edwin B. FISHER,SUN Xin-ying. Factors associated with quality of life in 747 patients with type 2 diabetes in Tongzhou District and Shunyi District of Beijing [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2021, 53(3): 523-529. |
| [8] | Yi-fan WANG,Zhen FAN,Yao-bin CHENG,Yue-bo JIN,Yang HUO,Jing HE. Investigation of sleep disturbance and related factors in patients with primary Sjögren’s syndrome [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2020, 52(6): 1063-1068. |
| [9] | Yan GENG,Zhi-bo SONG,Xiao-hui ZHANG,Xue-rong DENG,Yu WANG,Zhuo-li ZHANG. Depression and anxiety in patients with psoriatic arthritis: Prevalence and associated factors [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2020, 52(6): 1048-1055. |
| [10] | Duan YI,Wei ZHU,Xiu-li MENG,Xiao-guang LIU,Shui-qing LI,Bin ZHU,Dong-lin JIA. Analysis of anxiety, depression and related factors in patients with chronic lumbocrural pain before minimally invasive surgery [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2020, 52(2): 285-289. |
| [11] | JING Ri-ze, ZHANG Hu-yang, XU Ting-ting, ZHANG Lu-yu, FANG Hai. Study on the efficiency of tertiary public hospitals and its influencing factors in Beijing [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2018, 50(3): 408-415. |
| [12] | LEI Jie,LIU Mu-qing,FU Kai-yuan. Disturbedsleep, anxiety and stress are possible risk indicators for temporomandibular disorders with myofascialpain [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2016, 48(4): 692-696. |
| [13] | LIU Yi-Xuan, ZHANG Yong-Shen, DUAN Li-Ping, ZHANG Lu, YANG Chang-Qing. Effect of inherent depression on chronic visceral hypersensitivity induced by colon acetate stimulation in neonatal rats [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2015, 47(2): 289-294. |
|
||