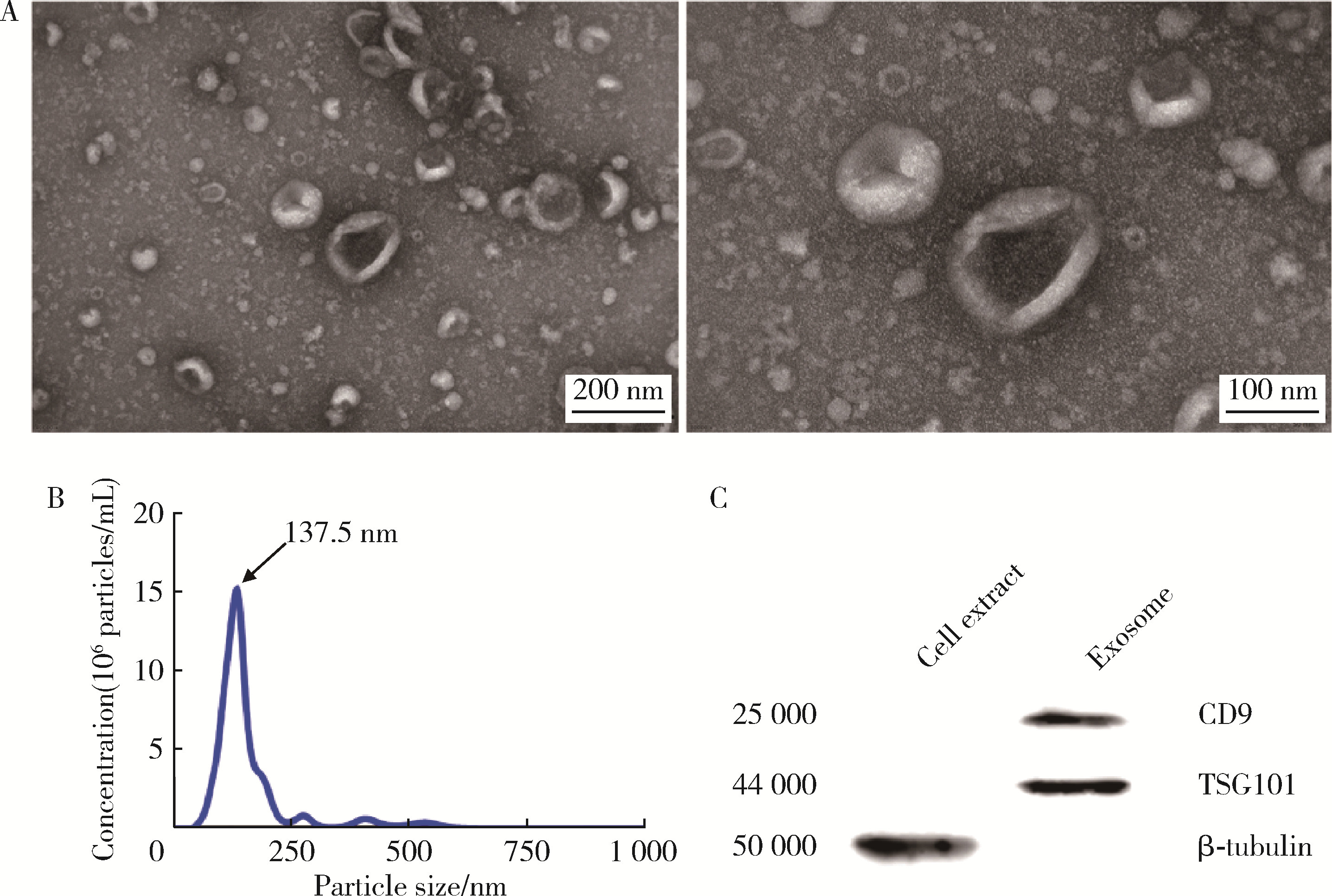
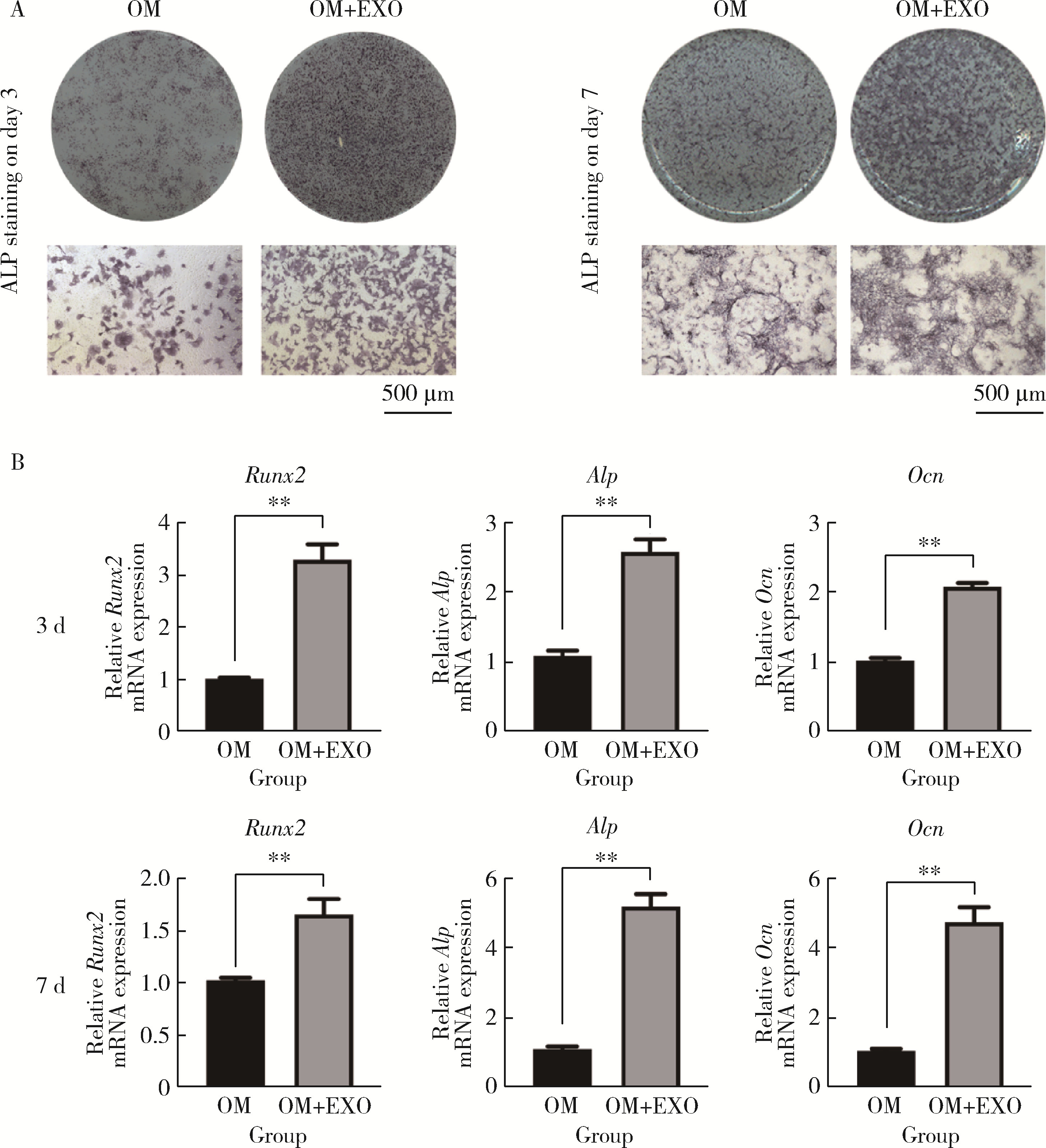
Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences) ›› 2025, Vol. 57 ›› Issue (2): 217-226. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2025.02.001
Exosome derived from human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells prevented bone loss induced by estrogen deficiency
Chunhui SHENG, Xiao ZHANG, Longwei LV*( ), Yongsheng ZHOU*(
), Yongsheng ZHOU*( )
)
- Department of Prosthodontics, Peking University School and Hospital of Stomatology & National Center for Stomatology & National Clinical Research Center for Oral Diseases & National Engineering Research Center of Oral Biomaterials and Digi-tal Medical Devices & National Health Commission Key Laboratory of Digital Stomatology, Beijing 100081, China
CLC Number:
- R787
| 1 |
Brown C . Osteoporosis: Staying strong[J]. Nature, 2017, 550 (7674): 15- 17.
doi: 10.1038/nature.2017.22694 |
| 2 |
中华医学会骨质疏松和骨矿盐疾病分会. 中国骨质疏松症流行病学调查及"健康骨骼"专项行动结果发布[J]. 中华骨质疏松和骨矿盐疾病杂志, 2019, 12 (4): 317- 318.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-2591.2019.04.001 |
| 3 | Kerschan-Schindl K . Prevention and rehabilitation of osteoporosis[J]. Wien Med Wochenschr, 2016, 166 (1/2): 22- 27. |
| 4 | Harvey NC , McCloskey E , Kanis JA , et al. Bisphosphonates in osteoporosis: NICE and easy?[J]. Lancet, 2017, 390 (10109): 2243- 2244. |
| 5 |
Rossouw JE , Anderson GL , Prentice RL , et al. Risks and benefits of estrogen plus progestin in healthy postmenopausal women: Principal results from the Women' s Health Initiative randomized controlled trial[J]. JAMA, 2002, 288 (3): 321- 333.
doi: 10.1001/jama.288.3.321 |
| 6 |
Phetfong J , Sanvoranart T , Nartprayut K , et al. Osteoporosis: The current status of mesenchymal stem cell-based therapy[J]. Cell Mol Biol Lett, 2016, 21, 12.
doi: 10.1186/s11658-016-0013-1 |
| 7 |
Berkowitz AL , Miller MB , Mir SA , et al. Glioproliferative lesion of the spinal cord as a complication of "stem-cell tourism"[J]. N Engl J Med, 2016, 375 (2): 196- 198.
doi: 10.1056/NEJMc1600188 |
| 8 | Sadat-Ali M , Al-Dakheel DA , Al-Mousa SA , et al. Stem-cell therapy for ovariectomy-induced osteoporosis in rats: A comparison of three treatment modalities[J]. Stem Cells Cloning, 2019, 12, 17- 25. |
| 9 |
Liew LC , Katsuda T , Gailhouste L , et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles: A glimmer of hope in treating Alzheimer' s disease[J]. Int Immunol, 2017, 29 (1): 11- 19.
doi: 10.1093/intimm/dxx002 |
| 10 | Li G , Zhang Y , Wu J , et al. Adipose stem cells-derived exosomes modified gelatin sponge promotes bone regeneration[J]. Front Bioeng Biotechnol, 2023, 11, 1096390. |
| 11 |
Soleimani M , Nadri S . A protocol for isolation and culture of mesenchymal stem cells from mouse bone marrow[J]. Nat Protoc, 2009, 4 (1): 102- 106.
doi: 10.1038/nprot.2008.221 |
| 12 |
Luo ZW , Li FX , Liu YW , et al. Aptamer-functionalized exosomes from bone marrow stromal cells target bone to promote bone regeneration[J]. Nanoscale, 2019, 11 (43): 20884- 20892.
doi: 10.1039/C9NR02791B |
| 13 |
Chen S , Zheng Y , Zhang S , et al. Promotion effects of miR-375 on the osteogenic differentiation of human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells[J]. Stem Cell Reports, 2017, 8 (3): 773- 786.
doi: 10.1016/j.stemcr.2017.01.028 |
| 14 |
Lv L , Ge W , Liu Y , et al. Lysine-specific demethylase 1 inhibitor rescues the osteogenic ability of mesenchymal stem cells under osteoporotic conditions by modulating H3K4 methylation[J]. Bone Res, 2016, 4, 16037.
doi: 10.1038/boneres.2016.37 |
| 15 | Li L , Wang Z . Ovarian aging and osteoporosis[J]. Adv Exp Med Biol, 2018, 1086, 199- 215. |
| 16 |
Garnero P , Chapuy MC , Pierre D . Increased bone turnover in late postmenopausal women is a major determinant of osteoporosis[J]. J Bone Miner Res, 1996, 11 (3): 337- 349.
doi: 10.1002/jbmr.5650110307 |
| 17 |
Shen G , Ren H , Shang Q , et al. Foxf1 knockdown promotes BMSC osteogenesis in part by activating the Wnt/beta-catenin signalling pathway and prevents ovariectomy-induced bone loss[J]. EBioMedicine, 2020, 52, 102626.
doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2020.102626 |
| 18 |
Prockop DJ . Marrow stromal cells as stem cells for nonhemato-poietic tissues[J]. Science, 1997, 276 (5309): 71- 74.
doi: 10.1126/science.276.5309.71 |
| 19 |
Pittenger MF , Mackay AM , Beck SC , et al. Multilineage potential of adult human mesenchymal stem cells[J]. Science, 1999, 284 (5411): 143- 147.
doi: 10.1126/science.284.5411.143 |
| 20 |
Li W , Liu Y , Zhang P , et al. Tissue-engineered bone immobilized with human adipose stem cells-derived exosomes promotes bone regeneration[J]. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces, 2018, 10 (6): 5240- 5254.
doi: 10.1021/acsami.7b17620 |
| 21 | Huang T , Yu Z , Yu Q , et al. Inhibition of osteogenic and adipogenic potential in bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells under osteoporosis[J]. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2020, 525 (4): 902- 908. |
| 22 |
Mohamed-Ahmed S , Fristad I , Lie SA , et al. Adipose-derived and bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells: A donor-matched comparison[J]. Stem Cell Res Ther, 2018, 9 (1): 168.
doi: 10.1186/s13287-018-0914-1 |
| 23 |
Ibrahim A , Marban E . Exosomes: Fundamental biology and roles in cardiovascular physiology[J]. Annu Rev Physiol, 2016, 78, 67- 83.
doi: 10.1146/annurev-physiol-021115-104929 |
| 24 |
Zhou Y , Xu H , Xu W , et al. Exosomes released by human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells pr otect against cisplatin-induced renal oxidati ve stress and apoptosis in vivo and in vitro[J]. Stem Cell Res Ther, 2013, 4 (2): 34.
doi: 10.1186/scrt194 |
| 25 |
Zhang B , Wang M , Gong A , et al. HucMSC-exosome mediated-Wnt4 signaling is required for cutaneous wound healing[J]. Stem Cells, 2015, 33 (7): 2158- 2168.
doi: 10.1002/stem.1771 |
| 26 | Zuo R , Liu M , Wang Y , et al. BM-MSC-derived exosomes alle-viate radiation-induced bone loss by restoring the function of recipient BM-MSCs and activating Wnt/beta-catenin signaling[J]. Stem Cell Res Ther, 2019, 10 (1): 30. |
| 27 | Yang BC , Kuang MJ , Kang JY , et al. Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes act via the miR-1263/Mob1/Hippo signaling pathway to prevent apoptosis in disuse osteoporosis[J]. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2020, 524 (4): 883- 889. |
| 28 | Wang X , Omar O , Vazirisani F , et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes have altered microRNA profiles and induce osteogenic differentiation depending on the stage of differentiation[J]. PLoS One, 2018, 13 (2): e0193059. |
| 29 | Liu T , Hu W , Zou X , et al. Human periodontal ligament stem cell-derived exosomes promote bone regeneration by altering microRNA profiles[J]. Stem Cells Int, 2020, 2020, 8852307. |
| 30 | Wang L , Pan Y , Liu M , et al. Wen-Shen-Tong-Luo-Zhi-Tong Decoction regulates bone-fat balance in osteoporosis by adipocyte-derived exosomes[J]. Pharm Biol, 2023, 61 (1): 568- 580. |
| 31 | Wiklander OP , Nordin JZ , O' Loughlin A , et al. Extracellular vesicle in vivo biodistribution is determined by cell source, route of administration and targeting[J]. J Extracell Vesicles, 2015, 4, 26316. |
| 32 | Song H , Li X , Zhao Z , et al. Reversal of osteoporotic activity by endothelial cell-secreted bone targeting and biocompatible exosomes[J]. Nano Lett, 2019, 19 (5): 3040- 3048. |
| [1] | Ju YANG, Yue LIU, Chunna QU, Jianbin SUN, Tianying LI, Lianjie SHI. Bisphosphonates-related osteonecrosis of the jaw: A case report [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2025, 57(2): 388-392. |
| [2] | Ting SHUAI, Yanyan GUO, Chunping LIN, Xiaomei HOU, Chanyuan JIN. Knockdown of NPTX1 promotes osteogenic differentiation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2025, 57(1): 7-12. |
| [3] | Yibo HU, Weijia LYU, Wei XIA, Yihong LIU. Hydrodynamic finite element analysis of biological scaffolds with different pore sizes for cell growth and osteogenic differentiation [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2025, 57(1): 97-105. |
| [4] | Zhihui WU, Mingzhi HU, Qiaoying ZHAO, Fengfeng LV, Jingying ZHANG, Wei ZHANG, Yongfu WANG, Xiaolin SUN, Hui WANG. Immunomodulatory mechanism of umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells modified by miR-125b-5p in systemic lupus erythematosus [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(5): 860-867. |
| [5] | Xinzhu BAI,Jinhui HE,Songsong LU,Chun LI,Yilin WANG,Jian XIONG. Vertebral fractures combined with prolonged activated partial prothrombin time: A case report [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(2): 371-374. |
| [6] | Wen-gen LI,Xiao-dong GU,Rui-qiang WENG,Su-dong LIU,Chao CHEN. Expression and clinical significance of plasma exosomal miR-34-5p and miR-142-3p in systemic sclerosis [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(6): 1022-1027. |
| [7] | Da-wei WANG,Hua-dong WANG,Li LI,Xin YIN,Wei HUANG,Ji-dong GUO,Ya-feng YANG,Yi-hao LIU,Yang ZHENG. Efficacy analysis of autologous facet joint bone block in lumbar interbody fusion of osteoporosis patients [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(5): 899-909. |
| [8] | Yu-yang YE,Lin YUE,Xiao-ying ZOU,Xiao-yan WANG. Characteristics and microRNA expression profile of exosomes derived from odontogenic dental pulp stem cells [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(4): 689-696. |
| [9] | Chao HAN,Zhu-xing ZHOU,You-rong CHEN,Zi-hui DONG,Jia-kuo YU. Biological characteristics of sheep peripheral blood mesenchymal stem cell [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(6): 1151-1157. |
| [10] | SHUAI Ting,LIU Juan,GUO Yan-yan,JIN Chan-yuan. Knockdown of long non-coding RNA MIR4697 host gene inhibits adipogenic differentiation in bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(2): 320-326. |
| [11] | PANG Yong,ZHANG Sha,YANG Hua,ZHOU Rou-li. Serum LAPTM4B-35 protein as a novel diagnostic marker for hepatocellular carcinoma [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2021, 53(4): 710-715. |
| [12] | Xiang-song BAI,Long-wei LV,Yong-sheng ZHOU. Tribbles pseudokinase 3 inhibits the adipogenic differentiation of human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2020, 52(1): 1-9. |
| [13] | Jie ZHU,Jian-hong LI,Ting-ting YUAN,Lu He,Yu-hong LIANG. Relationship between periodontitis and osteoporosis in postmenopausal women [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2019, 51(6): 1115-1118. |
| [14] | Peng WANG,Hua WU,Ying CHE,Dong-wei FAN,Jue LIU,Li-yuan TAO. Evaluation of screening accuracy on osteoporosis self-assessment tool for Asians and its cut-off value in healthy physical examination population [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2019, 51(6): 1085-1090. |
| [15] | Jing XIE,Yu-ming ZHAO,Nan-quan RAO,Xiao-tong WANG,Teng-jiao-zi FANG,Xiao-xia LI,Yue ZHAI,Jing-zhi LI,Li-hong GE,Yuan-yuan WANG. Comparative study of differentiation potential of mesenchymal stem cells derived from orofacial system into vascular endothelial cells [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2019, 51(5): 900-906. |
|
||