北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2021, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (4): 758-763. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2021.04.023
载药脂质体修饰的聚醚醚酮植入物的抑菌和骨整合性能
王立新1,许晓2,Δ( ),倪耀丰1,孙海涛1,余日月1,魏世成2,Δ(
),倪耀丰1,孙海涛1,余日月1,魏世成2,Δ( )
)
- 1.首都医科大学附属北京世纪坛医院口腔科, 北京 100038
2.北京大学口腔医学院·口腔医院,口腔颌面外科 国家口腔医学中心 国家口腔疾病临床医学研究中心 口腔数字化医疗技术和材料国家工程实验室, 北京 100081
In vivo study of liposome-modified polyetheretherketone implant on bacteriostasis and osseointegration
WANG Li-xin1,XU Xiao2,Δ( ),NI Yao-feng1,SUN Hai-tao1,YU Ri-yue1,WEI Shi-cheng2,Δ(
),NI Yao-feng1,SUN Hai-tao1,YU Ri-yue1,WEI Shi-cheng2,Δ( )
)
- 1. Department of Stomatology, Beijing Shijitan Hospital, Capital Medical University, Beijing 100038, China
2. Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Peking University School and Hospital of Stomatology & National Center of Stomatology & National Clinical Research Center for Oral Diseases & National Engineering Laboratory for Digital and Material Technology of Stomatology, Beijing 100081, China
摘要:
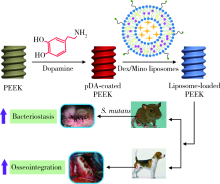
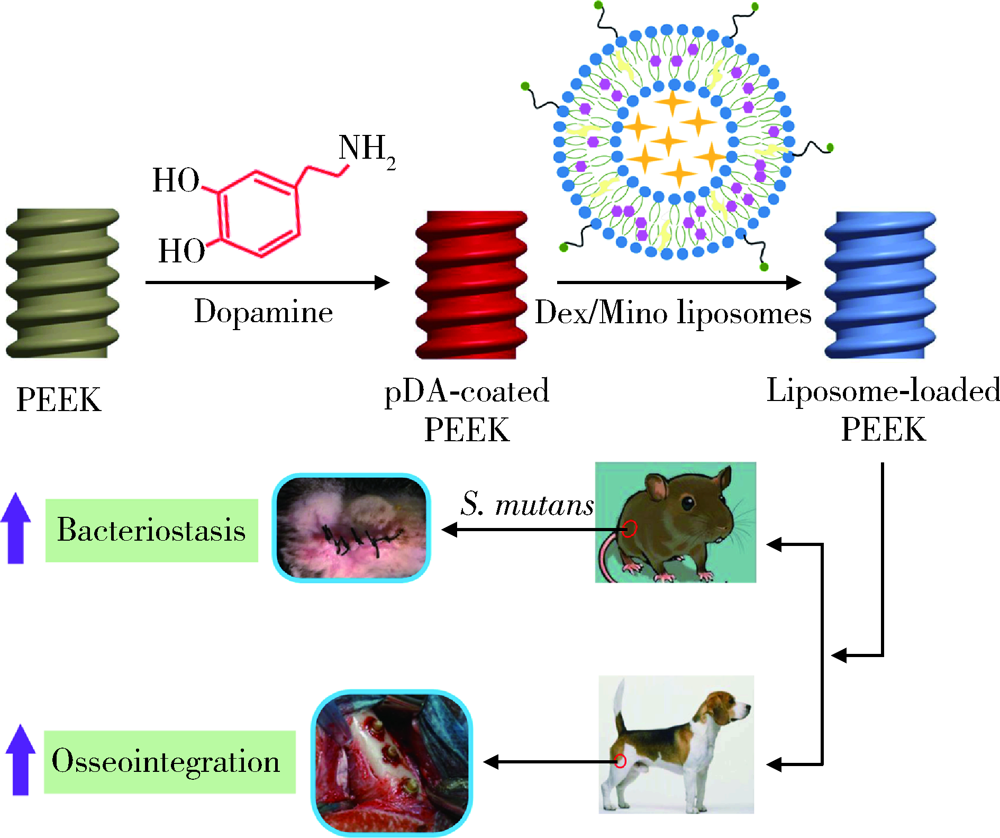
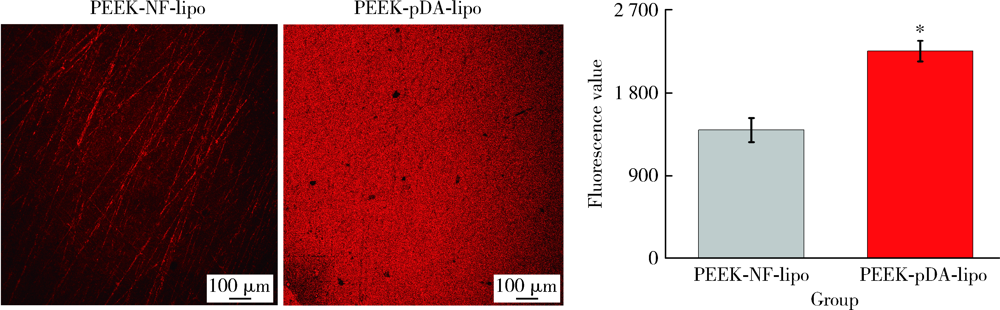
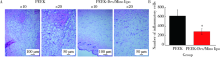
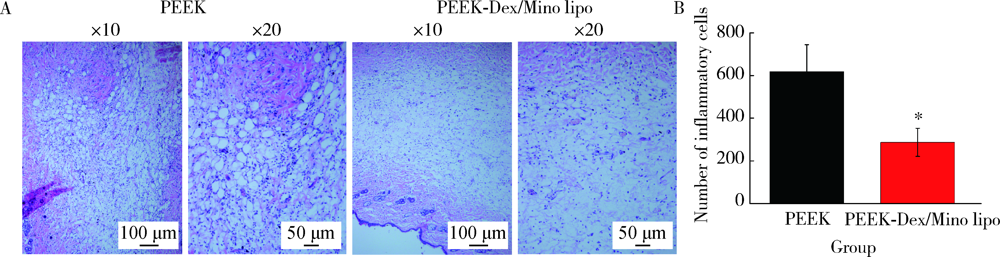
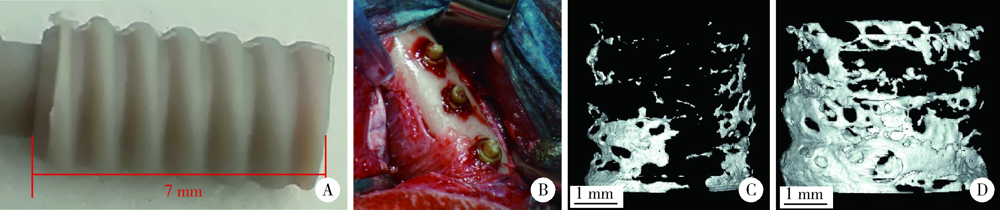
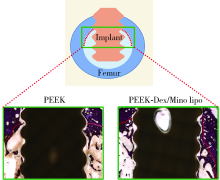
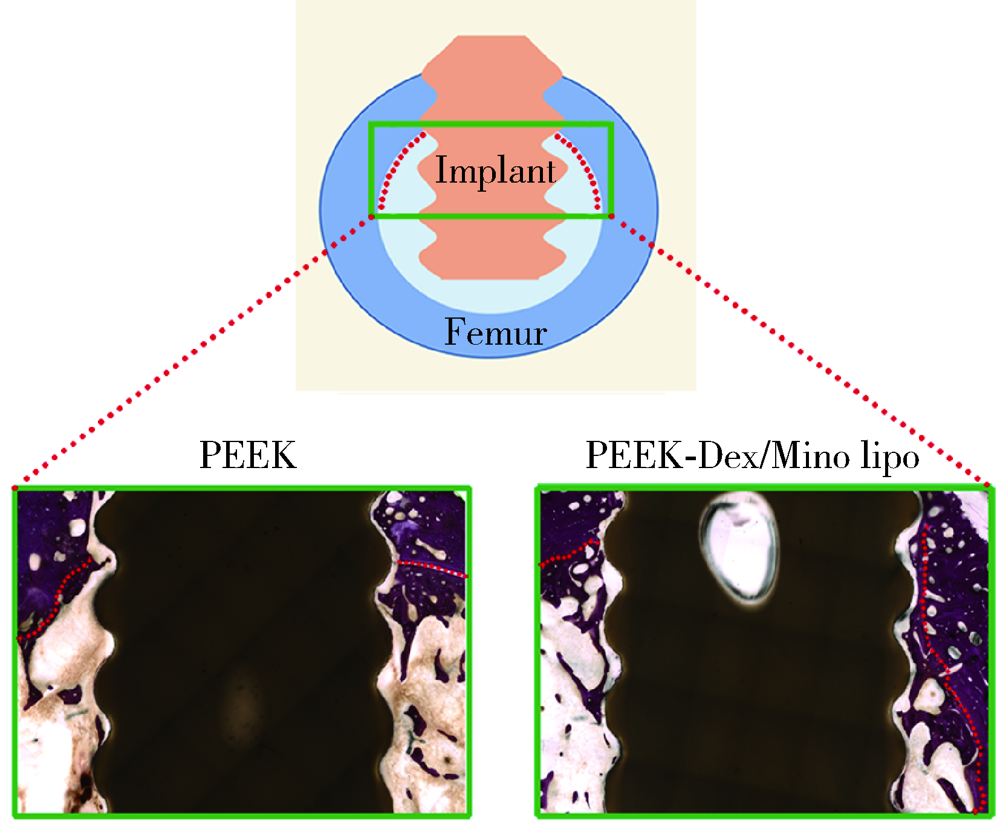
目的: 制备地塞米松/米诺环素(dexamethasone/minocycline,Dex/Mino)脂质体(liposome,lipo)修饰的聚醚醚酮(polyetheretherketone,PEEK),探究功能化PEEK在体内应用时是否能有效预防感染且促进新骨再生,实现生理骨整合。方法: 利用聚多巴胺(polydopamine,pDA)涂层作中间介质,将Dex/Mino脂质体修饰到PEEK表面,通过荧光脂质体接枝进行定性和定量检测,评价脂质体是否成功共价修饰在该表面。分别建立小鼠皮下植入感染模型和比格犬股骨植入模型,通过Micro-CT及苏木精-伊红(hematoxylin-eosin,HE)染色分析,评价Dex/Mino脂质体修饰的PEEK的体内生物活性。结果: 荧光脂质体接枝定性和定量结果显示,pDA功能化修饰组的红色荧光强度强于非功能化修饰组(P<0.05),由于pDA涂层的存在,脂质体成功接枝于PEEK表面并在其表面均匀分布。小鼠皮下PEEK片植入24 h后,HE染色结果显示,与纯PEEK组相比,PEEK-Dex/Mino lipo组的炎性细胞数量较低(P<0.05),即感染程度较低,提示脂质体中Mino的释放在体内能有效地预防感染。比格犬股骨植入8周后,Micro-CT和HE染色结果显示,在PEEK-Dex/Mino lipo组中,新骨形成比纯PEEK组多,且牢固地结合在功能化修饰的PEEK表面,沿着PEEK界面延伸,提示脂质体中Dex的释放在体内有效地刺激和引导了新骨再生。结论: Dex/Mino脂质体修饰提高了惰性PEEK的生物活性,功能化PEEK具有增强的骨整合能力(预防感染和促进新骨再生),其作为牙科/骨科替代修复材料极具临床应用前景。
中图分类号:
- R783.1
| [1] |
Ma R, Tang TT. Current strategies to improve the bioactivity of PEEK [J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2014, 15(4):5426-5445.
doi: 10.3390/ijms15045426 |
| [2] |
Luo HL, Xiong GY, Yang ZW, et al. Preparation of three-dimensional braided carbon fiber-reinforced PEEK composites for potential load-bearing bone fixations. Part Ⅰ. Mechanical properties and cytocompatibility [J]. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater, 2014, 29:103-113.
doi: 10.1016/j.jmbbm.2013.09.003 |
| [3] |
Goodman SB, Yao ZY, Keeney M, et al. The future of biologic coatings for orthopaedic implants [J]. Biomaterials, 2013, 34(13):3174-3183.
doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2013.01.074 pmid: 23391496 |
| [4] |
Lee DW, Yun YP, Park K, et al. Gentamicin and bone morphogenic protein-2 (BMP-2)-delivering heparinized-titanium implant with enhanced antibacterial activity and osteointegration [J]. Bone, 2012, 50(4):974-982.
doi: 10.1016/j.bone.2012.01.007 |
| [5] |
Wu JP, Li LL, Fu C, et al. Micro-porous polyetheretherketone implants decorated with BMP-2 via phosphorylated gelatin coating for enhancing cell adhesion and osteogenic differentiation [J]. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces, 2018, 169:233-241.
doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfb.2018.05.027 |
| [6] |
Mahjoubi H, Buck E, Manimunda P, et al. Surface phosphonation enhances hydroxyapatite coating adhesion on polyetheretherketone and its osseointegration potential [J]. Acta Biomater, 2017, 47:149-158.
doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2016.10.004 |
| [7] |
Shimizu T, Fujibayashi S, Yamaguchi S, et al. Bioactivity of sol-gel-derived TiO2 coating on polyetheretherketone: In vitro and in vivo studies [J]. Acta Biomater, 2016, 35:305-317.
doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2016.02.007 |
| [8] |
Liu MY, Zeng GJ, Wang K, et al. Recent developments in polydopamine: An emerging soft matter for surface modification and biomedical applications [J]. Nanoscale, 2016, 8(38):16819-16840.
doi: 10.1039/C5NR09078D |
| [9] |
He S, Zhou P, Wang LX, et al. Antibiotic-decorated titanium with enhanced antibacterial activity through adhesive polydopamine for dental/bone implant [J]. J R Soc Interface, 2014, 11(95):20140169.
doi: 10.1098/rsif.2014.0169 |
| [10] |
Qi HF, Chen Q, Ren HL, et al. Electrophoretic deposition of dexamethasone-loaded gelatin nanospheres/chitosan coating and its dual function in anti-inflammation and osteogenesis [J]. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces, 2018, 169:249-256.
doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfb.2018.05.029 |
| [11] |
Garrido-Mesa N, Zarzuelo A, Galvez J. Minocycline: Far beyond an antibiotic [J]. Br J Pharmacol, 2013, 169(2):337-352.
doi: 10.1111/bph.12139 |
| [12] |
Gauthier A, Fisch A, Seuwen K, et al. Glucocorticoid-loaded liposomes induce a pro-resolution phenotype in human primary macrophages to support chronic wound healing [J]. Biomaterials, 2018, 178:481-495.
doi: S0142-9612(18)30245-X pmid: 29650255 |
| [13] |
Xing CH, Levchenko T, Guo SZ, et al. Delivering minocycline into brain endothelial cells with liposome-based technology [J]. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab, 2012, 32(6):983-988.
doi: 10.1038/jcbfm.2012.48 |
| [14] |
Wang XX, Li YB, Yao HJ, et al. The use of mitochondrial target-ing resveratrol liposomes modified with a dequalinium polyethylene glycol-distearoylphosphatidyl ethanolamine conjugate to induce apoptosis in resistant lung cancer cells [J]. Biomaterials, 2011, 32(24):5673-5687.
doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2011.04.029 |
| [15] |
Oliveira R, El Hage M, Carrel JP, et al. Rehabilitation of the edentulous posterior maxilla after sinus floor elevation using deproteinized bovine bone: A 9-year clinical study [J]. Implant Dent, 2012, 21(5):422-426.
pmid: 22968571 |
| [16] |
Cook EA, Cook JJ. Bone graft substitutes and allografts for reconstruction of the foot and ankle [J]. Clin Podiatr Med Surg, 2009, 26(4):589-605.
doi: 10.1016/j.cpm.2009.07.003 |
| [17] |
Schindler OS, Cannon SR, Briggs TW, et al. Use of a novel bone graft substitute in peri-articular bone tumours of the knee [J]. Knee, 2007, 14(6):458-464.
pmid: 17869519 |
| [18] | Carson JS, Bostrom MP. Synthetic bone scaffolds and fracture repair [J]. Injury, 2007, 38(Suppl 1):S33-S37. |
| [19] |
Lu T, Wen J, Qian S, et al. Enhanced osteointegration on tantalum-implanted polyetheretherketone surface with bone-like elastic modulus [J]. Biomaterials, 2015, 51:173-183.
doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2015.02.018 |
| [20] |
Liu XY, Chu PK, Ding CX. Surface nano-functionalization of biomaterials [J]. Mater Sci Eng R, 2010, 70:275-302.
doi: 10.1016/j.mser.2010.06.013 |
| [21] |
Chen ML, Ouyang LP, Lu T, et al. Enhanced bioactivity and bacteriostasis of surface fluorinated polyetheretherketone [J]. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces, 2017, 9(20):16824-16833.
doi: 10.1021/acsami.7b02521 |
| [22] |
Vilarrasa J, Delgado LM, Galofre M, et al. In vitro evaluation of a multispecies oral biofilm over antibacterial coated titanium surfaces [J]. J Mater Sci Mater Med, 2018, 29(11):164.
doi: 10.1007/s10856-018-6168-8 |
| [23] |
Xu AX, Zhou LW, Deng Y, et al. A carboxymethyl chitosan and peptide-decorated polyetheretherketone ternary biocomposite with enhanced antibacterial activity and osseointegration as orthopedic/dental implants [J]. J Mater Chem B, 2016, 4(10):1878-1890.
doi: 10.1039/C5TB02782A |
| [24] |
Zhang J, Cai L, Wang TL, et al. Lithium doped silica nanos-pheres/poly (dopamine) composite coating on polyetheretherketone to stimulate cell responses, improve bone formation and osseointegration [J]. Nanomedicine, 2018, 14(3):965-976.
doi: S1549-9634(18)30028-5 pmid: 29408735 |
| [25] |
Li GL, Cao HL, Zhang WJ, et al. Enhanced osseointegration of hierarchical micro/nanotopographic titanium fabricated by microarc oxidation and electrochemical treatment [J]. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces, 2016, 8(6):3840-3852.
doi: 10.1021/acsami.5b10633 |
| [26] |
Zhou XJ, Feng W, Qiu KX, et al. BMP-2 derived peptide and dexamethasone incorporated mesoporous silica nanoparticles for enhanced osteogenic differentiation of bone mesenchymal stem cells [J]. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces, 2015, 7(29):15777-15789.
doi: 10.1021/acsami.5b02636 |
| [27] |
Li L, Zhou GL, Wang Y, et al. Controlled dual delivery of BMP-2 and dexamethasone by nanoparticle-embedded electrospun nanofibers for the efficient repair of critical-sized rat calvarial defect [J]. Biomaterials, 2015, 37:218-229.
doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2014.10.015 |
| [1] | 管仁珍, 丁士刚, 石岩岩, 薛艳. 含铋剂四联疗法根除幽门螺杆菌的疗效:4 261例患者的真实世界研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(5): 942-945. |
| [2] | 史成梅,王雪冬,刘又鲲,邓莹,郭向阳. 地塞米松联合盐酸奥布卡因凝胶用于预防鼻内镜术后咽喉痛[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(2): 289-293. |
| [3] | 李欣欣,柳玉树,孙玉春,陈虎,叶红强,周永胜. 计算机辅助设计与制作一体化聚醚醚酮可摘局部义齿不同形态组件的适合性评价[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2019, 51(2): 335-339. |
| [4] | 程小娥,彭慧浈,户雪雪,冯小金,马龙先,蒋昌宇,柳涛. 米诺环素抑制甲醛炎性痛及机制[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2018, 50(5): 797-804. |
| [5] | 朱林,王聿栋,董艳梅,陈晓峰. 缓释米诺环素的介孔纳米生物玻璃载药系统[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2018, 50(2): 249-255. |
| [6] | 张路, 袁重阳, 田福聪, 王晓燕, 高学军. 自酸蚀粘接剂系统对变形链球菌的抑制作用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2016, 48(1): 57-62. |
| [7] | 李志红, 刘丹, 何自静, 范志毅. 地塞米松对新辅助化疗后乳腺癌患者术后恶心呕吐发生率的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2015, 47(4): 685-689. |
| [8] | 徐璐, 王超, 沈文文, 祁荣. 辛伐他汀纳米脂质体对骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2014, 46(6): 883-888. |
| [9] | 马泽云, 王衣祥. 建立大鼠双膦酸盐相关颌骨骨坏死模型并初步分析其发病原因[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2014, 46(6): 945-949. |
| [10] | 王国文*, 郭卫, 汤小东, 彭长亮, 赵会. 顺铂纳米脂质体对骨肉瘤Saos-2细胞的杀伤作用及在荷瘤小鼠中的组织分布[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2009, 41(5): 525-530. |
| [11] | 王荣福, , 刘萌, 张春丽, 闫平, 于明明. 人端粒酶催化亚单位(hTERT)反义分子探针细胞摄取动力学与生物学性质[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2009, 41(4): 437-441. |
| [12] | 郭佳, 张淼, 李云峰, 甄鹏, 胡新. 骨靶向性柔性纳米脂质体[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2009, 41(2): 203-207. |
| [13] | 林琴, 王广发, 汤秀英, 邹水兰. 地塞米松对内毒素致急性肺损伤大鼠肺的保护作用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2006, 38(4): 393-396. |
| [14] | 严文伟, 齐宪荣, 魏来, 费然, 王宇. 阳离子脂质体对反义寡核苷酸抗乙型肝炎病毒作用的促进[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2003, 35(6): 629-633. |
| [15] | 严文伟, 费然, 王文浩, 齐宪荣, 魏来, 丛旭, 王宇. 大豆甾醇糖苷及两亲性聚乙二醇对阳离子脂质体细胞转染与膜各向异性的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2003, 35(3): 324-328. |
|
||