北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2023, Vol. 55 ›› Issue (6): 1125-1129. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2023.06.026
以十二指肠溃疡为突出表现的IgG4相关性疾病1例
- 北京医院风湿免疫科, 国家老年医学中心, 中国医学科学院老年医学研究院, 北京 100730
A case of duodenal ulcer as prominent manifestation of IgG4-related disease
Min FENG,Zhe CHEN,Yong-jing CHENG*( )
)
- Department of Rheumatology, Beijing Hospital; National Center of Gerontology; Institute of Geriatric Medicine, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences, Beijing 100730, China
摘要:
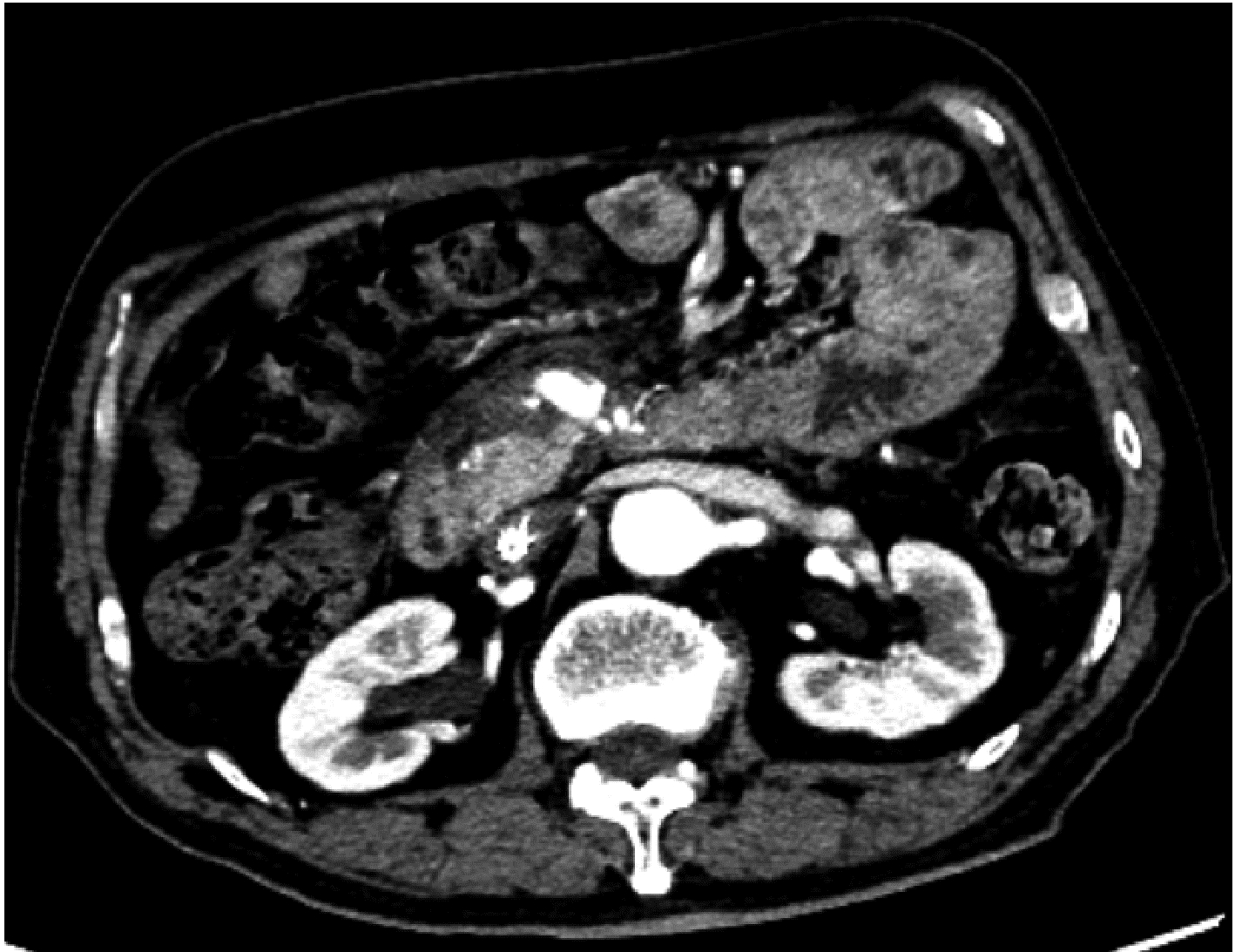
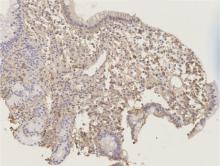
报告1例以十二指肠溃疡为主要表现的IgG4相关性疾病, 以提高对IgG4相关性疾病的认识。患者为70岁男性, 因间断皮肤瘙痒、腹痛4年, 伴黑便2月余入院。患者4年前因全身瘙痒、腹痛就诊外院, 检查血IgG4 3.09 g/L(参考值0~1.35 g/L)、谷丙转氨酶554 U/L(参考值9~40 U/L)、谷草转氨酶288 U/L(参考值5~40 U/L)、总胆红素54.16 μmol/L(参考值2~21 μmol/L)、直接胆红素29.64 μmol(参考值1.7~8.1 μmol/L), 均明显升高。腹部CT和磁共振胰胆管造影检查显示胰头及胰尾肿胀, 胆总管狭窄, 肝内外胆管扩张。诊断IgG4相关性疾病, 予醋酸泼尼松40 mg, 每日1次。治疗后患者皮肤瘙痒及黄疸消退, 后患者停药。2个月前患者出现黑便, 血常规提示重度贫血, 诊断消化道出血。在外院治疗未见好转来北京医院急诊, 胃镜显示十二指肠球部1.5 cm溃疡, 给予奥美拉唑治疗后复查仍便潜血阳性。检查正电子发射计算机断层扫描(positron emission tomography-CT, PET-CT)提示十二指肠壁的代谢活性未见明确异常, 未发现肿瘤病变, 考虑IgG4相关性疾病, 为进一步诊治收入北京医院风湿免疫科。患者既往有右侧颌下腺肿物切除术及糖尿病。入院后检查血IgG4 5.44 g/L(参考值0.03~2.01 g/L), 腹部增强CT可见胰腺轻度肿胀及异常强化, 自身免疫性胰腺炎可能; 肝内外胆管略扩张, 肠系膜上血管周围软组织影, 考虑腹膜后纤维化可能。十二指肠球部溃疡活检组织病理可见纤维组织增生及多量淋巴细胞浸润, 每高倍镜视野IgG4阳性浆细胞约20~30个, IgG4阳性浆细胞占IgG阳性浆细胞的比例超过40%。诊断为IgG4相关性疾病, 给予甲泼尼龙琥珀酸钠40 mg静脉滴注, 每日1次, 持续2周, 后改为口服醋酸泼尼松50 mg, 每日1次, 逐渐减量至醋酸泼尼松5 mg维持, 同时联合环磷酰胺0.4 g, 静脉滴注, 每2周1次, 复查患者十二指肠溃疡愈合。IgG4相关性疾病是一种较罕见的免疫介导的慢性炎症伴纤维化疾病, 可累及全身多个器官和系统, 临床表现复杂多样。IgG4相关性疾病的消化系统表现多为急性胰腺炎和胆管炎, 罕见表现为消化道溃疡。该病例证实IgG4相关性疾病可以表现为十二指肠溃疡, 是十二指肠溃疡的罕见原因之一。
中图分类号:
- R593.2
| 1 |
Löhr JM , Vujasinovic M , Rosendahl J , et al. IgG4-related diseases of the digestive tract[J]. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2022, 19 (3): 185- 197.
doi: 10.1038/s41575-021-00529-y |
| 2 |
Padniewski JJ , Thottam E , Nasr R . IgG4 sclerosing disease of the esophagus: A case-based review[J]. Rheumatol Int, 2020, 40 (10): 1733- 1737.
doi: 10.1007/s00296-020-04594-5 |
| 3 |
Koizumi S , Kamisawa T , Kuruma S , et al. Immunoglobulin G4-related gastrointestinal diseases, are they immunoglobulin G4-related diseases?[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2013, 19 (35): 5769- 5774.
doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i35.5769 |
| 4 |
Ramakrishna B , Yewale R , Vijayakumar K , et al. Gastric IgG4-related disease presenting as a mass lesion and masquerading as a gastrointestinal stromal tumor[J]. J Pathol Transl Med, 2020, 54 (3): 258- 262.
doi: 10.4132/jptm.2020.02.10 |
| 5 |
Kuran S , Parlak E , Oguz D , et al. Endoscopic sphincterotomy-induced hemorrhage: Treatment with heat probe[J]. Gastrointest Endosc, 2006, 63 (3): 506- 511.
doi: 10.1016/j.gie.2005.09.039 |
| 6 | Yang L , Jin P , Sheng JQ . Immunoglobulin G4-related disease (IgG4-RD) affecting the esophagus, stomach, and liver[J]. Endoscopy, 2015, 47 (Suppl 1): 96- 97. |
| 7 |
Khan S , Zhu LP , Jiang K , et al. Immunoglobulin G4-related disease manifesting as isolated, typical, and nontypical gastroesophageal lesion: A research of literature review[J]. Digestion, 2020, 101 (5): 506- 521.
doi: 10.1159/000501513 |
| 8 | Zhang X , Jin X , Guan L , et al. IgG4-related disease with gastrointestinal involvement: Case reports and literature review[J]. Front Immunol, 2022, 10 (13): 816- 830. |
| 9 |
Shinji A , Sano K , Hamamo H , et al. Autoimmune pancreatitis is closely associated with gastric ulcer presenting with abundant IgG4-bearing plasma cell infiltration[J]. Gastrointest Endosc, 2004, 59 (4): 506- 511.
doi: 10.1016/S0016-5107(03)02874-8 |
| 10 |
Chang MC , Chang YT , Wei SC , et al. Autoimmune pancreatitis associated with high prevalence of gastric ulcer independent of helicobacter pylori infection status[J]. Pancreas, 2009, 38 (4): 442- 446.
doi: 10.1097/MPA.0b013e31819b5f3c |
| 11 |
Fujita T , Ando T , Sakakibara M , et al. Refractory gastric ulcer with abundant IgG4-positive plasma cell infiltration: A case report[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2010, 16 (17): 2183- 2186.
doi: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i17.2183 |
| 12 |
Basteman AC , Sommerlad M , Underwood TJ . Chronic gastric ulceration: A novel manifestation of IgG4-related disease?[J]. J Clin Pathol, 2012, 65 (6): 569- 570.
doi: 10.1136/jclinpath-2011-200565 |
| 13 |
Umehara H , Okazaki K , Kawa S , et al. The 2020 revised comprehensive diagnostic (RCD) criteria for IgG4-RD[J]. Mod Rheumatol, 2021, 31 (3): 529- 553.
doi: 10.1080/14397595.2020.1859710 |
| 14 | Lanzillotta M , Mancuso G , Della-Torre E . Advances in the diagnosis and management of IgG4 related disease[J]. BMJ, 2020, 369, m1067. |
| 15 | Maritati F , Peyronel F , Vaglio A . IgG4-related disease: A clinical perspective[J]. Rheumatology (Oxford), 2020, 59 (Suppl 3): 123- 131. |
| 16 |
Sawada H , Czech T , Silangcruz K , et al. Clinicopathological characteristics of gastric IgG4-related disease: Systematic scoping review[J]. J Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2022, 37 (10): 1865- 1872.
doi: 10.1111/jgh.15980 |
| [1] | 丁汉东, 王琴, 廖贵益, 郝宗耀. 肾移植术后并发消化道出血的诊治[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(5): 902-907. |
| [2] | 冯璐,翟佳羽,赵金霞. IgG4相关性疾病患者就诊情况及其临床特征[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(6): 1028-1032. |
| [3] | 孟广艳,张筠肖,张渝昕,刘燕鹰. IgG4相关性疾病中枢神经系统受累的临床特点分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(6): 1043-1048. |
| [4] | 张意兰,王智峰,陈宁. 血清IgG4在不同疾病患者中的表达[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2017, 49(6): 961-964. |
| [5] | 张莉, 林三仁, 周丽雅, 丁士刚, 王阳, 朱红, 姚婉贞, 郑亚安, 张立强, 段丽萍. 上消化道出血并发SARS 1例报告[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2003, 35(z1): 143-143. |
|
||