北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2024, Vol. 56 ›› Issue (6): 1009-1016. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2024.06.010
类风湿关节炎患者低肌肉量综合征的临床特征及其对躯体功能的影响
贾霈雯, 杨迎, 邹耀威, 欧阳志明, 林建子, 马剑达, 杨葵敏, 戴冽*( )
)
- 中山大学孙逸仙纪念医院风湿免疫科,广州 510120
Clinical characteristics of overlapping syndromes of low muscle mass in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and their impact on physical function
Peiwen JIA, Ying YANG, Yaowei ZOU, Zhiming OUYANG, Jianzi LIN, Jianda MA, Kuimin YANG, Lie DAI*( )
)
- Department of Rheumatology and Immunology, Sun Yat-Sen Memorial Hospital, Sun Yat-Sen University, Guangzhou 510120, China
摘要:
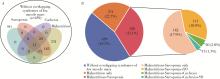
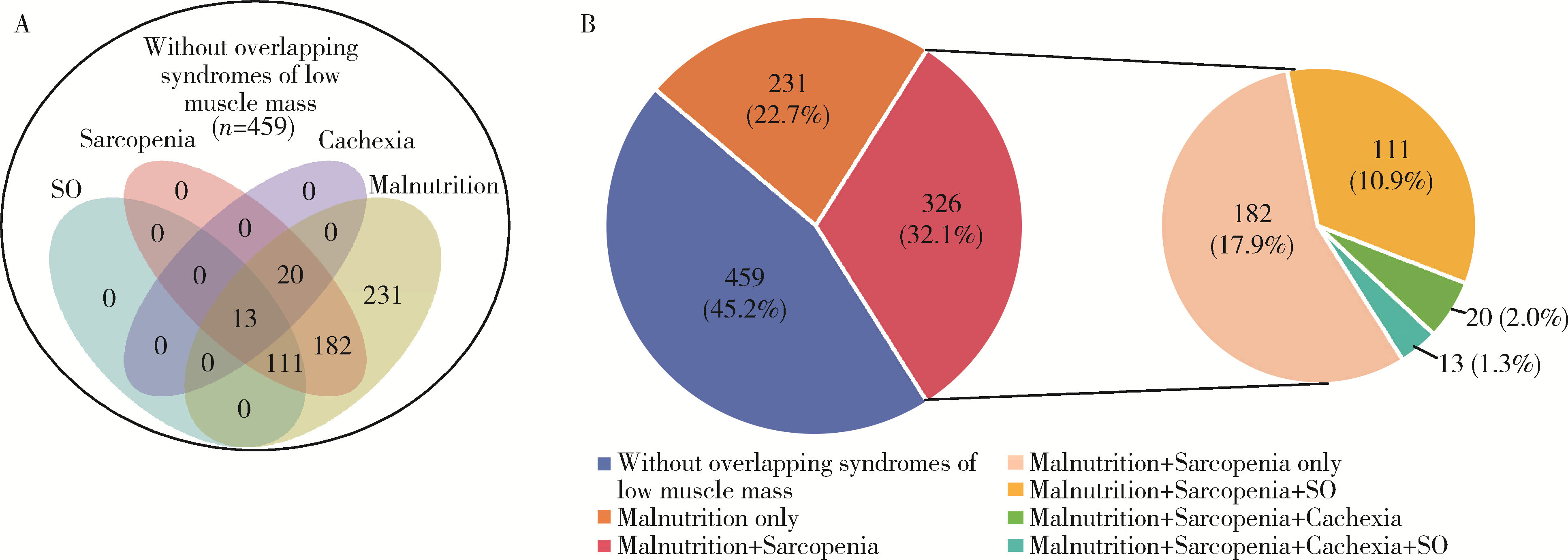
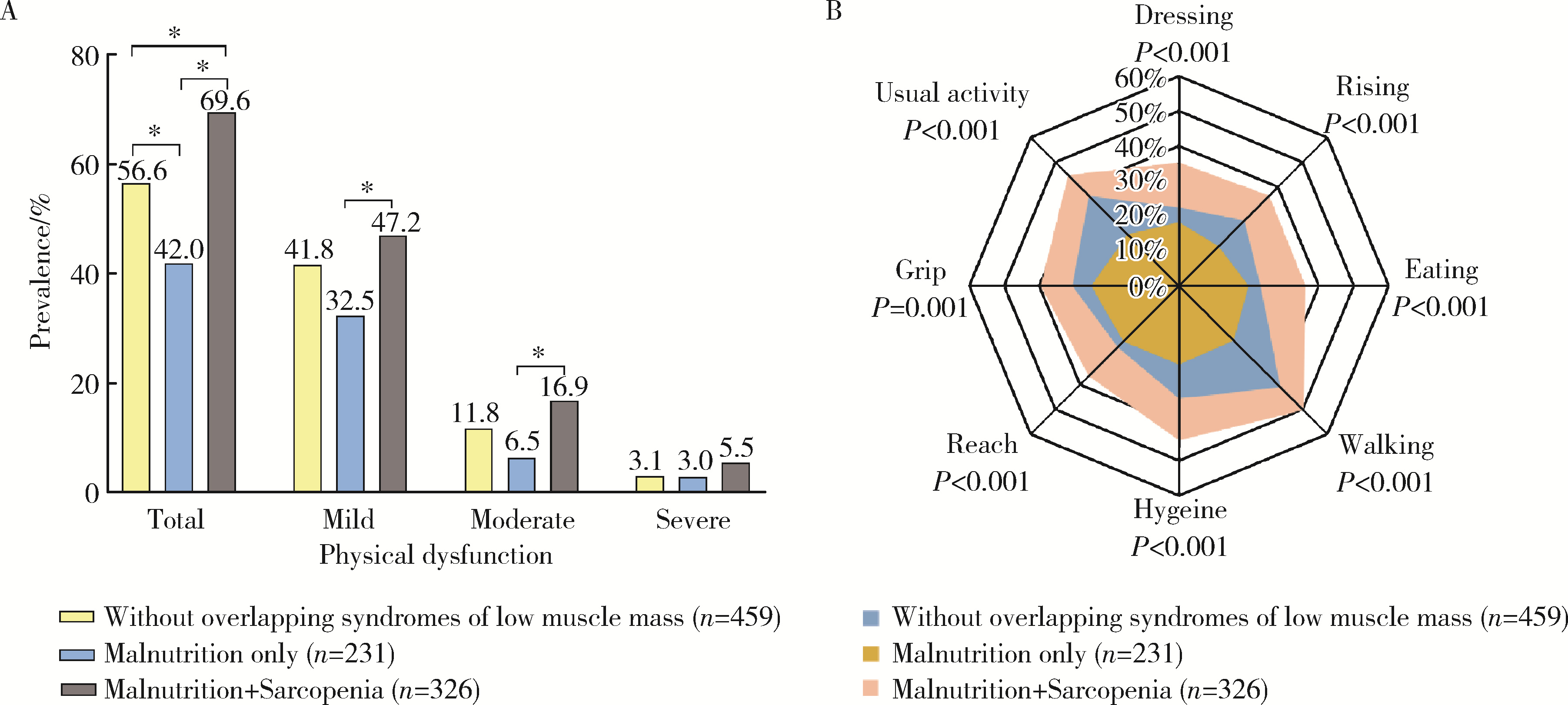
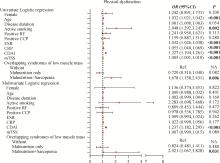
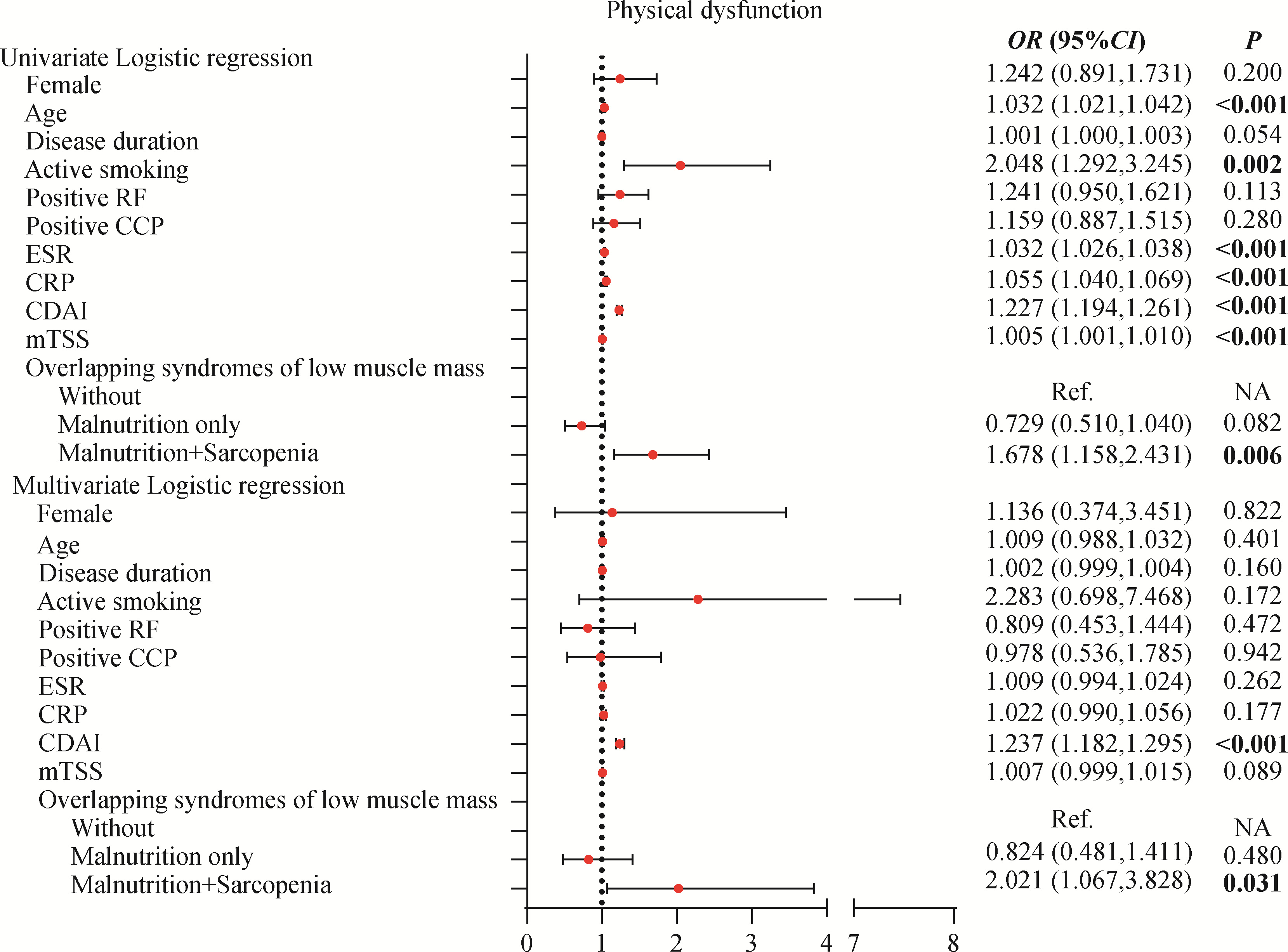
目的: 探讨类风湿关节炎(rheumatoid arthritis,RA)患者合并低肌肉量综合征的特征及其对躯体功能的影响。方法: 纳入2019年9月至2024年4月就诊于中山大学孙逸仙纪念医院风湿免疫科的RA患者。收集所有患者的临床资料,包括病情活动、躯体功能及放射学评估,同时进行身体成分、握力和步行速度的测量,评估有无低肌肉量综合征以及营养不良、肌少症、肌少症性肥胖和恶病质,采用斯坦福健康评估问卷-残疾指数(health assessment questionnaire-disability index,HAQ-DI)评估躯体功能,并通过Logistic回归分析躯体功能障碍的影响因素。结果: 共纳入RA患者1 016例,女性占82.5%,平均年龄(52.4±12.5)岁。557例(54.8%)为低肌肉量综合征且均合并营养不良,在此基础上,326例(32.1%)合并肌少症,124例(12.2%)合并肌少症性肥胖,33例(3.2%)合并恶病质。共584例(57.4%)RA患者有躯体功能障碍,轻度、中度和重度躯体功能障碍分别有421例(41.4%)、124例(12.2%)和39例(3.8%)。与无低肌肉量综合征(n=459)或仅营养不良(n=231)的患者相比,同时合并营养不良+肌少症(n=326)的RA患者病情活动性高,躯体功能障碍比例较高(69.6% vs. 42.0% vs. 56.6%),但仅营养不良的RA患者HAQ-DI评分(中位数0.0 vs. 0.1)和躯体功能障碍比例(42.0% vs. 56.6%)则较无低肌肉量综合征者低。多因素Logistic回归分析显示,营养不良+肌少症与躯体功能障碍呈独立正相关(OR=2.021,95%CI:1.067~3.828),而仅营养不良则与躯体功能障碍无明显相关。结论: 同时合并营养不良和肌少症会加重RA患者病情活动性和躯体功能障碍,临床应重视RA患者低肌肉量综合征尤其是肌少症的筛查与评估,并予以及时干预。
中图分类号:
- R593.22
| 1 | 耿研, 谢希, 王昱, 等. 类风湿关节炎诊疗规范[J]. 中华内科杂志, 2022, 61 (1): 51- 59. |
| 2 | 周云杉, 王秀茹, 安媛, 等. 全国多中心类风湿关节炎患者残疾及功能受限情况的调查[J]. 中华风湿病学杂志, 2013, 17 (8): 526- 532. |
| 3 | 邹耀威, 连舒燕, 陈楚涛, 等. 类风湿关节炎患者功能受限特征及相关因素分析[J]. 中华内科杂志, 2022, 61 (2): 193- 199. |
| 4 | Smolen JS , Breedveld FC , Burmester GR , et al. Treating rheumatoid arthritis to target: 2014 update of the recommendations of an international task force[J]. Ann Rheum Dis, 2015, 75 (1): 3- 15. |
| 5 |
Bennett JL , Pratt AG , Dodds R , et al. Rheumatoid sarcopenia: Loss of skeletal muscle strength and mass in rheumatoid arthritis[J]. Nat Rev Rheumatol, 2023, 19 (4): 239- 251.
doi: 10.1038/s41584-023-00921-9 |
| 6 | Elkan AC , Engvall IL , Tengstrand B , et al. Malnutrition in women with rheumatoid arthritis is not revealed by clinical anthropometrical measurements or nutritional evaluation tools[J]. Eur J Clin Nutr, 2007, 62 (10): 1239- 1247. |
| 7 |
Tański W , Wójciga J , Jankowska-Polańska B . Association between malnutrition and quality of life in elderly patients with rheumatoid arthritis[J]. Nutrients, 2021, 13 (4): 1259.
doi: 10.3390/nu13041259 |
| 8 |
Baker JF , George M , Baker DG , et al. Associations between body mass, radiographic joint damage, adipokines and risk factors for bone loss in rheumatoid arthritis[J]. Rheumatology, 2011, 50 (11): 2100- 2107.
doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/ker294 |
| 9 |
Cederholm T , Jensen GL , Correia MITD , et al. GLIM criteria for the diagnosis of malnutrition: A consensus report from the global clinical nutrition community[J]. Clin Nutr, 2019, 38 (1): 1- 9.
doi: 10.1016/j.clnu.2018.08.002 |
| 10 |
Chew STH , Tey SL , Yalawar M , et al. Prevalence and associated factors of sarcopenia in community-dwelling older adults at risk of malnutrition[J]. BMC Geriatr, 2022, 22 (1): 997.
doi: 10.1186/s12877-022-03704-1 |
| 11 |
Ngeuleu A , Allali F , Medrare L , et al. Sarcopenia in rheumatoid arthritis: Prevalence, influence of disease activity and associated factors[J]. Rheumatol Int, 2017, 37 (6): 1015- 1020.
doi: 10.1007/s00296-017-3665-x |
| 12 |
Giles JT , Ling SM , Ferrucci L , et al. Abnormal body composition phenotypes in older rheumatoid arthritis patients: Association with disease characteristics and pharmacotherapies[J]. Arthritis Rheum, 2008, 59 (6): 807- 815.
doi: 10.1002/art.23719 |
| 13 |
Torii M , Hashimoto M , Hanai A , et al. Prevalence and factors associated with sarcopenia in patients with rheumatoid arthritis[J]. Mod Rheumatol, 2019, 29 (4): 589- 595.
doi: 10.1080/14397595.2018.1510565 |
| 14 |
Santo RCE , Fernandes KZ , Lora PS , et al. Prevalence of rheumatoid cachexia in rheumatoid arthritis: A systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle, 2018, 9 (5): 816- 825.
doi: 10.1002/jcsm.12320 |
| 15 |
Arnett FC , Edworthy SM , Bloch DA , et al. The American rheumatism association 1987 revised criteria for the classification of rheumatoid arthritis[J]. Arthritis Rheum, 1988, 31 (3): 315- 324.
doi: 10.1002/art.1780310302 |
| 16 |
Aletaha D , Neogi T , Silman AJ , et al. 2010 rheumatoid arthritis classification criteria: An American College of Rheumatology/European League Against Rheumatism collaborative initiative[J]. Ann Rheum Dis, 2010, 69 (9): 1580- 1588.
doi: 10.1136/ard.2010.138461 |
| 17 |
Lin JZ , Liang JJ , Ma JD , et al. Myopenia is associated with joint damage in rheumatoid arthritis: A cross-sectional study[J]. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle, 2019, 10 (2): 355- 367.
doi: 10.1002/jcsm.12381 |
| 18 |
Oliveros E , Somers VK , Sochor O , et al. The concept of normal weight obesity[J]. Prog Cardiovasc Dis, 2014, 56 (4): 426- 433.
doi: 10.1016/j.pcad.2013.10.003 |
| 19 |
Abizanda P , Navarro JL , García-Tomás MI , et al. Validity and usefulness of hand-held dynamometry for measuring muscle strength in community-dwelling older persons[J]. Arch Gerontol Geriatr, 2012, 54 (1): 21- 27.
doi: 10.1016/j.archger.2011.02.006 |
| 20 |
Chen LK , Woo J , Assantachai P , et al. Asian working group for sarcopenia: 2019 consensus update on sarcopenia diagnosis and treatment[J]. J Am Med Dir Assoc, 2020, 21 (3): 300- 307.
doi: 10.1016/j.jamda.2019.12.012 |
| 21 |
Donini LM , Busetto L , Bischoff SC , et al. Definition and diagnostic criteria for sarcopenic obesity: ESPEN and EASO consensus statement[J]. Clin Nutr, 2022, 41 (4): 990- 1000.
doi: 10.1016/j.clnu.2021.11.014 |
| 22 |
Evans WJ , Morley JE , Argilés J , et al. Cachexia: A new definition[J]. Clin Nutr, 2008, 27 (6): 793- 799.
doi: 10.1016/j.clnu.2008.06.013 |
| 23 | Li TH , Chang YS , Liu CW , et al. The prevalence and risk factors of sarcopenia in rheumatoid arthritis patients: A systematic review and meta-regression analysis[J]. Semin Arthritis Rheu, 2020, 51 (1): 236- 245. |
| 24 |
Challal S , Minichiello E , Boissier MC , et al. Cachexia and adiposity in rheumatoid arthritis. Relevance for disease management and clinical outcomes[J]. Joint Bone Spine, 2016, 83 (2): 127- 133.
doi: 10.1016/j.jbspin.2015.04.010 |
| 25 |
Tian P , Xiong J , Wu W , et al. Impact of the malnutrition on mortality in rheumatoid arthritis patients: A cohort study from NHANES 1999-2014[J]. Front Nutr, 2023, 9, 993061.
doi: 10.3389/fnut.2022.993061 |
| 26 |
Rall LC , Roubenoff R . Rheumatoid cachexia: Metabolic abnormalities, mechanisms and interventions[J]. Rheumatology, 2004, 43 (10): 1219- 1223.
doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/keh321 |
| 27 |
Jutley GS , Sahota K , Sahbudin I , et al. Relationship between inflammation and metabolism in patients with newly presenting rheumatoid arthritis[J]. Front Immunol, 2021, 12, 676105.
doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.676105 |
| 28 |
Cano-García L , Manrique-Arija S , Domínguez-Quesada C , et al. Sarcopenia and nutrition in elderly rheumatoid arthritis patients: A cross-sectional study to determine prevalence and risk factors[J]. Nutrients, 2023, 15 (11): 2440.
doi: 10.3390/nu15112440 |
| 29 |
Pan J , Wu T , Ma JD , et al. Geriatric nutrition risk index: A more powerful index identifying muscle mass loss in patients with rheumatoid arthritis[J]. Clin Rheumatol, 2024, 43 (4): 1299- 1310.
doi: 10.1007/s10067-024-06918-3 |
| 30 |
Engvall IL , Elkan AC , Tengstrand B , et al. Cachexia in rheumatoid arthritis is associated with inflammatory activity, physical dis-ability, and low bioavailable insulin-like growth factor[J]. Scand J Rheumatol, 2008, 37 (5): 321- 328.
doi: 10.1080/03009740802055984 |
| 31 |
Baker JF , Giles JT , Weber D , et al. Sarcopenic obesity in rheumatoid arthritis: Prevalence and impact on physical functioning[J]. Rheumatology (Oxford), 2022, 61 (6): 2285- 2294.
doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/keab710 |
| 32 |
Pan J , Zou YW , Zhu YY , et al. Muscle mass loss is associated with physical dysfunction in patients with early rheumatoid arthritis[J]. Front Nutr, 2022, 9, 1007184.
doi: 10.3389/fnut.2022.1007184 |
| 33 |
Dent E , Morley JE , Cruz-Jentoft AJ , et al. International Clinical Practice Guidelines for Sarcopenia (ICFSR): Screening, diagnosis and management[J]. J Nutr Health Aging, 2018, 22 (10): 1148- 1161.
doi: 10.1007/s12603-018-1139-9 |
| 34 | Liao CD , Chen HC , Huang SW , et al. Exercise therapy for sarcopenia in rheumatoid arthritis: A meta-analysis and meta-regression of randomized controlled trials[J]. Clin Rehabil, 2002, 36 (2): 145- 157. |
| 35 |
Rausch Osthoff AK , Juhl CB , Knittle K , et al. Effects of exercise and physical activity promotion: Meta-analysis informing the 2018 EULAR recommendations for physical activity in people with rheumatoid arthritis, spondyloarthritis and hip/knee osteoarthritis[J]. RMD Open, 2018, 4 (2): e000713.
doi: 10.1136/rmdopen-2018-000713 |
| 36 |
Deutz NE , Bauer JM , Barazzoni R , et al. Protein intake and exercise for optimal muscle function with aging: Recommendations from the ESPEN Expert Group[J]. Clin Nutr, 2014, 33 (6): 929- 936.
doi: 10.1016/j.clnu.2014.04.007 |
| 37 |
Groen BB , Horstman AM , Hamer HM , et al. Post-prandial protein handling: You are what you just ate[J]. PLoS One, 2015, 10 (11): e0141582.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0141582 |
| 38 |
De Spiegeleer A , Beckwée D , Bautmans I , et al. Sarcopenia Guidelines Development group of the Belgian Society of Gerontology and Geriatrics (BSGG). Pharmacological interventions to improve muscle mass, muscle strength and physical performance in older people: An umbrella review of systematic reviews and meta-analyses[J]. Drugs Aging, 2018, 35 (8): 719- 734.
doi: 10.1007/s40266-018-0566-y |
| [1] | 马豆豆, 卢哲敏, 郭倩, 朱莎, 古今, 丁艳, 石连杰. 小剂量利妥昔单抗成功治疗类风湿关节炎合并重症肌无力1例[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(6): 1110-1114. |
| [2] | 闫蕊, 柯丹, 张妍, 李丽, 苏焕然, 陈伟, 孙明霞, 刘晓敏, 罗靓. 血清趋化因子CXCL-10和涎液化糖链抗原6水平在类风湿关节炎合并肺间质病变患者中的诊断和病情评估价值[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(6): 956-962. |
| [3] | 赵亮, 史成龙, 马柯, 赵静, 王潇, 邢晓燕, 莫万星, 练益瑞, 高超, 李玉慧. 抗合成酶综合征重叠类风湿关节炎患者的免疫学特征[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(6): 972-979. |
| [4] | 韩艺钧, 陈小莉, 李常虹, 赵金霞. 甲氨蝶呤在类风湿关节炎患者中的应用现状[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(6): 994-1000. |
| [5] | 刘东武, 陈杰, 高明利, 于静. 类风湿关节炎伴发淋巴结Castleman样病理改变1例[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(5): 928-931. |
| [6] | 黄会娜,赵静,赵祥格,白自然,李霞,王冠. 乳酸对类风湿关节炎患者外周血CD4+T细胞亚群的调控作用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(3): 519-525. |
| [7] | 汤晓菲,李永红,丁秋玲,孙卓,张阳,王育梅,田美伊,刘坚. 类风湿关节炎患者下肢深静脉血栓发病率及危险因素[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(2): 279-283. |
| [8] | 邹雪,白小娟,张丽卿. 艾拉莫德联合托法替布治疗难治性中重度类风湿关节炎的疗效[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(6): 1013-1021. |
| [9] | 吴琦,蔡月明,何娟,黄文蒂,王庆文. 血脂异常与类风湿关节炎肺间质病变的相关性分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(6): 982-992. |
| [10] | 张警丰,金银姬,魏慧,姚中强,赵金霞. 体重指数与类风湿关节炎临床特征的相关性分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(6): 993-999. |
| [11] | 闫晓晋,刘云飞,马宁,党佳佳,张京舒,钟盼亮,胡佩瑾,宋逸,马军. 《中国儿童发展纲要(2011-2020年)》实施期间中小学生营养不良率变化及其政策效应分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(4): 593-599. |
| [12] | 金银姬,孙琳,赵金霞,刘湘源. 血清IgA型抗鼠科肉瘤病毒癌基因同源物B1抗体在类风湿关节炎中的意义[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(4): 631-635. |
| [13] | 蔡文心,李仕成,刘一鸣,梁如玉,李静,郭建萍,胡凡磊,孙晓麟,李春,刘栩,叶华,邓立宗,李茹,栗占国. 类风湿关节炎临床分层及其特征的横断面研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(6): 1068-1073. |
| [14] | 程昉,杨邵英,房星星,王璇,赵福涛. CCL28-CCR10通路在类风湿关节炎单核细胞迁移中的作用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(6): 1074-1078. |
| [15] | 刘蕊,赵金霞,闫良. 类风湿关节炎合并下肢静脉血栓患者的临床特点[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(6): 1079-1085. |
|
||