北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2019, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (4): 632-635. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2019.04.006
显微取精时代下睾丸内情况分析
赵连明1,姜辉1,△( ),洪锴1,林浩成1,唐文豪1,刘德风2,毛加明2,张哲1,林胜利2,马潞林1
),洪锴1,林浩成1,唐文豪1,刘德风2,毛加明2,张哲1,林胜利2,马潞林1
- 1. 北京大学第三医院泌尿外科,北京 100191
2. 北京大学第三医院妇产科,北京 100191
Analysis of intratesticular condition in micro-dissection testicular sperm extraction era
Lian-ming ZHAO1,Hui JIANG1,△( ),Kai HONG1,Hao-cheng LIN1,Wen-hao TANG1,De-feng LIU2,Jia-ming MAO2,Zhe ZHANG1,Sheng-li LIN2,Lu-lin MA1
),Kai HONG1,Hao-cheng LIN1,Wen-hao TANG1,De-feng LIU2,Jia-ming MAO2,Zhe ZHANG1,Sheng-li LIN2,Lu-lin MA1
- 1.Department of Urology, Peking University Third Hospital, Beijing 100191, China
2. Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Peking University Third Hospital, Beijing 100191, China
摘要:
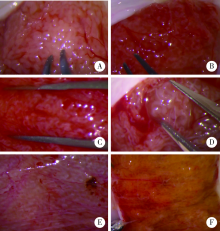
目的:让临床医生更直观认识无精症患者睾丸内生精小管形态,提高临床医生预测无精症患者显微取精成功率的能力。方法:选择2014年1月至2018年1月在北京大学第三医院做了显微取精的非克氏(Klinefelter)征无精症患者的病例资料进行回顾性分析,总结患者睾丸内生精小管类型,对比不同类型睾丸内生精小管类型的临床特点及取精成功率。结果:共472例非梗阻性无精症患者完成了显微取精手术纳入本研究,患者的平均年龄31(23,46)岁,平均睾丸大小10(1,20) mL,平均卵泡刺激素(follicle-stimulating hormone,FSH) 15.4(1.21,68.4) IU/L,平均睾酮(testosterone,T) 8.34(0.69,30.2) nmol/L,总共202人(42.7%,202/472)取到精子。根据术中所见睾丸内生精小管类型可以分为以下6种:a类:生精小管外观发育良好,均匀一致;b类:生精小管外观发育良好,偶见稍粗;c类:生精小管普遍偏细;d类:生精小管基本萎缩,偶有发育良好的生精小管;e类:全部生精小管萎缩;f类:生精小管被黄色物质浸润。各类患者的显微取精成功率有极大差异。a类患者共78人,平均年龄29(24,40)岁,FSH 11.1(1.21,15.8) IU/L,T10.2(3.29,26.5) nmol/L,睾丸大小12(12,20) mL,显微取精成功率为 6.41%;b类患者共82人,平均年龄为31(23,42)岁,FSH 13.8(3.23,19.6) IU/L,T 9.44(3.58,30.2) nmol/L,睾丸大小12(8,15) mL,显微取精成功率为74.39%;c类患者共162人,平均年龄为31(25,40)岁,FSH19.6(9.28,26.6) IU/L,T8.75(5.66,18.6) nmol/L,睾丸大小8(5,12) mL,显微取精成功率为45.06%;d类患者共36人,平均年龄为25(23,38)岁,FSH28.5(19.3,45.6) IU/L,T6.52(2.12,9.83) nmol/L,睾丸大小5(3,8) mL,显微取精成功率为94.44%;e类患者共26人,平均年龄为28(23,46)岁,FSH 31.3(18.5,68.4) IU/L,T 6.72(0.69,18.2) nmol/L,睾丸大小5(1,8) mL,显微取精成功率为15.38%;f类患者共88人,平均年龄为29(24,38)岁,FSH 18.5(5.23,31.6) IU/L,T 8.32(3.58,16.5) nmol/L,睾丸大小12(6,20) mL,显微取精成功率为28.41%。结论:睾丸内不同生精小管类型显微取精成功率的差异能够给术者术中判断带来帮助,提高术中预测显微取精成功率的能力。
中图分类号:
- R699
| [1] | Schlegel PN . Testicular sperm extraction: microdissection improves sperm yield with minimal tissue excision[J]. Hum Reprod, 1999,14(1):131-135. |
| [2] | AbdellRaheem A, Garaffa G, Rushwan N , et al. Testicular histopathology as a predictor of a positive sperm retrieval in men with non-obstructive azoospermia[J]. BJU Int, 2013,111(3):492-499. |
| [3] | Ramasamy R, Ricci JA, Palermo GD , et al. Successful fertility treatment for Klinefelter’s syndrome[J]. J Urol, 2009,182(3):1108-1113. |
| [4] | Jarow JP, Espeland MA, Lipshultz LI . Evaluation of the azoospermic patient[J]. J Urol, 1989,142(1):62-65. |
| [5] | Walker WH, Cheng J . FSH and testosterone signaling in Sertoli cells[J]. Reproduction, 2005,130(1):15-28 |
| [6] | Valenti D, La Vignera S, Condorelli RA , et al. Follicle-stimu-lating hormone treatment in normogonadotropic infertile men[J]. Nat Rev Urol, 2013,10(1):55-62 |
| [7] | Acosta AA, Khalifa E, Oehninger S . Pure human follicle stimu-lating hormone has a role in the treatment of severe male infertility by assisted reproduction: Norfolk’s total experience[J]. Hum Reprod, 1992,7(8):1067-1072. |
| [8] | 杨俊, 刘继红 . 睾丸活检在非梗阻性无精症中应用前景及问题[J]. 中国男科学杂志, 2011,25(4):61-64. |
| [9] | Bryson CF, Ramasamy R, Sheehan M , et al. Severe testi-cular atrophy does not affect the success of microdissection testicular sperm extraction[J]. J Urol, 2014,191(1):175-178. |
| [10] | Ramasamy R, Lin K, Gosden LV , et al. High serum FSH levels in men with nonobstructive azoospermia does not affect success of microdissection testicular sperm extraction[J]. Fertil Steril, 2009,92(2):590-593. |
| [1] | 毛加明,赵连明,刘德风,林浩成,杨宇卓,张海涛,洪锴,李蓉,姜辉. Y染色体无精子症因子c区缺失男性不育患者同步显微取精术后行卵胞浆内单精子显微注射的临床结局[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(4): 652-657. |
| [2] | 毛加明,刘德风,赵连明,洪锴, 张丽,马潞林,姜辉,乔杰. 睾丸穿刺活检对特发性非梗阻性无精子症患者显微取精成功率的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2018, 50(4): 613-616. |
| [3] | 洪锴,毛加明. 显微镜下睾丸切开取精术在非梗阻性无精子症治疗中的临床应用新进展[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2018, 50(4): 585-589. |
| [4] | Guo-hui LU, Janice G. EDWARDS, Gail WHITMAN-ELIA. 体质性镶嵌型21三体与无精症一例报告[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2005, 37(1): 94-95. |
|
||