北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2024, Vol. 56 ›› Issue (6): 1075-1082. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2024.06.021
阴茎远端尿道狭窄疾病的手术治疗方式
王杰, 王建伟, 夏海缀, 徐啸, 翟建坡, 何峰, 黄广林*( ), 李贵忠
), 李贵忠
- 首都医科大学附属北京积水潭医院泌尿外科,北京 100035
Surgical management of the distal urethral stricture diseases
Jie WANG, Jianwei WANG, Haizhui XIA, Xiao XU, Jianpo ZHAI, Feng HE, Guanglin HUANG*( ), Guizhong LI
), Guizhong LI
- Department of Urology, Beijing Jishuitan Hospital, Capital Medical Universitay, Beijing 100035, China
摘要:
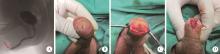
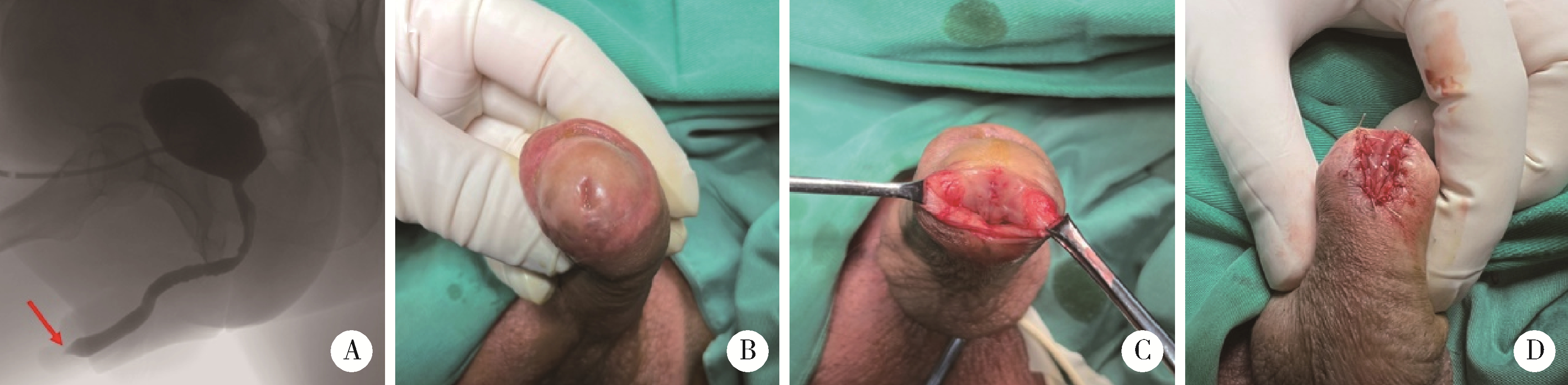
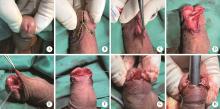
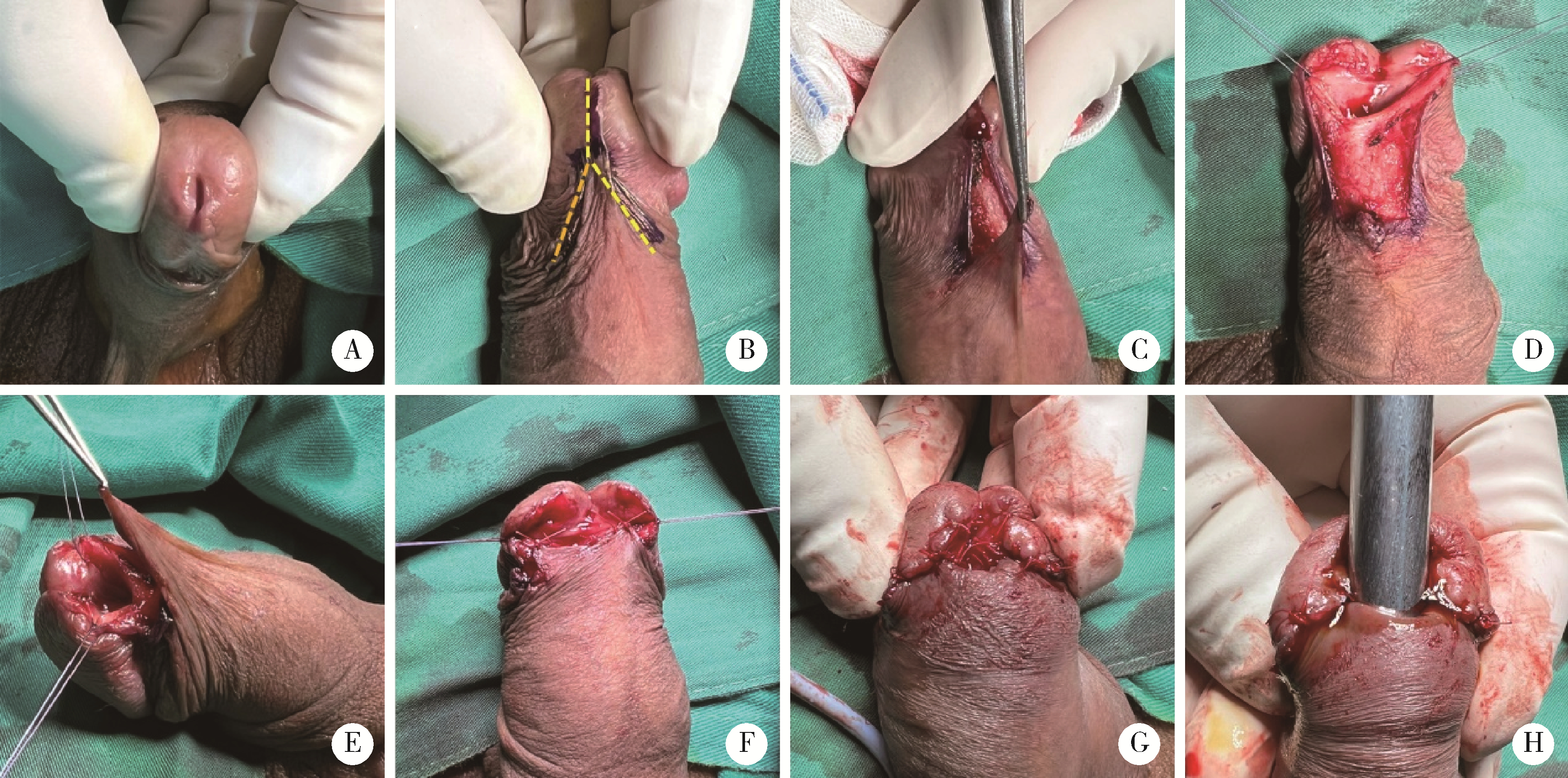
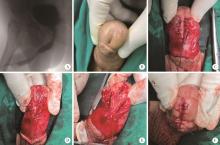
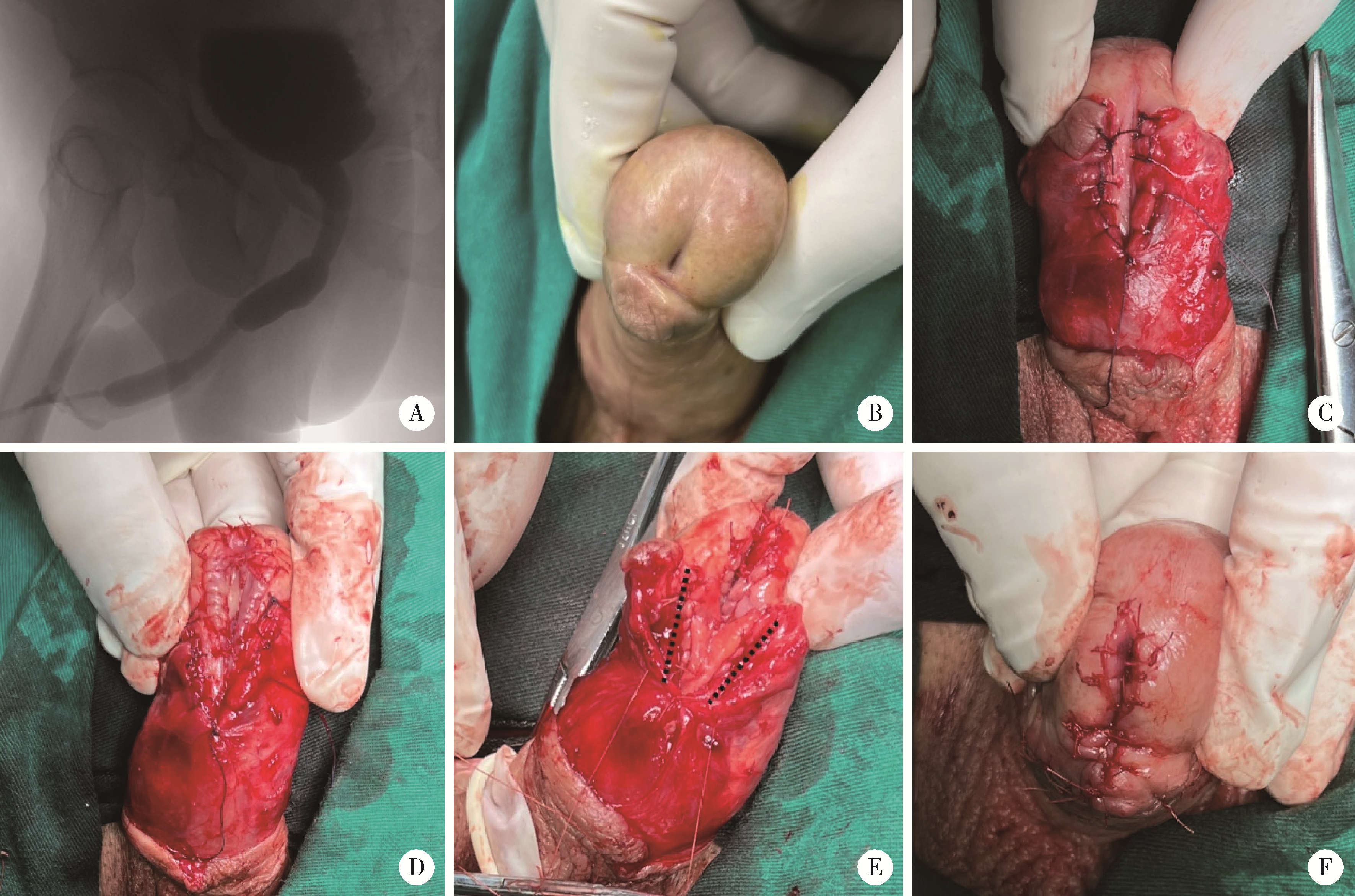
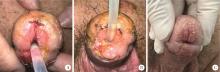
目的: 探讨阴茎远端尿道狭窄疾病的手术治疗方式。方法: 回顾性收集自2018年1月至2022年12月就诊于首都医科大学附属北京积水潭医院的80例阴茎远端尿道狭窄患者的临床资料,包括男性生殖器苔藓样硬化(male genital lichen sclerosus, MGLS) 33例,医源性损伤25例,尿道下裂术后12例,外伤等其他原因10例。狭窄仅累及尿道外口54例,其中38例行尿道外口切开术(meatotomy, MO),7例行阴茎皮瓣尿道成形术(penile skin flap urethroplasty, PSFU), 9例行口腔黏膜尿道成形术(oral mucosa graft urethroplasty, OMGU);狭窄同时累及尿道外口和舟状窝26例,其中1例行PSFU,25例行OMGU。以术式不同将80例患者分为MO、PSFU、OMGU 3组,平均年龄分别为(48.8±20.0) 岁、(53.3±21.8) 岁、(44.5±16.4) 岁;平均体重指数(body mass index, BMI) 分别为(28.6±3.9) kg/m2、(29.6±3.2) kg/m2、(29.2±4.8) kg/m2;平均术前最大尿流率分别为(5.8±2.3) mL/s、(6.8±2.4) mL/s、(5.7±3.1) mL/s。结果: 所有手术均顺利完成,围术期无Clavien Ⅲ或Ⅳ级并发症发生。3组中位狭窄长度(术中测量)分别为1.1 (1.0, 1.6)、1.5 (1.1, 2.0)、4.0 (2.5, 5.0) cm;中位手术时间分别为60.0 (60.0, 75.0)、85.0 (75.0, 112.5)、180.0 (75.0, 330.0) min;中位估计出血量分别为5.0 (2.0, 10.0)、15.0 (5.0, 42.5)、180.0 (135.0, 216.3) mL;术后中位住院日分别为3.5 (2.0, 5.0)、6.5 (3.5, 7.0)、7.5 (7.0, 11.3) d;术后中位随访时间分别为40.0 (26.3, 57.3)、55.0 (18.8, 62.8)、52.5 (30.5, 64.0) 个月;术后中位最大尿流率分别为18.3 (15.5, 19.8)、19.2 (16.1, 20.1)、17.2 (14.2, 19.6) mL/s。38例MO中33例排尿通畅,无需干预;5例狭窄复发,需定期尿道扩张。8例PSFU中7例排尿通畅,无需干预;1例出现尿瘘,建议干预,但患者决定维持现状。34例OMGU中28例排尿通畅,无需干预;6例狭窄复发,其中5例需定期尿道扩张,1例再行重建手术。所有病例术后成功率为85.0%,再干预率为15.0%。统计分析发现,3组患者的狭窄病因(P=0.002)、狭窄部位(P < 0.001)、狭窄长度(P < 0.001)、手术时间(P < 0.001)、估计出血量(P < 0.001) 及术后住院日(P < 0.001)差异有统计学意义;年龄、BMI、既往尿道狭窄手术史、术前最大尿流率、随访时间、术后最大尿流率及再干预率均差异无统计学意义。单因素及多因素Logistic回归分析发现,既往尿道狭窄手术史是术后再干预的危险因素(P=0.026)。结论: MO和PSFU主要适用于短段(≤1.5 cm) 阴茎远端尿道狭窄,OMGU则适用于处理更长段狭窄;MO和OMGU可用于MGLS病例;PSFU和OMGU更有利于改善尿道外口外观;阴茎远端尿道狭窄手术治疗的成功率为85.0%,15.0%的患者术后仍需外科干预,既往尿道狭窄手术史是术后再干预的危险因素。
中图分类号:
- R697.1
| 1 |
Fenton AS , Morey AF , Aviles R , et al.Anterior urethral strictures: Etiology and characteristics[J].Urology,2005,65(6):1055-1058.
doi: 10.1016/j.urology.2004.12.018 |
| 2 |
Abbasi B , Shaw NM , Lui JL , et al.Comparative review of the guidelines for anterior urethral stricture[J].World J Urol,2022,40(8):1971-1980.
doi: 10.1007/s00345-022-03988-3 |
| 3 |
Meeks JJ , Barbagli G , Mehdiratta N , et al.Distal urethroplasty for isolated fossa navicularis and meatal strictures[J].BJU Int,2012,109(4):616-619.
doi: 10.1111/j.1464-410X.2011.10248.x |
| 4 | Dielubanza EJ , Han JS , Gonzalez CM .Distal urethroplasty for fossa navicularis and meatal strictures[J].Transl Androl Urol,2014,3(2):163-169. |
| 5 |
Vetterlein MW , Fisch MM , Zumstein V .Update on the management of penile and meatal strictures[J].Curr Opin Urol,2021,31(5):493-497.
doi: 10.1097/MOU.0000000000000910 |
| 6 | 黄晓东, 吕军, 张小明, 等.MGLSc并发阴茎头部尿道狭窄手术治疗的临床研究[J].中国男科学杂志,2014,(5):3-6. |
| 7 |
Virasoro R , Eltahawy EA , Jordan GH .Long-term follow-up for reconstruction of strictures of the fossa navicularis with a single technique[J].BJU Int,2007,100(5):1143-1145.
doi: 10.1111/j.1464-410X.2007.07078.x |
| 8 | 冯超, 张炯, 谢弘, 等.带蒂岛状转位筋膜皮瓣治疗尿道外口及舟状窝狭窄的临床研究[J].中华泌尿外科杂志,2019,40(6):408-411. |
| 9 | 张楷乐, 傅强.尿道狭窄治疗中的误区[J].中华泌尿外科杂志,2018,39(11):867-869. |
| 10 | 赵亚伟, 刘园园, 马龙, 等.超声在尿道狭窄诊治中的诊断价值[J].中国超声医学杂志,2018,34(12):1126-1128. |
| 11 | 张林琳.评估分析男性尿道狭窄的术前诊断手段: 尿道造影、超声尿道成像和磁共振尿道成像, 谁是诊断的金标准?[J].现代泌尿外科杂志,2022,27(2):166. |
| 12 |
Mikolaj F , Karolina M , Oliwia K , et al.Retrograde urethrography, sonouretrography and magnetic resonance urethrography in evaluation of male urethral strictures. Should the novel methods become the new standard in radiological diagnosis of urethral stricture disease?[J].Int Urol Nephrol,2021,53(12):2423-2435.
doi: 10.1007/s11255-021-02994-5 |
| 13 | 刘启宇, 李养群, 杨喆, 等.V形瓣法在尿道外口和阴茎头成形术中的应用[J].中华整形外科杂志,2016,32(1):49-51. |
| 14 |
Campos-Juanatey F , Osman NI , Greenwell T , et al.European Association of Urology Guidelines on urethral stricture disease (Part 2): Diagnosis, perioperative management, and follow-up in males[J].Eur Urol,2021,80(2):201-212.
doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2021.05.032 |
| 15 | 张伟, 张志明, 焦点, 等.经尿道口腔黏膜尿道成形术修复尿道外口和舟状窝狭窄的安全性和疗效[J].中华泌尿外科杂志,2023,44(8):581-585. |
| 16 |
Daneshvar M , Simhan J , Blakely S , et al.Transurethral ventral buccal mucosa graft inlay for treatment of distal urethral strictures: International multi-institutional experience[J].World J Urol,2020,38(10):2601-2607.
doi: 10.1007/s00345-019-03061-6 |
| [1] | 周培茹, 蒋析, 华红. 口腔黏膜病患者口腔种植的时机及注意事项[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(1): 5-8. |
| [2] | 王建伟,满立波,黄广林,何峰,王海,王海东,徐啸,李伟,翟建坡,刘振华. 口腔黏膜背侧移植结合阴茎带蒂皮瓣腹侧覆盖治疗阴茎部尿道狭窄[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2019, 51(4): 641-645. |
| [3] | 王莺, Obada Barry, Gerhard Wahl, 陈波,林野. 应用激光多普勒血流仪监测口腔黏膜血流[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2016, 48(4): 697-701. |
| [4] | 丁宁, 闫志敏, 华红. 实时荧光定量PCR法检测原发性Sjögren综合征口腔真菌菌群[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2013, 45(1): 17-21. |
| [5] | 曹婕*, 刘宏伟, 刘晓松, 金建秋, 张平. 口腔黏膜微核细胞数与上皮异常增生病损癌变的关系[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2011, 43(4): 600-602. |
| [6] | 林野, 邱立新, 胡秀莲, 王莺, 李健慧. 硬腭游离黏膜移植在种植体周软组织结构重建中的应用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2007, 39(1): 21-25. |
| [7] | 杨天智, 陈大兵, 张强. 不同吸收促进剂及酶抑制剂对胰岛素体内及体外口腔黏膜渗透性的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2001, 33(3): 238-242. |
|
||