北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2025, Vol. 57 ›› Issue (5): 926-933. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2025.05.017
左金丸中吴茱萸生物碱和小檗碱联合用药对HepG2细胞毒性的影响
高亚东1,2, 朱安1,3, 李璐迪1, 李盈姿1, 王旗1,4,5,*( )
)
- 1. 北京大学公共卫生学院毒理学系,北京 100191
2. 福建省疾病预防控制中心福建省人兽共患病研究重点实验室,福州 350012
3. 福建医科大学基础医学院消化道恶性肿瘤教育部重点实验室,福州 350108
4. 国家中医药管理局中药配伍减毒重点研究室,北京 100191
5. 食品安全毒理学研究与评价北京市重点实验室,北京 100191
Effect of the combination of alkaloids from Euodiae Fructus and berberine in Zuojin Pill on cytotoxicity in HepG2 cells
Yadong GAO1,2, An ZHU1,3, Ludi LI1, Yingzi LI1, Qi WANG1,4,5,*( )
)
- 1. Department of Toxicology, Peking University School of Public Health, Beijing 100191, China
2. Fujian Provincial Key Laboratory of Zoonosis Research, Fujian Provincial Center for Disease Control and Prevention, Fuzhou 350012, China
3. Key Laboratory of Ministry of Education for Gastrointestinal Cancer, School of Basic Medical Sciences, Fujian Medical University, Fuzhou 350108, China
4. Key Laboratory of State Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine for Compatibility Toxicology, Beijing 100191, China
5. Beijing Key Laboratory of Toxicological Research and Risk Assessment for Food Safety, Beijing 100191, China
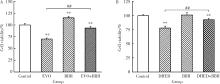
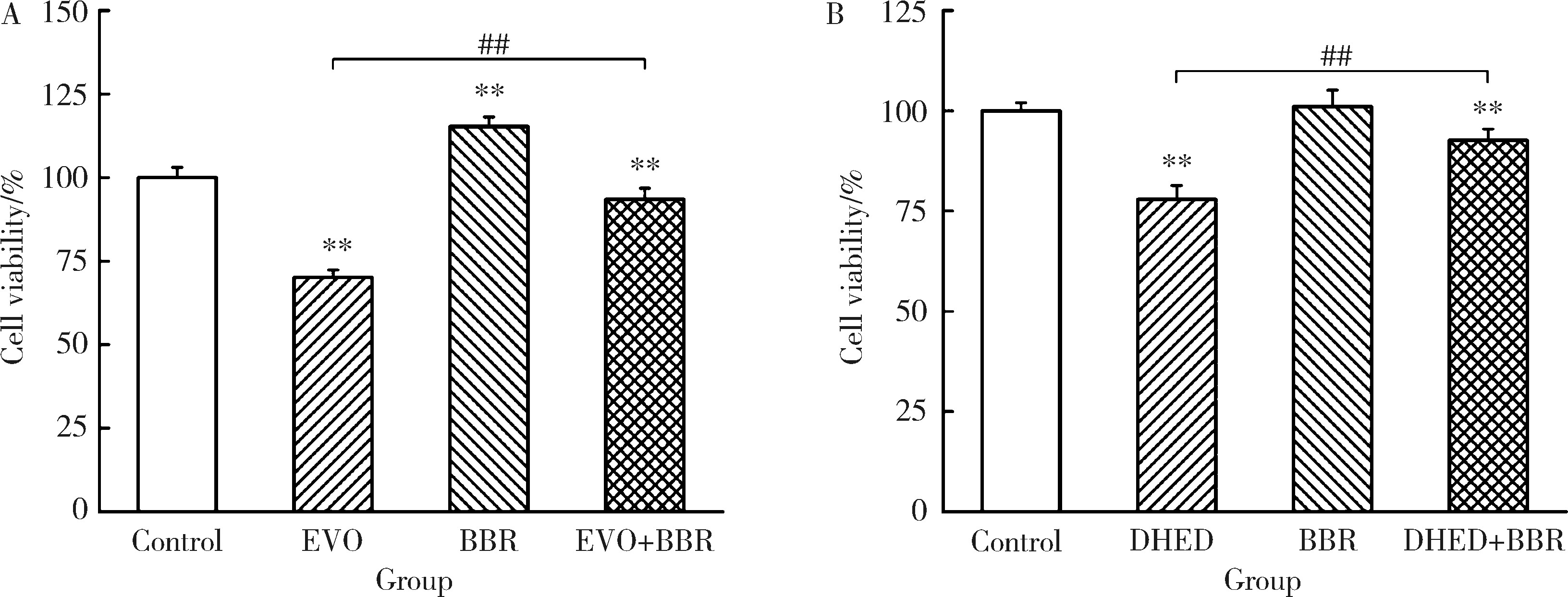
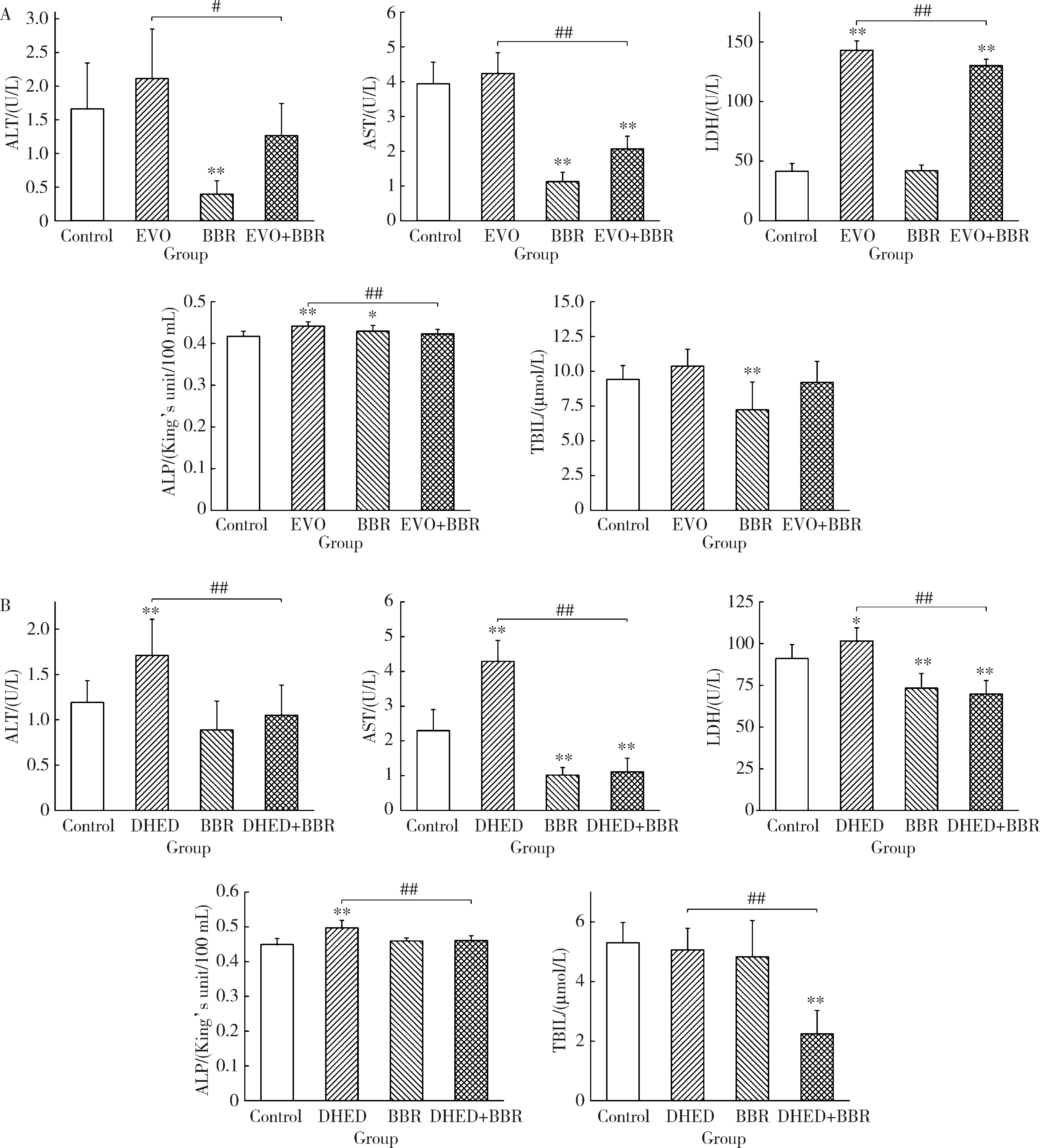
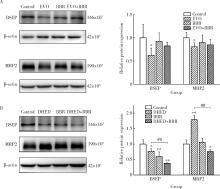
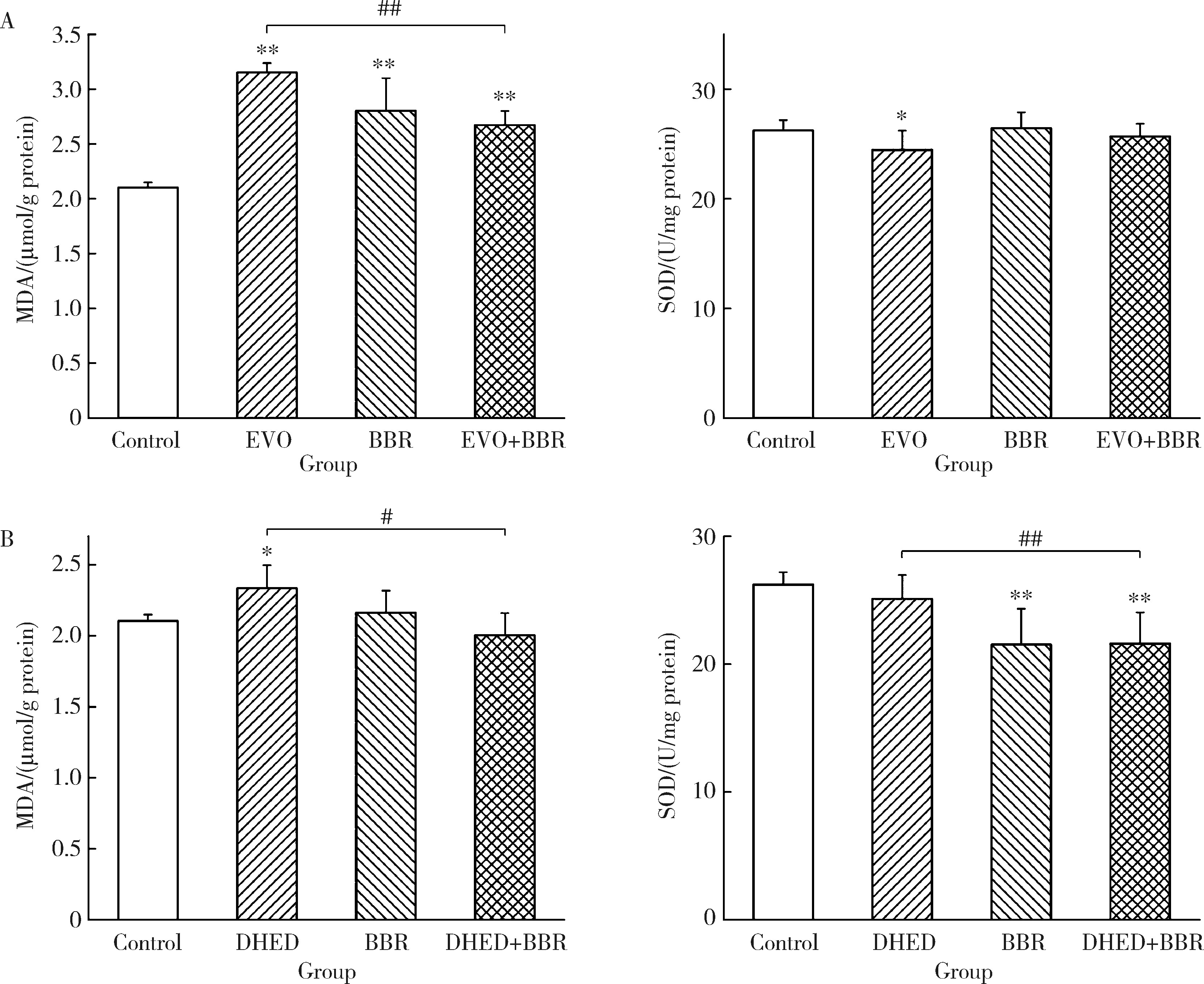
摘要: 目的: 研究左金丸中吴茱萸生物碱和小檗碱联合用药对肝细胞毒性的影响,探讨联合用药的减毒机制。方法: 参照左金丸中各化学成分吸收入血的峰浓度(maximum concentration,Cmax)确定成分配伍比例,采用HepG2细胞模型研究吴茱萸中肝毒性成分吴茱萸碱(evodiamine,EVO)、去氢吴茱萸碱(dehydroevodiamine,DHED)与小檗碱联合用药48 h的细胞毒性。实验分为溶剂对照组、EVO组、DHED组、小檗碱组,以及EVO或DHED与小檗碱的联合用药组。以细胞计数试剂盒法(cell counting kit-8,CCK-8)测定细胞存活率,并采用联合指数判断药物的毒性作用。检测细胞上清液中谷丙转氨酶(alanine transaminase,ALT)、谷草转氨酶(aspartate aminotransferase,AST)、乳酸脱氢酶(lactate dehydrogenase,LDH)、碱性磷酸酶(alkaline phosphatase,ALP)活性及总胆红素(total bilirubin,TBIL)含量。采用Western blot检测胆汁酸转运体胆盐输出泵(bile salt export pump,BSEP)和多耐药相关蛋白2(multidrug resistance-associated protein 2,MRP2)的表达水平。检测HepG2细胞丙二醛(malondialdehyde,MDA)含量和超氧化物歧化酶(superoxide dismutase,SOD)活性。结果: 与EVO或DHED组相比,EVO 1 μmol/L与小檗碱10 μmol/L联用、DHED 50 μmol/L与小檗碱35 μmol/L联用,均可显著提高HepG2细胞的存活率(P<0.01),其联合指数值分别为77.89和4.49,远大于1。联用小檗碱可降低细胞上清液中ALT、AST、LDH和ALP活性,并减少TBIL含量(P<0.05、P<0.01)。与EVO组相比,EVO联用小檗碱可上调BSEP和MRP2蛋白表达;与DHED组相比,DHED联用小檗碱可显著下调BSEP和MRP2蛋白表达(P<0.01)。EVO或DHED与小檗碱联用均可显著减少MDA含量(P<0.05、P<0.01)。结论: 一定配比的小檗碱与EVO或DHED联用,对其HepG2细胞毒性具有拮抗作用,其减毒作用的机制与调节胆汁酸转运体表达、减轻脂质过氧化损伤有关。
中图分类号:
- R114
| 1 |
国家药典委员会. 中华人民共和国药典(一部2020年版)[M]. 北京: 中国医药科技出版社, 2020: 178.
|
| 2 |
黄伟, 李晓骄阳, 孙蓉. 吴茱萸水提组分多次给药对小鼠肝毒性的"量-时-毒"关系研究[J]. 中国中药杂志, 2012, 37(15): 2223- 2227.
|
| 3 |
刘颖, 杨润芳, 夏祺悦, 等. 吴茱萸醇提物重复给药的靶器官毒性研究[J]. 现代预防医学, 2015, 42(14): 2600- 2603.
|
| 4 |
彭成. 试论中药配伍研究的方法与实践[J]. 中药与临床, 2012, 3(1): 1- 4.
|
| 5 |
doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2020.173655 |
| 6 |
doi: 10.3390/molecules22020214 |
| 7 |
doi: 10.1124/pr.58.3.10 |
| 8 |
彭求贤, 蔡红兵, 史珏, 等. 黄连配伍吴茱萸后生物碱类成分的含量变化[J]. 中药材, 2012, 35(5): 742- 744.
|
| 9 |
倪建新, 林跃虹, 陈妙珠. 左金丸配伍意义的药物代谢动力学分析[J]. 中国当代医药, 2012, 19(5): 19- 20.
|
| 10 |
梁瑞峰, 张峰, 刘方洲, 等. 吴茱萸对黄连中小檗碱组织分布及肝脏摄取的影响[J]. 中医研究, 2014, 27(1): 64- 66.
|
| 11 |
黄果, 李凯鹏, 杨洁, 等. 黄连与吴茱萸合用大鼠体外肝代谢研究[J]. 中国中药杂志, 2010, 35(5): 651- 653.
|
| 12 |
doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2008.05.002 |
| 13 |
doi: 10.1186/s12944-017-0628-x |
| 14 |
高亚东, 朱安, 李璐迪, 等. 吴茱萸碱对HepG2细胞毒性及其机制[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(6): 1107- 1114.
doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2021.06.017 |
| 15 |
|
| 16 |
|
| 17 |
doi: 10.1016/j.hepres.2006.01.009 |
| 18 |
doi: 10.3748/wjg.15.1677 |
| 19 |
doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2005.03.017 |
| 20 |
doi: 10.1038/clpt.2014.158 |
| 21 |
doi: 10.1067/mcp.2001.114667 |
| 22 |
|
| 23 |
doi: 10.1186/s12906-016-1367-7 |
| 24 |
doi: 10.1074/jbc.M116.757567 |
| 25 |
doi: 10.1124/dmd.118.083691 |
| 26 |
doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2013.07.006 |
| 27 |
doi: 10.1038/35030140 |
| 28 |
doi: 10.1080/13510002.2016.1140406 |
| 29 |
doi: 10.1007/s11356-019-07232-1 |
| [1] | 高亚东,朱安,李璐迪,张涛,王硕,单丹萍,李盈姿,王旗. 吴茱萸碱对HepG2细胞毒性及其机制[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(6): 1107-1114. |
|
||