1 资料与方法
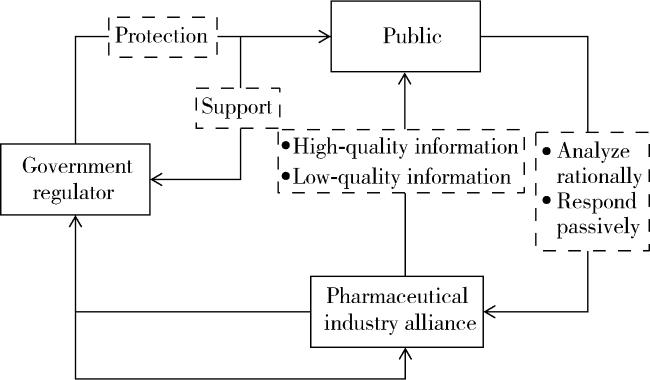
1.1 研究框架
1.1.1 三方策略空间及核心参数
表1 医药产业联盟、公众、政府监管部门三方主题策略空间Table 1 Three-way thematic strategy space for pharmaceutical industry alliances, the public, and government regulators |
| Game subjects | Tactical symbol | Strategy description | Probability |
| Pharmaceutical industry alliance | A1/A2 | Publish high quality/low quality information | α/(1-α) |
| The public | B1/B2 | Analyze rationally/respond passively | β/(1-β) |
| Government regulators | C1/C2 | Enforce regulation/no regulation | γ/(1-γ) |
表2 核心参数定义Table 2 Core parameter definitions |
| Parameter symbol | Full name of parameter | Economic implications | Theoretical foundation |
| α | Selection probability of high quality information | Degree to which industry alliances assess reputational value | Kreps reputation game model |
| β | Rational analysis selection probability | Crowd perception of willingness to invest resources | Dual systems cognitive theory |
| γ | Probability of regulatory implementation | Government risk prevention and control efforts | Polycentric governance theory |
| Iyy | Benefits of industry information release | Direct economic benefits from information dissemination | Fombrun’s reputational competition model |
| Cyy | High-bquality information argumentation cost | Input costs of professional verification, data collection, etc. | Kreps signaling costs |
| Cyy1 | Argumentation cost of low quality information | Cost of false information cover-up (Cyy1 < Cyy) | Adverse selection theory |
| Iqz | Benefits of information acquisition by the public | Value of health improvement due to correct information | Health behavior theory |
| Nqz | Negative utility for the public | Economic loss of health due to misinformation | Risk perception model |
| Cqz | Cost of information identification | Cognitive resource consumption such as time and energy | Cognitive load theory |
| Izf | Gains in government governance | Political gains from public health order maintenance | Public choice theory |
| Nzf | Government credibility loss | Cost of crisis of confidence due to regulatory failure | Institutional legitimacy theory |
| Czf | Regulatory enforcement costs | Regulatory resource inputs such as manpower and technology | Regulatory cost curve theory |
| Czf1 | Expost intervention costs | Additional administrative costs of crisis response | Contingency management theory |
| Fyy | Penalties for industry violations | Financial penalties for low-quality information | Becker deterrence theory |
| Ryy | Industry reputation loss | Long-term revenue loss due to scandal exposure | Reputational capital theory |
| Pyy | Industry compliance incentives | Policy incentives for the release of high-quality information | Positive reinforcement theory |
1.1.2 模型假设
1.1.2.1 假设一(有限理性动态博弈)
1.1.2.2 假设二(动态博弈时序)
1.1.3 三方支付函数
1.2 模型构建
表3 医药产业联盟、公众、政府监管部门的博弈矩阵Table 3 The game matrix of the pharmaceutical industry alliance, the masses, and government regulators |
| Public | Government regulator | |||
| Regulated (γ) | Unregulated (1-γ) | |||
| Pharmaceutical industry alliance | High-quality information (α) | Rational analysis (β) | Iyy-Cyy+Pyy, Iqz-Cqz,Izf-Czf-Pyy | Iyy-Cyy,Iqz-Cqz,Izf-Czf1 |
| Passive response (1-β) | Iyy-Cyy+Pyy,0,Izf-Czf-Pyy | Iyy-Cyy,0,Izf-Czf1 | ||
| Low-quality information (1-α) | Rational analysis (β) | -Cyy1-Fyy-Ryy,-Nqz-Cqz,-Nzf-Czf | -Cyy1,-Nqz-Cqz,-Nzf-Czf1-Fzf | |
| Passive response (1-β) | -Cyy1-Fyy-Ryy,-Nqz,-Nzf-Czf-Fzf | -Cyy1,-Nqz,-Nzf-Czf1-Fzf | ||
2 结果与讨论
2.1 医药产业联盟的策略稳定性分析
2.2 公众的策略稳定性分析
2.3 政府监管部门策略稳定性分析
2.4 策略组合稳定性分析
表4 三方演化博弈均衡点特征值表Table 4 Table of eigenvalues of equilibrium points of the three-way evolutionary game |
| Balance point | Jacobian matrix eigenvalues |
| λ1,λ2,λ3 | |
| E1 (0,0,0) | -Cyy+Cyy1+Iyy,-Cqz,-Czf+Czf1 |
| E2 (1,0,0) | Cyy-Cyy1-Iyy,-Cqz+Iqz-Czf+Czf1-Pyy |
| E3 (0,1,0) | -Cyy+Cyy1+Iyy,Cqz,-Czf+Czf1+Fzf |
| E4 (0,0,1) | -Cyy+Cyy1+Fyy+Iyy+Pyy+Ryy,-Cqz,Czf-Czf1 |
| E5 (1,1,0) | Cyy-Cyy1-Iyy,Cqz-Iqz,-Czf+Czf1-Pyy |
| E6 (1,0,1) | Cyy-Cyy1-Fyy-Iyy-Pyy-Ryy,-Cqz+Iqz,Czf-Czf1+Pyy |
| E7 (0,1,1) | -Cyy+Cyy1+Fyy+Iyy+Pyy+Ryy,Cqz,Czf-Czf1-Fzf |
| E8 (1,1,1) | Cyy-Cyy1-Fyy-Iyy-Pyy-Ryy,Cqz-Iqz,Czf-Czf1+Pyy |
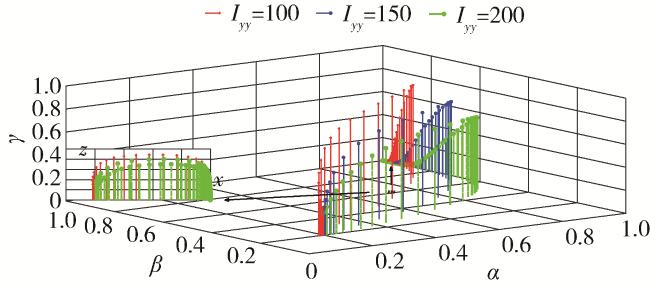
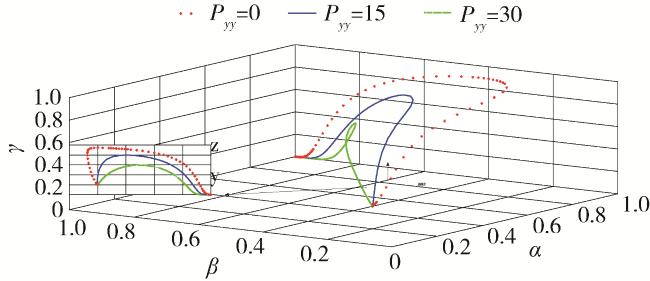
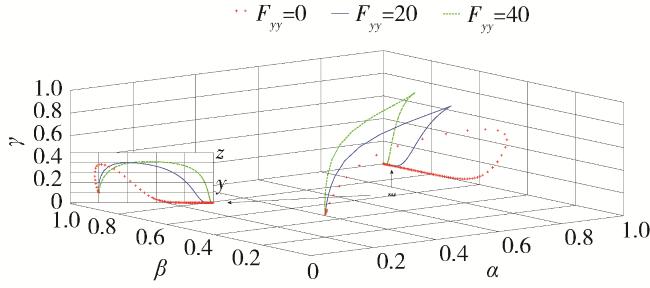
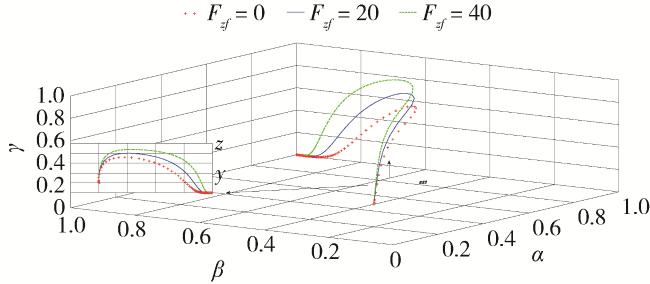
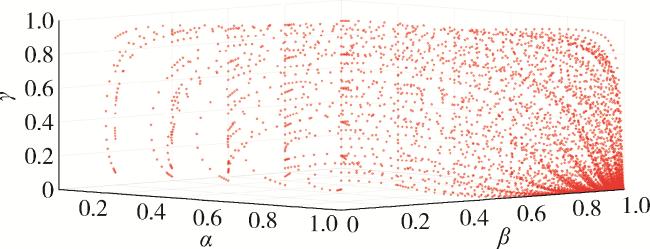
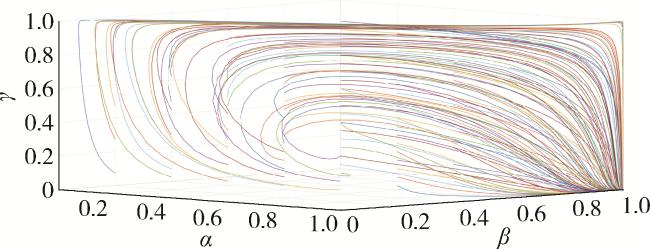
2.5 仿真分析
表5 核心参数赋值依据Table 5 Basis for assigning values to core parameters |
| Parameter symbol | Assign a value | Theoretical foundation |
| Iyy=150 | Reference value | Extrapolated with reference to the average marketing ROI of the pharmaceutical industry in 2021 |
| Cyy-Cyy1 | 85/105 | Third-party certification (Cyy) required for high-quality information, format review only for low-quality information(Cyy1=Cyy×0.3) |
| Fyy=20/25 | Degree of punishment | Standardized to the minimum fine under article 118 of the drug administration Act |
| Pyy=35 | Reward value | Average value of government funding for science and technology projects |
| Nqz=30 | Loss value | Equivalent QALY loss (0.05 quality-adjusted life year per misinformation) |
ROI, return on investment; QALY, guality-adjusted lift year. |