1 资料与方法
1.1 一般资料
表1 复杂输尿管狭窄患者的临床资料Table 1 Clinical data of patients with complex ureteral strictures |
| Variables | Data (n=21) |
| Gender (male/female), n | 10/11 |
| Age/years, ${\bar x}$±s | 44.1±13.3 |
| Causes of stenosis, n | |
| Calculus | 15 |
| Injury | 1 |
| Radiotherapy | 1 |
| Congenital factors | 4 |
| Location of stenosis, n | |
| Left/right side | 9/12 |
| Upper/middle/lower segment | 4/12/5 |
| Length of stenosis/cm, ${\bar x}$±s | 4.81±4.33 |
| Reconstruction methods, n | |
| Pyeloplasty | 4 |
| Ureteroneocystostomy | 2 |
| Bladder flap ureteroplasty | 4 |
| Lingual mucosal graft ureteroplasty | 6 |
| Appendix graft ureteroplasty | 2 |
| Ureteroureterostomy | 1 |
| Ileal segment replacement of ureter | 1 |
| Renal pelvis flap + ureteroneocystostomy | 1 |
| Surgical approaches, n | |
| Laparoscopy | 17 |
| da Vinci robot-assisted laparoscopy | 4 |
1.2 手术方法
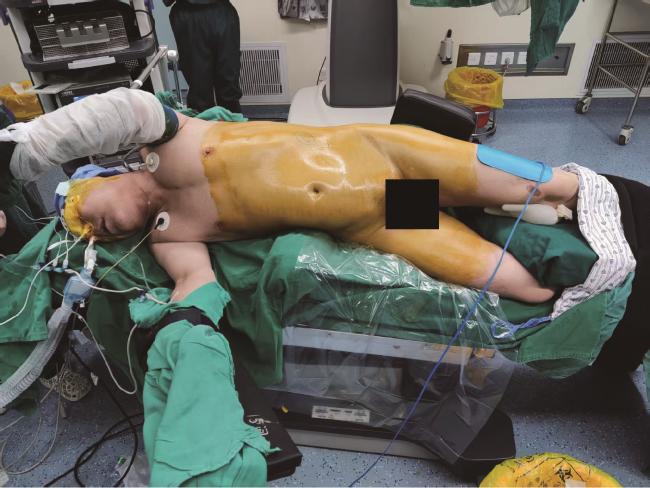
图1 体位:斜仰卧位,背部与水平面呈60°Figure 1 An inclined supine position with the back inclined at a 60° angle relative to the horizontal plane |
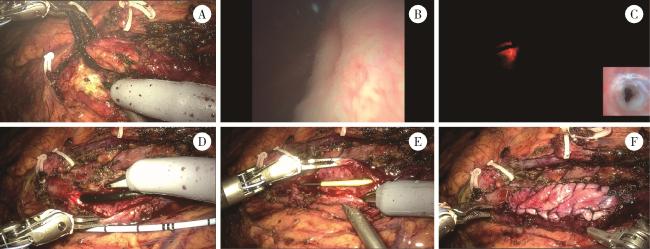
图2 输尿管软镜联合机器人辅助腹腔镜定位中段狭窄Figure 2 Robot-assisted laparoscopic ureteroplasty with flexible ureteroscopic guidance for mid-ureteral stricture localization A, dissection of the ureter; B, flexible ureteroscopy exploration of the ureter in lateral position (bare scope technique); C, deactivation of robotic laparoscopic light source for stricture localization; D, resection of strictured segment with patency confirmation via flexible scope; E, retrograde ureteral stent placement; F, lingual mucosa graft ureteroplasty. |