1 病例报告
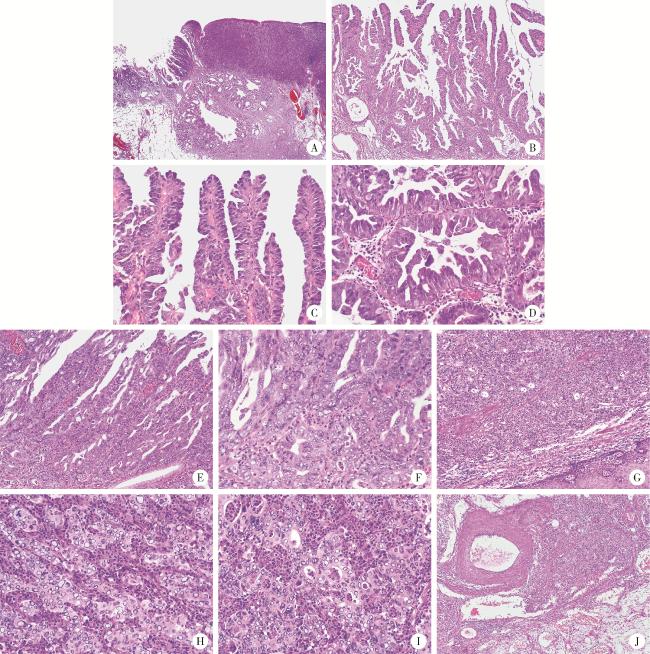
图1 食管胃结合部具有显著空泡状核特征的神经内分泌癌的形态学特征(HE染色)Figure 1 Morphological characteristics of neuroendocrine carcinoma with significantly vacuolar nucleus at the esophagogastric junction (HE staining) A, the hierarchical structure of mucosa and submucosa existed; abnormal branched glands were seen in the tumor area, some were solid, and nodular glands and cystic expansion were seen in the submucosa; B, intramucosal tumor with branching papillary structure; C, D, the surface of the papillary and the glandular was lined with boot-like or cuboidal cells, and a few nuclei were slightly vacuolated; E, F, the lining epithelium of some papillae and glandular cord hyperplasia fused to form a cribriform structure; the nucleus was obviously vacuolated; G, the main body of the tumor is solid, with diffuse arrangement of cells and no involvement of the surface squamous epithelium; H, I, the cells of the solid area were structured with nests, cord, and glandular tubes, with significantly vacuolar changes in nuclei, atypical mitoses, and a large capillary network with a large number of neutrophils in the tumor stroma; J, cancer cell mass seen in submucosa veins. A, 20×; B, G, 100×; C-F, H, I, 400×; J, 40×. HE, hematoxylin and eosin. |
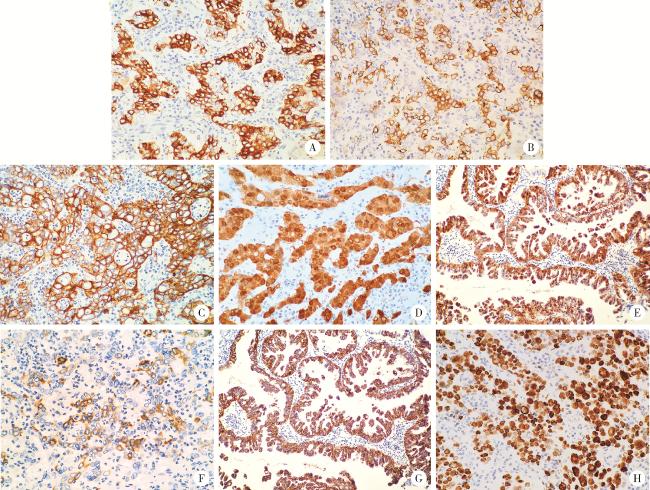
图2 食管胃结合部具有显著空泡状核特征的神经内分泌癌的免疫表型特征(IHC染色)Figure 2 Immunophenotypic characteristics of neuroendocrine carcinoma with significantly vacuolar nucleus at the esophagogastric junction (IHC staining) A, the cells of the solid area showed positive staining for chromogranin A (CgA); B, the cells of the solid area showed positive staining for synaptophy-sin (Syn); C, the tumor cells showed cytokeratin-pan (CKpan) positive for cytoplasmic membrane and negative for nucleus and intranuclear vacuoles; D, the cells of the solid area showed diffusely positive staining for P16; E, the papillary adenocarcinoma component showed diffusely positive staining for P16; F, the cells of the solid area showed partially positive for MUC5AC; G, the papillary adenocarcinoma component showed diffusely positive staining for MUC5AC; H, the cells of the solid area showed diffusely positive staining for p53. A, B, E, G, 200×; C, D, F, H, 400×. IHC, immunohistochemical. |