1 资料与方法
1.1 主要试剂
1.2 细胞培养
1.3 构建pKO.1-shUSP35-puro质粒
1.4 构建pLVX-USP35-puro质粒
1.5 稳转株的构建
1.6 细胞分组及Erastin诱导干预
1.7 CCK8实验
1.8 qPCR实验
1.9 蛋白免疫印迹实验(Western blotting)
1.10 ROS检测实验
1.11 MDA检测实验
1.12 GSH/GSSH检测实验
1.13 Fe2+检测实验
1.14 统计学分析
2 结果
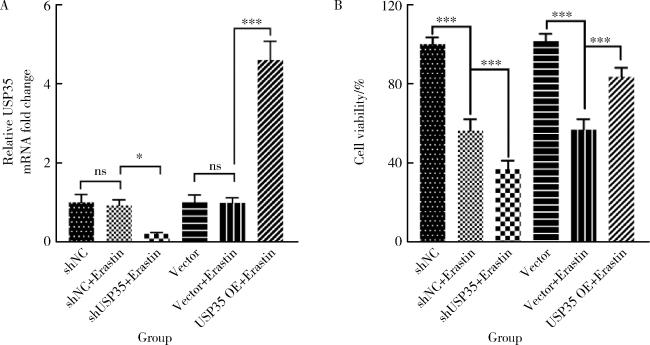
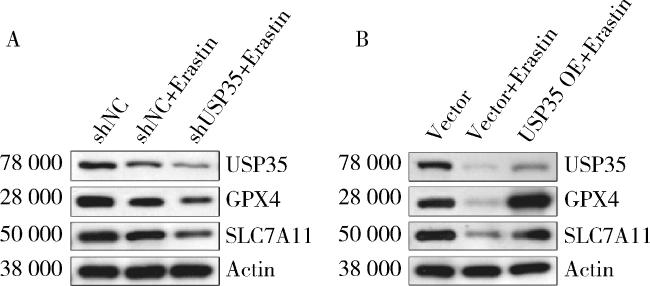
2.1 沉默USP35加剧Erastin对RA-FLS细胞活力的抑制
图1 USP35对RA-FLS细胞活力的影响(n=3)Figure 1 Influence of USP35 on the viability of RA-FLS cells (n=3) *P < 0.05, ***P < 0.001. A, qPCR detection of USP35 mRNA expression; B, CCK8 detection of RA-FLS cell viability. shNC, negtive control of short hairpin ribonucleic acid; shUSP35, short hairpin ribonucleic acid of USP35; USP35 OE, overexpression of USP35; USP35, ubiquitin-specific protease 35; qPCR, quantitative real-time PCR; CCK8, cell counting kit-8; RA-FLS, rheumatoid arthritis-fibroblast like synoviocytes; ns, no statistic. |
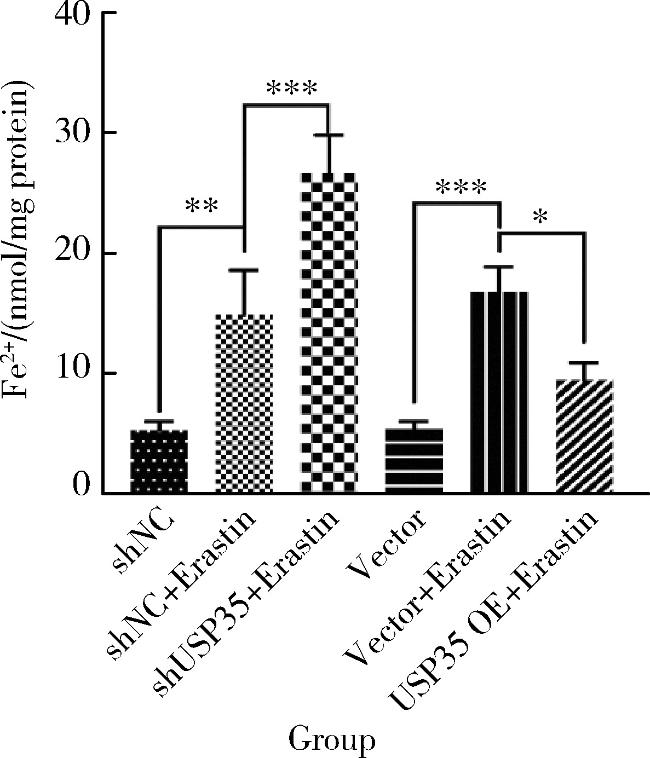
2.2 USP35可降低Erastin诱导RA-FLS细胞中Fe2+的水平
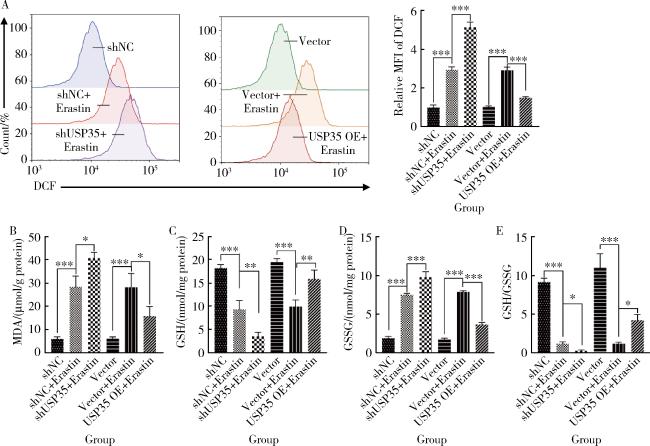
2.3 USP35抑制Erastin诱导RA-FLS细胞的ROS和MDA水平,并提升GSH/GSSG比值
图3 RA-FLS细胞中活性氧、丙二醛、谷胱甘肽和氧化型谷胱甘肽的含量检测(n=3)Figure 3 Detection of ROS, MDA, GSH, and GSSG levels in RA-FLS cells (n=3) *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001. A, cellular ROS assay; B, cellular MDA assay; C, cellular GSH assays; D, cellular GSSG assays; E, cellular GSH/GSSG assays. MFI, mean fluorescent intensity; DCF, 2', 7'-dichlorofluorescein; ROS, reactive oxygen species; MDA, malondialdehyde; GSH, glutathione; GSSG, glutathione sulfide; Other abbreviations as in Figure 1. |