Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences) ›› 2018, Vol. 50 ›› Issue (6): 991-997. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2018.06.009
• Article • Previous Articles Next Articles
Effect of functional exercises on patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a meta-analysis
Li WANG,Chao GAO,Di ZHU,Li-hong CHEN( )
)
- Department of Rheumatology and Immunology, Peking University People’s Hospital, Beijing 100044, China
CLC Number:
- R593.22
| [1] |
Smolen JS, Landewé R, Breedveld FC , et al. EULAR recommendations for the management of rheumatoid arthritis with synthetic and biological disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs[J]. Ann Rheum Dis, 2010,69(6):964-975.
doi: 10.1136/ard.2009.126532 |
| [2] |
McInnes IB, Schett G . Pathogenetic insights from the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis[J]. Lancet, 2017,389(10086):2328-2337.
doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(17)31472-1 pmid: 28612747 |
| [3] |
曾小峰, 朱松林, 谭爱春 , 等. 我国类风湿关节炎疾病负担和生存质量研究的系统评价[J]. 中国循证医学杂志, 2013,13(3):300-307.
doi: 10.7507/1672-2531.20130052 |
| [4] |
周云杉, 王秀茹, 安媛 , 等. 全国多中心类风湿关节炎患者残疾及功能受限情况的调查[J]. 中华风湿病学杂志, 2013,17(8):526-532.
doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1007-7480.2013.08.006 |
| [5] |
王秀丽, 唐玉萍, 孙树萍 , 等. 类风湿关节炎患者功能锻炼现状及影响因素分析[J]. 护理进修杂志, 2016,31(5):442-444.
doi: 10.16821/j.cnki.hsjx.2016.05.020 |
| [6] | 王庆, 徐桂华, 周学平 , 等. 功能锻炼在类风湿关节炎患者康复中的作用研究近况[J]. 风湿病与关节炎, 2013,2(5):46-48. |
| [7] |
风湿免疫疾病慢病管理全国护理协作组. 类风湿关节炎患者的慢病管理专家共识(2014版)[J]. 中华风湿病学杂志, 2016,20(2):127-130.
doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1007-7480.2016.02.013 |
| [8] |
Arnett FC, Edworthy SM, Bloch DA , et al. The American rheumatism association 1987 revised criteria for the classification of rheumatoid arthritis[J]. Arthritis Rheum, 1988,31(3):315-324.
doi: 10.1002/art.1780310302 pmid: 3358796 |
| [9] | Higgins JPT , Green S. Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions version 5.1.0 [EB/OL]. ( 2011 -04-10) (2015-07-05). |
| [10] |
Baillet A, Payraud E, Niderprim VA , et al. A dynamic exercise programme to improve patients’ disability in rheumatoid arthritis: A prospective randomized controlled trial[J]. Rheumatology, 2009,48(4):410-415.
doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/ken511 pmid: 19211654 |
| [11] |
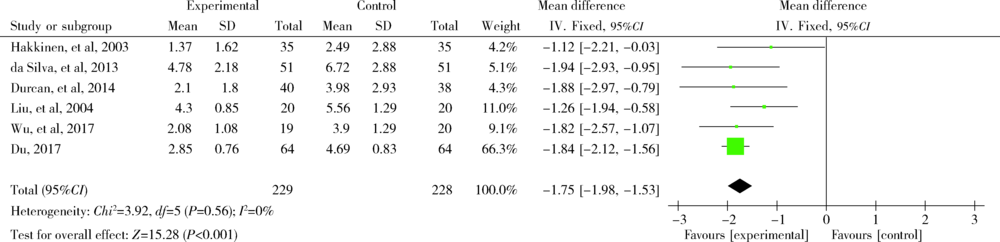
da Silva KN, Teixeira LE, Imoto AM , et al. Effectiveness of sensorimotor training in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a rando-mized controlled trial[J]. Rheumatol Int, 2013,33(9):2269-2275.
doi: 10.1007/s00296-013-2706-3 pmid: 23455663 |
| [12] |
Siqueira US , Orsini Valente LG, de Mello MT, et al. Effectiveness of aquatic exercises in women with rheumatoid arthritis: a rando-mized, controlled, 16-week intervention-the HydRA trial[J]. Am J Phys Med Rehabil, 2017,96(3):167-175.
doi: 10.1097/PHM.0000000000000564 |
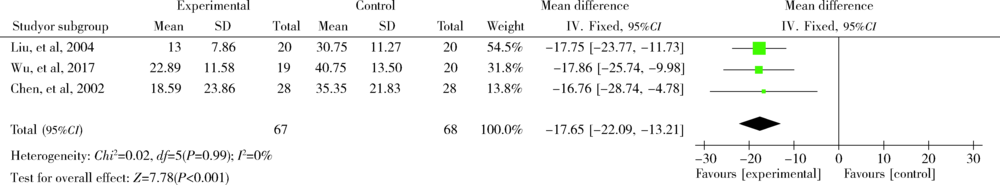
| [13] | 陈立红, 杨玉琴, 吴鸥 , 等. 手腕部锻炼对类风湿关节炎手功能恢复的影响[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2002,37(9):668-669. |
| [14] | 刘启华, 王玉玲, 孙美红 , 等. 手腕部关节功能操减轻类风湿关节炎局部症状的观察[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2004,39(7):508-510. |
| [15] |
Cima SR, Barone A, Porto JM , et al. Strengthening exercises to improve hand strength and functionality in rheumatoid arthritis with hand deformities: a randomized, controlled trial[J]. Rheumatol Int, 2013,33(3):725-732.
doi: 10.1007/s00296-012-2447-8 pmid: 22565655 |
| [16] |
张标新, 朱庆云 . 个体化系统锻炼对类风湿关节炎患者活动能力的影响[J]. 护士进修杂志, 2008,23(22):2029-2030.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-6975.2008.22.005 |
| [17] | 杜晓云 . 功能锻炼及个性化运动对类风湿关节炎患者预后及生活质量的影响[J]. 当代护士, 2017(6):31-33. |
| [18] |
吴莉萍, 张子云, 李晓倩 , 等. 活动期类风湿关节炎患者关节功能锻炼的延续护理[J]. 护理学杂志, 2017,32(4):83-85.
doi: 10.3870/j.issn.1001-4152.2017.07.083 |
| [19] |
Durcan L, Wilson F, Cunnane G . The effect of exercise on sleep and fatigue in rheumatoid arthritis: a randomized controlled study[J]. J Rheumatol, 2014,41(10):1966-1973.
doi: 10.3899/jrheum.131282 pmid: 25128510 |
| [20] |
Stavropoulos-Kalinoglou A, Metsios GS , Veldhuijzen van Zanten JJ, et al. Individualised aerobic and resistance exercise training improves cardiorespiratory fitness and reduces cardiovascular risk in patients with rheumatoid arthritis[J]. Ann Rheum Dis, 2013,72(11):1819-1825.
doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2012-202075 pmid: 23155222 |
| [21] |
Häkkinen A, Sokka T, Lietsalmi AM , et al. Effects of dynamic strength training on physical function, Valpar 9 work sample test, and working capacity in patients with recent-onset rheumatoid arthritis[J]. Arthritis Rheum, 2003,49(1):71-77.
doi: 10.1002/art.10902 pmid: 12579596 |
| [22] |
Bilberg A, Ahlmén M, Mannerkorpi K . Moderately intensive exercise in a temperate pool for patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a randomized controlled study[J]. Rheumatology, 2005,44(4):502-508.
doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/keh528 pmid: 15728422 |
| [23] |
Prioreschi A, Makda MA, Tikly M , et al. In patients with established RA, positive effects of a randomised three month WBV therapy intervention on functional ability, bone mineral density and fatigue are sustained for up to six months[J]. PLoS One, 2016,11(4):e0153470.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0153470 pmid: 27073832 |
| [24] |
McKenna S, Tierney M, O’Neill A , et al. Sleep and physical activity: a cross-sectional objective profile of people with rheumatoid arthritis[J]. Rheumatol Int, 2018,38(5):845-853.
doi: 10.1007/s00296-018-4009-1 pmid: 29541902 |
| [25] |
Agca R, Heslinga SC, Rollefstad S , et al. EULAR recommendations for cardiovascular disease risk management in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and other forms of inflammatory joint disorders: 2015/2016 update[J]. Ann Rheum Dis, 2017,76(1):17-28.
doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2016-209775 |
| [26] | 中华医学会风湿病学分会. 2018中国类风湿关节炎诊疗指南[J]. 中华内科杂志, 2018,57(4):242-251. |
| [1] | Dongwu LIU, Jie CHEN, Mingli GAO, Jing YU. Rheumatoid arthritis with Castleman-like histopathology in lymph nodes: A case report [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(5): 928-931. |
| [2] | Huina HUANG,Jing ZHAO,Xiangge ZHAO,Ziran BAI,Xia LI,Guan WANG. Regulatory effect of lactate on peripheral blood CD4+ T cell subsets in patients with rheumatoid arthritis [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(3): 519-525. |
| [3] | Xiaofei TANG,Yonghong LI,Qiuling DING,Zhuo SUN,Yang ZHANG,Yumei WANG,Meiyi TIAN,Jian LIU. Incidence and risk factors of deep vein thrombosis in patients with rheumatoid arthritis [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(2): 279-283. |
| [4] | Xue ZOU,Xiao-juan BAI,Li-qing ZHANG. Effectiveness of tofacitinib combined with iguratimod in the treatment of difficult-to-treat moderate-to-severe rheumatoid arthritis [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(6): 1013-1021. |
| [5] | Qi WU,Yue-ming CAI,Juan HE,Wen-di HUANG,Qing-wen WANG. Correlation between dyslipidemia and rheumatoid arthritis associated interstitial lung disease [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(6): 982-992. |
| [6] | Jing-feng ZHANG,Yin-ji JIN,Hui WEI,Zhong-qiang YAO,Jin-xia ZHAO. Correlation analysis between body mass index and clinical characteristics of rheumatoid arthritis [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(6): 993-999. |
| [7] | Jin-hui LAI,Qi WANG,Jia-xiang JI,Ming-rui WANG,Xin-wei TANG,Ke-xin XU,Tao XU,Hao HU. Effects of delayed ureteral stents removal during the COVID-19 pandemic on the quality of life and psychological status of postoperative patients with urinary calculi [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(5): 857-864. |
| [8] | Yin-ji JIN,Lin SUN,Jin-xia ZHAO,Xiang-yuan LIU. Significance of IgA isotype of anti-v-raf murine sarcoma viral oncogene homologue B1 antibody in rheumatoid arthritis [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(4): 631-635. |
| [9] | Wen-xin CAI,Shi-cheng LI,Yi-ming LIU,Ru-yu LIANG,Jing LI,Jian-ping GUO,Fan-lei HU,Xiao-lin SUN,Chun LI,Xu LIU,Hua YE,Li-zong DENG,Ru LI,Zhan-guo LI. A cross-sectional study on the clinical phenotypes of rheumatoid arthritis [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(6): 1068-1073. |
| [10] | Fang CHENG,Shao-ying YANG,Xing-xing FANG,Xuan WANG,Fu-tao ZHAO. Role of the CCL28-CCR10 pathway in monocyte migration in rheumatoid arthritis [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(6): 1074-1078. |
| [11] | Rui LIU,Jin-xia ZHAO,Liang YAN. Clinical characteristics of patients with rheumatoid arthritis complicated with venous thrombosis of lower extremities [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(6): 1079-1085. |
| [12] | Jing-feng ZHANG,Yin-ji JIN,Hui WEI,Zhong-qiang YAO,Jin-xia ZHAO. Cross-sectional study on quality of life and disease activity of rheumatoid arthritis patients [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(6): 1086-1093. |
| [13] | GAO Chao,CHEN Li-hong,WANG Li,YAO Hong,HUANG Xiao-wei,JIA Yu-bo,LIU Tian. Validation of the Pollard’s classification criteria (2010) for rheumatoid arthritis patients with fibromyalgia [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(2): 278-282. |
| [14] | LOU Xue,LIAO Li,LI Xing-jun,WANG Nan,LIU Shuang,CUI Ruo-mei,XU Jian. Methylation status and expression of TWEAK gene promoter region in peripheral blood of patients with rheumatoid arthritis [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2021, 53(6): 1020-1025. |
| [15] | ZHONG Hua,XU Li-ling,BAI Ming-xin,SU Yin. Effect of chemokines CXCL9 and CXCL10 on bone erosion in patients with rheumatoid arthritis [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2021, 53(6): 1026-1031. |
|
||