Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences) ›› 2018, Vol. 50 ›› Issue (6): 1014-1021. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2018.06.013
• Article • Previous Articles Next Articles
Efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells on systemic lupus erythematosus:a meta-analysis
Shuang LIU1,Yu-long GUO2,Jing-yi YANG3,Wei WANG1,Jian XU1,△( )
)
- 1. Department of Rheumatology and Immunology, First Affiliated Hospital of Kunming Medical University, Kunming 650032, China
2. Department of Cardiology, Yunnan Provincial Fuwai Cardiovascular Disease Hospital, Kunming 650000, China
3. Yunnan Shunxi Regeneration Medical Engineering Co., Ltd, Kunming 650000, China
CLC Number:
- R593.24
| [1] | 中华医学会风湿病学分会. 系统性红斑狼疮诊断及治疗指南[J]. 中华风湿病学杂志, 2010,14(5):342-346. |
| [2] |
van Vollenhoven RF, Mosca M, Bertsias G , et al. Treat-to-target in systemic lupus erythematosus: recommendations from an international task force[J]. Ann Rheum Dis, 2014,73(6):958-967.
doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2013-205139 pmid: 24739325 |
| [3] |
He J, Zhang X, Wei Y , et al. Low-dose interleukin-2 treatment selectively modulates CD4(+) T cell subsets in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus[J]. Nat Med, 2016,22(9):991-993.
doi: 10.1038/nm.4148 pmid: 27500725 |
| [4] | 王丹丹, 孙凌云 . 间充质干细胞移植治疗重症自身免疫病[J]. 中国实用内科杂志, 2015,35(10):831-834. |
| [5] | 梁军, 孙凌云 . 间充质干细胞治疗系统性红斑狼疮的基础和临床研究[J]. 浙江医学, 2017,39(21):1836-1841. |
| [6] |
Carrion F, Nova E, Ruiz C , et al. Autologous mesenchymal stem cell treatment increased T regulatory cells with no effect on disease activity in two systemic lupuserythematosus patients[J]. Lupus, 2010,19(3):317-322.
doi: 10.1177/0961203309348983 |
| [7] |
Deng D, Zhang P, Guo Y , et al. A randomised double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of allogeneic umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cell for lupus nephritis[J]. Ann RheumDis, 2017,76(8):1436-1439.
doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2017-211073 |
| [8] | Hochberg MC . Updating the American College of Rheumatology revised criteria for the classification of systemic lupus erythematosus[J]. Arthritis Rheum, 1997,40(9):1725. |
| [9] |
Petri M, Orbai A, Alarcón GS , et al. Derivation and validation of the Systemic Lupus International Collaborating Clinics classification criteria for systemic lupus erythematosus[J]. Arthritis Rheum, 2012,64(8):2677-2686.
doi: 10.1002/art.34473 |
| [10] |
Gladman DD, Iba ED, Urowitz MB . Systemic lupus erythematosus disease activity index 2000[J]. J Rheumatol, 2002,29(2):288-291.
doi: 10.1097/00124743-200202000-00018 pmid: 11838846 |
| [11] |
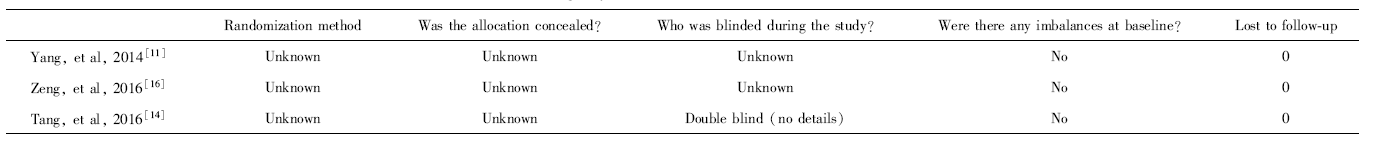
杨桂鲜, 潘丽萍, 陈志琴 , 等. 脐带间充质干细胞移植治疗狼疮性肾炎的临床疗效[J]. 实用医学杂志, 2014,30(17):2779-2781.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-5725.2014.17.029 |
| [12] |
白茹, 戚燕, 吕昭萍 , 等. 脐带间充质干细胞移植治疗难治性系统性红斑狼疮3年随访[J]. 中国免疫学杂志, 2017,33(6):905-909.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-484X.2017.06.020 |
| [13] |
李俊霞, 林强, 陈建 , 等. 脐带间充质干细胞对增殖型狼疮性肾炎的临床疗效观察[J]. 中华细胞与干细胞杂志: 电子版, 2016,6(3):174-178.
doi: 10.3877/cma.j.issn.2095-1221.2016.03.007 |
| [14] |
唐帮丽, 邓丹琪, 张佩莲 , 等. 脐带间充质干细胞移植治疗狼疮性肾炎的疗效与机制[J]. 昆明医科大学学报, 2016,37(7):93-98.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-4706.2016.07.022 |
| [15] |
Gu F, Wang D, Zhang H , et al. Allogeneic mesenchymal stem cell transplantation for lupus nephritis patients refractory to conventional therapy[J]. Clin Rheumatol, 2014,33(11):1611-1619.
doi: 10.1007/s10067-014-2754-4 pmid: 25119864 |
| [16] | 曾雯, 胡英, 杨霞 , 等. 间充质干细胞联合吗替麦考酚酯治疗狼疮性肾炎的临床效果[J]. 中国当代医药, 2016,23(7):67-70. |
| [17] |
朱宁, 毛静, 张小莲 , 等. 脐带间充质干细胞移植在系统性红斑狼疮患者中的应用研究[J]. 疑难病杂志, 2016,15(1):44-47.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6450.2016.01.011 |
| [18] | 裘影影, 何建强, 汤郁 , 等. 脐带间充质干细胞移植治疗难治性系统性红斑狼疮患者的疗效分析[J]. 中国实用医药, 2016,11(25):68-69. |
| [19] |
Sun L, Akiyama K, Zhang H , et al. Mesenchymal stem cell transplantation reverses multiorgan dysfunction in systemic lupus erythematosus mice and humans[J]. Stem Cells, 2009,27(6):1421-1432.
doi: 10.1002/stem.68 pmid: 19489103 |
| [20] | 杨桂鲜, 潘丽萍, 曹礼应 , 等. 脐带间充质干细胞治疗难治性系统性红斑狼疮的临床研究[J]. 云南医药, 2018,39(1):38-41. |
| [21] | 杨桂鲜, 潘丽萍, 陈志琴 , 等. 脐带间充质干细胞治疗系统性红斑狼疮的量效关系[J]. 云南医药, 2015,36(6):579-584. |
| [22] |
杨桂鲜, 潘丽萍, 宋薇 , 等. 脐带间充质干细胞治疗难治性系统性红斑狼疮临床分析[J]. 实用医学杂志, 2014,30(5):735-738.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-5725.2014.05.019 |
| [23] | 杨桂鲜, 潘丽萍, 周巧艳 , 等. 脐带间充质干细胞移植辅助治疗系统性红斑狼疮的疗效观察[J]. 四川大学学报(医学版), 2014,45(2):338-341. |
| [24] |
Klimczak A, Kozlowska U . Mesenchymal stromal cells and tissue-specific progenitor cells: their role in tissue homeostasis[J]. Stem Cells Int, 2016,4285215. doi: 10.1155/2016/4285215.
doi: 10.1155/2016/4285215 pmid: 4707334 |
| [25] |
Sun LY, Zhang HY, Feng XB , et al. Abnormality of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus[J]. Lupus, 2007,16(2):121-128.
doi: 10.1177/0961203306075793 |
| [26] |
Nie Y, Lau C, Lie A , et al. Defective phenotype of mesenchymal stem cells in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus[J]. Lupus, 2010,19(7):850-859.
doi: 10.1177/0961203310361482 pmid: 20118163 |
| [27] |
Li X, Liu L, Meng D , et al. Enhanced apoptosis and senescence of bone-marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus[J]. Stem Cells Dev, 2012,21(13):2387-2394.
doi: 10.1089/scd.2011.0447 pmid: 22375903 |
| [28] |
Gu Z, Tan W, Feng G , et al. Wnt/beta-catenin signaling me-diates the senescence of bone marrow-mesenchymal stem cells from systemic lupus erythematosus patients through the p53/p21 pathway[J]. Mol Cell Biochem, 2014,387(1-2):27-37.
doi: 10.1007/s11010-013-1866-5 pmid: 24130040 |
| [29] |
Wang D, Feng X, Lu L , et al. A CD8 T cell/indoleamine 2, 3-dioxygenase axis is required for mesenchymal stem cell suppression of human systemic lupus erythematosus[J]. Arthritis Rheum, 2014,66(8):2234-2245.
doi: 10.1002/art.38674 pmid: 24756936 |
| [30] |
Feng X, Che N, Liu Y , et al. Restored immunosuppressive effect of mesenchymal stem cells on B cells after olfactory 1/early B cell factor-associated zinc-finger protein down-regulation in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus[J]. Arthritis Rheum, 2014,66(12):3413-3423.
doi: 10.1002/art.v66.12 |
| [31] |
Fathollahi A, Gabalou NB, Aslani S . Mesenchymal stem cell transplantation in systemic lupus erythematous, a mesenchymal stem cell disorder[J]. Lupus, 2018,27(7):1053-1064.
doi: 10.1177/0961203318768889 |
| [32] |
Choi EW, Shin IS, Park SY , et al. Reversal of serologic, immunologic, and histologic dysfunction in mice with systemic lupus erythematosus by long-term serial adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cell transplantation[J]. Arthritis Rheum, 2012,64(1):243-253.
doi: 10.1002/art.33313 pmid: 21904997 |
| [33] |
Choi EW, Lee M, Song JW , et al. Mesenchymal stem cell transplantation can restore lupus disease-associated miRNA expression and Th1/Th2 ratios in a murine model of SLE[J]. Sci Rep, 2016(6):38237.
doi: 10.1038/srep38237 pmid: 27924862 |
| [34] |
Zhou K, Zhang H, Jin O , et al. Transplantation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell ameliorates the autoimmune pathogenesis in MRL/lpr mice[J]. Cell Mol Immunol, 2008,5(6):417-424.
doi: 10.1038/cmi.2008.52 |
| [35] |
Tang Y, Xie H, Chen J , et al. Activated NF-kappaB in bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells from systemic lupus erythematosus patients inhibits osteogenic differentiation through downregulating Smad signaling[J]. Stem Cells Dev, 2013,22(4):668-678.
doi: 10.1089/scd.2012.0226 |
| [36] |
Sun L, Wang D, Liang J , et al. Umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell transplantation in severe and refractory systemic lupus erythematosus[J]. Arthritis Rheum, 2010,62(8):2467-2475.
doi: 10.1002/art.v62:8 |
| [37] |
Zhang Z, Feng R, Niu L , et al. Humanumbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells inhibit T follicular helper cell expansion through the activation of iNOS in lupus-prone B6.MRL-Fas(lpr) mice[J]. Cell Transplant, 2017,26(6):1031-1042.
doi: 10.3727/096368917X694660 pmid: 28105982 |
| [38] |
Deng W, Chen W, Zhang Z , et al. Mesenchymal stem cells promote CD206 expression and phagocytic activity of macrophages through IL-6 in systemic lupus erythematosus[J]. Clin Immunol, 2015,161(2):209-216.
doi: 10.1016/j.clim.2015.07.011 pmid: 26209923 |
| [39] |
Che N, Li X, Zhou S , et al. Umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells suppress B-cell proliferation and differentiation[J]. Cell Immunol, 2012,274(1-2):46-53.
doi: 10.1016/j.cellimm.2012.02.004 pmid: 22414555 |
| [40] |
Le Blanc K, Ringden O . Immunomodulation by mesenchymal stem cells andclinical experience[J]. J Intern Med, 2007,262(5):509-525.
doi: 10.1016/j.placenta.2011.07.035 pmid: 17949362 |
| [41] |
Chamberlain G, Fox J, Ashton B , et al. Concise review: mesenchymal stem cells: their phenotype, differentiation capacity, immunological features, and potential for homing[J]. Stem Cells, 2007,25(11):2739-2749.
doi: 10.1634/stemcells.2007-0197 |
| [42] |
Alunno A, Bistoni O, Montanucci P , et al. Umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells for the treatment of autoimmune diseases: beware of cell-to-cell contact[J]. Ann RheumDis, 2018,77(3):e14.
doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2017-211790 pmid: 28611081 |
| [43] |
Lalu MM, Mcintyre L, Pugliese C , et al. Safety of cell therapy with mesenchymal stromal cells (SafeCell): a systematic review and meta-analysis of clinical trials[J]. PLoS One, 2012,7(10):e47559.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0047559 |
| [44] | 汤郁, 雷芳, 宋东明 , 等. 脐带间充质干细胞治疗结缔组织病不良反应分析[J]. 南京医科大学学报(自然科学版), 2014,34(12):1687-1689. |
| [1] | Zhihui WU, Mingzhi HU, Qiaoying ZHAO, Fengfeng LV, Jingying ZHANG, Wei ZHANG, Yongfu WANG, Xiaolin SUN, Hui WANG. Immunomodulatory mechanism of umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells modified by miR-125b-5p in systemic lupus erythematosus [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(5): 860-867. |
| [2] | Limin REN,Chuchu ZHAO,Yi ZHAO,Huiqiong ZHOU,Liyun ZHANG,Youlian WANG,Lingxun SHEN,Wenqiang FAN,Yang LI,Xiaomei LI,Jibo WANG,Yongjing CHENG,Jiajing PENG,Xiaozhen ZHAO,Miao SHAO,Ru Li. Low disease activity and remission status of systemic lupus erythematosus in a real-world study [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(2): 273-278. |
| [3] | Zhi-jun LUO,Jia-jia WU,You SONG,Chun-li MEI,Rong DU. Systemic lupus erythematosus associated macrophage activation syndrome with neuropsychiatric symptoms: A report of 2 cases [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(6): 1111-1117. |
| [4] | Hai-hong YAO,Fan YANG,Su-mei TANG,Xia ZHANG,Jing HE,Yuan JIA. Clinical characteristics and diagnostic indicators of macrophage activation syndrome in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus and adult-onset Still's disease [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(6): 966-974. |
| [5] | Xiang-ge ZHAO,Jia-qing LIU,Hui-na HUANG,Zhi-min LU,Zi-ran BAI,Xia LI,Jing-jing QI. Interferon-α mediating the functional damage of CD56dimCD57+natural killer cells in peripheral blood of systemic lupus erythematosuss [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(6): 975-981. |
| [6] | Lu ZHANG,Cheng CHEN,Mei-ting WENG,Ai-ping ZHENG,Mei-ling SU,Qing-wen WANG,Yue-ming CAI. Characteristics of serum autoantibodies in patients with lupus nephritis and tubulointerstitial damage [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(6): 1094-1098. |
| [7] | Lin-qi ZHANG,Jing ZHAO,Hong-yan WANG,Zong-yi WANG,Ying-ni LI,Ji-yang TANG,Si-ying LI,Jin-feng QU,Ming-wei ZHAO. Relationship between anti-ENO1 antibody and systemic lupus erythematosus patients with retinopathy [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(6): 1099-1105. |
| [8] | Min LI,Lin-qing HOU,Yue-bo JIN,Jing HE. Clinical and immunological characteristics of systemic lupus erythematosus with retinopathy [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(6): 1106-1111. |
| [9] | Miao SHAO,Hui-fang GUO,Ling-yan LEI,Qing ZHAO,Yan-jie DING,Jin LIN,Rui WU,Feng YU,Yu-cui LI,Hua-li MIAO,Li-yun ZHANG,Yan DU,Rui-ying JIAO,Li-xia PANG,Li LONG,Zhan-guo LI,Ru LI. A multicenter study on the tolerance of intravenous low-dose cyclophosphamide in systemic lupus erythematosus [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(6): 1112-1116. |
| [10] | Chao HAN,Zhu-xing ZHOU,You-rong CHEN,Zi-hui DONG,Jia-kuo YU. Biological characteristics of sheep peripheral blood mesenchymal stem cell [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(6): 1151-1157. |
| [11] | YUAN Chang-wei,WANG Ying-jin,ZHANG Shu-jie,SHEN Sheng-li,DUAN Hong-zhou. Clinical outcomes following microsurgery and endovascular embolization in the management of spinal dural arteriovenous fistula: A meta-analysis study [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(2): 304-314. |
| [12] | SHUAI Ting,LIU Juan,GUO Yan-yan,JIN Chan-yuan. Knockdown of long non-coding RNA MIR4697 host gene inhibits adipogenic differentiation in bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(2): 320-326. |
| [13] | TIAN Jia-yi,ZHANG Xia,CHENG Gong,LIU Qing-hong,WANG Shi-yang,HE Jing. Serum interleukin-2 receptor α as a clinical biomarker in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2021, 53(6): 1083-1087. |
| [14] | Jian-mei ZOU,Li-jun WU,Cai-nan LUO,Ya-mei SHI,Xue WU. Relationship of serum 25- hydroxy vitamin D and systemic lupus erythematosus [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2021, 53(5): 938-941. |
| [15] | YOU Peng-yue,LIU Yu-hua,WANG Xin-zhi,WANG Si-wen,TANG Lin. Biocompatibility and effect on bone formation of a native acellular porcine pericardium: Results of in vitro and in vivo [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2021, 53(4): 776-784. |
|
||