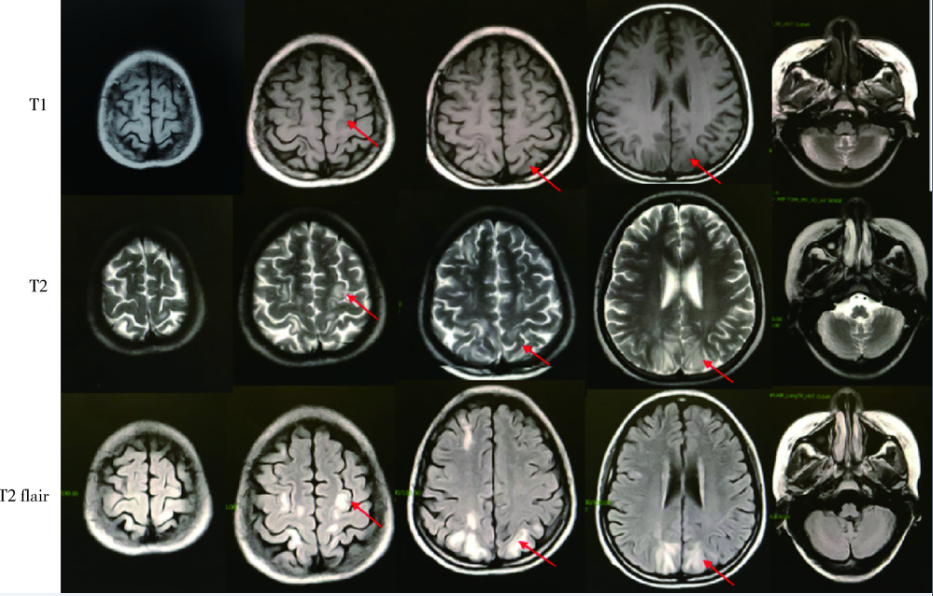
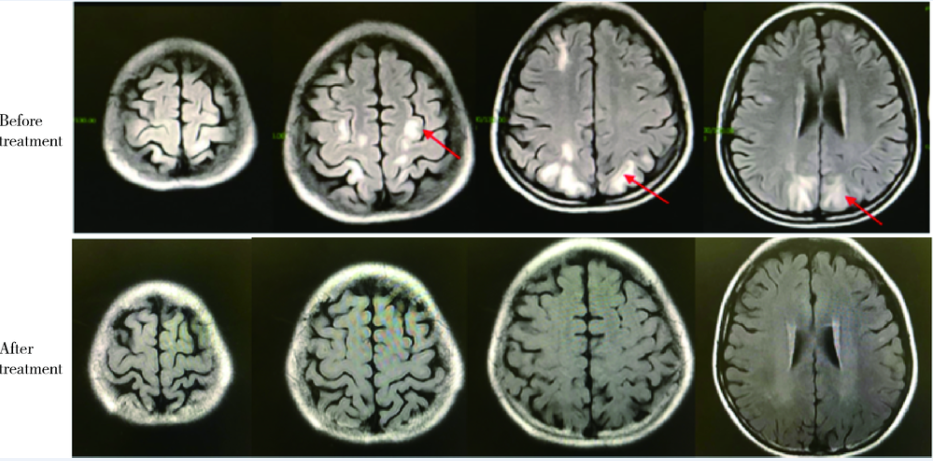
Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences) ›› 2018, Vol. 50 ›› Issue (6): 1102-1107. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2018.06.029
• Article • Previous Articles Next Articles
Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome in systemic lupus erythematosus: a case report
Xiao-hui ZHANG1,Xue-rong DENG1,Fan Li2,Ying ZHU3,Zhuo-li ZHANG1,△( )
)
- 1. Department of Rheumatology and Immunology
2. Department of Neurology
3. Department of Radiology, Peking University First Hospital, Beijing 100034, China
CLC Number:
- R593.24 +1
| [1] |
Tay SH, Mak A . Diagnosing and attributing neuropsychiatric events to systemic lupus erythematosus:time to untie the Gordian knot[J]. Rheumatology (Oxford), 2017,56(Suppl1):i14-i23.
doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/kex017 pmid: 28339930 |
| [2] |
Shankar J, Banfield J . Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome: a review[J]. Can Assoc Radiol J, 2017,68(2):147-153.
doi: 10.1016/j.carj.2016.08.005 pmid: 28131335 |
| [3] |
Toledano M, Fugate JE . Posterior reversible encephalopathy in the intensive care unit[J]. Handb Clin Neurol, 2017,141:467-483.
doi: 10.1016/B978-0-444-63599-0.00026-0 |
| [4] |
Fugate JE, Rabinstein AA . Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome: clinical and radiological manifestations, pathophysiology, and outstanding questions[J]. Lancet Neurol, 2015,14(9):914-925.
doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(15)00111-8 pmid: 26184985 |
| [5] |
Datar S, Singh TD, Fugate JE , et al. Albuminocytologic dissociation in posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome[J]. Mayo Clin Proc, 2015,90(10):1366-1371.
doi: 10.1016/j.mayocp.2015.07.018 pmid: 26349950 |
| [6] |
Lee VH, Wijdicks EF, Manno EM , et al. Clinical spectrum of reversible posterior leukoencephalopathy syndrome[J]. Arch Neurol, 2008,65(2):205-210.
doi: 10.1016/S0887-8994(01)00265-X pmid: 18268188 |
| [7] |
Varaprasad IR, Agrawal S, Prabu VN , et al. Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome in systemic lupus erythematosus[J]. J Rheumatol, 2011,38(8):1607-1611.
doi: 10.1097/RHU.0b013e3182a21ffd pmid: 23965484 |
| [8] | Casey SO, Sampaio RC, Michel E , et al Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome: utility of fluid-attenuated inversion re-covery MR imaging in the detection of cortical and subcortical lesions[J]. Am J Neuroradiol, 2000,21(7):1199-1206. |
| [9] |
Magnano MD, Bush TM, Herrera I , et al. Reversible posterior leukoencephalopathy in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus[J]. Semin Arthritis Rheum, 2006,35(6):396-402.
doi: 10.1016/j.semarthrit.2006.01.002 pmid: 16765717 |
| [10] |
Brady E, Parikh NS, Navi BB , et al. The imaging spectrum of posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome: a pictorial review[J]. Clin Imaging, 2018,47:80-89.
doi: 10.1016/j.clinimag.2017.08.008 pmid: 28910681 |
| [11] |
Bartynski WS, Boardman JF . Distinct imaging patterns and lesion distribution in posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome[J]. Am J Neuroradiol, 2007,28(7):1320-1327.
doi: 10.3174/ajnr.A0549 |
| [12] |
McKinney AM, Short J, Truwit CL , et al. Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome: incidence of atypical regions of involvement and imaging findings[J]. Am J Roentgenol, 2007,189(4):904-912.
doi: 10.2214/AJR.07.2024 pmid: 17885064 |
| [13] |
Gao B, Lyu C, Lerner A , et al. Controversy of posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome: what have we learnt in the last 20 years[J]. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry, 2018,89(1):14-20.
doi: 10.1136/jnnp-2017-316225 pmid: 28794149 |
| [14] |
Gatla N, Annapureddy N, Sequeira W , et al Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome in systemic lupus erythematosus[J]. J Clin Rheumatol, 2013,19(6):334-340.
doi: 10.1097/RHU.0b013e3182a21ffd pmid: 23965484 |
| [15] |
Junewar V, Verma R, Sankhwar PL , et al. Neuroimaging features and predictors of outcome in eclamptic encephalopathy: a prospective observational study[J]. Am J Neuroradiol, 2014,35(9):1728-1734.
doi: 10.3174/ajnr.A3923 pmid: 24722310 |
| [16] |
Karia SJ, Rykken JB , McKinney ZJ, et al. Utility and significance of gadolinium-based contrast enhancement in posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome[J]. Am J Neuroradiol, 2016,37(3):415-422.
doi: 10.3174/ajnr.A4563 pmid: 26564441 |
| [17] |
Covarrubias DJ, Luetmer PH, Campeau NG . Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome: prognostic utility of quantitative diffusion-weighted MR images[J]. Am J Neuroradiol, 2002,23(6):1038-1048.
doi: 10.1055/s-2002-32034 pmid: 12063238 |
| [18] |
Schweitzer AD, Parikh NS, Askin G , et al. Imaging characteristics associated with clinical outcomes in posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome[J]. Neuroradiology, 2017,59(4):379-386.
doi: 10.1007/s00234-017-1815-1 pmid: 28289809 |
| [19] |
Rabinstein AA, Mandrekar J, Merrell R , et al. Blood pressure fluctuations in posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome[J]. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis, 2012,21(4):254-258.
doi: 10.1016/j.jstrokecerebrovasdis.2011.03.011 pmid: 21536456 |
| [20] |
van Beek AH, Claassen JA, Rikkert MG , et al. Cerebral auto-regulation: an overview of current concepts and methodology with special focus on the elderly[J]. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab, 2008,28(6):1071-1085.
doi: 10.1038/jcbfm.2008.13 pmid: 18349877 |
| [21] |
Gao B, Lerner A, Law M . The Clinical outcome of posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome[J]. Am J Neuroradiol, 2016,37(9):E55-E56.
doi: 10.3174/ajnr.A4853 |
| [22] |
Sha Z, Moran BP , McKinney AMT, et al. Seizure outcomes of posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome and correlations with electroencephalographic changes[J]. Epilepsy Behav, 2015,48:70-74.
doi: 10.1016/j.yebeh.2015.05.027 pmid: 26071927 |
| [23] |
Legriel S, Schraub O, Azoulay E , et al. Determinants of recovery from severe posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome[J]. PLoS One, 2012,7(9):e44534.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0044534 pmid: 23024751 |
| [24] |
Shaharir SS, Remli R, Marwan AA , et al. Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome in systemic lupus erythematosus: pooled analysis of the literature reviews and report of six new cases[J]. Lupus, 2013,22(5):492-496.
doi: 10.1177/0961203313478303 pmid: 23435619 |
| [25] |
Damrongpipatkul U, Oranratanachai K, Kasitanon N , et al. Clinical features, outcome, and associated factors for posterior reversible encephalopathy in Thai patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: a case-control study[J]. Clin Rheumatol, 2018,37(3):691-702.
doi: 10.1007/s10067-017-3892-2 pmid: 29103182 |
| [26] |
Jung SM, Moon SJ, Kwok SK , et al. Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome in Korean patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: risk factors and clinical outcome[J]. Lupus, 2013,22(9):885-891.
doi: 10.1177/0961203313496341 pmid: 23846231 |
| [27] |
Lai CC, Chen WS, Chang YS , et al. Clinical features and outcomes of posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus[J]. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken), 2013,65(11):1766-1774.
doi: 10.1002/acr.22047 pmid: 23687067 |
| [28] |
Budhoo A, Mody GM . The spectrum of posterior reversible encephalopathy in systemic lupus erythematosus[J]. Clin Rheumatol, 2015,34(12):2127-2134.
doi: 10.1007/s10067-015-3055-2 pmid: 26298534 |
| [29] |
Ferreira TS, Reis F, Appenzeller S . Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome and association with systemic lupus erythematosus[J]. Lupus, 2016,25(12):1369-1376.
doi: 10.1177/0961203316643598 pmid: 27084028 |
| [30] |
Merayo-Chalico J, Apodaca E, Barrera-Vargas A , et al. Clinical outcomes and risk factors for posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome in systemic lupus erythematosus: a multicentric case-control study[J]. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry, 2016,87(3):287-294.
doi: 10.1136/jnnp-2014-310145 pmid: 25804426 |
| [31] |
Ishimori ML, Pressman BD, Wallace DJ , et al. Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome: another manifestation of CNS SLE[J]. Lupus, 2007,16(6):436-443.
doi: 10.1177/0961203307078682 pmid: 17664235 |
| [32] |
Barber CE, Leclerc R, Gladman DD , et al. Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome: an emerging disease manifestation in systemic lupus erythematosus[J]. Semin Arthritis Rheum, 2011,41(3):353-363.
doi: 10.1016/j.semarthrit.2011.07.001 pmid: 21868061 |
| [1] | Zhihui WU, Mingzhi HU, Qiaoying ZHAO, Fengfeng LV, Jingying ZHANG, Wei ZHANG, Yongfu WANG, Xiaolin SUN, Hui WANG. Immunomodulatory mechanism of umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells modified by miR-125b-5p in systemic lupus erythematosus [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(5): 860-867. |
| [2] | Limin REN,Chuchu ZHAO,Yi ZHAO,Huiqiong ZHOU,Liyun ZHANG,Youlian WANG,Lingxun SHEN,Wenqiang FAN,Yang LI,Xiaomei LI,Jibo WANG,Yongjing CHENG,Jiajing PENG,Xiaozhen ZHAO,Miao SHAO,Ru Li. Low disease activity and remission status of systemic lupus erythematosus in a real-world study [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(2): 273-278. |
| [3] | Zhi-jun LUO,Jia-jia WU,You SONG,Chun-li MEI,Rong DU. Systemic lupus erythematosus associated macrophage activation syndrome with neuropsychiatric symptoms: A report of 2 cases [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(6): 1111-1117. |
| [4] | Hai-hong YAO,Fan YANG,Su-mei TANG,Xia ZHANG,Jing HE,Yuan JIA. Clinical characteristics and diagnostic indicators of macrophage activation syndrome in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus and adult-onset Still's disease [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(6): 966-974. |
| [5] | Xiang-ge ZHAO,Jia-qing LIU,Hui-na HUANG,Zhi-min LU,Zi-ran BAI,Xia LI,Jing-jing QI. Interferon-α mediating the functional damage of CD56dimCD57+natural killer cells in peripheral blood of systemic lupus erythematosuss [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(6): 975-981. |
| [6] | Lin-qi ZHANG,Jing ZHAO,Hong-yan WANG,Zong-yi WANG,Ying-ni LI,Ji-yang TANG,Si-ying LI,Jin-feng QU,Ming-wei ZHAO. Relationship between anti-ENO1 antibody and systemic lupus erythematosus patients with retinopathy [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(6): 1099-1105. |
| [7] | Min LI,Lin-qing HOU,Yue-bo JIN,Jing HE. Clinical and immunological characteristics of systemic lupus erythematosus with retinopathy [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(6): 1106-1111. |
| [8] | Miao SHAO,Hui-fang GUO,Ling-yan LEI,Qing ZHAO,Yan-jie DING,Jin LIN,Rui WU,Feng YU,Yu-cui LI,Hua-li MIAO,Li-yun ZHANG,Yan DU,Rui-ying JIAO,Li-xia PANG,Li LONG,Zhan-guo LI,Ru LI. A multicenter study on the tolerance of intravenous low-dose cyclophosphamide in systemic lupus erythematosus [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(6): 1112-1116. |
| [9] | Jing LIU,Ai-dong LU,Ying-xi ZUO,Jun WU,Zhi-zhuo HUANG,Yue-ping JIA,Ming-ming DING,Le-ping ZHANG,Jiong QIN. Clinical characteristics and prognosis of seizures in 75 children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(5): 948-953. |
| [10] | Yan-yan DU,Jian WANG,Lan HE,Li-na JI,Xi-wei XU. Kawasaki disease complicated with mild encephalitis/encephalopathy with a reversible splenial lesion: A case report and literature review [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(4): 756-761. |
| [11] | TIAN Jia-yi,ZHANG Xia,CHENG Gong,LIU Qing-hong,WANG Shi-yang,HE Jing. Serum interleukin-2 receptor α as a clinical biomarker in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2021, 53(6): 1083-1087. |
| [12] | Zheng-fang LI,Xue WU,Li-jun WU,Cai-nan LUO,Ya-mei SHI,Yan ZHONG,Xiao-mei CHEN,Xin-yan MENG. Clinical features of patients with Rhupus syndrome [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2021, 53(5): 933-937. |
| [13] | Jian-mei ZOU,Li-jun WU,Cai-nan LUO,Ya-mei SHI,Xue WU. Relationship of serum 25- hydroxy vitamin D and systemic lupus erythematosus [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2021, 53(5): 938-941. |
| [14] | XIA Fang-fang,LU Fu-ai,LV Hui-min,YANG Guo-an,LIU Yuan. Clinical characteristics and related factors of systemic lupus erythematosus with interstitial pneumonia [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2021, 53(2): 266-272. |
| [15] | Yue HOU,Xu-tong ZHAO,Zhi-ying XIE,Yun YUAN,Zhao-xia WANG. Mitochondrial encephalopathy, lactic acidosis and stroke-like episodes / myoclonus epilepsy with ragged-red fibers /Leigh overlap syndrome caused by mitochondrial DNA 8344A>G mutation [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2020, 52(5): 851-855. |
| Viewed | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Full text 556
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Abstract 1259
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Cited |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Shared | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Discussed | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||