Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences) ›› 2019, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (2): 349-355. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2019.02.028
Previous Articles Next Articles
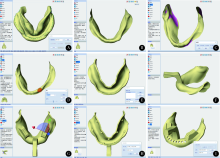
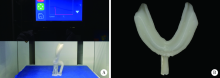
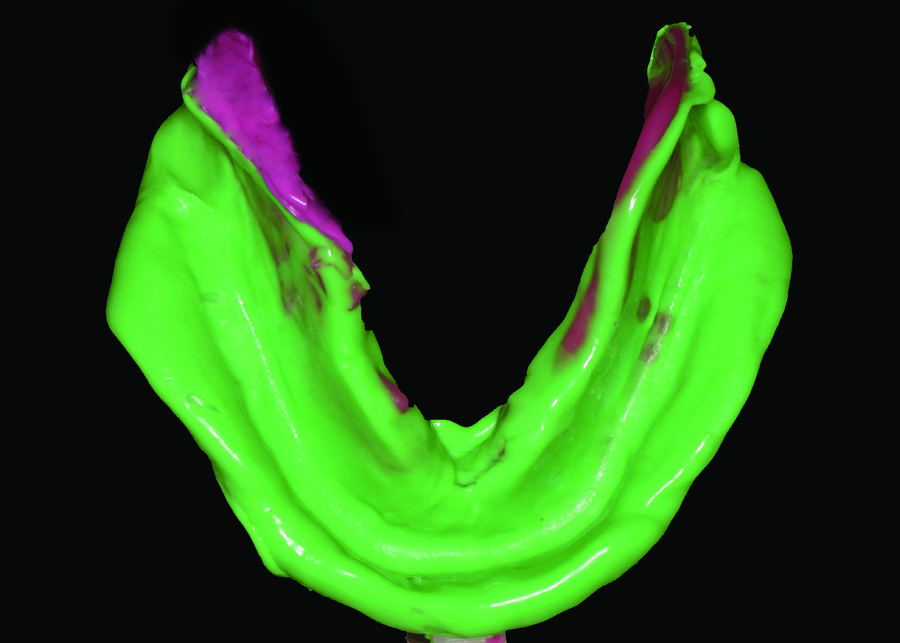
Establishment and preliminary clinical evaluation of edentulous custom trays designed and fabricated by chair-side CAD and 3D printing systems
Kuan-paul WANG1,Hong-qiang YE1,Hu CHEN2,Yong WANG2,Yu-chun SUN2,∆( ),Yong-sheng ZHOU1,∆(
),Yong-sheng ZHOU1,∆( )
)
- 1. Department of Prosthodontics, Peking University School and Hospital of Stomatology & National Clinical Research Center for Oral Diseases & National Engineering Laboratory for Digital and Material Technology of Stomatology & Beijing Key Laboratory of Digital Stomatology, Beijing 100081, China;
2. Center of Digital Dentistry, Peking University School and Hospital of Stomatology & National Clinical Research Center for Oral Diseases & National Engineering Laboratory for Digital and Material Technology of Stomatology & Beijing Key Laboratory of Digital Stomatology,Research Center of Engineering and Technology for Digital Dentistry, Ministry of Health, Beijing 100081, China;
CLC Number:
- R783.6
| [1] | 冯海兰, 徐军 . 口腔修复学[M]. 2版. 北京: 北京大学医学出版社, 2013: 267-269. |
| [2] | Basker RM, Davenport JC, Thomason JM . Prosthetic treatment of the edentulous patient[M]. 4th ed. Oxford: Blackwell, 2002: 130-149. |
| [3] | Zarb GA, Bolender GL, Eckert SE , et al. Prosthodontic treatment for edentulous patients[M]. 13th ed. St. Louis: Elsevier Mosby, 2013: 170-179. |
| [4] |
Boucher CO . Complete dentureprosthodontics: the state of the art[J]. J Prosthet Dent, 2004,92(4):309-315.
doi: 10.1016/j.prosdent.2004.05.017 |
| [5] | Rahn AO, Ivanhoe JR, Plummer KD. 全口义齿教科书[M]. 6版. 冯海兰,译. 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 2011: 74-79. |
| [6] |
Petrie CS, Walker MP, Williams K . A Survey of U.S. prosthodontists and dental schools on the current materials and methods for final impressions for complete denture prosthodontics[J]. J Prosthodont, 2005,14(4):253-262.
doi: 10.1111/jopr.2005.14.issue-4 |
| [7] | Al-Ahmar AO, Lynch CD, Locke M , et al. Quality of master impressions and related materials for fabrication of complete dentures in the UK[J]. J Oral Rehabil, 2008,35(2):111-115. |
| [8] |
van Noort R . The future of dental devices is digital[J]. Dent Mater, 2012,28(1):3-12.
doi: 10.1016/j.dental.2011.10.014 |
| [9] |
Dawood A, Marti Marti B, Sauret-Jackson V , et al. 3D printing in dentistry[J]. Br Dent J, 2015,219(11):521-529.
doi: 10.1038/sj.bdj.2015.914 |
| [10] | Baroudi K, Ibraheem SN . Assessment of chair-side computer-aided design and computer-aided manufacturing restorations: a review of the literature[J]. J Int Oral Health, 2015,7(4):96-104. |
| [11] | Patzelt SBM, Spies BC, Kohal RJ . CAD/CAM-fabricated implant-supported restorations: a systematic review[J]. Clin Oral Implants Res, 2015,26(Suppl.11):77-85. |
| [12] |
Williams RJ, Bibb R, Eggbeer D , et al. Use of CAD/CAM technology to fabricate a removable partial denture framework[J]. J Prosthet Dent, 2006,96(2):96-99.
doi: 10.1016/j.prosdent.2006.05.029 |
| [13] | 吴琳, 吕培军, 王勇 , 等. 可摘局部义齿支架铸型的计算机辅助设计与制作[J]. 中华口腔医学杂志, 2006,41(7):432-435. |
| [14] | 孙玉春, 吕培军, 王勇 , 等. 计算机辅助设计与快速成形技术辅助制作全口义齿的探讨[J]. 中华口腔医学杂志, 2007,42(6):324-329. |
| [15] |
Chen H, Yang X, Chen L , et al. Application of FDM three-dimensional printing technology in the digital manufacture of custom edentulous mandible trays[J]. Sci Rep, 2016,6:19207.
doi: 10.1038/srep19207 |
| [16] |
陈虎, 赵甜, 王勇 , 等. 基于初印模三维扫描的无牙颌上颌个性化托盘计算机辅助设计及三维打印[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2016,48(5):900-904.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-167X.2016.05.028 |
| [17] | 魏菱, 陈虎, 周永胜 , 等. 数字化全口义齿个别托盘制作与临床应用时间评价[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2017,49(1):86-91. |
| [18] |
Liu Q, Leu MC, Schmitt SM . Rapid prototyping in dentistry: technology and application[J]. Int J Adv Manuf Technol, 2006,29(3):317-335.
doi: 10.1007/s00170-005-2523-2 |
| [19] | Torabi K, Farjood E, Hamedani S . Rapid prototyping technologies and their applications in prosthodontics, a review of literature[J]. J Dent, 2015,16(1):1-9. |
| [20] | 徐军 . 总义齿与可摘局部义齿的设计[M]. 北京: 中国大百科全书出社, 2005: 16-17. |
| [21] | Chang JJ, Chen JH, Lee HE , et al. Maximizing mandibular denture retention in the sublingual space[J]. Int J Prosthodont, 2011,24(5):460-464. |
| [1] | Xinxin ZHAN,Lulu CAO,Dong XIANG,Hao TANG,Dandan XIA,Hong LIN. Effect of printing orientation on physical and mechanical properties of 3D printing prosthodontic base resin materials [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(2): 345-351. |
| [2] | Liang LYU,Mingjin ZHANG,Aonan WEN,Yijiao ZHAO,Yong WANG,Jing LI,Gengchen YANG,Dawei LIU. Preliminary evaluation of chin symmetry with three dimentional soft tissue spatial angle wireframe template [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(1): 106-110. |
| [3] | Bochun MAO,Yajing TIAN,Xuedong WANG,Jing LI,Yanheng ZHOU. Soft and hard tissue changes of hyperdivergent class Ⅱ patients before and after orthodontic extraction treatment [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(1): 111-119. |
| [4] | Xiaotong LING,Liuyang QU,Danni ZHENG,Jing YANG,Xuebing YAN,Denggao LIU,Yan GAO. Three-dimensional radiographic features of calcifying odontogenic cyst and calcifying epithelial odontogenic tumor [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(1): 131-137. |
| [5] | Panpan HU,Yan LI,Xiao LIU,Yanchao TANG,Zihe LI,Zhongjun LIU. Clinical outcomes of 3D-printing stand-alone artificial vertebral body in anterior cervical surgeries [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(1): 161-166. |
| [6] | Xinyu XU,Ling WU,Fengqi SONG,Zili LI,Yi ZHANG,Xiaojing LIU. Mandibular condyle localization in orthognathic surgery based on mandibular movement trajectory and its preliminary accuracy verification [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(1): 57-65. |
| [7] | Sui LI,Wenjie MA,Shimin WANG,Qian DING,Yao SUN,Lei ZHANG. Trueness of different digital design methods for incisal guidance of maxillary anterior implant-supported single crowns [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(1): 81-87. |
| [8] | Wen ZHANG,Xiao-jing LIU,Zi-li LI,Yi ZHANG. Effect of alar base cinch suture based on anatomic landmarks on the morphology of nasolabial region in patients after orthognathic surgery [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(4): 736-742. |
| [9] | Meng-en OU,Yun DING,Wei-feng TANG,Yong-sheng ZHOU. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of cement flow in abutment margin-crown platform switching [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(3): 548-552. |
| [10] | Ao-nan WEN,Wei LIU,Da-wei LIU,Yu-jia ZHU,Ning XIAO,Yong WANG,Yi-jiao ZHAO. Preliminary evaluation of the trueness of 5 chairside 3D facial scanning techniques [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(2): 343-350. |
| [11] | Tuan-feng ZHOU,Xue YANG,Rui-jie WANG,Ming-xuan CHENG,Hua ZHANG,Jin-qi WEI. A clinical application study of digital manufacturing simple intraoral Gothic arch-tracing device in determining the centric relation of complete dentures [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(1): 101-107. |
| [12] | Shi-kai XIONG,Wei-li SHI,An-hong WANG,Xing XIE,Qin-wei GUO. Radiographic diagnosis of distal fibula avulsion fractures: Comparison of ankle X-ray and three-dimensional reconstruction of CT [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(1): 156-159. |
| [13] | Zi-xiang GAO,Yong WANG,Ao-nan WEN,Yu-jia ZHU,Qing-zhao QIN,Yun ZHANG,Jing WANG,Yi-jiao ZHAO. Automatic determination of mandibular landmarks based on three-dimensional mandibular average model [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(1): 174-180. |
| [14] | ABUDUREHEMAN Kaidierya,Rong-geng ZHANG,Hao-nan QIAN,Zhen-yang ZOU,YESITAO Danniya,Tian-yuan FAN. Preparation and in vitro evaluation of FDM 3D printed theophylline tablets with personalized dosage [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(6): 1202-1207. |
| [15] | Hai-ying XING,Yu-hui CHEN,Ke XU,Dian-dian HUANG,Qing PENG,Ran LIU,Wei SUN,Yi-ning HUANG. Evaluation of carotid atherosclerotic plaques by vascular plaque quantification (VPQ) technology of three-dimensional ultrasonography [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(5): 991-999. |
|
||