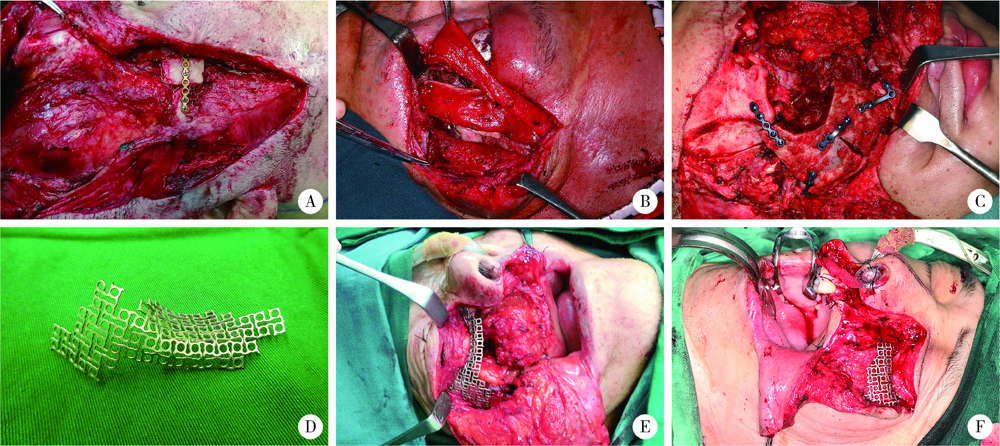
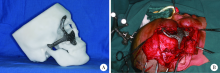
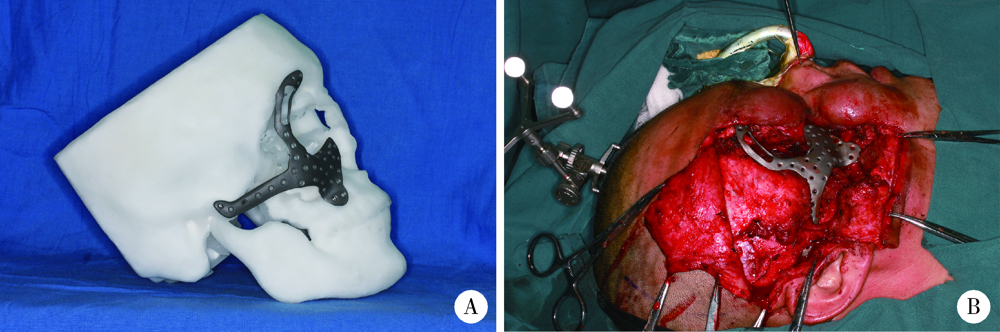
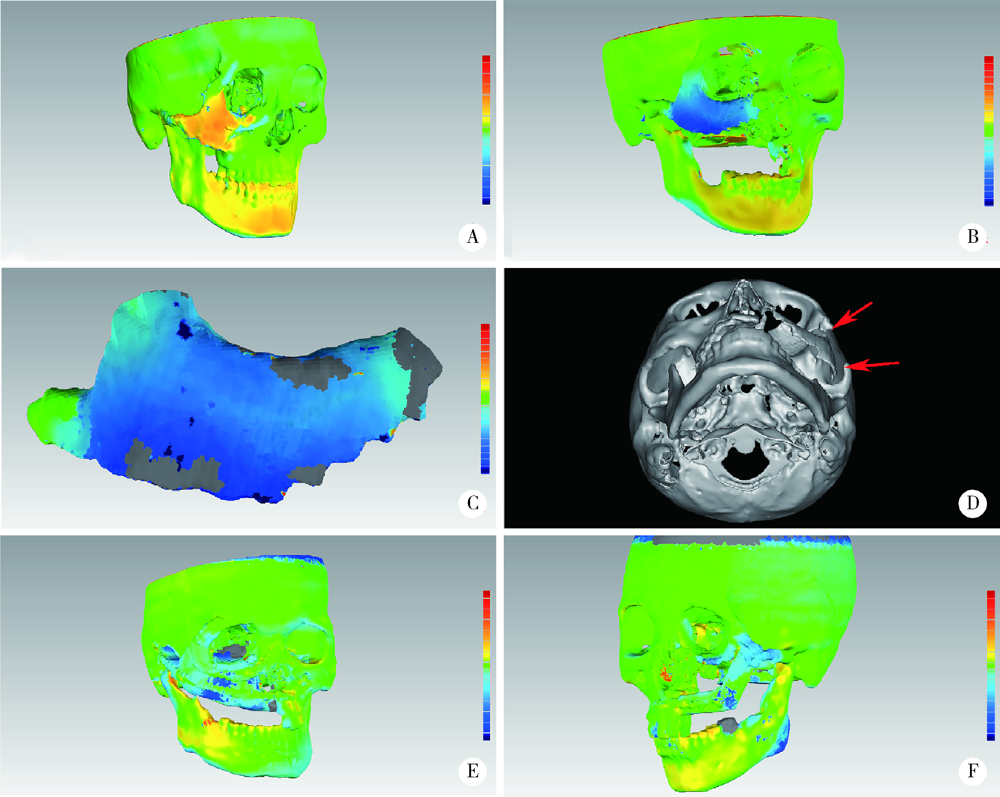
Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences) ›› 2022, Vol. 54 ›› Issue (2): 356-362. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2022.02.025
Previous Articles Next Articles
Relationship between prognosis and different surgical treatments of zygomatic defects: A retrospective study
LAN Lin,HE Yang( ),AN Jin-gang,ZHANG Yi
),AN Jin-gang,ZHANG Yi
- Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Peking University School and Hospital of Stomatology & National Center of Stomatology & National Clinical Research Center for Oral Diseases & National Engineering Research Center of Oral Biomaterials and Digital Medical Devices & Beijing Key Laboratory of Digital Stomatology, Beijing 100081, China
CLC Number:
- R782.26
| [1] |
Kokemueller H, Tavassol F, Rücker M, et al. Complex midfacial reconstruction: A combined technique of computer-assisted surgery and microvascular tissue transfer[J]. J Oral Maxillofac Surg, 2008, 66(11):2398-2406.
doi: 10.1016/j.joms.2007.12.030 |
| [2] |
Zunz E, Blanc O, Leibovitch I. Traumatic orbital floor fractures: Repair with autogenous bone grafts in a tertiary trauma center[J]. J Oral Maxillofac Surg, 2012, 70(3):584-592.
doi: 10.1016/j.joms.2011.02.048 |
| [3] | 白萍, 刘和荣, 郝月军. Medpor在眼眶重建和眼球内陷复位手术中的应用[J]. 中国美容医学, 2004, 13(3):353-354. |
| [4] |
Butscher A, Bohner M, Hofmann S, et al. Structural and material approaches to bone tissue engineering in powder-based three-dimensional printing[J]. Acta Biomater, 2011, 7(3):907-920.
doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2010.09.039 pmid: 20920616 |
| [5] |
Pensler J, McCarthy JG. The calvarial donor site: An anatomic study in cadavers[J]. Plast Reconstr Surg, 1985, 75(5):648-651.
pmid: 3983272 |
| [6] |
Markowitz NR. Cranial bone grafting in oral and maxillofacial surgery[J]. J Am Dent Assoc, 1992, 123(7):206-211.
pmid: 1619161 |
| [7] |
Tatum SA, Kellman RM. Cranial bone grafting in maxillofacial trauma and reconstruction[J]. Facial Plast Surg, 1998, 14(1):117-129.
pmid: 10371899 |
| [8] |
Kusiak JF, Zins JE, Whitaker LA. The early revascularization of membranous bone[J]. Plast Reconstr Surg, 1985, 76(4):510-516.
pmid: 4034769 |
| [9] |
Rogers GF, Greene AK. Autogenous bone graft: Basic science and clinical implications[J]. J Craniofac Surg, 2012, 23(1):323-327.
doi: 10.1097/SCS.0b013e318241dcba pmid: 22337435 |
| [10] |
Movahed R, Pinto LP, Morales-Ryan C, et al. Application of cranial bone grafts for reconstruction of maxillofacial deformities[J]. Proc (Bayl Univ Med Cent), 2013, 26(3):252-255.
doi: 10.1080/08998280.2013.11928973 pmid: 23814382 |
| [11] |
Vandervord JG, Watson JD, Teasdale GM. Forehead reconstruction using a bi-pedicled bone flap[J]. Br J Plast Surg, 1982, 35(1):75-79.
pmid: 7066592 |
| [12] |
He W, Gong X, He Y, et al. Application of a lateral pedicled cranial bone flap for the treatment of secondary zygomaticomaxillary defects[J]. J Craniofac Surg, 2019, 30(7):e661-e664.
doi: 10.1097/SCS.0000000000005776 |
| [13] |
Gerressen M, Pastaschek CI, Riediger D, et al. Microsurgical free flap reconstructions of head and neck region in 406 cases: A 13-year experience[J]. J Oral Maxillofac Surg, 2013, 71(3):628-635.
doi: 10.1016/j.joms.2012.07.002 |
| [14] |
Ghassemi A, Ghassemi M, Riediger D, et al. Comparison of donor-site engraftment after harvesting vascularized and nonvascularized iliac bone grafts[J]. J Oral Maxillofac Surg, 2009, 67(8):1589-1594.
doi: 10.1016/j.joms.2009.04.013 |
| [15] |
Takano M, Sugahara K, Koyachi M, et al. Maxillary reconstruction using tunneling flap technique with 3D custom-made titanium mesh plate and particulate cancellous bone and marrow graft: A case report[J]. Maxillofac Plast Reconstr Surg, 2019, 41(1):43.
doi: 10.1186/s40902-019-0228-y |
| [16] |
Ghanaati S, Al-Maawi S, Conrad T, et al. Biomaterial-based bone regeneration and soft tissue management of the individualized 3D-titanium mesh: An alternative concept to autologous transplantation and flap mobilization[J]. J Craniomaxillofac Surg, 2019, 47(10):1633-1644.
doi: S1010-5182(19)30459-7 pmid: 31420282 |
| [17] |
Zhang WB, Yu Y, Mao C, et al. Outcomes of zygomatic complex reconstruction with patient-specific titanium mesh using computer-assisted techniques[J]. J Oral Maxillofac Surg, 2019, 77(9):1915-1927.
doi: 10.1016/j.joms.2019.03.014 |
| [18] |
Mischkowski RA, Selbach I, Neugebauer J, et al. Lateral femoral cutaneous nerve and iliac crest bone grafts:Anatomical and clinical considerations[J]. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg, 2006, 35(4):366-372.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijom.2005.08.010 |
| [19] |
Wei FC, Celik N, Yang WG, et al. Complications after reconstruction by plate and soft-tissue free flap in composite mandibular defects and secondary salvage reconstruction with osteocutaneous flap[J]. Plast Reconstr Surg, 2003, 112(1):37-42.
doi: 10.1097/01.PRS.0000065911.00623.BD |
| [20] |
Hidalgo DA, Pusic AL. Free-flap mandibular reconstruction: A 10-year follow-up study[J]. Plastic Reconstr Surg, 2002, 110(2):438-449.
doi: 10.1097/00006534-200208000-00010 |
| [21] | Nickels L. World’s first patient-specific jaw implant[J]. Metal Powder Report, 2012, 67(2):12-14. |
| [22] |
Macheras G, Kateros K, Kostakos A, et al. Eight- to ten-year clinical and radiographic outcome of a porous tantalum monoblock acetabular component[J]. J Arthroplasty, 2009, 24(5):705-709.
doi: 10.1016/j.arth.2008.06.020 pmid: 18703310 |
| [23] |
Whitehouse MR, Masri BA, Duncan CP, et al. Continued good results with modular trabecular metal augments for acetabular defects in hip arthroplasty at 7 to 11 years[J]. Clin Orthop Relat Res, 2015, 473(2):521-527.
doi: 10.1007/s11999-014-3861-x |
| [1] | Junyong OU,Kunming NI,Lulin MA,Guoliang WANG,Ye YAN,Bin YANG,Gengwu LI,Haodong SONG,Min LU,Jianfei YE,Shudong ZHANG. Prognostic factors of patients with muscle invasive bladder cancer with intermediate-to-high risk prostate cancer [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(4): 582-588. |
| [2] | Shuai LIU,Lei LIU,Zhuo LIU,Fan ZHANG,Lulin MA,Xiaojun TIAN,Xiaofei HOU,Guoliang WANG,Lei ZHAO,Shudong ZHANG. Clinical treatment and prognosis of adrenocortical carcinoma with venous tumor thrombus [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(4): 624-630. |
| [3] | Yicen YING,Yicong DU,Zhihua LI,Yiming ZHANG,Xinfei LI,Bing WANG,Peng ZHANG,Hongjian ZHU,Liqun ZHOU,Kunlin YANG,Xuesong LI. Robot-assisted laparoscopic ureteroplasty with buccal mucosa graft for complex ureteral stricture [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(4): 640-645. |
| [4] | Le YU,Shaohui DENG,Fan ZHANG,Ye YAN,Jianfei YE,Shudong ZHANG. Clinicopathological characteristics and prognosis of multilocular cystic renal neoplasm of low malignant potential [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(4): 661-666. |
| [5] | Zezhen ZHOU,Shaohui DENG,Ye YAN,Fan ZHANG,Yichang HAO,Liyuan GE,Hongxian ZHANG,Guoliang WANG,Shudong ZHANG. Predicting the 3-year tumor-specific survival in patients with T3a non-metastatic renal cell carcinoma [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(4): 673-679. |
| [6] | Yangyi FANG,Qiang LI,Zhigao HUANG,Min LU,Kai HONG,Shudong ZHANG. Well-differentiated papillary mesothelial tumour of the tunica vaginalis: A case report [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(4): 741-744. |
| [7] | Yuanyuan ZENG,Yun XIE,Daonan CHEN,Ruilan WANG. Related factors of euthyroid sick syndrome in patients with sepsis [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(3): 526-532. |
| [8] | Xiaoying CHEN,Yi ZHANG,Yuke LI,Lin TANG,Yuhua LIU. Effects of different polymers on biomimetic mineralization of small intestine submucosal scaffolds [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(1): 17-24. |
| [9] | Yuan PAN,Hang GU,Han XIAO,Lijun ZHAO,Yiman TANG,Wenshu GE. Ubiquitin-specific protease 42 regulates osteogenic differentiation of human adipose-derived stem cells [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(1): 9-16. |
| [10] | Jian-bin LI,Meng-na LYU,Qiang CHI,Yi-lin PENG,Peng-cheng LIU,Rui WU. Early prediction of severe COVID-19 in patients with Sjögren’s syndrome [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(6): 1007-1012. |
| [11] | Huan-rui LIU,Xiang PENG,Sen-lin LI,Xin GOU. Risk modeling based on HER-2 related genes for bladder cancer survival prognosis assessment [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(5): 793-801. |
| [12] | Zi-xuan XUE,Shi-ying TANG,Min QIU,Cheng LIU,Xiao-jun TIAN,Min LU,Jing-han DONG,Lu-lin MA,Shu-dong ZHANG. Clinicopathologic features and prognosis of young renal tumors with tumor thrombus [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(5): 802-811. |
| [13] | Jian-xun MA,You-chen XIA,Bi LI,Hong-mei ZHAO,Yu-tao LEI,Xi BU. Choice of immediate breast reconstructive methods after modified radical mastectomy [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(4): 612-618. |
| [14] | Han LU,Jian-yun ZHANG,Rong YANG,Le XU,Qing-xiang LI,Yu-xing GUO,Chuan-bin GUO. Clinical factors affecting the prognosis of lower gingival squamous cell carcinoma [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(4): 702-707. |
| [15] | Yun-fei SHI,Hao-jie WANG,Wei-ping LIU,Lan MI,Meng-ping LONG,Yan-fei LIU,Yu-mei LAI,Li-xin ZHOU,Xin-ting DIAO,Xiang-hong LI. Analysis of clinicopathological and molecular abnormalities of angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(3): 521-529. |
|
||