Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences) ›› 2022, Vol. 54 ›› Issue (2): 376-380. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2022.02.028
Previous Articles Next Articles
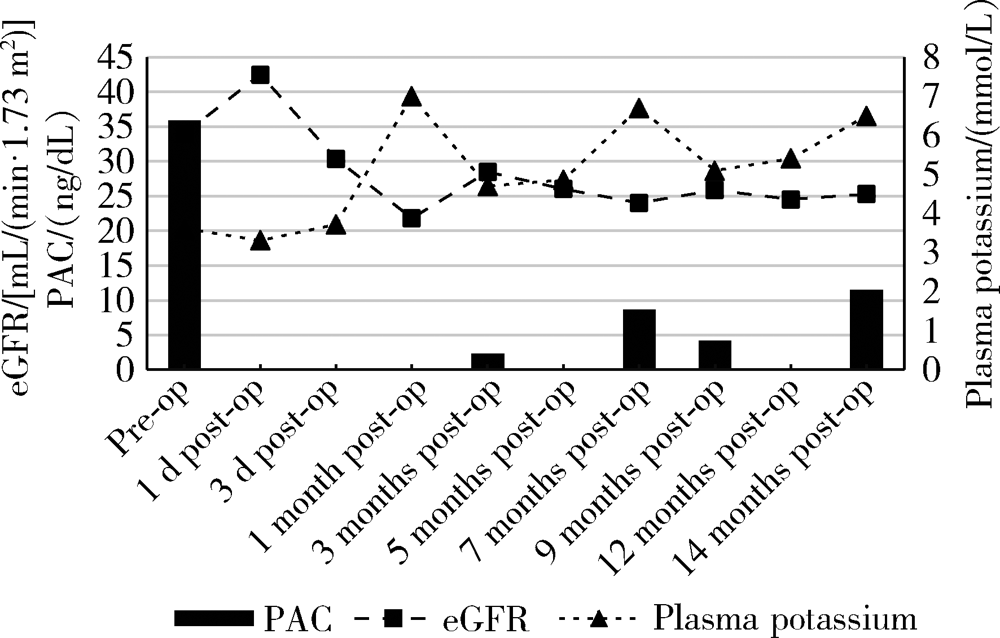
Persistent and serious hyperkalemia after surgery of primary aldosteronism: A case report
WANG Wei1,CAI Lin2,GAO Ying1,GUO Xiao-hui1,ZHANG Jun-qing1,△( )
)
- 1. Department of Endocrinology, Peking University First Hospital, Beijing 100034, China
2. Department of Urology, Peking University First Hospital, Beijing 100034, China
CLC Number:
- R589.4
| [1] |
Huang WT, Chau T, Wu ST, et al. Prolonged hyperkalemia following unilateral adrenalectomy for primary hyperaldosteronism[J]. Clin Nephrol, 2010, 73(5):392-397.
pmid: 20420801 |
| [2] |
Fischer E, Hanslik G, Pallauf A, et al. Prolonged zona glomerulosa insufficiency causing hyperkalemia in primary aldosteronism after adrenalectomy[J]. J Clin Endocrinol Metab, 2012, 97(11):3965-3973.
doi: 10.1210/jc.2012-2234 pmid: 22893716 |
| [3] |
Chiang WF, Cheng CJ, Wu ST, et al. Incidence and factors of post-adrenalectomy hyperkalemia in patients with aldosterone producing adenoma[J]. Clin Chim Acta, 2013, 424(9):114-118.
doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2013.05.017 |
| [4] |
Hibi Y, Hayakawa N, Hasegawa M, et al. Unmasked renal impairment and prolonged hyperkalemia after unilateral adrenalectomy for primary aldosteronism coexisting with primary hyper-parathyroidism: Report of a case[J]. Surg Today, 2015, 45(2):241-246.
doi: 10.1007/s00595-013-0813-0 |
| [5] |
Tahir A, McLaughlin K, Kline G. Severe hyperkalemia following adrenalectomy for aldosteronoma: Prediction, pathogenesis and approach to clinical management: A case series[J]. BMC Endocr Disord, 2016, 16(1):43.
doi: 10.1186/s12902-016-0121-y pmid: 27460219 |
| [6] |
Park KS, Kim JH, Yang YS, et al. Outcomes analysis of surgical and medical treatments for patients with primary aldosteronism[J]. Endocr J, 2017, 64(6):623-632.
doi: 10.1507/endocrj.EJ16-0530 |
| [7] |
Wada N, Shibayama Y, Umakoshi H, et al. Hyperkalemia in both surgically and medically treated patients with primary aldosteronism[J]. J Hum Hypertens, 2017, 31(10):627-632.
doi: 10.1038/jhh.2017.38 pmid: 28540931 |
| [8] |
Takeda M, Yamamoto K, Akasaka H, et al. Clinical characteristics and postoperative outcomes of primary aldosteronism in the elderly[J]. J Clin Endocrinol Metab, 2018, 103(10):3620-3629.
doi: 10.1210/jc.2018-00059 pmid: 30099522 |
| [9] | 丁韶丽, 阎文军, 赫曼, 等. 原发性醛固酮增多症患者肾上腺切除术中并发严重高钾血症1例[J]. 中华麻醉学杂志, 2018, 38(4):509-510. |
| [10] |
Shariq OA, Bancos I, Cronin PA, et al. Contralateral suppression of aldosterone at adrenal venous sampling predicts hyperkalemia following adrenalectomy for primary aldosteronism[J]. Surgery, 2018, 163(1):183-190.
doi: 10.1016/j.surg.2017.07.034 |
| [11] |
Taniguchi R, Koshiyama H, Yamauchi M, et al. A case of aldosterone-producing adenoma with severe postoperative hyperkalemia[J]. Tohoku J Exp Med, 1998, 186(3):215-223.
pmid: 10348217 |
| [1] | Le YU,Shaohui DENG,Fan ZHANG,Ye YAN,Jianfei YE,Shudong ZHANG. Clinicopathological characteristics and prognosis of multilocular cystic renal neoplasm of low malignant potential [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(4): 661-666. |
| [2] | Kewei CHEN,Shaohui DENG,Zhuo LIU,Hongxian ZHANG,Lulin MA,Shudong ZHANG. Discussion on the surgical timing of rupture and hemorrhage of renal angiomyolipoma [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(2): 326-331. |
| [3] | Silan AN,Qunyi ZHENG,Kai WANG,Shan GAO. Characteristics and influencing factors of early pain in patients after total knee arthroplasty [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(1): 167-173. |
| [4] | Hai MAO,Fan ZHANG,Zhan-yi ZHANG,Ye YAN,Yi-chang HAO,Yi HUANG,Lu-lin MA,Hong-ling CHU,Shu-dong ZHANG. Predictive model of early urinary continence recovery based on prostate gland MRI parameters after laparoscopic radical prostatectomy [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(5): 818-824. |
| [5] | Yue WEI,Xi LU,Jing ZHANG,Kun-peng LIU,Yong-jun WANG,Lan YAO. Effect of preoperative carbohydrates intake on the gastric volume and the risk of reflux aspiration in patients positioning in trendelenburg undergoing gynecological laparoscopic procedures [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(5): 893-898. |
| [6] | Xin-ling ZHANG,Zhi-yu LIN,Yu-jie CHEN,Wen-fang DONG,Xin YANG. Plastic and reconstruction surgery for non-healing wound after posterior spinal surgery [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(5): 910-914. |
| [7] | Guo-zhong LIN,Jing-cheng XIE,Xiao-dong CHEN,Jun YANG. Classification and microsurgical treatment of primary tethered cord syndrome in adults [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(4): 641-645. |
| [8] | Xi-yan PEI,Wen YANG,Xiang-ying OUYANG,Feng SUN. Comparison of clinical effects between periodontal endoscopy aiding subgingival debridement and flap surgery [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(4): 716-720. |
| [9] | Chao WU,Bin LIU,Jing-cheng XIE,Zhen-yu WANG,Chang-cheng MA,Jun YANG,Jian-jun SUN,Xiao-dong CHEN,Tao YU,Guo-zhong LIN,Yu SI,Yun-feng HAN,Su-hua CHEN,Xiao-liang YIN,Qian-quan MA,Mu-tian ZHENG,Lin ZENG. Reinforced radiculoplasty for the treatment of symptomatic sacral Tarlov cysts: A clinical analysis of 71 cases [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(1): 133-138. |
| [10] | Jing-cheng XIE,Xiao-dong CHEN,Jun YANG. Diagnosis and surgical treatment of tethered cord syndrome accompanied by congenital dermal sinus tract in adults [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(6): 1163-1166. |
| [11] | Yu-chao HUANG-FU,Yi-qing DU,Lu-ping YU,Tao XU. Risk factors of persistent hypertension in primary aldosteronism patients after surgery [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(4): 686-691. |
| [12] | YUAN Chang-wei,WANG Ying-jin,ZHANG Shu-jie,SHEN Sheng-li,DUAN Hong-zhou. Clinical outcomes following microsurgery and endovascular embolization in the management of spinal dural arteriovenous fistula: A meta-analysis study [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(2): 304-314. |
| [13] | WANG Xin-guang,GENG Xiao,LI Yang,WU Tian-chen,LI Zi-jian,TIAN Hua. Comparison of alignment and operative time between portable accelerometer-based navigation device and computer assisted surgery in total knee arthroplasty [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2021, 53(4): 728-733. |
| [14] | YUE Lei,WANG Yue-tian,BAI Chun-bi,CHEN Hao,FU Hao-yong,YU Zheng-rong,LI Chun-de,SUN Hao-lin. Analysis of surgical strategy of percutaneous endoscopic lumbar discectomy in young and middle-aged double-segment patients with lumbar disc herniation [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2021, 53(4): 734-739. |
| [15] | LIN Guo-zhong, MA Chang-cheng, WANG Zhen-yu, XIE Jing-cheng, LIU Bin, CHEN Xiao-dong. Minimally invasive treatment of cervical1-2 epidural neurilemmoma [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2021, 53(3): 586-589. |
|
||