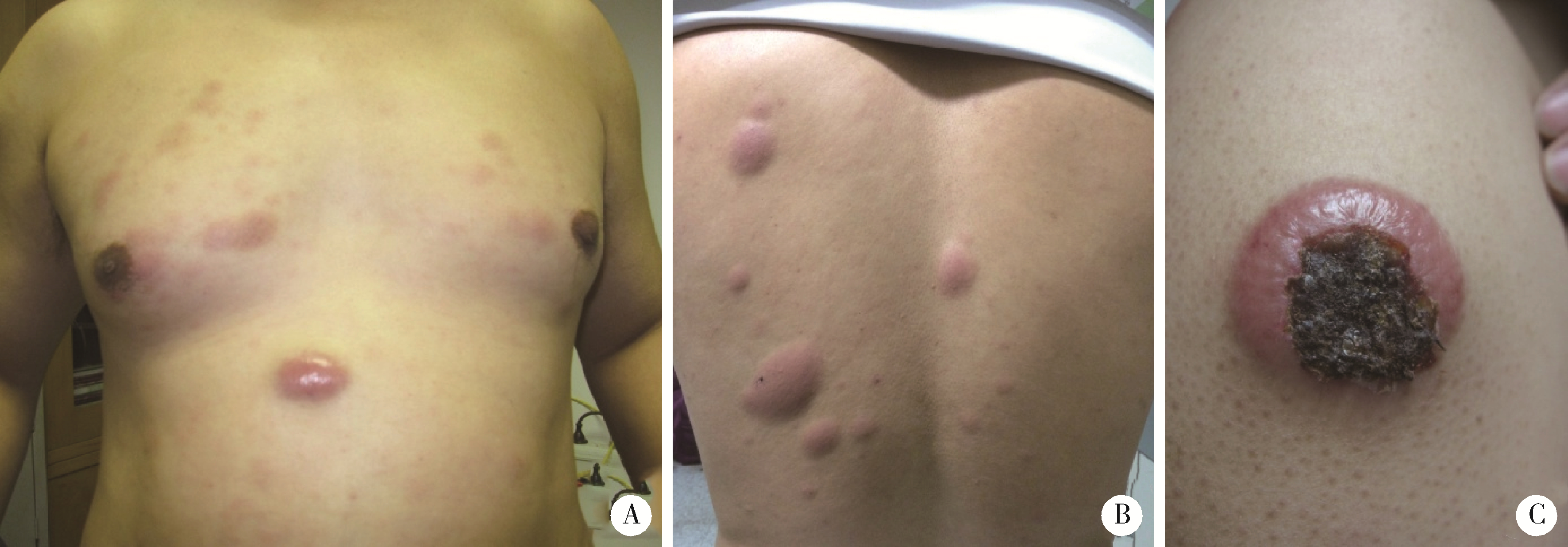
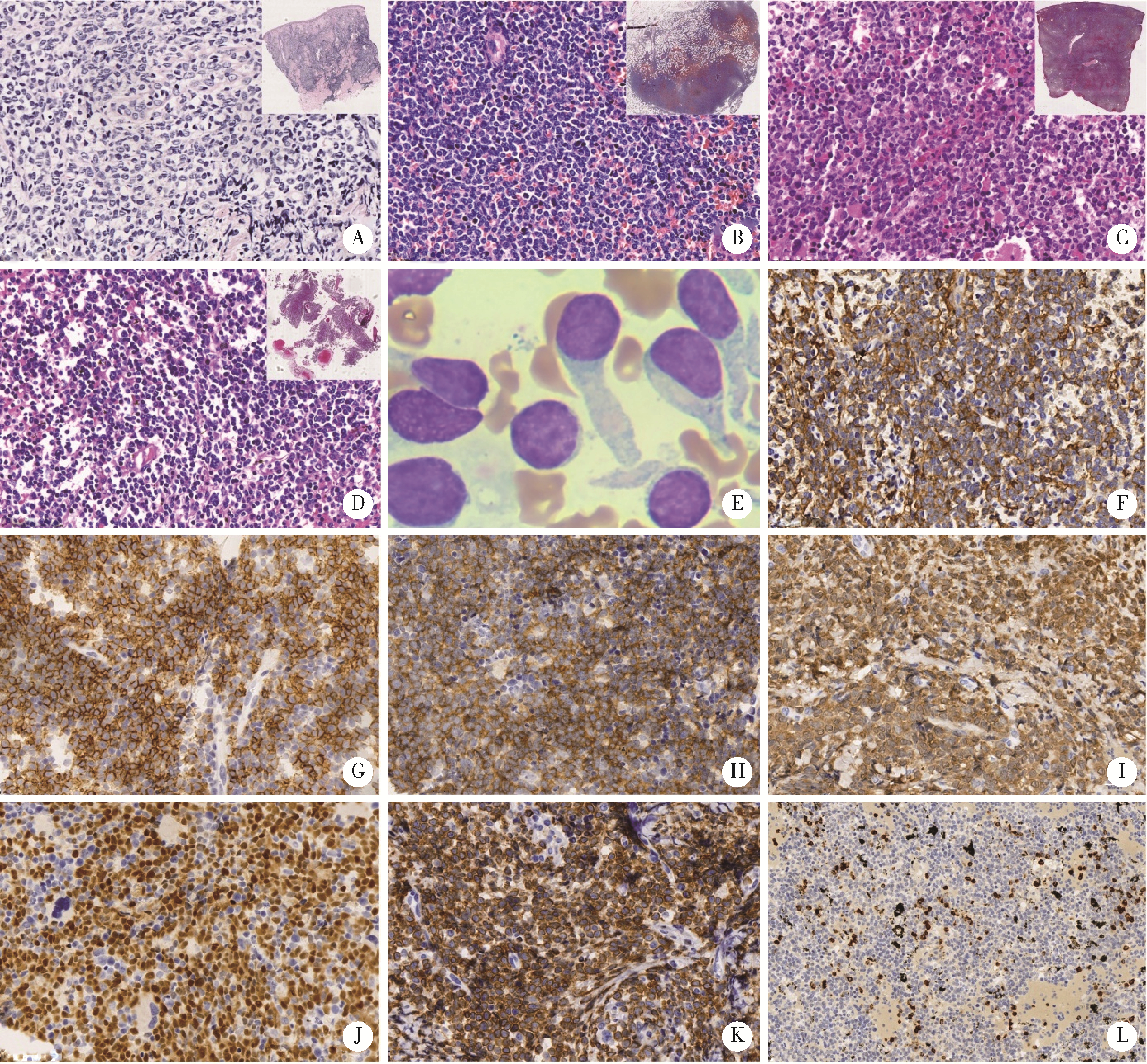
Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences) ›› 2023, Vol. 55 ›› Issue (2): 308-314. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2023.02.015
Previous Articles Next Articles
Blastic plasmacytoid dendritic cell neoplasm: A clinico-pathological retrospective analysis of thirteen cases
Lin NONG*( ),Wei WANG,Li LIANG,Dong LI,Xin LI,Ting LI
),Wei WANG,Li LIANG,Dong LI,Xin LI,Ting LI
- Department of Pathology, Peking University First Hospital, Beijing 100034, China
CLC Number:
- R733
| 1 |
Herling M , Jones D . CD4+/CD56+ hematodermic tumor: the features of an evolving entity and its relationship to dendritic cells[J]. Am J Clin Pathol, 2007, 127 (5): 687- 700.
doi: 10.1309/FY6PK436NBK0RYD4 |
| 2 |
Brody JP , Allen S , Schulman P , et al. Acute agranular CD4-positive natural killer cell leukemia. Comprehensive clinicopathologic studies including virologic and in vitro culture with inducing agents[J]. Cancer, 1995, 75 (10): 2474- 2483.
doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19950515)75:10<2474::AID-CNCR2820751013>3.0.CO;2-Y |
| 3 | Facchetti F, Jones D, Petrella T. Blastic plasmacytoid dendritic cell neoplasm [M]//Swerdlow SH, Campo E, Harris NL, et al. WHO classification of tumors of haematopoietic and lymphoid tissues. Lyon, France: IARC Press, 2008: 145-147. |
| 4 | Facchetti F, Petrella T, Pileri SA. Blastic plasmacytoid dendritic cell neoplasm [M]// Swerdlow SH, Campo E, Harris NL, et al. WHO classification of tumours of haematopoietic and lymphoid tissues. Lyon, France: IARC Press, 2017: 174-177. |
| 5 |
Khoury JD , Solary E , Abla O , et al. The 5th edition of the World Health Organization classification of haematolymphoid tumours: Myeloid and histiocytic/dendritic neoplasms[J]. Leukemia, 2022, 36 (7): 1703- 1719.
doi: 10.1038/s41375-022-01613-1 |
| 6 |
Liao C , Hu NX , Song H , et al. Pediatric blastic plasmacytoid dendritic cell neoplasm: Report of four cases and review of literature[J]. Int J Hematol, 2021, 113 (5): 751- 759.
doi: 10.1007/s12185-020-03070-x |
| 7 |
Garnache-Ottou F , Vidal C , Biichlé S , et al. How should we diagnose and treat blastic plasmacytoid dendritic cell neoplasm patients[J]. Blood Adv, 2019, 3 (24): 4238- 4251.
doi: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2019000647 |
| 8 |
Sweet K . Blastic plasmacytoid dendritic cell neoplasm: Diagnosis, manifestations, and treatment[J]. Curr Opin Hematol, 2020, 27 (2): 103- 107.
doi: 10.1097/MOH.0000000000000569 |
| 9 | Adnan A, Powell PR, Staples CJ, et al. Blastic plasmacytoid dendritic cell neoplasm: A case series and review [J]. Am J Dermatopathol, 2021(2021-05-11)[2022-11-01]. https://journals.lww.com/amjdermatopathology/Abstract/9000/Blastic_Plasmacytoid_Dendritic_Cell_Neoplasm__A.97747.aspx. |
| 10 |
Julia F , Petrella T , Beylot-Barry M , et al. Blastic plasmacytoid dendritic cell neoplasm: Clinical features in 90 patients[J]. Br J Dermatol, 2013, 169 (3): 579- 586.
doi: 10.1111/bjd.12412 |
| 11 |
Taylor J , Haddadin M , Upadhyay VA , et al. Multicenter analysis of outcomes in blastic plasmacytoid dendritic cell neoplasm offers a pretargeted therapy benchmark[J]. Blood, 2019, 134 (8): 678- 687.
doi: 10.1182/blood.2019001144 |
| 12 |
Brunetti L , Di Battista V , Venanzi A , et al. Blastic plasmacytoid dendritic cell neoplasm and chronic myelomonocytic leukemia: A shared clonal origin[J]. Leukemia, 2017, 31 (5): 1238- 1240.
doi: 10.1038/leu.2017.38 |
| 13 |
Pagano L , Valentini CG , Grammatico S , et al. Blastic plasmacytoid dendritic cell neoplasm: diagnostic criteria and therapeutical approaches[J]. Br J Haematol, 2016, 174 (2): 188- 202.
doi: 10.1111/bjh.14146 |
| 14 |
Jen EY , Gao X , Li L , et al. FDA approval summary: Tagraxofusp-erzs for treatment of blastic plasmacytoid dendritic cell neoplasm[J]. Clin Cancer Res, 2020, 26 (3): 532- 536.
doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-19-2329 |
| 15 |
Pemmaraju N , Lane AA , Sweet KL , et al. Tagraxofusp in blastic plasmacytoid dendritic-cell neoplasm[J]. N Engl J Med, 2019, 380 (17): 1628- 1637.
doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1815105 |
| [1] | 媛 刘,婉琼 原,婷 李,平章 王,平 吕,利新 吴,国瑞 阮,文玲 韩,晓宁 莫. [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(6): 1238-1243. |
| [2] | Le-qing CAO,Jing-rui ZHOU,Yu-hong CHEN,Huan CHEN,Wei HAN,Yao CHEN,Yuan-yuan ZHANG,Chen-hua YAN,Yi-fei CHENG,Xiao-dong MO,Hai-xia FU,Ting-ting HAN,Meng LV,Jun KONG,Yu-qian SUN,Yu WANG,Lan-ping XU,Xiao-hui ZHANG,Xiao-jun HUANG. Relationship between treatment and prognosis in patients with late-onset severe pneumonia after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(5): 1013-1020. |
| [3] | Jing LIU,Ai-dong LU,Ying-xi ZUO,Jun WU,Zhi-zhuo HUANG,Yue-ping JIA,Ming-ming DING,Le-ping ZHANG,Jiong QIN. Clinical characteristics and prognosis of seizures in 75 children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(5): 948-953. |
| [4] | Mei-xiang ZHANG,Wen-zhi SHI,Jian-xin LIU,Chun-jian WANG,Yan LI,Wei WANG,Bin JIANG. Clinical characteristics and prognosis of MLL-AF6 positive patients with acute myeloid leukemia [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2021, 53(5): 915-920. |
| [5] | CHI Yan-ting,ZHANG Yan-ping,ZHANG Qiu-lu,LIU Cui-ling,LI bin-bin. Clinicopathological analysis of mucosa associated lymphoid tissue lymphoma secondary to Sjögren’s syndrome in salivary gland [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2021, 53(1): 40-45. |
| [6] | Gong CHENG,Xia ZHANG,Fei YANG,Jia-yu CHENG,Yan-ying LIU. Angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma with fever, arthritis and skin pigmentation: A case report [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2020, 52(6): 1150-1152. |
| [7] | Qian SU,Xin PENG,Chuan-xiang ZHOU,Guang-yan YU. Clinicopathological features and possible prognostic factors in parotid lymphomas [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2019, 51(1): 35-42. |
| [8] | DUAN Wen-bing, GONG Li-zhong, JIA Jin-song, ZHU Hong-hu, ZHAO Xiao-su, JIANG Qian, ZHAO Ting, WANG Jing, QIN Ya-zhen, HUANG Xiao-jun, JIANG Hao. Clinical features and early treatment effects in intermediate risk and poor risk acute myeloid leukemia with EVI1 positive [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2017, 49(6): 990-995. |
| [9] | WAN Wenli, WANG Jing, ZHU Mingxia,ZHANG Wei, KE Xiaoyan. Retrospective analyses of CHOPE plus L-asparaginase regimen in treatment of T-cell lymphoma [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2016, 48(5): 841-845. |
| Viewed | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Full text 108
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Abstract 435
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Cited |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Shared | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Discussed | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||