Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences) ›› 2024, Vol. 56 ›› Issue (6): 1089-1096. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2024.06.023
Previous Articles Next Articles
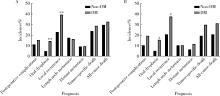
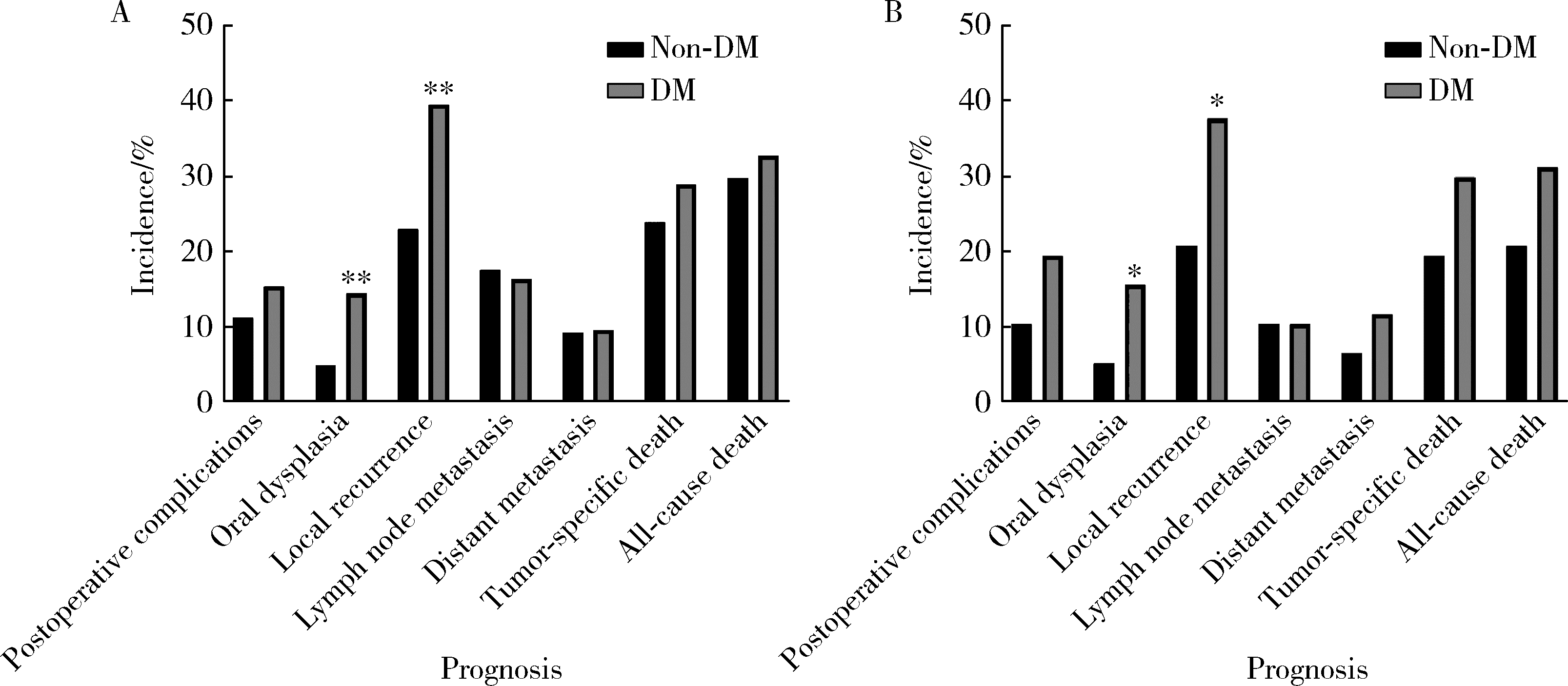
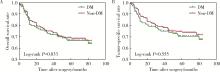
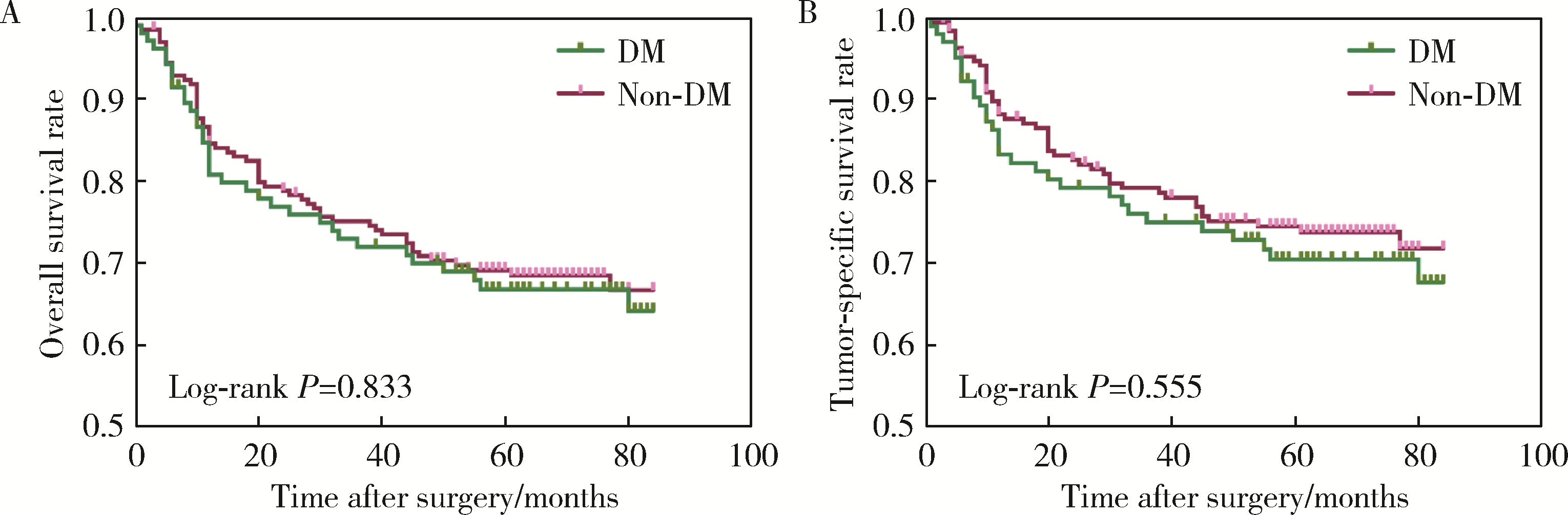
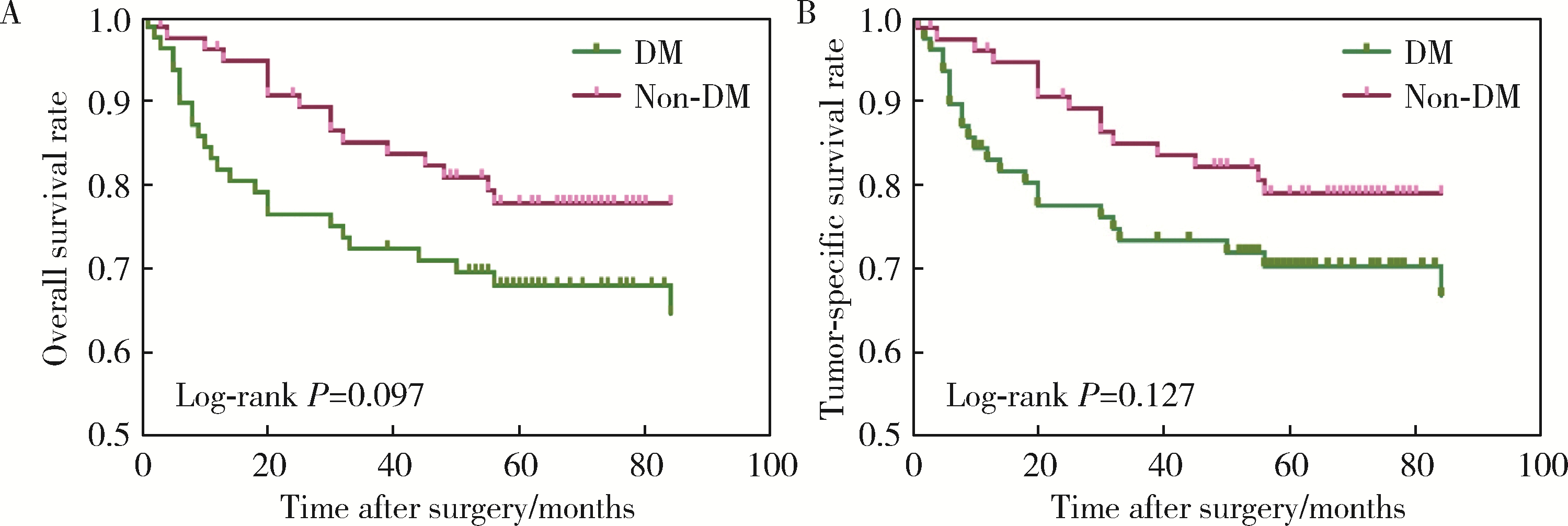
Impact of type 2 diabetes mellitus on the prognosis of patients with oral squamous cell carcinoma
Yaqing MAO1, Zhen CHEN1, Yao YU1, Wenbo ZHANG1, Yang LIU2,*( ), Xin PENG1,*(
), Xin PENG1,*( )
)
- 1. Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Peking University School and Hospital of Stomatology & National Center for Stomatology & National Clinical Research Center for Oral Diseases & National Engineering Research Center of Oral Biomaterials and Digital Medical Devices & Beijing Key Laboratory of Digital Stomatology, Beijing 100081, China
2. Department of Oral Medicine, Peking University School and Hospital of Stomatology & National Center for Stomatology & National Clinical Research Center for Oral Diseases & National Engineering Research Center of Oral Biomaterials and Digital Medical Devices & Beijing Key Laboratory of Digital Stomatology, Beijing 100081, China
CLC Number:
- R739.8
| 1 |
Campbell PT , Newton CC , Patel AV , et al.Diabetes and cause-specific mortality in a prospective cohort of one million U.S. adults[J].Diabetes Care,2012,35(9):1835-1844.
doi: 10.2337/dc12-0002 |
| 2 | 赵佳, 韩雪, 谢梦, 等.2型糖尿病并发恶性肿瘤患者的流行病学分析[J].中国慢性病预防与控制,2018,26(7):514-516. |
| 3 |
Tsilidis KK , Kasimis JC , Lopez DS , et al.Type 2 diabetes and cancer: Umbrella review of meta-analyses of observational studies[J].BMJ,2015,350,g7607.
doi: 10.1136/bmj.g7607 |
| 4 | Vairaktaris E , Spyridonidou S , Goutzanis L , et al.Diabetes and oral oncogenesis[J].Anticancer Res,2007,27(6B):4185-4193. |
| 5 |
Wu CH , Wu TY , Li CC , et al.Impact of diabetes mellitus on the prognosis of patients with oral squamous cell carcinoma: A retrospective cohort study[J].Ann Surg Oncol,2010,17(8):2175-2183.
doi: 10.1245/s10434-010-0996-1 |
| 6 |
Stott-Miller M , Chen C , Schwartz SM .Type Ⅱ diabetes and metabolic syndrome in relation to head and neck squamous cell carcinoma risk: A SEER-Medicare database study[J].Cancer Epidemiol,2013,37(4):428-433.
doi: 10.1016/j.canep.2013.03.006 |
| 7 |
Tseng CH .Oral cancer in Taiwan: Is diabetes a risk factor?[J].Clin Oral Investig,2013,17(5):1357-1364.
doi: 10.1007/s00784-012-0820-3 |
| 8 |
中华医学会糖尿病学分会.中国2型糖尿病防治指南(2020年版)[J].中华内分泌代谢杂志,2021,37(4):311-398.
doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn311282-20210304-00142 |
| 9 |
Pfister DG , Spencer S , Adelstein D , et al.Head and neck cancers, version 2.2020, NCCN clinical practice guidelines in oncology[J].J Natl Compr Canc Netw,2020,18(7):873-898.
doi: 10.6004/jnccn.2020.0031 |
| 10 | Amin MB , Edge SB , Greene FL , et al.AJCC cancer staging manual[M].8th ed. New York: Springer,2017. |
| 11 |
高柳, 毛驰, 俞光岩, 等.成人并存疾病评价指数27条目中文简体版引进的授权、翻译回译和语义调适[J].中华口腔医学杂志,2016,51(10):623-627.
doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1002-0098.2016.10.010 |
| 12 |
Austin PC .An introduction to propensity score methods for reducing the effects of confounding in observational studies[J].Multivariate Behav Res,2011,46(3):399-424.
doi: 10.1080/00273171.2011.568786 |
| 13 | Ling S , Brown K , Miksza JK , et al.Risk of cancer incidence and mortality associated with diabetes: A systematic review with trend analysis of 203 cohorts[J].Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis,2020,31(1):14-22. |
| 14 |
Pearson-Stuttard J , Bennett J , Cheng YJ , et al.Trends in predominant causes of death in individuals with and without diabetes in England from 2001 to 2018: An epidemiological analysis of linked primary care records[J].Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol,2021,9(3):165-173.
doi: 10.1016/S2213-8587(20)30431-9 |
| 15 | 周维, 何明艳, 沈婉莹, 等.2005—2015年中国口腔癌发病及死亡趋势分析[J].华中科技大学学报(医学版),2020,49(6):58-63. |
| 16 | Végh D , Bányai D , Ujpál M .Change in the incidence of diabetes mellitus in oral cancer patients based on a long-term comparative study[J].Fogorv Sz,2015,108(1):9-12. |
| 17 |
Yan P , Wang Y , Yu X , et al.Type 2 diabetes mellitus and risk of head and neck cancer subtypes: A systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies[J].Acta Diabetol,2021,58(5):549-565.
doi: 10.1007/s00592-020-01643-0 |
| 18 | 王新革. 舌鳞癌与肿瘤侵袭模式、2型糖尿病的相关性研究[D]. 西安: 第四军医大学, 2017: 42. |
| 19 |
Supabphol S , Seubwai W , Wongkham S , et al.High glucose: An emerging association between diabetes mellitus and cancer progression[J].J Mol Med (Berl),2021,99(9):1175-1193.
doi: 10.1007/s00109-021-02096-w |
| 20 |
Cignarelli A , Annamaria Genchi V , Caruso I , et al.Diabetes and cancer: Pathophysiological fundamentals of a "dangerous affair"[J].Diabetes Res Clin Pract,2018,143,378-388.
doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2018.04.002 |
| 21 | Liu CJ , Chang WJ , Chen CY , et al.Dynamic cellular and mole-cular modulations of diabetes mediated head and neck carcinogenesis[J].Oncotarget,2015,30(6):29268-29284. |
| 22 | 张东升, 郑家伟, 张陈平, 等.口腔癌合并全身系统性疾病患者的多学科协作诊疗模式专家共识[J].华西口腔医学杂志,2020,38(6):603-615. |
| 23 | 李金, 华红. 口腔癌中国流行病学趋势及口腔白斑癌变危险因素分析[D]. 北京: 北京大学, 2019. |
| 24 |
Villa A , Woo SB .Leukoplakia: A diagnostic and management algorithm[J].J Oral Maxillofac Surg,2017,75(4):723-734.
doi: 10.1016/j.joms.2016.10.012 |
| 25 |
Li G , Da M , Zhang W , et al.Alteration of serum lipid profile and its prognostic value in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma[J].J Oral Pathol Med,2016,45(3):167-172.
doi: 10.1111/jop.12344 |
| 26 |
Shalapour S , Karin M .Immunity, inflammation, and cancer: An eternal fight between good and evil[J].J Clin Invest,2015,125(9):3347-3355.
doi: 10.1172/JCI80007 |
| 27 | Lu A , Li H , Zheng Y , et al.Prognostic significance of neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio, lymphocyte to monocyte ratio, and platelet to lymphocyte ratio in patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma[J].Biomed Res Int,2017,2017,3047802. |
| [1] | Peiheng ZHANG, Ying GAO, Honghua WU, Jian ZHANG, Junqing ZHANG. Fulminant type 1 diabetes mellitus with acute pancreatitis: A case report and literature review [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(5): 923-927. |
| [2] | Junyong OU,Kunming NI,Lulin MA,Guoliang WANG,Ye YAN,Bin YANG,Gengwu LI,Haodong SONG,Min LU,Jianfei YE,Shudong ZHANG. Prognostic factors of patients with muscle invasive bladder cancer with intermediate-to-high risk prostate cancer [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(4): 582-588. |
| [3] | Shuai LIU,Lei LIU,Zhuo LIU,Fan ZHANG,Lulin MA,Xiaojun TIAN,Xiaofei HOU,Guoliang WANG,Lei ZHAO,Shudong ZHANG. Clinical treatment and prognosis of adrenocortical carcinoma with venous tumor thrombus [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(4): 624-630. |
| [4] | Le YU,Shaohui DENG,Fan ZHANG,Ye YAN,Jianfei YE,Shudong ZHANG. Clinicopathological characteristics and prognosis of multilocular cystic renal neoplasm of low malignant potential [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(4): 661-666. |
| [5] | Zezhen ZHOU,Shaohui DENG,Ye YAN,Fan ZHANG,Yichang HAO,Liyuan GE,Hongxian ZHANG,Guoliang WANG,Shudong ZHANG. Predicting the 3-year tumor-specific survival in patients with T3a non-metastatic renal cell carcinoma [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(4): 673-679. |
| [6] | Yangyi FANG,Qiang LI,Zhigao HUANG,Min LU,Kai HONG,Shudong ZHANG. Well-differentiated papillary mesothelial tumour of the tunica vaginalis: A case report [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(4): 741-744. |
| [7] | Yuanyuan ZENG,Yun XIE,Daonan CHEN,Ruilan WANG. Related factors of euthyroid sick syndrome in patients with sepsis [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(3): 526-532. |
| [8] | Yujia MA,Ranli LU,Zechen ZHOU,Xiaoyi LI,Zeyu YAN,Yiqun WU,Dafang CHEN. Association between insomnia and type 2 diabetes: A two-sample Mendelian rando-mization study [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(1): 174-178. |
| [9] | Jian-bin LI,Meng-na LYU,Qiang CHI,Yi-lin PENG,Peng-cheng LIU,Rui WU. Early prediction of severe COVID-19 in patients with Sjögren’s syndrome [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(6): 1007-1012. |
| [10] | Huan-rui LIU,Xiang PENG,Sen-lin LI,Xin GOU. Risk modeling based on HER-2 related genes for bladder cancer survival prognosis assessment [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(5): 793-801. |
| [11] | Zi-xuan XUE,Shi-ying TANG,Min QIU,Cheng LIU,Xiao-jun TIAN,Min LU,Jing-han DONG,Lu-lin MA,Shu-dong ZHANG. Clinicopathologic features and prognosis of young renal tumors with tumor thrombus [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(5): 802-811. |
| [12] | Lei BAO,Xia-xia CAI,Ming-yuan ZHANG,Lei-lei REN. Effect of vitamin D3 on mild cognitive impairment in type 2 diabetic mice and its possible mechanism [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(4): 587-592. |
| [13] | Han LU,Jian-yun ZHANG,Rong YANG,Le XU,Qing-xiang LI,Yu-xing GUO,Chuan-bin GUO. Clinical factors affecting the prognosis of lower gingival squamous cell carcinoma [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(4): 702-707. |
| [14] | Yun-fei SHI,Hao-jie WANG,Wei-ping LIU,Lan MI,Meng-ping LONG,Yan-fei LIU,Yu-mei LAI,Li-xin ZHOU,Xin-ting DIAO,Xiang-hong LI. Analysis of clinicopathological and molecular abnormalities of angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(3): 521-529. |
| [15] | Xiao-juan ZHU,Hong ZHANG,Shuang ZHANG,Dong LI,Xin LI,Ling XU,Ting LI. Clinicopathological features and prognosis of breast cancer with human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 low expression [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(2): 243-253. |
|
||