Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences) ›› 2019, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (5): 835-839. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2019.05.008
Previous Articles Next Articles
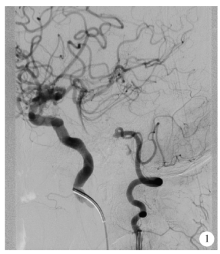
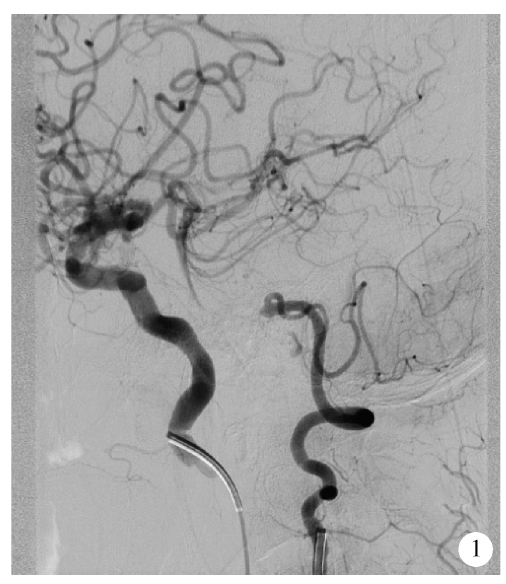
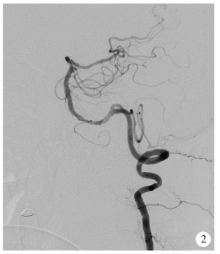
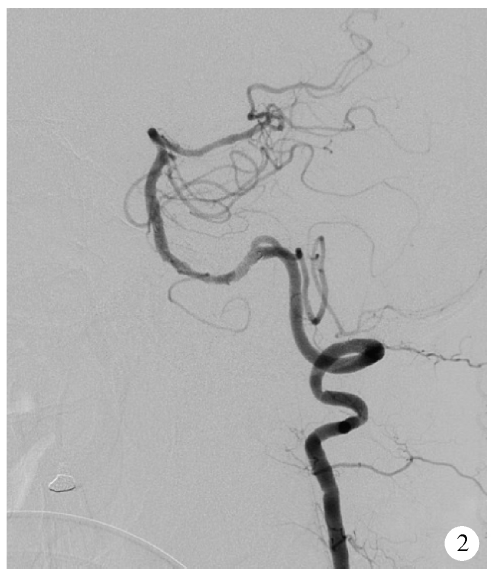
Application of Neuroform EZ stent in the treatment of severe intracranial arterial stenosis with complex symptomatic
Zi-chang JIA1,Huan-ju BIAN2,Xuan LI1,Jing-yuan LUAN1,Chang-ming WANG1,Qi-jia LIU1,Jin-tao HAN1,△( )
)
- 1. Department of Interventional Radiology and Vascular Surgery, Peking University Third Hospital, Beijing 100191, ChinaDepartment of Neurology, Peking University Third Hospital, Beijing 100191, China
2. Department of Neurology, Guanxian People’s Hospital, Liaocheng 252500, Shandong, China
CLC Number:
- R743.3
| [1] | Wang Y, Zhao X, Liu L , et al. Prevalence and outcomes of symptomatic intracranial large artery stenoses and occlusions in China: the Chinese Intracranial Atherosclerosis (CICAS) Study[J]. Stroke, 2014,45(3):663-669. |
| [2] | Wong LK . Global burden of intracranial atherosclerosis[J]. Int J Stroke, 2006,1(3):158-159. |
| [3] | Chimowitz MI, Lynn MJ, Howlett-Smith H , et al. Comparison of warfarin and aspirin for symptomatic intracranial arterial stenosis[J]. N Engl J Med, 2005,352(13):1305-1316. |
| [4] | Chimowitz MI, Lynn MJ, Derdeyn CP , et al. Stenting versus aggressive medical therapy for intracranial arterial stenosis[J]. N Engl J Med, 2011,365(11):993-1003. |
| [5] | Zaidat OO, Fitzsimmons BF, Woodward BK , et al. Effect of a balloon-expandable intracranial stent vs. medical therapy on risk of stroke in patients with symptomatic intracranial stenosis: the VISSIT randomized clinical trial[J]. JAMA, 2015,313(12):1240-1248. |
| [6] | Miao Z, Zhang Y, Shuai J . Study Group of registry study of sten-ting for symptomatic intracranial artery stenosis in China: Thirty-day outcome of a multicenter registry study of stenting for sympto-matic intracranial artery stenosis in China[J]. Stroke, 2015,46(10):2822-2829. |
| [7] | Wang Y, Miao Z, Wang Y , et al. Protocol for a prospective, multicenter registry study of stenting for symptomatic intracranial artery stenosis in China[J]. BMJ Open, 2014,4(8):e005175. |
| [8] | Sacco RL, Kargman DE, Gu Q , et al. Race-ethnicity and determinants of intracranial atherosclerotic cerebral infarction. The Northern Manhattan Stroke Study[J]. Stroke, 1995,26(1):14-20. |
| [9] | Cheng XQ, Tian JM, Zuo CJ , et al. Hemodynamic alterations in unilateral chronic middle cerebral artery stenosis patients and the effect of percutaneous transluminal angioplasty and stenting: A perfusion-computed tomography study[J]. Acta Radiol, 2015,56(6):754-760. |
| [10] | Duan G, Feng Z, Zhang L , et al. Solitaire stents for the treatment of complex symptomatic intracranial stenosis after antithrombotic failure: Safety and efficacy evaluation[J]. Neurointerv Surg, 2016,8(7):680-684. |
| [11] | Marks MP . Is there a future for endovascular treatment of intracranial atherosclerotic disease after stenting and aggressive medical management for preventing recurrent stroke and intracranial stenosis (SAMMPRIS)?[J]. Stroke, 2012,43(2):580-584. |
| [12] | Vajda Z, Guthe T, Perez MA , et al. Prevention of intracranial in-stent restenosis: Predilatation with a drug eluting balloon, followed by the deployment of a self-expanding stent[J]. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol, 2013,36(2):346-352. |
| [13] | Hahnel S, Ringleb P, Hartmann M . Treatment of intracranial stenosis using the Neuroform stent system: Initial experience in five cases[J]. Neuroradiology, 2016,48(7):479-485. |
| [14] | Liu L, Ma N, Mo DP , et al. Enterprise stent in treatment of symptomatic complex intracranial atherosclerotic stenosis[J]. Chin J Stroke, 2017,12(7):592-597. |
| [15] | Liu L, Zhao X, Mo D , et al. Stenting for symptomatic intracranial vertebrobasilar artery stenosis: 30-day results in a high-volume stroke center[J]. Clin Neurol Neurosurg, 2016,4(143):132-138. |
| [16] | Krischek Ö, Miloslavski E, Fischer S , et al. A comparison of functional and physical properties of self-expanding intracranial stents[J]. Minim Invasive Neurosurg, 2011,54(1):21-28. |
| [17] | Shin YS, Kim BM, Suh SH , et al. Wingspan stenting for intracranial atherosclerotic stenosis: Clinical outcomes and risk factors for in-stent restenosis[J]. Neurosurgery, 2013,72(4):596-604. |
| [18] | Vajda Z, Schmid E, Guthe T , et al. The modified Bose method for the endovascular treatment of intracranial atherosclerotic arterial stenoses using the Enterprise stent[J]. Neurosurgery, 2012,70(1):91-101. |
| [1] | Wenbo YANG,Lei YU,Weiyu ZHANG,Tao XU,Qiang WANG. Effect and safety of self-draining ureteral stent with thread in kidney transplant reci-pients [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(4): 656-660. |
| [2] | Huan YU,Ruo-tong YANG,Si-yue WANG,Jun-hui WU,Meng-ying WANG,Xue-ying QIN,Tao WU,Da-fang CHEN,Yi-qun WU,Yong-hua HU. Metformin use and risk of ischemic stroke in patients with type 2 diabetes: A cohort study [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(3): 456-464. |
| [3] | Ruo-tong YANG,Meng-ying WANG,Chun-nan LI,Huan YU,Xiao-wen WANG,Jun-hui WU,Si-yue WANG,Jia-ting WANG,Da-fang CHEN,Tao WU,Yong-hua HU. Interaction between ischemic stroke risk loci identified by genome-wide association studies and sleep habits [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(3): 412-420. |
| [4] | Yu-han DENG,Yong JIANG,Zi-yao WANG,Shuang LIU,Yu-xin WANG,Bao-hua LIU. Long short-term memory and Logistic regression for mortality risk prediction of intensive care unit patients with stroke [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(3): 458-467. |
| [5] | WU Jun-hui,WU Yi-qun,WU Yao,WANG Zi-jing,WU Tao,QIN Xue-ying,WANG Meng-ying,WANG Xiao-wen,WANG Jia-ting,HU Yong-hua. Incidence and risk factors of ischemic stroke in patients with type 2 diabetes among urban workers in Beijing, China [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(2): 249-254. |
| [6] | REN Guo-yong,WU Xue-mei, ,LI Jie-yu,SUN Wei-ping,HUANG Yi-ning. Susceptibility vessel sign in subacute stroke patients with large vessel occlusion [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2021, 53(6): 1133-1138. |
| [7] | Ya-fei LIU,Lin-lin SONG,Mao-wei XING,Li-xin CAI,Dong-xin WANG. Comparison of pulse pressure variation, stroke volume variation, and plethysmographic variability index in pediatric patients undergoing craniotomy [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2021, 53(5): 946-951. |
| [8] | Yue HOU,Xu-tong ZHAO,Zhi-ying XIE,Yun YUAN,Zhao-xia WANG. Mitochondrial encephalopathy, lactic acidosis and stroke-like episodes / myoclonus epilepsy with ragged-red fibers /Leigh overlap syndrome caused by mitochondrial DNA 8344A>G mutation [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2020, 52(5): 851-855. |
| [9] | Xun TANG,Du-dan ZHANG,Xiao-fei LIU,Qiu-ping LIU,Yang CAO,Na LI,Shao-ping HUANG,Hui-dong DOU,Pei GAO,Yong-hua HU. Application of the China-PAR stroke risk equations in a rural northern Chinese population [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2020, 52(3): 444-450. |
| [10] | Zi-chang JIA,Xuan LI,Mei ZHENG,Jing-yuan LUAN,Chang-ming WANG,Jin-tao HAN. Hybrid treatment for symptomatic long-segment chronic internal carotid artery occlusion without stump [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2020, 52(1): 177-180. |
| [11] | Hai-yan ZHAO,Dong-sheng FAN,Jin-tao HAN. Management of severe internal carotid stenosis with unruptured intracranial aneurysm [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2019, 51(5): 829-834. |
| [12] | Zi-chang JIA,Xuan LI,Xiao-gang LI,Xiang-zhu ZENG,Jing-yuan LUAN,Chang-ming WANG,Jin-tao HAN. Mechanical thrombectomy treatment in patients with acute ischemic stroke: a single center study [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2019, 51(2): 256-259. |
| [13] | SUN Zhuo-nan, MENG Xiu-li, WANG Jun, GUO Xiang-yang, HAN Jin-tao, QI Qiang. Perioperative stroke effectively treated by an acute stroke team including anesthesia department: a case report [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2017, 49(6): 1090-1094. |
| [14] | FENG Qi-chen, LI Xuan, LUAN Jing-yuan, WANG Chang-ming, LI Tian-run. Significance of renal filtration fraction evaluation of renal artery stenting for atherosclerotic renal artery stenosis treatment [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2017, 49(1): 158-163. |
| [15] | XIAO Tian-yi, LIU Yan, LI Ji-lai, WANG Rui-tong, DU Ji-chen. Diagnostic value of carotid atherosclerosis score for ischemic stroke [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2016, 48(6): 1000-1005. |
|
||