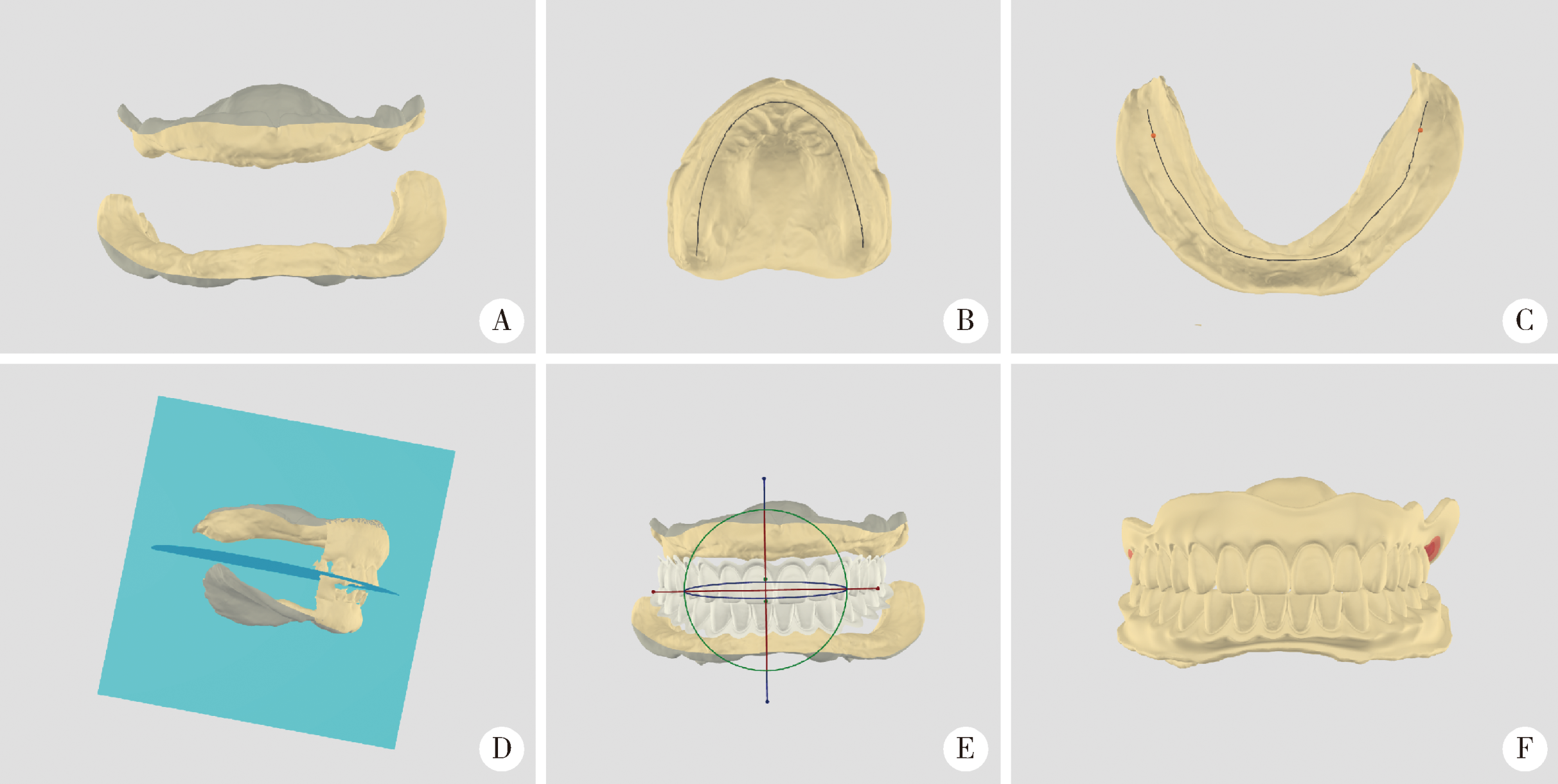
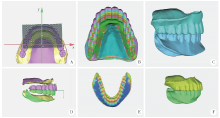
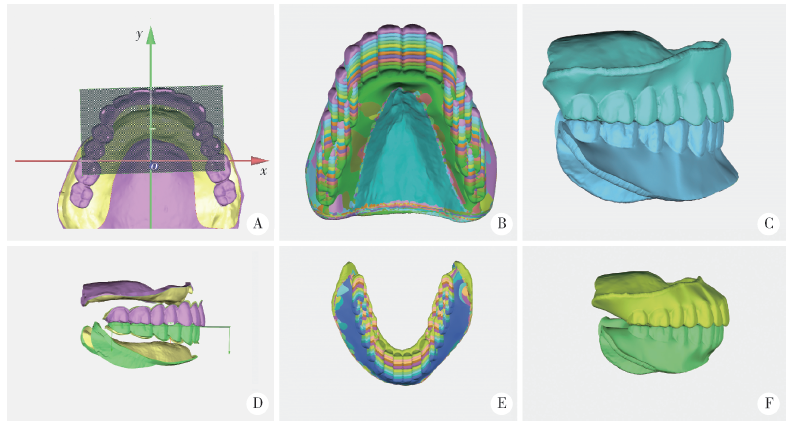
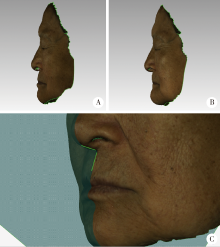
Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences) ›› 2020, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (1): 107-112. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2020.01.017
Previous Articles Next Articles
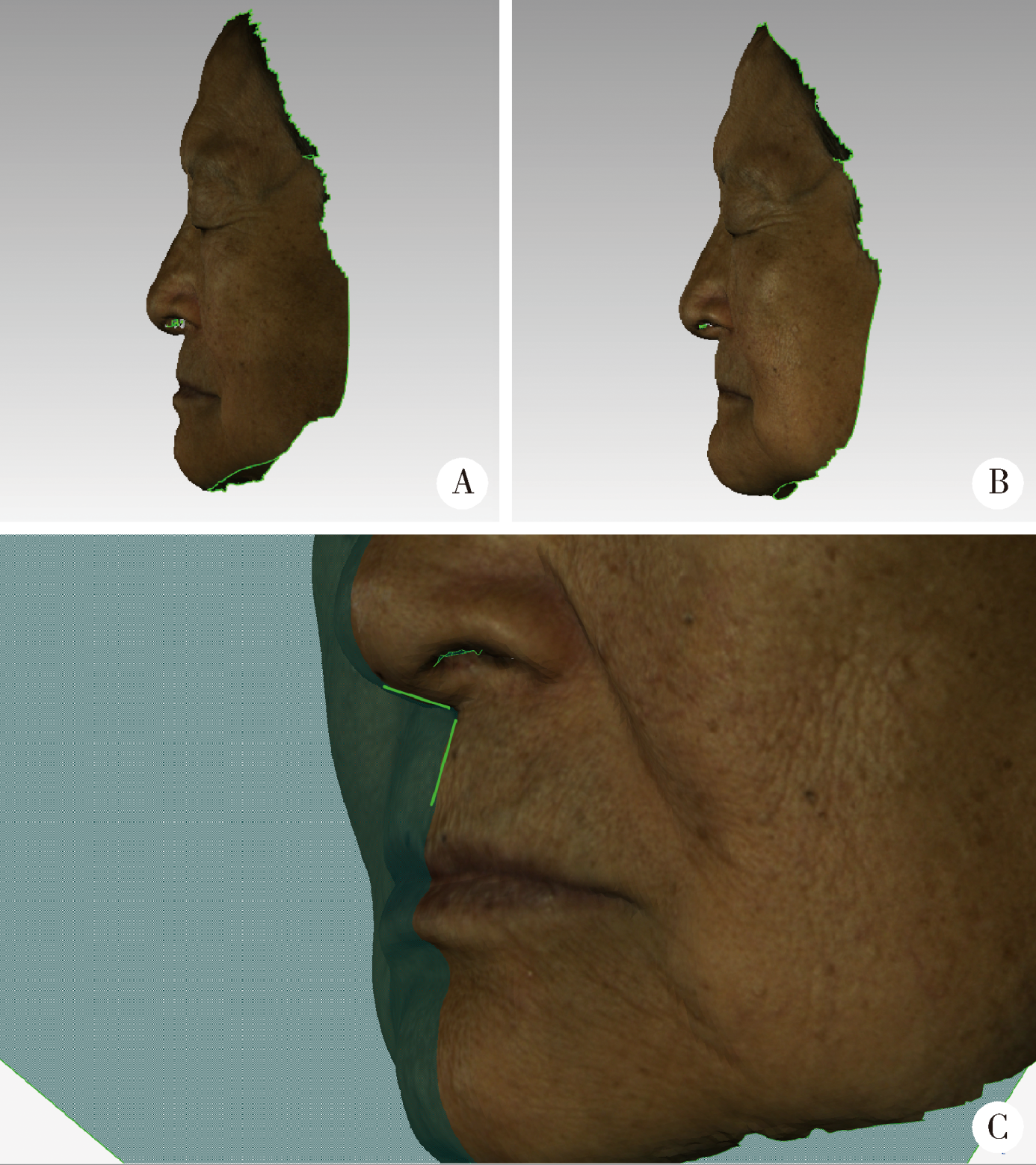
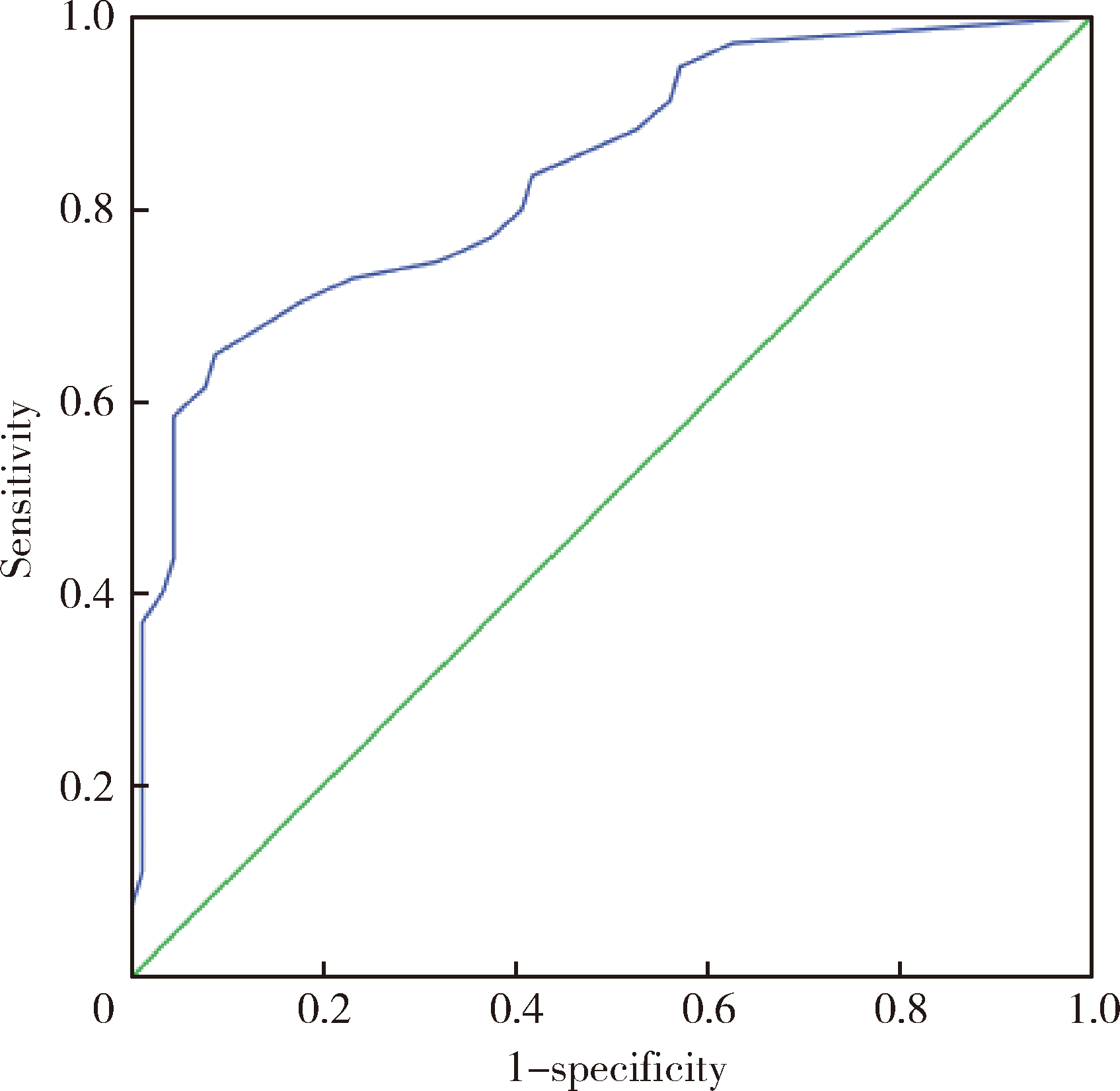
Visual sensitivity threshold of lateral view of nasolabial Angle changes in edentulous jaw patients
Lang YOU1,Ke-hui DENG2,Wei-wei LI2,Yi-jiao ZHAO2,△( ),Yu-chun SUN2,△(
),Yu-chun SUN2,△( ),Yong-sheng ZHOU1
),Yong-sheng ZHOU1
- 1. Center of Digital Dentistry, Peking University School and Hospital of Stomatology & Department of Prosthodontics, Beijing 100081, China
2. Center of Digital Dentistry, Peking University School and Hospital of Stomatology & National Clinical Research Center for Oral Diseases & National Engineering Laboratory for Digital and Material Technology of Stomatology & Beijing Key Laboratory of Digital Stomatology, Beijing 100081, China
CLC Number:
- R783
| [1] | Harris R, Nagarkar P, Amirlak B . Varied definitions of nasolabial angle[J]. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open, 2016,4(6):e752. |
| [2] | 徐安秀, 邓锋, 王芬芬 , 等. 鼻唇角改变对骨性Ⅰ类软组织侧貌影响的审美评价[J]. 华西口腔医学杂志, 2015,33(5):492-496. |
| [3] | 马玥, 任嫒姝, 付钢 , 等. 鼻唇角、颏唇角改变对骨性Ⅱ类和Ⅲ类患者面容影响的三维美学评价[J]. 实用口腔医学杂志, 2017,33(5):647-652. |
| [4] | Desesa CR, Metzler P, Sawh-Martinez R , et al. Three-dimensional nasolabial morphologic alterations following Le Fort I[J]. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open, 2016,4(8):e848. |
| [5] | Aniruddh YV, Ravi K, Edeinton A. Comparative evaluation of soft tissue changes in Class Ⅰ borderline patients treated with extraction and nonextraction modalities[J]. Dental Press J Orthod, 2016,21(4):50-59. |
| [6] | Kamashita Y, Kamada Y, Kawahata N , et al. Influence of lip support on the soft-tissue profile of complete denture wearers[J]. J Oral Rehabil, 2006,33(2):102-109. |
| [7] | Kaipatur NR, Flores-Mir C . Accuracy of computer programs in predicting orthognathic surgery soft tissue response[J]. J Oral Maxillofac Surg, 2009,67(4):751-759. |
| [8] | Raschke GF, Rieger UM, Bader RD , et al. Perioral aging: an anthropometric appraisal[J]. J Craniomaxillofac Surg, 2014,42(5):e312-e317. |
| [9] | Sierpinska T, Golebiewska M, Kuc J , et al. The influence of the occlusal vertical dimension on masticatory muscle activities and hyoid bone position in complete denture wearers[J]. Adv Med Sci, 2009,54(1):104-108. |
| [10] | Krajicek DD . Guides for natural facial appearance as related to complete denture construction[J]. J Prosthet Dent, 1969,21(6):654-662. |
| [11] | Coleman SR, Grover R . The anatomy of the aging face: volume loss and changes in 3-dimensional topography[J]. Aesthet Surg J, 2006,26(Suppl 1):S4-S9. |
| [12] | Owens EG, Goodacre CJ, Loh PL , et al. A multicenter interracial study of facial appearance. Part 1: A comparison of extraoral parameters[J]. Int J Prosthodont, 2002,15(3):273-282. |
| [13] | Yuan F, Cheng C, Dai N , et al. Prediction of aesthetic reconstruction effects in edentulous patients[J]. Sci Rep, 2017,7(1):18077. |
| [14] | Denes BJ, Bolton C, Illsley CS , et al. Notch coordinates periodontal ligament maturation through regulating lamin A[J]. J Dent Res, 2019,98(12):1357-1366. |
| [15] | Katase H, Kanazawa M, Inokoshi M , et al. Face simulation system for complete dentures by applying rapid prototyping[J]. J Prosthet Dent, 2013,109(6):353-360. |
| [16] | Schweiger J, Güth JF, Edelhoff D , et al. Virtual evaluation for cad-cam-fabricated complete dentures[J]. J Prosthet Dent, 2017,117(1):28-33. |
| [17] | Franco SGC, Libdy MR, Normando D . Scan time, reliability and accuracy of craniofacial measurements using a 3D light scanner[J]. J Oral Biol Craniofac Res, 2019,9(4):331-335. |
| [18] | Modabber A, Peters F, Kniha K , et al. Evaluation of the accuracy of a mobile and a stationary system for three-dimensional facial scanning[J]. J Craniomaxillofac Surg, 2016,44(10):1719-1724. |
| [19] | Grant CA, Johnston M, Adam CJ , et al. Accuracy of 3D surface scanners for clinical torso and spinal deformity assessment[J]. Med Eng Phys, 2019,63:63-71. |
| [20] | Li H, Lyu P, Sun Y , et al. A quantitative study of 3D-scanning frequency and Δd of tracking points on the tooth surface[J]. Sci Rep, 2015,5(2):14350. |
| [21] | 萧宁, 王勇, 赵一姣 . 三维颜面部软组织正中矢状面确定方法的研究进展[J]. 中华口腔医学杂志, 2018,53(7):495-499. |
| [22] | Lee JK, Jung PK, Moon CH . Three-dimensional cone beam computed tomographic image reorientation using soft tissues as reference for facial asymmetry diagnosis[J]. Angle Orthod, 2014,84(1):38-47. |
| [23] | Nur RB, Çakan DG, Arun T . Evaluation of facial hard and soft tissue asymmetry using cone-beam computed tomography[J]. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop, 2016,149(2):225-237. |
| [1] | Yuxuan TIAN,Mingjian RUAN,Yi LIU,Derun LI,Jingyun WU,Qi SHEN,Yu FAN,Jie JIN. Predictive effect of the dual-parametric MRI modified maximum diameter of the lesions with PI-RADS 4 and 5 on the clinically significant prostate cancer [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(4): 567-574. |
| [2] | Xinxin ZHAN,Lulu CAO,Dong XIANG,Hao TANG,Dandan XIA,Hong LIN. Effect of printing orientation on physical and mechanical properties of 3D printing prosthodontic base resin materials [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(2): 345-351. |
| [3] | Liang LYU,Mingjin ZHANG,Aonan WEN,Yijiao ZHAO,Yong WANG,Jing LI,Gengchen YANG,Dawei LIU. Preliminary evaluation of chin symmetry with three dimentional soft tissue spatial angle wireframe template [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(1): 106-110. |
| [4] | Bochun MAO,Yajing TIAN,Xuedong WANG,Jing LI,Yanheng ZHOU. Soft and hard tissue changes of hyperdivergent class Ⅱ patients before and after orthodontic extraction treatment [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(1): 111-119. |
| [5] | Xiaotong LING,Liuyang QU,Danni ZHENG,Jing YANG,Xuebing YAN,Denggao LIU,Yan GAO. Three-dimensional radiographic features of calcifying odontogenic cyst and calcifying epithelial odontogenic tumor [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(1): 131-137. |
| [6] | Panpan HU,Yan LI,Xiao LIU,Yanchao TANG,Zihe LI,Zhongjun LIU. Clinical outcomes of 3D-printing stand-alone artificial vertebral body in anterior cervical surgeries [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(1): 161-166. |
| [7] | Xinyu XU,Ling WU,Fengqi SONG,Zili LI,Yi ZHANG,Xiaojing LIU. Mandibular condyle localization in orthognathic surgery based on mandibular movement trajectory and its preliminary accuracy verification [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(1): 57-65. |
| [8] | Sui LI,Wenjie MA,Shimin WANG,Qian DING,Yao SUN,Lei ZHANG. Trueness of different digital design methods for incisal guidance of maxillary anterior implant-supported single crowns [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(1): 81-87. |
| [9] | Yi LIU,Chang-wei YUAN,Jing-yun WU,Qi SHEN,Jiang-xi XIAO,Zheng ZHAO,Xiao-ying WANG,Xue-song LI,Zhi-song HE,Li-qun ZHOU. Diagnostic efficacy of prostate cancer using targeted biopsy with 6-core systematic biopsy for patients with PI-RADS 5 [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(5): 812-817. |
| [10] | Chang-wei YUAN,De-run LI,Zhi-hua LI,Yi LIU,Gang-zhi SHAN,Xue-song LI,Li-qun ZHOU. Application of dynamic contrast enhanced status in multiparametric magnetic resonance imaging for prostatic cancer with PI-RADS 4 lesion [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(5): 838-842. |
| [11] | Zhan-yi ZHANG,Fan ZHANG,Ye YAN,Cai-guang CAO,Chang-jian LI,Shao-hui DENG,Yue-hao SUN,Tian-liang HUANG,Yun-he GUAN,Nan LI,Min LU,Zhen-hua HU,Shu-dong ZHANG. Near-infrared targeted probe designed for intraoperative imaging of prostatic neurovascular bundles [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(5): 843-850. |
| [12] | Zhuo-hua LIN,Ru-yi CAI,Yang SUN,Rong MU,Li-gang CUI. Methodology and clinical use of superb microvascular imaging in assessing micro-circulation changes of fingertips in systemic sclerosis [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(4): 636-640. |
| [13] | Ying LIU,Ran HUO,Hui-min XU,Zheng WANG,Tao WANG,Hui-shu YUAN. Correlations between plaque characteristics and cerebral blood flow in patients with moderate to severe carotid stenosis using magnetic resonance vessel wall imaging [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(4): 646-651. |
| [14] | Qiang FU,Guan-ying GAO,Yan XU,Zhuo-hua LIN,You-jing SUN,Li-gang CUI. Comparative study of ultrasound and magnetic resonance imaging in the diagnosis of asymptomatic anterosuperior acetabular labrum tears [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(4): 665-669. |
| [15] | Xiang LIU,Hui-hui XIE,Yu-feng XU,Xiao-dong ZHANG,Xiao-feng TAO,Lin LIU,Xiao-ying WANG. Value of artificial intelligence in the improvement of diagnostic consistency of radiology residents [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(4): 670-675. |
|
||