Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences) ›› 2024, Vol. 56 ›› Issue (3): 487-494. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2024.03.016
Previous Articles Next Articles
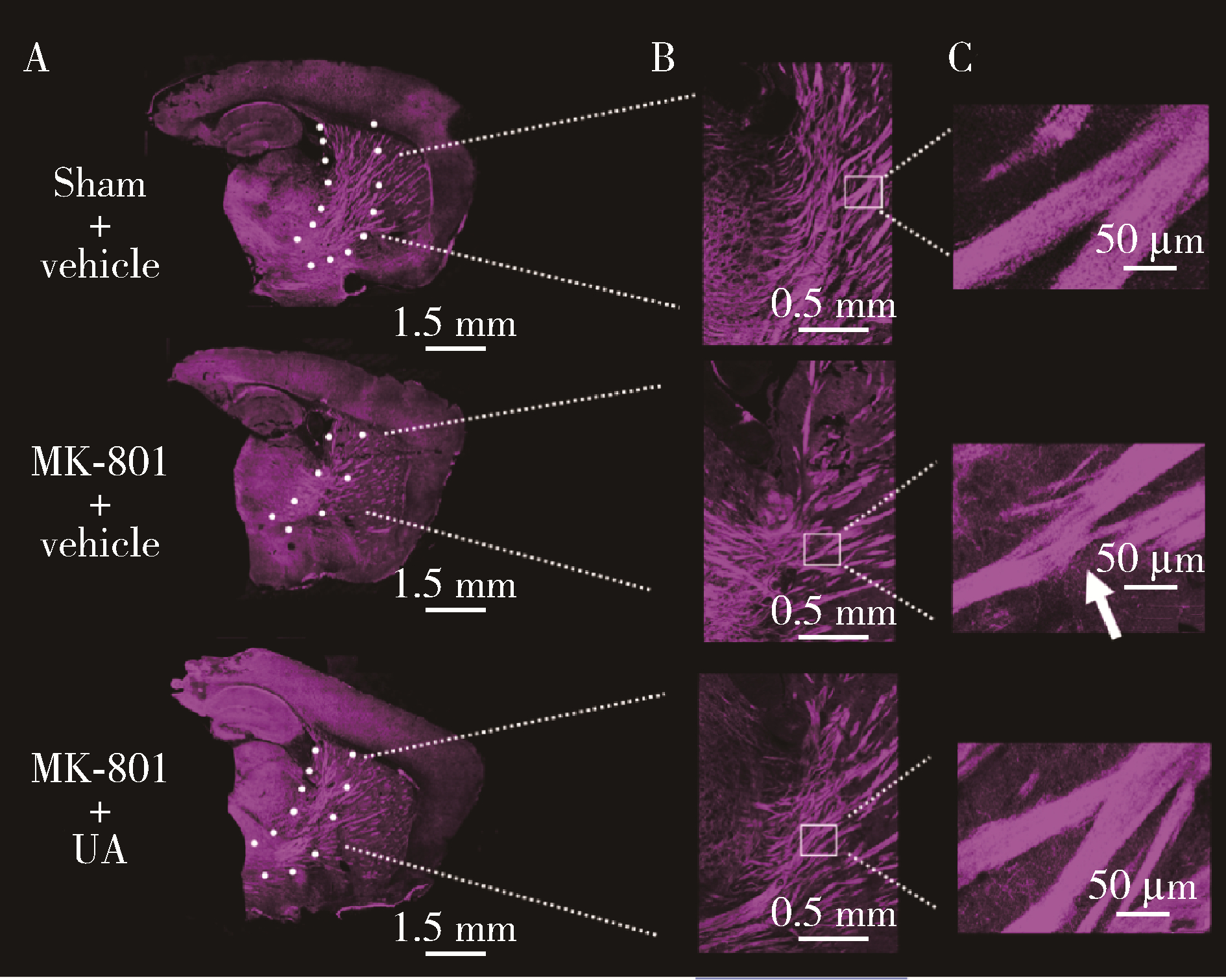
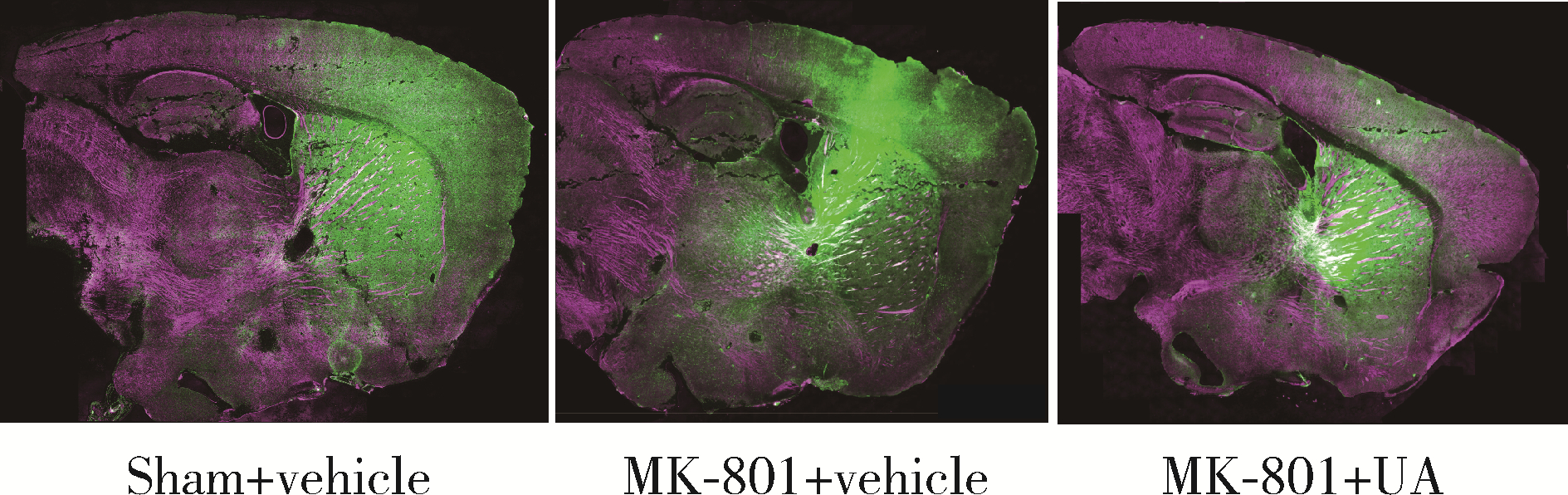
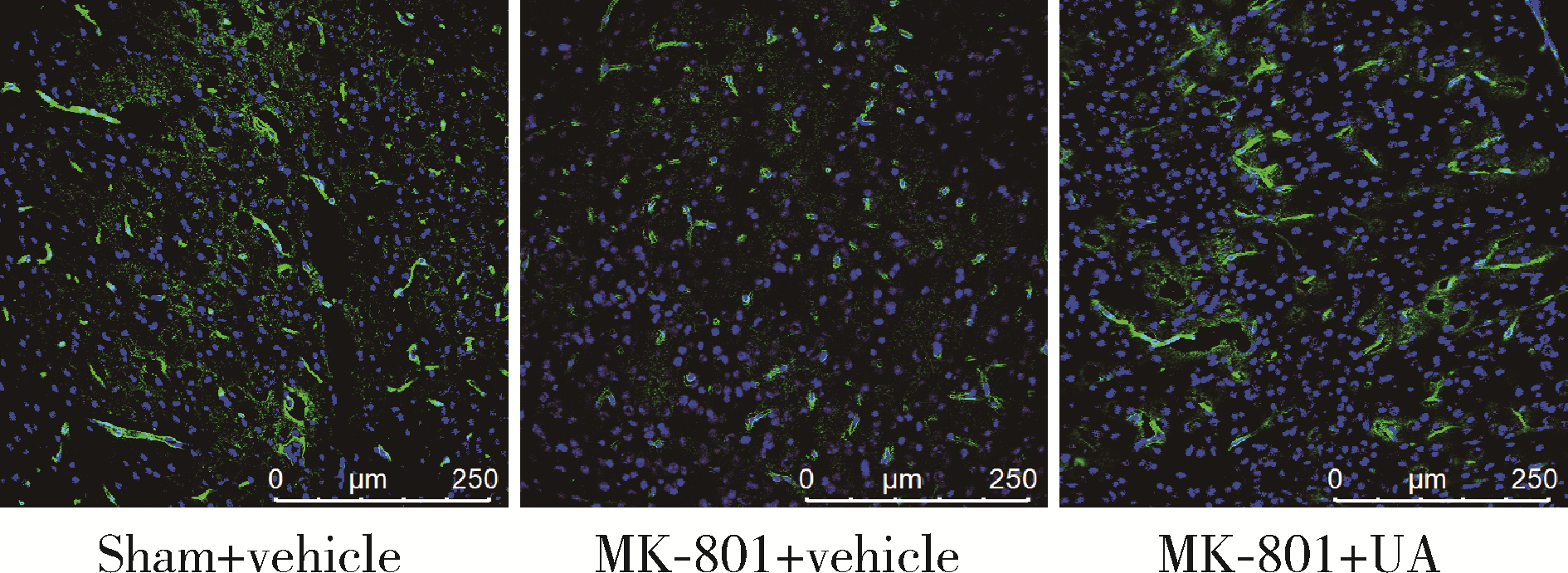
Ursolic acid improved demyelination and interstitial fluid drainage disorders in schizophrenia mice
Ren LONG1, Xin MAO2, Tianzi GAO1, Qian XIE3, Hanbo TAN1, Ziyin LI1, Hongbin HAN1,2,*( ), Lan YUAN1,*(
), Lan YUAN1,*( )
)
- 1. Department of Medical Imaging Technology, Institute of Medical Technology, Peking University & Beijing Key Lab of Magnetic Resonance Imaging Device and Technique, Beijing 100191, China
2. Department of Radiology, Peking University Third Hispital, Beijing 100191, China
3. Department of Nephrology, Peking University Third Hispital, Beijing 100191, China
CLC Number:
- R285.5
| 1 |
Stewart LA .Chemotherapy in adult high-grade glioma: A systematic review and meta-analysis of individual patient data from 12 randomised trials[J].Lancet,2002,359(9311):1011-1018.
doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(02)08091-1 |
| 2 |
Falkai P , Raabe F , Bogerts B , et al.Association between altered hippocampal oligodendrocyte number and neuronal circuit structures in schizophrenia: A postmortem analysis[J].Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci,2020,270(4):413-424.
doi: 10.1007/s00406-019-01067-0 |
| 3 | Stępnicki P, Kondej M, Kaczor AA. Current concepts and treatments of schizophrenia[J/OL]. Molecules, 2018, 23(8) (2018-08-20)[2023-03-01]. https://www.mdpi.com/1420-3049/23/8/2087. |
| 4 |
Koshiyama D , Fukunaga M , Okada N , et al.White matter microstructural alterations across four major psychiatric disorders: Nega-analysis study in 2937 individuals[J].Mol Psychiatry,2020,25(4):883-895.
doi: 10.1038/s41380-019-0553-7 |
| 5 |
Karlsgodt KH .White matter microstructure across the psychosis spectrum[J].Trends Neurosci,2020,43(6):406-416.
doi: 10.1016/j.tins.2020.03.014 |
| 6 |
Wang A , Wang R , Cui D , et al.the drainage of interstitial fluid in the deep brain is controlled by the integrity of myelination[J].Aging Dis,2019,10(5):937-948.
doi: 10.14336/AD.2018.1206 |
| 7 |
赵越, 李昀倩, 李怀业, 等.荧光及磁示踪法观测脑组织液的引流分区特征[J].北京大学学报(医学版),2017,49(2):303-309.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-167X.2017.02.021 |
| 8 |
Wang R , Han H , Shi K , et al.The alteration of brain interstitial fluid drainage with myelination development[J].Aging Dis,2021,12(7):1729-1740.
doi: 10.14336/AD.2021.0305 |
| 9 |
Mccutcheon RA , Abi-Dargham A , Howes OD .Schizophrenia, dopamine and the Striatum: From biology to symptoms[J].Trends Neurosci,2019,42(3):205-220.
doi: 10.1016/j.tins.2018.12.004 |
| 10 |
Kashyap D , Tuli HS , Sharma AK .Ursolic acid (UA): A metabolite with promising therapeutic potential[J].Life Sci,2016,146,201-213.
doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2016.01.017 |
| 11 |
Yamamoto S , Sakemoto C , Iwasa K , et al.Ursolic acid treatment suppresses cuprizone-induced demyelination and motor dysfunction via upregulation of IGF-1[J].J Pharmacol Sci,2020,144(3):119-122.
doi: 10.1016/j.jphs.2020.08.002 |
| 12 |
Ramos-Hryb AB , Pazini FL , Kaster MP , et al.Therapeutic potential of ursolic acid to manage neurodegenerative and psychiatric diseases[J].CNS Drugs,2017,31(12):1029-1041.
doi: 10.1007/s40263-017-0474-4 |
| 13 | He J , Zu Q , Wen C , et al.Quetiapine attenuates schizophrenia-like behaviors and demyelination in a MK-801-induced mouse model of schizophrenia[J].Front Psychiatry,2020,11,843. |
| 14 |
Nakamoto C , Kawamura M , Nakatsukasa E , et al.GluD1 knockout mice with a pure C57BL/6N background show impaired fear memory, social interaction, and enhanced depressive-like behavior[J].PLoS One,2020,15(2):e0229288.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0229288 |
| 15 |
Kraeuter AK , Mashavave T , Suvarna A , et al.Effects of beta-hydroxybutyrate administration on MK-801-induced schizophrenia-like behaviour in mice[J].Psychopharmacology (Berl),2020,237(5):1397-1405.
doi: 10.1007/s00213-020-05467-2 |
| 16 |
Schilke ED , Tremolizzo L , Appollonio I , et al.Tics: Neurological disorders determined by a deficit in sensorimotor gating processes[J].Neurol Sci,2022,43(10):5839-5850.
doi: 10.1007/s10072-022-06235-0 |
| 17 |
Ruggiero RN , Rossignoli MT , De ross JB , et al.Cannabinoids and vanilloids in schizophrenia: Neurophysiological evidence and directions for basic research[J].Front Pharmacol,2017,8,399.
doi: 10.3389/fphar.2017.00399 |
| 18 | Iliff JJ , Wang M , Liao Y , et al.A paravascular pathway facilitates CSF flow through the brain parenchyma and the clearance of interstitial solutes, including amyloid β[J].Sci Transl Med,2012,4(147):147r. |
| 19 |
Chen S , Tang Y , Fan X , et al.The role of white matter abnor-mality in the left anterior corona radiata: In relation to formal thought disorder in patients with schizophrenia[J].Psychiatry Res,2022,307,114302.
doi: 10.1016/j.psychres.2021.114302 |
| 20 |
Di biase MA , Zhang F , Lyall A , et al.Neuroimaging auditory verbal hallucinations in schizophrenia patient and healthy populations[J].Psychol Med,2020,50(3):403-412.
doi: 10.1017/S0033291719000205 |
| 21 |
Walch E , Fiacco TA .Honey, I shrunk the extracellular space: Measurements and mechanisms of astrocyte swelling[J].Glia,2022,70(11):2013-2031.
doi: 10.1002/glia.24224 |
| 22 |
Walch E , Bilas A , Bebawy V , et al.Contributions of astrocyte and neuronal volume to CA1 neuron excitability changes in elevated extracellular potassium[J].Front Cell Neurosci,2022,16,930384.
doi: 10.3389/fncel.2022.930384 |
| 23 | DoiT, Fan Y, Gold J I, et al. The caudate nucleus contributes causally to decisions that balance reward and uncertain visual information[J]. Elife, 2020, 9(2020-06-22)[2023-03-01]. https://elifesciences.org/articles/56694. |
| 24 |
Kirino E , Tanaka S , Fukuta M , et al.Functional connectivity of the caudate in schizophrenia evaluated with simultaneous resting-state functional MRI and electroencephalography recordings[J].Neuropsychobiology,2019,77(4):165-175.
doi: 10.1159/000490429 |
| 25 |
Teng Z , Wang A , Wang P , et al.The effect of aquaporin-4 knockout on interstitial fluid flow and the structure of the extracellular space in the deep brain[J].Aging Dis,2018,9(5):808-816.
doi: 10.14336/AD.2017.1115 |
| 26 |
Tekieh T , Robinson P A , Postnova S .Cortical waste clearance in normal and restricted sleep with potential runaway tau buildup in Alzheimer's disease[J].Sci Rep,2022,12(1):13740.
doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-15109-6 |
| 27 | Carotenuto A , Cacciaguerra L , Pagani E , et al.Glymphatic system impairment in multiple sclerosis: relation with brain damage and disability[J].Brain,2021,145(8):2785-2795. |
| 28 | Aggleton JP , O'mara SM .The anterior thalamic nuclei: Core components of a tripartite episodic memory system[J].Nat Rev Neurosci,2022,23(8):505-516. |
| 29 |
Halassa MM , Sherman SM .Thalamocortical circuit motifs: A general framework[J].Neuron,2019,103(5):762-770.
doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2019.06.005 |
| 30 |
Byne W , Hazlett EA , Buchsbaum MS , et al.The thalamus and schizophrenia: Current status of research[J].Acta Neuropathol,2009,117(4):347-368.
doi: 10.1007/s00401-008-0404-0 |
| 31 |
Zhang Y , Li X , Ciric B , et al.A dual effect of ursolic acid to the treatment of multiple sclerosis through both immunomodulation and direct remyelination[J].Proc Natl Acad Sci USA,2020,117(16):9082-9093.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.2000208117 |
| 32 |
Faden J , Citrome L .Schizophrenia: One name, many different manifestations[J].Med Clin North Am,2023,107(1):61-72.
doi: 10.1016/j.mcna.2022.05.005 |
| 33 |
Flint J , Munafò M .Schizophrenia: Genesis of a complex disease[J].Nature,2014,511(7510):412-413.
doi: 10.1038/nature13645 |
| [1] | Xue-ping WANG,Yu-ya-nan ZHANG,Tian-lan LU,Zhe LU,Zhe-wei KANG,Yao-yao SUN,Wei-hua YUE. Variations in fecal microbiota of first episode schizophrenia associated with clinical assessment and serum metabolomics [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(5): 863-873. |
| [2] | Hong-bin HAN. Discovery of a new division system in brain and the regionalized drainage route of brain interstitial fluid [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2019, 51(3): 397-401. |
| [3] | BAI Ning,YANG Ling-fei,AN Li-hua,WANG wen,LI Yun-qian,SHENG Hui,WANG Tong,LI Hua-kan,YUAN Lan. Dynamic visual analysis of neutrophils chemotaxis in peritoneal cavity of schizophrenic model in mice [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2018, 50(2): 226-230. |
|
||