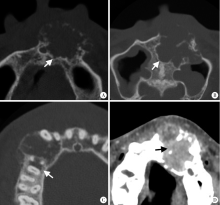
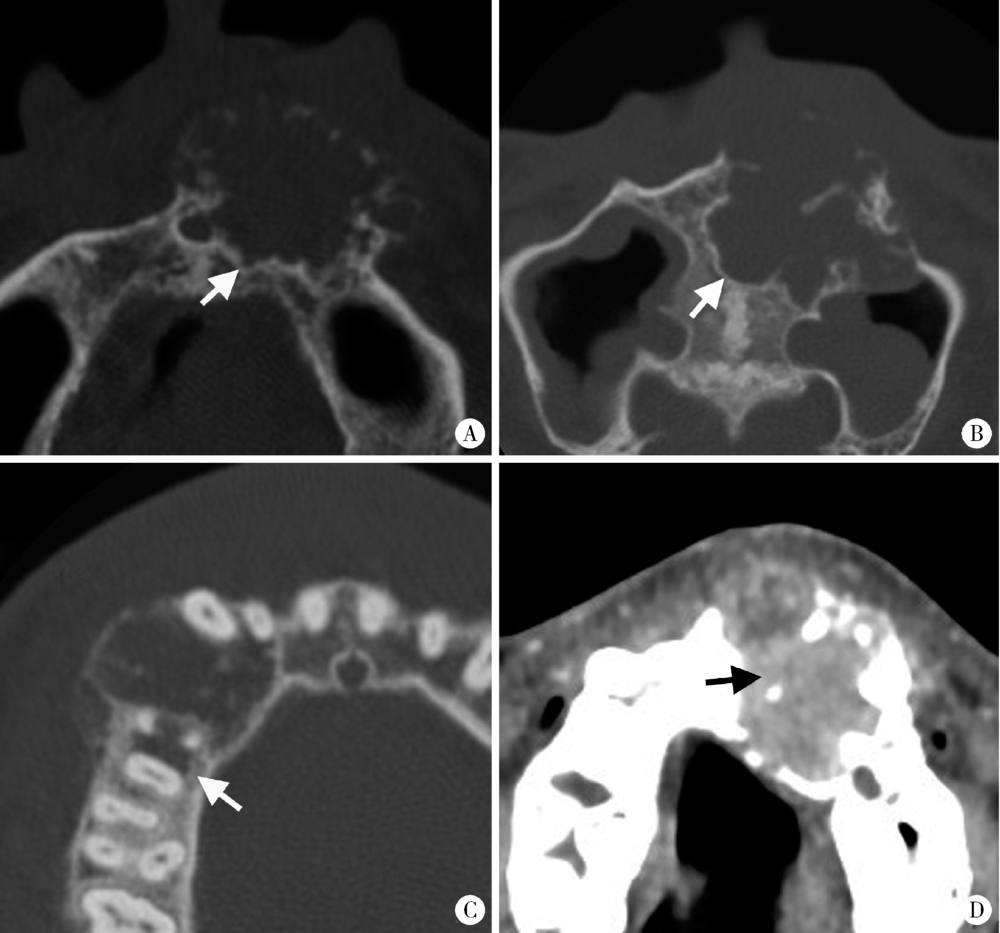
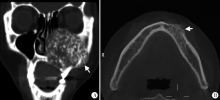
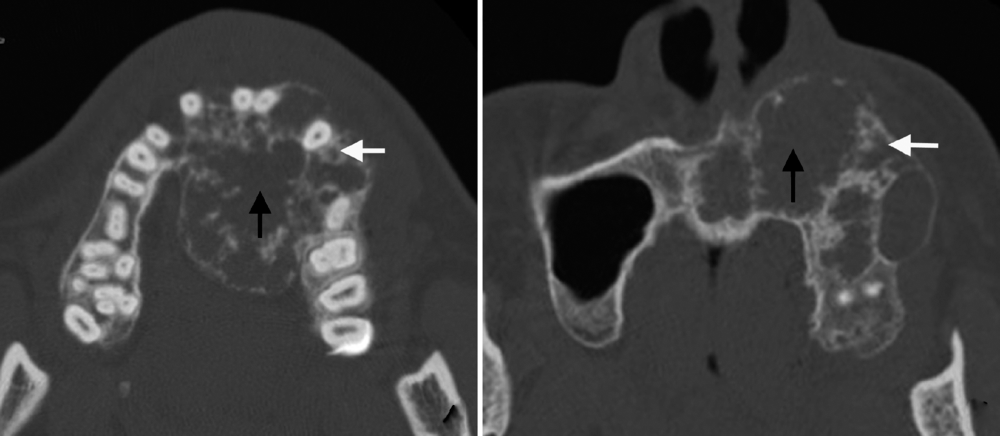
Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences) ›› 2019, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (6): 1138-1143. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2019.06.028
Previous Articles Next Articles
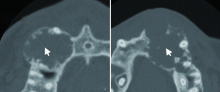
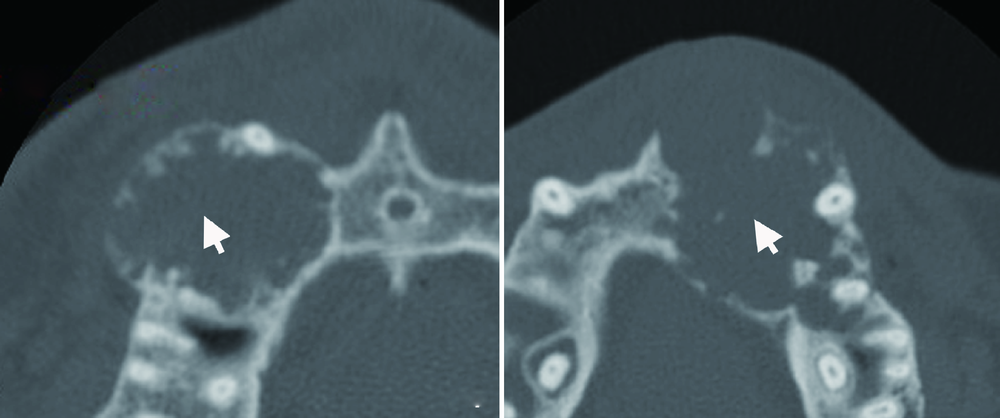
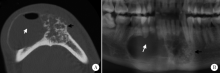
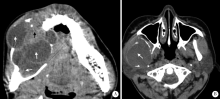
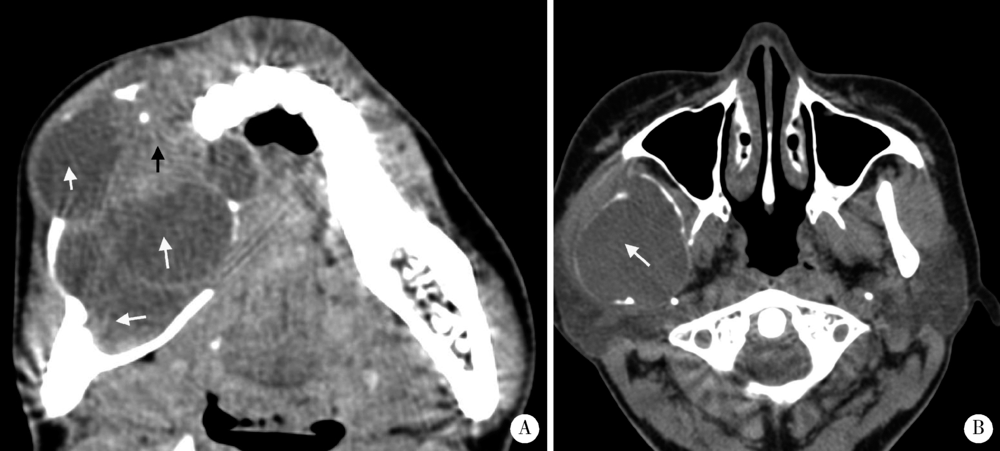
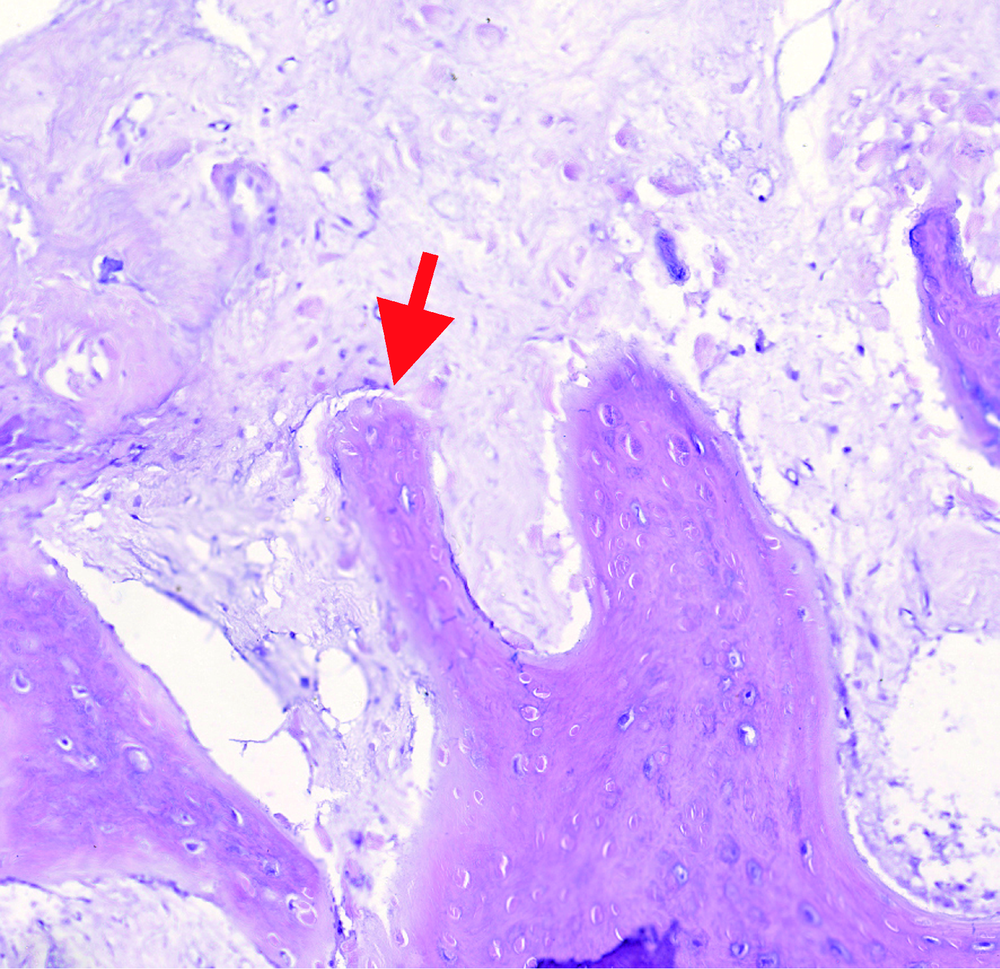
Computed tomographic features of desmoplastic ameloblastoma of the jaw
Chong-ke SUN1,Jian-yun ZHANG2,Zhi-peng SUN1,△( ),Kai-yuan FU1,Yan-ping ZHAO1,Zu-yan ZHANG1,Xu-chen MA1
),Kai-yuan FU1,Yan-ping ZHAO1,Zu-yan ZHANG1,Xu-chen MA1
- 1. Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology,Peking University School and Hospital of Stomatology & National Clinical Research Center for Oral Diseases & National Engineering Laboratory for Digital and Material Technology of Stomatology & Beijing Key Laboratory of Digital Stomatology, Beijing 100081, China
2. Department of Oral Pathology, Peking University School and Hospital of Stomatology & National Clinical Research Center for Oral Diseases & National Engineering Laboratory for Digital and Material Technology of Stomatology & Beijing Key Laboratory of Digital Stomatology, Beijing 100081, China
CLC Number:
- R739.82
| [1] | 于世凤, 高岩, 李铁军 , 等. 口腔组织学与病理学[M]. 北京: 北京大学医学出版社, 2009: 359-361. |
| [2] | Eversole LR, Leider AS, Hansen LS . Ameloblastomas with pronounced desmoplasia[J]. J Oral Maxillofac Surg, 1984,42(11):735-740. |
| [3] | Kramer IR, Pindborg JJ, Shear M . The WHO histological typing of odontogenic tumours. A commentary on the Second Edition[J]. Cancer, 1992,70(12):2988-2994. |
| [4] | Thompson L . World Health Organization classification of tumours: Pathology and genetics of head and neck tumours[J]. Ear Nose Throat J, 2006,85(2):74. |
| [5] |
刘浏, 张新宇, 胡永杰 , 等. 890例颌骨成釉细胞瘤发病构成比分析[J]. 口腔颌面外科杂志, 2015,25(3):213-215.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-4979.2015.03.011 |
| [6] | 李江, 张伟国 . 15例促结缔组织增生型成釉细胞瘤的临床病理分析[J]. 华西口腔医学杂志, 1998,25(2):405-410. |
| [7] | El-Naggar AK, Chan JKC, Grandis JR , et al. WHO classification of head and neck tumours[M].4th ed. Lyon, France: IARC Press, 2017: 215-218. |
| [8] | 王世平, 陈新明, 程勇 , 等. 促结缔组织增生性成釉细胞瘤的X线分析[J]. 中华口腔医学杂志, 2001,36(4):253-255. |
| [9] | 郭小科, 刘冰, 赵怡芳 . 76例单囊型成釉细胞瘤的回顾性分析[J]. 临床口腔医学杂志, 2015,31(5):296-298. |
| [10] | 马绪臣 . 口腔颌面医学影像诊断学[M]. 6版. 北京: 人民卫生出版社. 2012: 121-123. |
| [11] | 王恩博, 李铁军, 俞光岩 , 等. 109例成釉细胞瘤病理类型、影像学表现、治疗方法和预后的对比研究[J]. 现代口腔医学杂志, 2002,16(4):352-354. |
| [12] | 左金华, 刘道峰, 李金荣 , 等. 153例成釉细胞瘤X线分析[J]. 滨州医学院学报, 2008,31(2):101-103. |
| [13] | 张炳, 刘鸿雁, 王国华 , 等. 颌骨成釉细胞瘤与牙源性角化囊性瘤的CT鉴别诊断[J]. 中国医学计算机成像杂志, 2016,22(4):313-316. |
| [14] | Gardner DG . Some current concepts on the pathology of ameloblastomas[J]. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod, 1996,82(6):660-669. |
| [15] | 郭兰田, 马珍珍, 秦东京 . 单囊型成釉细胞瘤临床病理及螺旋CT征象分析[J]. 滨州医学院学报, 2013,36(1):38-40. |
| [16] | 郭兰田, 马珍珍, 王宁 , 等. 单囊型成釉细胞瘤149例临床及X线征象分析[J]. 中华临床医师杂志: 电子版, 2011,5(8):2480-2482. |
| [1] | Xinxin CHEN, Zhe TANG, Yanchun QIAO, Wensheng RONG. Caries experience and its correlation with caries activity of 4-year-old children in Miyun District of Beijing [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(5): 833-838. |
| [2] | Hua ZHONG, Yuan LI, Liling XU, Mingxin BAI, Yin SU. Application of 18F-FDG PET/CT in rheumatic diseases [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(5): 853-859. |
| [3] | Zhengfang LI,Cainan LUO,Lijun WU,Xue WU,Xinyan MENG,Xiaomei CHEN,Yamei SHI,Yan ZHONG. Application value of anti-carbamylated protein antibody in the diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(4): 729-734. |
| [4] | Shishi BO,Chengzhi GAO. Tooth segmentation and identification on cone-beam computed tomography with convolutional neural network based on spatial embedding information [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(4): 735-740. |
| [5] | Xiaotong LING,Liuyang QU,Danni ZHENG,Jing YANG,Xuebing YAN,Denggao LIU,Yan GAO. Three-dimensional radiographic features of calcifying odontogenic cyst and calcifying epithelial odontogenic tumor [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(1): 131-137. |
| [6] | Deng-hui DUAN,Hom-Lay WANG,En-bo WANG. Role of collagen membrane in modified guided bone regeneration surgery using buccal punch flap approach: A retrospective and radiographical cohort study [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(6): 1097-1104. |
| [7] | Hai-hong YAO,Fan YANG,Su-mei TANG,Xia ZHANG,Jing HE,Yuan JIA. Clinical characteristics and diagnostic indicators of macrophage activation syndrome in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus and adult-onset Still's disease [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(6): 966-974. |
| [8] | Xiang LIU,Hui-hui XIE,Yu-feng XU,Xiao-dong ZHANG,Xiao-feng TAO,Lin LIU,Xiao-ying WANG. Value of artificial intelligence in the improvement of diagnostic consistency of radiology residents [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(4): 670-675. |
| [9] | Yan XIONG,Xin LI,Li LIANG,Dong LI,Li-min YAN,Xue-ying LI,Ji-ting DI,Ting LI. Evaluation of accuracy of pathological diagnosis based on thyroid core needle biopsy [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(2): 234-242. |
| [10] | Jin-hua ZHANG,Jie PAN,Zhi-peng SUN,Xiao WANG. Effect of various intracanal materials on the diagnostic accuracy of cone-beam computed tomography in vertical root fractures [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(2): 333-338. |
| [11] | Xue-mei HA,Yong-zheng YAO,Li-hua SUN,Chun-yang XIN,Yan XIONG. Solid placental transmogrification of the lung: A case report and literature review [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(2): 357-361. |
| [12] | Bo-han NING,Qing-xia ZHANG,Hui YANG,Ying DONG. Endometrioid adenocarcinoma with proliferated stromal cells, hyalinization and cord-like formations: A case report [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(2): 366-369. |
| [13] | Jia-xue YE,Yu-hong LIANG. A prevalence survey of cone-beam computed tomography use among endodontic practitioners [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(1): 114-119. |
| [14] | Meng-qiao PAN,Jian LIU,Li XU,Xiao XU,Jian-xia HOU,Xiao-tong LI,Xiao-xia WANG. A long-term evaluation of periodontal phenotypes before and after the periodontal-orthodontic-orthognathic combined treatment of lower anterior teeth in patients with skeletal Angle class Ⅲ malocclusion [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(1): 52-61. |
| [15] | Yu FU,Xin-nong HU,Sheng-jie CUI,Jie SHI. Decompensation effectiveness and alveolar bone remodeling analysis of mandibular anterior teeth after preoperative orthodontic treatment in high-angle patients with skeletal class Ⅱ malocclusion [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(1): 62-69. |
|
||