Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences) ›› 2020, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (1): 187-192. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2020.01.030
Previous Articles Next Articles
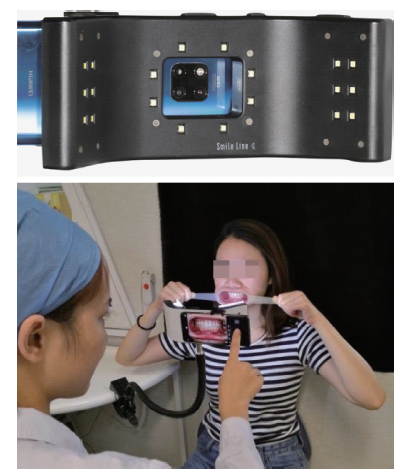
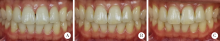
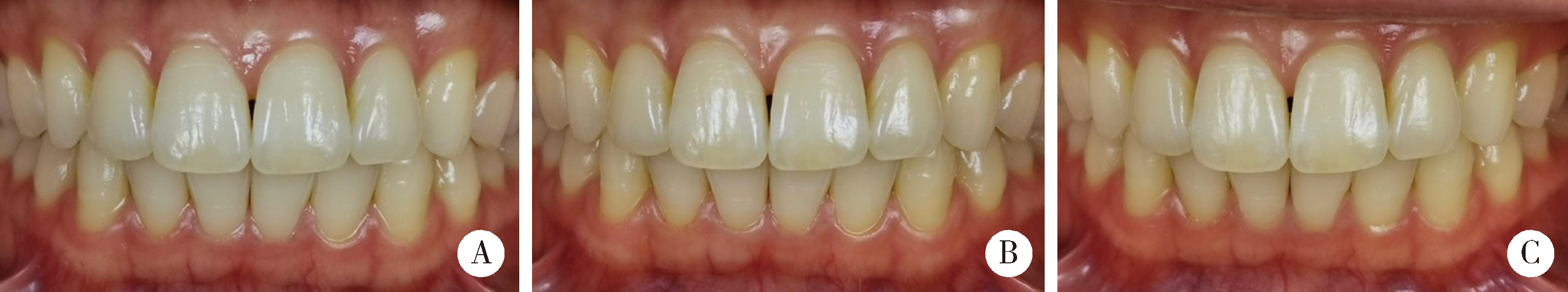
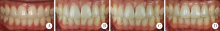
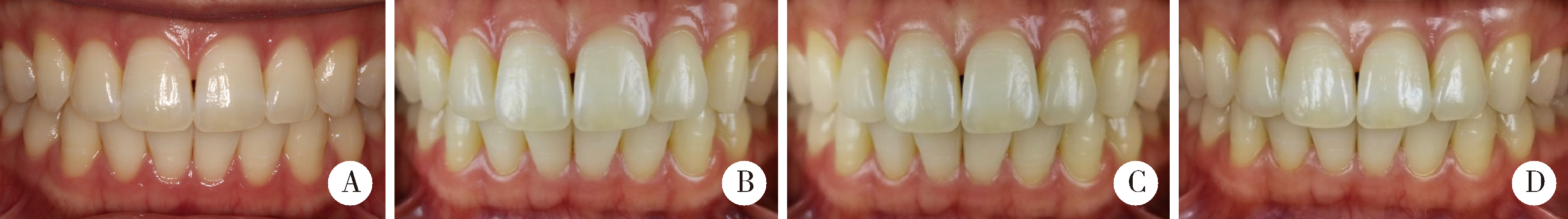
Application and exploration of Smile Lite MDP portable photography system in aesthetic photography of anterior teeth
Min LIU1,Jun-dang ZHANG1,Hong-qiang YE1,Yi-jiao ZHAO2,Xu-bin ZHAO3,Wen-yan ZHAO4,Yun-song LIU1,△( ),Yong-sheng ZHOU1
),Yong-sheng ZHOU1
- 1. Department of Prosthodontics, Peking University School and Hospital of Stomatology & National Clinical Research Center for Oral Diseases & National Engineering Laboratory for Digital and Material Technology of Stomatology & Beijing Key Laboratory of Digital Stomatology, Beijing 100081, China
2. Center of Digital Dentistry, Peking University School and Hospital of Stomatology, Beijing 100081, China
3. Department of Prosthodontics, Yinchuan Stomatology Hosptial, Yinchuan 750002, China
4. Department of Implantation, Yinchuan Stomatology Hosptial, Yinchuan 750002, China
CLC Number:
- R783
| [1] | 谭建国 . 口腔美学临床摄影专家共识[J]. 中华口腔医学杂志, 2017,52(5):265-269. |
| [2] | 于海洋 . 口腔微距摄影速成 [M]. 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 2014. |
| [3] | Wee AG, Lindsey DT, Kuo S , et al. Color accuracy of commercial digital cameras for use in dentistry[J]. Dent Mater, 2006,22(6):553-559. |
| [4] | 徐明明, 刘峰 . 数码摄影在口腔医学领域的应用[J]. 中国口腔颌面外科杂志, 2008,6(4):292-298. |
| [5] | Casaglia A, De DP, Arcuri L , et al. Dental photography today. Part 1: basic concepts[J]. Oral Implantol (Rome), 2016,8(4):122-129. |
| [6] | Cho SH . Color-to-grayscale conversion using a smart phone camera for value comparison[J]. J Prosthet Dent, 2015,114(3):462-463. |
| [7] | 李祎, 刘峰 . 口腔美学临床摄影细节上的几点思考[J]. 中国实用口腔科杂志, 2015,8(7):385-388. |
| [8] | Lombardi RE . The principles of visual perception and their clinical application to denture esthetics[J]. J Prosthet Dent, 1973,29(4):358-382. |
| [9] | Levin EI . Dental esthetics and the golden proportion[J]. J Prosthet Dent, 1978,40(3):244-252. |
| [10] | Snow SR . Esthetic smile analysis of maxillary anterior tooth width: the golden percentage[J]. J Esthet Dent, 1999,11(4):177-184. |
| [11] | Richer P . Artistic Anatomy[M]. New York: Watson-Guptill, 1971. |
| [12] | Preston JD . The golden proportion revisited[J]. J Esthet Dent, 1993,5(6):247-251. |
| [13] | Jin MX, Hong MH, Lee KJ , et al. Does the maxillary anterior ratio in Korean adults follow the golden proportion?[J]. J Adv Prosthodont, 2016,8(2):125-130. |
| [14] | 刘云松, 叶红强, 谷明 , 等. 患者参与的数字化设计在前牙美学修复中的应用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2014,46(1):90-94. |
| [15] | 叶红强, 柳玉树, 刘云松 , 等. 口内数码摄影辅助构建三维彩色数字牙列模型[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2016,48(1):138-142. |
| [16] | 刘峰 . 口腔数码摄影: 从口腔临床摄影到数字化微笑设计 [M]. 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 2017. |
| [17] | Bourouis A, Zerdazi A, Feham M , et al. M-health: Skin disease analysis system using smartphone’s camera[J]. Procedia Comput Sci, 2013,19:1116-1120. |
| [18] | Kwon S, Kim H, Park KS . Validation of heart rate extraction using video imaging on a built-in camera system of a smartphone[J]. Conf Proc IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc, 2012,2012:2174-2177. |
| [19] | Grimaldi D, Kurylyak Y, Lamonaca F, et al. Photoplethysmography detection by smartphone’s videocamera [C]. Prague: IEEE International Conference on Intelligent Data Acquisition & Advanced Computing Systems, 2011. |
| [1] | Xinxin CHEN, Zhe TANG, Yanchun QIAO, Wensheng RONG. Caries experience and its correlation with caries activity of 4-year-old children in Miyun District of Beijing [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(5): 833-838. |
| [2] | Han ZHANG,Yixuan QIN,Diyuan WEI,Jie HAN. A preliminary study on compliance of supportive treatment of patients with periodontitis after implant restoration therapy [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(1): 39-44. |
| [3] | Han ZHAO,Yan WEI,Xuehui ZHANG,Xiaoping YANG,Qing CAI,Chengyun NING,Mingming XU,Wenwen LIU,Ying HUANG,Ying HE,Yaru GUO,Shengjie JIANG,Yunyang BAI,Yujia WU,Yusi GUO,Xiaona ZHENG,Wenjing LI,Xuliang DENG. Bionic design, preparation and clinical translation of oral hard tissue restorative materials [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(1): 4-8. |
| [4] | Congwei WANG,Min GAO,Yao YU,Wenbo ZHANG,Xin PENG. Clinical analysis of denture rehabilitation after mandibular fibula free-flap reconstruction [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(1): 66-73. |
| [5] | Sui LI,Wenjie MA,Shimin WANG,Qian DING,Yao SUN,Lei ZHANG. Trueness of different digital design methods for incisal guidance of maxillary anterior implant-supported single crowns [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(1): 81-87. |
| [6] | Xiaoqiang LIU,Yin ZHOU. Risk factors of perioperative hypertension in dental implant surgeries with bone augmentation [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(1): 93-98. |
| [7] | Yu-yang YE,Lin YUE,Xiao-ying ZOU,Xiao-yan WANG. Characteristics and microRNA expression profile of exosomes derived from odontogenic dental pulp stem cells [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(4): 689-696. |
| [8] | Qian DING,Wen-jin LI,Feng-bo SUN,Jing-hua GU,Yuan-hua LIN,Lei ZHANG. Effects of surface treatment on the phase and fracture strength of yttria- and magnesia-stabilized zirconia implants [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(4): 721-728. |
| [9] | Meng-en OU,Yun DING,Wei-feng TANG,Yong-sheng ZHOU. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of cement flow in abutment margin-crown platform switching [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(3): 548-552. |
| [10] | Si-yu WU,Ya-ning LI,Xiao ZHANG,Long-wei LV,Yun-song LIU,Hong-qiang YE,Yong-sheng ZHOU. Prediction, analysis and application of learning curve of tooth preparation for all ceramic crowns of maxillary central incisors [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(1): 108-113. |
| [11] | Fei SUN,Jian LIU,Si-qi LI,Yi-ping WEI,Wen-jie HU,Cui WANG. Profiles and differences of submucosal microbial in peri-implantitis and health implants: A cross-sectional study [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(1): 30-37. |
| [12] | TIAN Jing,QIN Man,CHEN Jie,XIA Bin. Early loss of primary molar and permanent tooth germ caused by the use of devitalizer during primary molar root canal therapy: Two cases report [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(2): 381-385. |
| [13] | MA Ke-nan,CHEN Hu,SHEN Yan-ru,ZHOU Yong-sheng,WANG Yong,SUN Yu-chun. Finite element analyses of retention of removable partial denture circumferential clasps manufactured by selective laser melting [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(1): 105-112. |
| [14] | Fei SUN,Si-qi LI,Yi-ping WEI,Jin-sheng ZHONG,Cui WANG,Wen-jie HU. Efficacy of combined application of glycine powder air-polishing in non-surgical treatment of peri-implant diseases [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(1): 119-125. |
| [15] | LI Yi,YU Hua-jie,QIU Li-xin. Clinical classification and treatment decision of implant fracture [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(1): 126-133. |
|
||