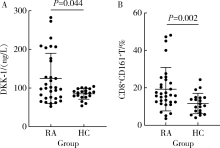
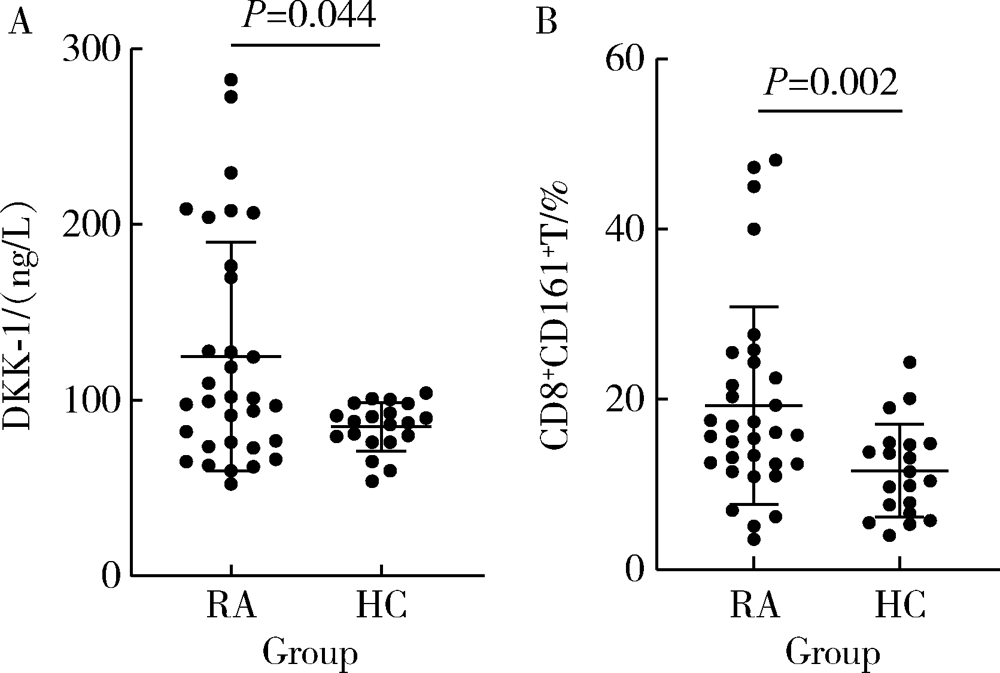
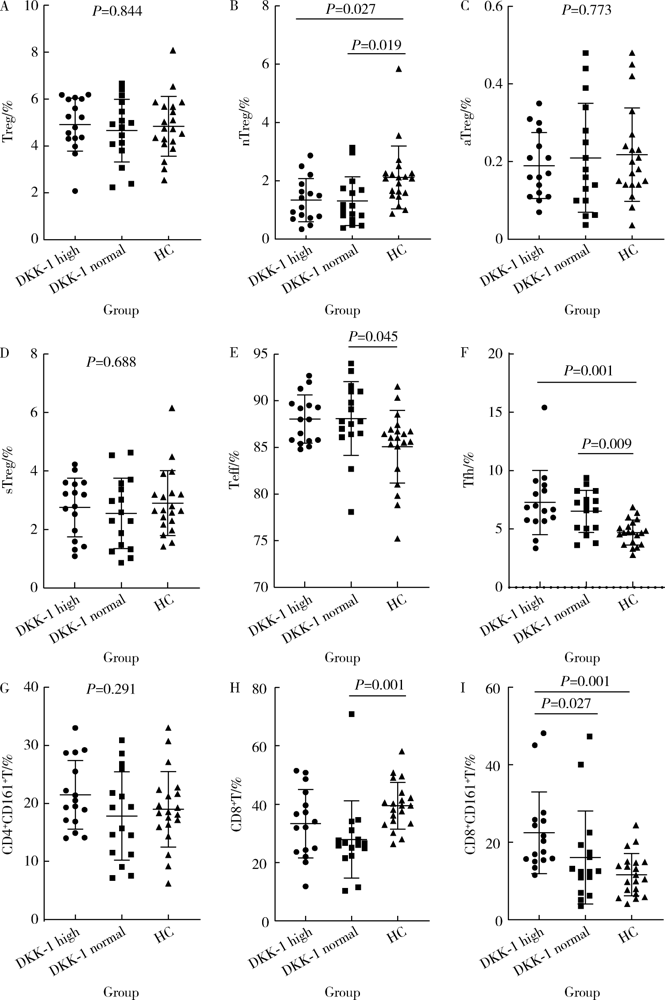
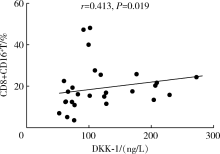
Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences) ›› 2021, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (2): 255-260. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2021.02.004
Previous Articles Next Articles
Expression of plasma Dickkopf-1 in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and its correlation with peripheral blood T cell subsets
CAO Di1,WANG Yan1,Δ( ),WANG Liu-qing1,SUN Xiao-lin2,HUANG Fei3,MENG Yang1,REN Li-li1,ZHANG Xue-wu2,Δ(
),WANG Liu-qing1,SUN Xiao-lin2,HUANG Fei3,MENG Yang1,REN Li-li1,ZHANG Xue-wu2,Δ( )
)
- 1. Department of Rheumatology and Immunology, The Fifth Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou 450000, China
2. Department of Rheumatology and Immunology, Peking University People’s Hospital, Beijing 100044, China
3. Department of Rheumatology and Immunology,Affiliated Hospital of Zunyi Medical University, Zunyi 563000, Guizhou, China
CLC Number:
- R593.2
| [1] |
Smolen JS, Aletaha D, Mcinnes IB. Rheumatoid arthritis[J]. Lancet, 2016,388(10055):2023-2038.
pmid: 27156434 |
| [2] | Lee GR. The balance of Th17 versus Treg cells in autoimmunity[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2018,19(3):730. |
| [3] |
Chae WJ, Park JH, Henegariu O, et al. Membrane-bound Dickkopf-1 in Foxp3+ regulatory T cells suppresses T-cell-mediated autoimmune colitis[J]. Immunology, 2017,152(2):265-275.
pmid: 28556921 |
| [4] |
Chae WJ, Ehrlich AK, Chan PY, et al. The Wnt antagonist Dickkopf-1 promotes pathological type 2 cell-mediated Inflammation[J]. Immunity, 2016,44(2):246-258.
pmid: 26872695 |
| [5] | Aletaha D, Neogi T, Silman AJ, et al. 2010 rheumatoid arthritis classification criteria: an American College of Rheumatology/European League Against Rheumatism collaborative initiative[J]. Ann Rheum Dis, 2010,62(9):2569-2581. |
| [6] |
Glinka A, Wu W, Delius H, et al. Dickkopf-1 is a member of a new family of secreted proteins and functions in head induction[J]. Nature, 1998,391(6665):357-362.
pmid: 9450748 |
| [7] | Fujita K, Janz S. Attenuation of WNT signaling by DKK-1 and -2 regulates BMP2-induced osteoblast differentiation and expression of OPG, RANKL and M-CSF[J]. Mol Cancer, 2007,6(1):71. |
| [8] |
Diarra D, Stolina M, Polzer K, et al. Dickkopf-1 is a master regulator of joint remodeling[J]. Nat Med, 2007,13(2):156-163.
pmid: 17237793 |
| [9] | Gómez-Vaquero C, Martín I, Loza E, et al. Effect of osteoprotegerin and Dickkopf-related protein 1 on radiological progression in tightly controlled rheumatoid arthritis[J]. PLoS One, 2016,11(12):e0166691. |
| [10] |
Rout N. Enhanced Th1/Th17 functions of CD161+CD8+T cells in mucosal tissues of rhesus macaques[J]. PLoS One, 2016,11(6):e0157407.
pmid: 27309719 |
| [11] | Mitsuo A, Morimoto S, Nakiri Y, et al. Decreased CD161+CD8+ T cells in the peripheral blood of patients suffering from rheumatic diseases[J]. Rheumatology (Oxford), 2006,45(12):1477-1484. |
| [12] |
Nicol B, Salou M, Vogel I, et al. An intermediate level of CD161 expression defines a novel activated, inflammatory, and pathogenic subset of CD8+T cells involved in multiple sclerosis[J]. J Autoimmun, 2018,88:61-74.
doi: 10.1016/j.jaut.2017.10.005 |
| [1] | Dongwu LIU, Jie CHEN, Mingli GAO, Jing YU. Rheumatoid arthritis with Castleman-like histopathology in lymph nodes: A case report [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(5): 928-931. |
| [2] | Huina HUANG,Jing ZHAO,Xiangge ZHAO,Ziran BAI,Xia LI,Guan WANG. Regulatory effect of lactate on peripheral blood CD4+ T cell subsets in patients with rheumatoid arthritis [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(3): 519-525. |
| [3] | Xiaofei TANG,Yonghong LI,Qiuling DING,Zhuo SUN,Yang ZHANG,Yumei WANG,Meiyi TIAN,Jian LIU. Incidence and risk factors of deep vein thrombosis in patients with rheumatoid arthritis [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(2): 279-283. |
| [4] | Xue ZOU,Xiao-juan BAI,Li-qing ZHANG. Effectiveness of tofacitinib combined with iguratimod in the treatment of difficult-to-treat moderate-to-severe rheumatoid arthritis [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(6): 1013-1021. |
| [5] | Qi WU,Yue-ming CAI,Juan HE,Wen-di HUANG,Qing-wen WANG. Correlation between dyslipidemia and rheumatoid arthritis associated interstitial lung disease [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(6): 982-992. |
| [6] | Jing-feng ZHANG,Yin-ji JIN,Hui WEI,Zhong-qiang YAO,Jin-xia ZHAO. Correlation analysis between body mass index and clinical characteristics of rheumatoid arthritis [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(6): 993-999. |
| [7] | Yin-ji JIN,Lin SUN,Jin-xia ZHAO,Xiang-yuan LIU. Significance of IgA isotype of anti-v-raf murine sarcoma viral oncogene homologue B1 antibody in rheumatoid arthritis [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(4): 631-635. |
| [8] | Wen-xin CAI,Shi-cheng LI,Yi-ming LIU,Ru-yu LIANG,Jing LI,Jian-ping GUO,Fan-lei HU,Xiao-lin SUN,Chun LI,Xu LIU,Hua YE,Li-zong DENG,Ru LI,Zhan-guo LI. A cross-sectional study on the clinical phenotypes of rheumatoid arthritis [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(6): 1068-1073. |
| [9] | Fang CHENG,Shao-ying YANG,Xing-xing FANG,Xuan WANG,Fu-tao ZHAO. Role of the CCL28-CCR10 pathway in monocyte migration in rheumatoid arthritis [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(6): 1074-1078. |
| [10] | Rui LIU,Jin-xia ZHAO,Liang YAN. Clinical characteristics of patients with rheumatoid arthritis complicated with venous thrombosis of lower extremities [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(6): 1079-1085. |
| [11] | Jing-feng ZHANG,Yin-ji JIN,Hui WEI,Zhong-qiang YAO,Jin-xia ZHAO. Cross-sectional study on quality of life and disease activity of rheumatoid arthritis patients [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(6): 1086-1093. |
| [12] | GAO Chao,CHEN Li-hong,WANG Li,YAO Hong,HUANG Xiao-wei,JIA Yu-bo,LIU Tian. Validation of the Pollard’s classification criteria (2010) for rheumatoid arthritis patients with fibromyalgia [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(2): 278-282. |
| [13] | ZHONG Hua,XU Li-ling,BAI Ming-xin,SU Yin. Effect of chemokines CXCL9 and CXCL10 on bone erosion in patients with rheumatoid arthritis [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2021, 53(6): 1026-1031. |
| [14] | LOU Xue,LIAO Li,LI Xing-jun,WANG Nan,LIU Shuang,CUI Ruo-mei,XU Jian. Methylation status and expression of TWEAK gene promoter region in peripheral blood of patients with rheumatoid arthritis [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2021, 53(6): 1020-1025. |
| [15] | LUO Liang,HUO Wen-gang,ZHANG Qin,LI Chun. Clinical characteristics and risk factors of rheumatoid arthritis with ulcerative keratitis [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2021, 53(6): 1032-1036. |
|
||