Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences) ›› 2022, Vol. 54 ›› Issue (6): 1214-1218. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2022.06.026
Previous Articles Next Articles
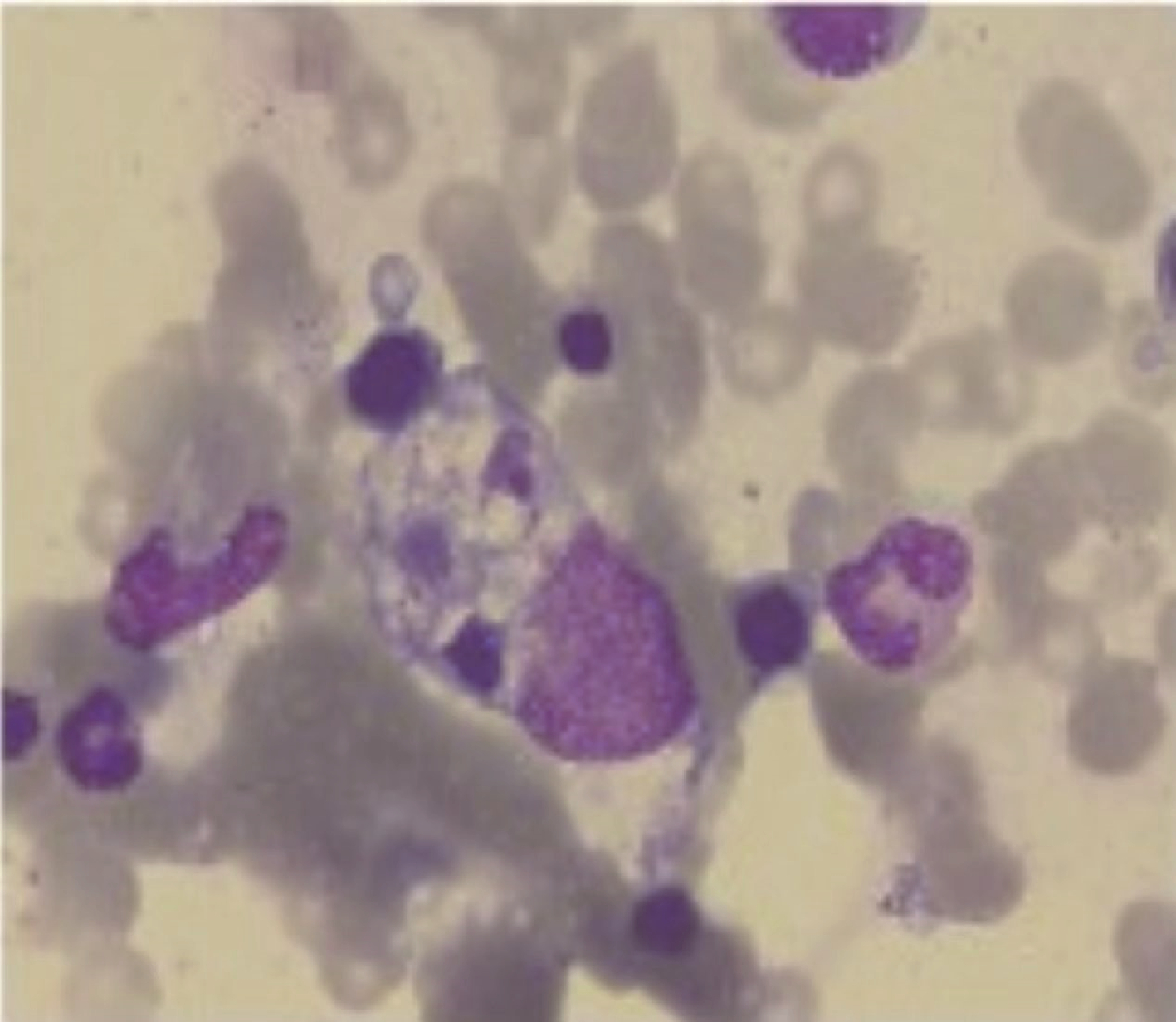
Clinical analysis of 5 cases of dermatomyositis complicated with macrophage activation syndrome
Xiao-yan XING1,Jun-xiao ZHANG2,Feng-yun-zhi ZHU1,Yi-fan WANG1,Xin-yao ZHOU3,Yu-hui LI1,*( )
)
- 1. Department of Rheumatology and Immunology, Peking University People' s Hospital, Beijing 100044, China
2. Department of Internal Medicine, Beijing Prison Administration Qinghe Branch, Tianjin 300481, China
3. Department of Rheumatology and Immunology, Guang' anmen Hospital of China Academy of Chinese Medical Sciences, Beijing 100053, China
CLC Number:
- R593.26
| 1 |
Bohan A , Peter JB . Polymyositis and dermatomyositis (first of two parts)[J]. N Engl J Med, 1975, 292 (7): 344- 347.
doi: 10.1056/NEJM197502132920706 |
| 2 |
Lundberg IE , Tjarnlund A , Bottai M , et al. 2017 European League Against Rheumatism/American College of Rheumatology classification criteria for adult and juvenile idiopathic inflammatory myopathies and their major subgroups[J]. Ann Rheum Dis, 2017, 76 (12): 1955- 1964.
doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2017-211468 |
| 3 |
Henter JI , Horne A , Arico M , et al. HLH-2004: Diagnostic and therapeutic guidelines for hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis[J]. Pediatr Blood Cancer, 2007, 48 (2): 124- 131.
doi: 10.1002/pbc.21039 |
| 4 |
Lerkvaleekul B , Vilaiyuk S . Macrophage activation syndrome: Early diagnosis is key[J]. Open Access Rheumatol, 2018, 10, 117- 128.
doi: 10.2147/OARRR.S151013 |
| 5 |
Kumakura S , Murakawa Y . Clinical characteristics and treatment outcomes of autoimmune-associated hemophagocytic syndrome in adults[J]. Arthritis Rheumatol, 2014, 66 (8): 2297- 2307.
doi: 10.1002/art.38672 |
| 6 |
Liang J , Xu D , Sun C , et al. Hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis: Prevalence, risk factors, outcome, and outcome-related factors in adult idiopathic inflammatory myopathies[J]. J Rheumatol, 2020, 47 (10): 1532- 1540.
doi: 10.3899/jrheum.190542 |
| 7 |
Minoia F , Davi S , Horne A , et al. Clinical features, treatment, and outcome of macrophage activation syndrome complicating systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis: A multinational, multicenter study of 362 patients[J]. Arthritis Rheumatol, 2014, 66 (11): 3160- 3169.
doi: 10.1002/art.38802 |
| 8 |
Tang S , Li S , Zheng S , et al. Understanding of cytokines and targeted therapy in macrophage activation syndrome[J]. Semin Arthritis Rheum, 2021, 51 (1): 198- 210.
doi: 10.1016/j.semarthrit.2020.12.007 |
| 9 |
Kostik MM , Dubko MF , Masalova VV , et al. Identification of the best cutoff points and clinical signs specific for early recognition of macrophage activation syndrome in active systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis[J]. Semin Arthritis Rheum, 2015, 44 (4): 417- 422.
doi: 10.1016/j.semarthrit.2014.09.004 |
| 10 |
Fardet L , Galicier L , Lambotte O , et al. Development and validation of the HScore, a score for the diagnosis of reactive hemophagocytic syndrome[J]. Arthritis Rheumatol, 2014, 66 (9): 2613- 2620.
doi: 10.1002/art.38690 |
| 11 |
Schulert GS . The storm beneath the storm: MAS-HLH in inflammatory myopathies[J]. J Rheumatol, 2020, 47 (10): 1461- 1463.
doi: 10.3899/jrheum.191274 |
| 12 |
Gono T , Kawaguchi Y , Ozeki E , et al. Serum ferritin correlates with activity of anti-MDA5 antibody-associated acute interstitial lung disease as a complication of dermatomyositis[J]. Mod Rheumatol, 2011, 21 (2): 223- 227.
doi: 10.3109/s10165-010-0371-x |
| 13 |
La Rosee P , Horne A , Hines M , et al. Recommendations for the management of hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis in adults[J]. Blood, 2019, 133 (23): 2465- 2477.
doi: 10.1182/blood.2018894618 |
| 14 |
Canna SW , Girard C , Malle L , et al. Life-threatening NLRC4-associated hyperinflammation successfully treated with IL-18 inhibition[J]. J Allergy Clin Immunol, 2017, 139 (5): 1698- 1701.
doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2016.10.022 |
| 15 |
Gabr JB , Liu E , Mian S , et al. Successful treatment of secondary macrophage activation syndrome with emapalumab in a patient with newly diagnosed adult-onset Still's disease: Case report and review of the literature[J]. Ann Transl Med, 2020, 8 (14): 887.
doi: 10.21037/atm-20-3127 |
| 16 |
Ahmed A , Merrill SA , Alsawah F , et al. Ruxolitinib in adult patients with secondary haemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis: An open-label, single-centre, pilot trial[J]. Lancet Haematol, 2019, 6 (12): e630- e637.
doi: 10.1016/S2352-3026(19)30156-5 |
| 17 |
Verweyen E , Holzinger D , Weinhage T , et al. Synergistic signaling of TLR and IFNalpha/beta facilitates escape of IL-18 expression from endotoxin tolerance[J]. Am J Respir Crit Care Med, 2020, 201 (5): 526- 539.
doi: 10.1164/rccm.201903-0659OC |
| 18 | Wu J, Sun L, Tang X, et al. Effective therapy of tocilizumab on systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis associated refractory macrophage activation syndrome[J]. Mod Rheumatol, 2021[2022-08-01]. https://doi.org/10.1093/mr/roab119. |
| 19 |
Fujita Y , Fukui S , Suzuki T , et al. Anti-MDA5 antibody-positive dermatomyositis complicated by autoimmune-associated hemophagocytic syndrome that was successfully treated with immunosuppressive therapy and plasmapheresis[J]. Intern Med, 2018, 57 (23): 3473- 3478.
doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.1121-18 |
| 20 |
Kaieda S , Yoshida N , Yamashita F , et al. Successful treatment of macrophage activation syndrome in a patient with dermatomyositis by combination with immunosuppressive therapy and plasmapheresis[J]. Mod Rheumatol, 2015, 25 (6): 962- 966.
doi: 10.3109/14397595.2013.844402 |
| 21 |
Komiya Y , Saito T , Mizoguchi F , et al. Hemophagocytic syndrome complicated with dermatomyositis controlled successfully with infliximab and conventional therapies[J]. Intern Med, 2017, 56 (23): 3237- 3241.
doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.7966-16 |
| 22 |
Sasaki H , Kohsaka H . Current diagnosis and treatment of polymyositis and dermatomyositis[J]. Mod Rheumatol, 2018, 28 (6): 913- 921.
doi: 10.1080/14397595.2018.1467257 |
| 23 |
Gavand PE , Serio I , Arnaud L , et al. Clinical spectrum and therapeutic management of systemic lupus erythematosus-associated macrophage activation syndrome: A study of 103 episodes in 89 adult patients[J]. Autoimmun Rev, 2017, 16 (7): 743- 749.
doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2017.05.010 |
| [1] | Junyong OU,Kunming NI,Lulin MA,Guoliang WANG,Ye YAN,Bin YANG,Gengwu LI,Haodong SONG,Min LU,Jianfei YE,Shudong ZHANG. Prognostic factors of patients with muscle invasive bladder cancer with intermediate-to-high risk prostate cancer [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(4): 582-588. |
| [2] | Shuai LIU,Lei LIU,Zhuo LIU,Fan ZHANG,Lulin MA,Xiaojun TIAN,Xiaofei HOU,Guoliang WANG,Lei ZHAO,Shudong ZHANG. Clinical treatment and prognosis of adrenocortical carcinoma with venous tumor thrombus [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(4): 624-630. |
| [3] | Le YU,Shaohui DENG,Fan ZHANG,Ye YAN,Jianfei YE,Shudong ZHANG. Clinicopathological characteristics and prognosis of multilocular cystic renal neoplasm of low malignant potential [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(4): 661-666. |
| [4] | Zezhen ZHOU,Shaohui DENG,Ye YAN,Fan ZHANG,Yichang HAO,Liyuan GE,Hongxian ZHANG,Guoliang WANG,Shudong ZHANG. Predicting the 3-year tumor-specific survival in patients with T3a non-metastatic renal cell carcinoma [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(4): 673-679. |
| [5] | Yangyi FANG,Qiang LI,Zhigao HUANG,Min LU,Kai HONG,Shudong ZHANG. Well-differentiated papillary mesothelial tumour of the tunica vaginalis: A case report [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(4): 741-744. |
| [6] | Yuanyuan ZENG,Yun XIE,Daonan CHEN,Ruilan WANG. Related factors of euthyroid sick syndrome in patients with sepsis [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(3): 526-532. |
| [7] | Jian-bin LI,Meng-na LYU,Qiang CHI,Yi-lin PENG,Peng-cheng LIU,Rui WU. Early prediction of severe COVID-19 in patients with Sjögren’s syndrome [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(6): 1007-1012. |
| [8] | Zhi-jun LUO,Jia-jia WU,You SONG,Chun-li MEI,Rong DU. Systemic lupus erythematosus associated macrophage activation syndrome with neuropsychiatric symptoms: A report of 2 cases [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(6): 1111-1117. |
| [9] | Li-fang WANG,Lian-jie SHI,Wu NING,Nai-shu GAO,Kuan-ting WANG. Sjögren's syndrome combined with cold agglutinin disease: A case report [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(6): 1130-1134. |
| [10] | Hai-hong YAO,Fan YANG,Su-mei TANG,Xia ZHANG,Jing HE,Yuan JIA. Clinical characteristics and diagnostic indicators of macrophage activation syndrome in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus and adult-onset Still's disease [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(6): 966-974. |
| [11] | Huan-rui LIU,Xiang PENG,Sen-lin LI,Xin GOU. Risk modeling based on HER-2 related genes for bladder cancer survival prognosis assessment [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(5): 793-801. |
| [12] | Zi-xuan XUE,Shi-ying TANG,Min QIU,Cheng LIU,Xiao-jun TIAN,Min LU,Jing-han DONG,Lu-lin MA,Shu-dong ZHANG. Clinicopathologic features and prognosis of young renal tumors with tumor thrombus [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(5): 802-811. |
| [13] | Han LU,Jian-yun ZHANG,Rong YANG,Le XU,Qing-xiang LI,Yu-xing GUO,Chuan-bin GUO. Clinical factors affecting the prognosis of lower gingival squamous cell carcinoma [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(4): 702-707. |
| [14] | Jie QIAO,Li-xia LU,Yu-ting HE,Chun-cui MEN,Xin-xin CHU,Bei WU,Hui-ping ZHAO,Mei WANG. Fungal peritoneal dialysis catheter-related exit-site infection combined with tunnel infection: A case report [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(4): 748-754. |
| [15] | Hao LIN,Jing-hua LI,Xiao YANG,Xiao-ting CHEN,Yu-hui SHI,Chun CHANG,Yuan-tao HAO,Wang-nan CAO. Discrepancy between behavioral-indicated and perceived candidacy for HIV pre-exposure prophylaxis among men who have sex with men in Chengdu, China [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(3): 511-520. |
|
||