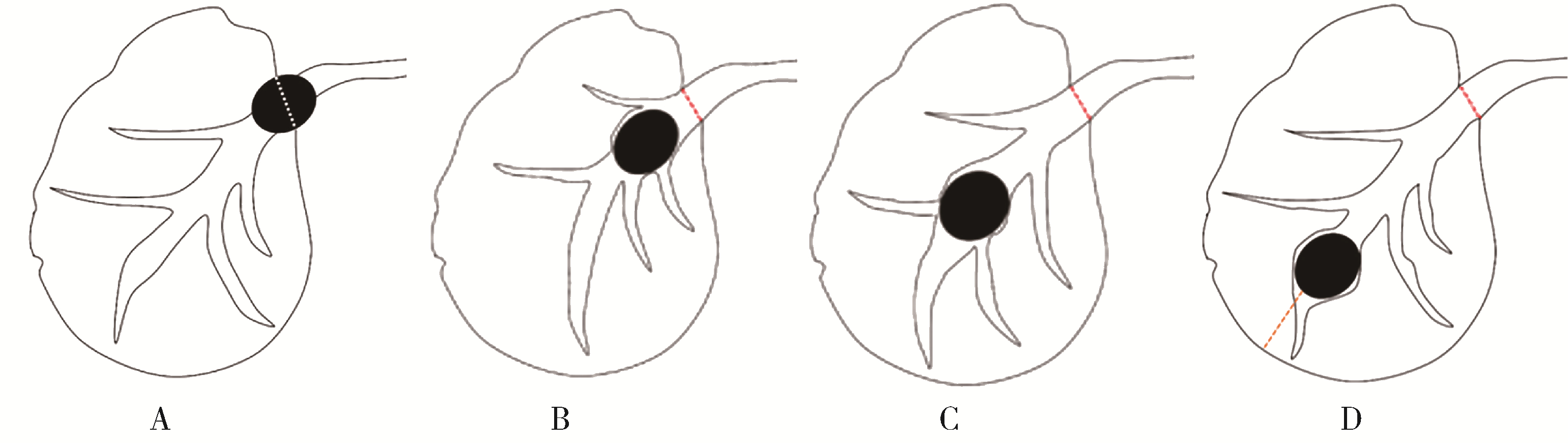
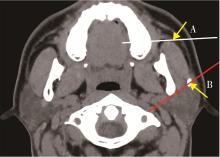
Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences) ›› 2023, Vol. 55 ›› Issue (1): 8-12. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2023.01.002
Previous Articles Next Articles
Recent progress in the treatment of intractable sialolithiasis
Deng-gao LIU*( ),Dan-ni ZHENG,Ya-ning ZHAO,Ya-qiong ZHANG,Xin YE,Li-qi ZHANG,Xiao-yan XIE,Lei ZHANG,Zu-yan ZHANG,Guang-yan YU
),Dan-ni ZHENG,Ya-ning ZHAO,Ya-qiong ZHANG,Xin YE,Li-qi ZHANG,Xiao-yan XIE,Lei ZHANG,Zu-yan ZHANG,Guang-yan YU
- Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology, Peking University School and Hospital of Stomatology & National Center of Stomatology & National Clinical Research Center for Oral Diseases & National Engineering Research Center of Oral Biomaterials and Digital Medical Devices & Beijing Key Laboratory of Digital Stomatology & NHC Research Center of Engineering and Technology for Computerized Dentistry & NMPA Key Laboratory for Dental Materials, Beijing 100081, China
CLC Number:
- R781.75
| 1 |
姜岚, 张晔, 柳登高, 等. 涎腺内镜辅助颌下腺腺门结石取出术疗效分析[J]. 中华口腔医学杂志, 2012, 43 (3): 157- 159.
doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1002-0098.2012.03.007 |
| 2 |
叶欣, 谢晓艳, 柳登高, 等. 内镜辅助腮腺结石取出术67例疗效分析[J]. 中华口腔医学杂志, 2014, 49 (11): 645- 648.
doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1002-0098.2014.11.002 |
| 3 | Zhang YQ , Ye X , Meng Y , et al. Evaluation of parotid gland function before and after endoscopy-assisted stone removal[J]. J Oral Maxillofac Surg, 2019, 77 (2): 327.e2- 328.e9. |
| 4 |
Liu DG , Jiang L , Xie XY , et al. Sialoendoscopy-assisted sialolithectomy for submandibular hilar calculi[J]. J Oral Maxillofac Surg, 2013, 71 (2): 295- 301.
doi: 10.1016/j.joms.2012.02.016 |
| 5 |
赵雅宁, 张亚琼, 叶欣, 等. 内镜辅助下颌下腺腺门和腺内结石不同取石方法的探讨[J]. 中华口腔医学杂志, 2018, 53 (12): 826- 831.
doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1002-0098.2018.12.007 |
| 6 |
McGurk M , MacBean AD , Fan KFM , et al. Endoscopically assisted operative retrieval of parotid stones[J]. Br J Oral and Maxillofac Surg, 2006, 44 (2): 157- 160.
doi: 10.1016/j.bjoms.2005.03.026 |
| 7 |
Zhao YN , Zhang YQ , Zhang LQ , et al. Treatment strategy of hilar and intraglandular stones in Wharton's duct: 12-year experience[J]. Laryngoscope, 2020, 130 (10): 2360- 2365.
doi: 10.1002/lary.28361 |
| 8 |
Ye X , Zhang YQ , Xie XY , et al. Transoral and transcutaneous approach for removal of parotid gland calculi: A 10-year endosco-pic experience[J]. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pahtol Oral Radiol, 2017, 124 (2): 121- 127.
doi: 10.1016/j.oooo.2017.04.005 |
| 9 | Zhao Y, Zheng D, Zhang L, et al. Recovery of gland function after endoscopy-assisted removal of impacted hilo-parenchymal stones in the Wharton's duct[J/OL]. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg, (2022-10-07)[2022-11-05]. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijom.2022.09.035. |
| 10 |
Schapher M , Mantsopoulos K , Messbacher ME , et al. Transoral submandibulotomy for deep hilar submandibular gland sialolithiasis[J]. Laryngoscope, 2017, 127 (9): 2038- 2044.
doi: 10.1002/lary.26459 |
| 11 |
Capaccio P , Gaffuri M , Rossi V , et al. Sialendoscope-assisted transoral removal of hilo-parenchymal sub-mandibular stones: Surgical results and subjective scores[J]. Acta Otorhinolaryngol Ital, 2017, 37 (2): 122- 127.
doi: 10.14639/0392-100X-1601 |
| 12 |
Xu H , Mao C , Liu J M , et al. Microanatomic study of the vascular and duct system of the submandibular gland[J]. Oral Maxillofac Surg, 2011, 69 (4): 1103- 1107.
doi: 10.1016/j.joms.2010.03.006 |
| 13 |
Xiao JQ , Sun HJ , Qiao QH , et al. Advantages of submandibular gland preservation surgery over submandibular gland resection for proximal submandibular stones[J]. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol, 2018, 125 (5): e113- e117.
doi: 10.1016/j.oooo.2017.12.009 |
| 14 |
Xie L , Pu Y , Yu C , et al. Transfacial lithotomy approach to intraparenchymal stones in the submandibular gland: Our primary exploration[J]. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg, 2022, 60 (2): 201- 203.
doi: 10.1016/j.bjoms.2021.03.008 |
| 15 | Zheng DN, Zhao YN, Zhang LQ, et al. Comparison of two transcutaneous approaches for the removal of impacted parotid stones[J/OL]. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg, (2022-10-19)[2022-11-05]. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijom.2022.10.007. |
| 16 | 叶欣, 张亚琼, 赵雅宁, 等. 内镜辅助腮腺结石口内途径取出术的适应证与疗效分析[J]. 中华口腔医学杂志, 2019, 54 (1): 17- 22. |
| 17 |
Koch M , Schapher M , Mantsopoulos K , et al. Intraductal lithotripsy in sialolithiasis using the calculase Ⅲ Ho ∶YAG laser: First experiences[J]. Lasers Surg Med, 2021, 53 (4): 488- 498.
doi: 10.1002/lsm.23325 |
| 18 |
Hills AJ , Holden AM , McGurk M . Sialendoscopy-assisted transfacial removal of parotid calculi[J]. Acta Otorhinolaryngol Ital, 2017, 37 (2): 128- 131.
doi: 10.14639/0392-100X-1602 |
| 19 |
Thomas G , Stephan H , Niels H , et al. Sialendoscopy plus laser lithotripsy in sialolithiasis of the submandibular gland in 64 patients: A simple and safe procedure[J]. Auris Nasus Larynx, 2019, 46 (5): 797- 802.
doi: 10.1016/j.anl.2019.01.009 |
| 20 |
Jason S , Lee MJ , Ben HC , et al. Optimal power settings for Holmium ∶YAG lithotripsy[J]. J Urol, 2012, 187 (3): 914- 919.
doi: 10.1016/j.juro.2011.10.147 |
| 21 |
Sionis S , Caria RA , Trucas M , et al. Sialoendoscopy with and without holmium ∶YAG laser-assisted lithotripsy in the management of obstructive sialadenitis of major salivary glands[J]. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg, 2014, 52 (1): 58- 62.
doi: 10.1016/j.bjoms.2013.06.015 |
| 22 |
Catra F , Farneti P , Cantore S , et al. Sialendoscopy for salivary stones: Principles, technical skills and therapeutic experiences[J]. Acta Otorhinolaryngol Ital, 2017, 37 (2): 102- 112.
doi: 10.14639/0392-100X-1599 |
| 23 | Koch M , Hung SH , Iro H , et al. Intraductal lithotripsy in sialolithiasis with two different Ho ∶YAG lasers: Presetting parameters, effectiveness, success rates[J]. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci, 2019, 23 (13): 5548- 5557. |
| [1] | Guang-yan YU,Jia-zeng SU,Deng-gao LIU,Li-ling WU,Xin CONG. Establishment and application of new techniques for submandibular gland preservation [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(5): 842-845. |
| [2] | CHEN Chao-lun,SU Jia-zeng,YU Guang-yan. Effects of acid stimulation on saliva flow rate and compositions of human parotid and submandibular glands [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(1): 89-94. |
| [3] | YU Guang-yan,LIU Deng-gao,LI Wei,HONG Xia,ZHANG Yan-yan,ZHU Wen-xuan,ZHANG Ke-fu,LI Xiao,LI Zhan-guo,LIU Yan-ying,CHEN Yan,GAO Yan,SU Jia-zeng. Studies on newly recognized chronic sialadenitis [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(1): 13-17. |
| [4] | ZHU Yi-ying,MIN Sai-nan,YU Guang-yan. Effect of topical injection of cyclosporine A on saliva secretion and inflammation in the submandibular gland of non-obese diabetic mice [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2021, 53(4): 750-757. |
| [5] | DAI Xiang,ZUO Mei-ni,ZHANG Xiao-peng,HU Hao,XU Tao. Comparison of long-term outcomes in different managements of diverticular neck in percutaneous nephrolithotomy for diverticular calculi [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2021, 53(4): 704-709. |
| [6] | WANG Yi-ping,CAI Zhi-gang,PENG Xin,ZHANG Jie,SUN Zhi-peng,LI Wei,ZHANG Lei,YU Guang-yan. Measurement of the weight and volume of submandibular gland in vitro [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2021, 53(1): 126-132. |
| [7] | Ming-rui WANG,Qi WANG,Hao HU,Jin-hui LAI,Yong-xin HE,Jie XIONG,Xian-hui LIU,Shi-jun LIU,Ke-xin XU,Tao XU. Long-term analysis of safety and efficacy of standard percutaneous nephrolithotomy in patients with solitary kidneys [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2020, 52(4): 663-666. |
| [8] | Xin CONG,Sai-nan MIN,Li-ling WU,Zhi-gang CAI,Guang-yan YU. Role and mechanism of muscarinic acetylcholine receptor in the regulation of submandibular gland secretion [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2019, 51(3): 390-396. |
| [9] | Qian SU,Xin PENG,Chuan-xiang ZHOU,Guang-yan YU. Clinicopathological features and possible prognostic factors in parotid lymphomas [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2019, 51(1): 35-42. |
| [10] | Guang-ya YU,Xia HONG,Wei LI,Yan-yan ZHANG,Yan GAO,Yan CHEN,Zu-yan ZHANG,Xiao-yan XIE,Zhan-guo LI,Yan-ying LIU,Jia-zeng SU,Wen-xuan ZHU,Zhi-peng SUN. Clinicopathological characteristics and diagnosis of IgG4-related sialadenitis [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2019, 51(1): 1-3. |
| [11] | ZHANG Ya-qiong, YE Xin, LIU Deng-gao, ZHAO Ya-ning, XIE Xiao-yan, YU Guang-yan. Endoscopy-assisted sialodochoplasty for the treatment of severe sialoduct stenosis [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2018, 50(1): 160-164. |
| [12] | YU Guang-yan, WU Li-ling, CAI Zhi-gang, LV Lan, CONG Xin. A 20-year study on microvascular autologous transplantation of submandibular gland for treatment of severe dry eye [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2018, 50(1): 1-4. |
| [13] | SHEN Cheng, ZHANG Bo, HAN Wen-ke, LIN Jian, WANG Gang, ZHANG Xiao-chun, SONG Yi, ZHAO Zheng, ZHANG Zhong-yuan, JIN Jie, YU Wei. Percutaneous renal access for percutaneous nephrolithotomy guided by contrast enhanced ultrasound: a single-center preliminary experience in China [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2017, 49(6): 1071-1075. |
| [14] | YU Lu-ping, XU Tao. Analysis of development, safety and efficacy of percutaneous nephrolithotomy for management of upper urinary tract calculi in pediatric patients [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2017, 49(4): 626-631. |
| [15] | CONG Xin, ZHANG Yan, YU Guang-Yan, WU Li-Ling. Activation of transient receptor potential vanilloid subtype 1 serves as a novel pathway to modulate secretion in submandibular gland [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2015, 47(1): 8-12. |
|
||