Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences) ›› 2023, Vol. 55 ›› Issue (5): 812-817. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2023.05.006
Previous Articles Next Articles
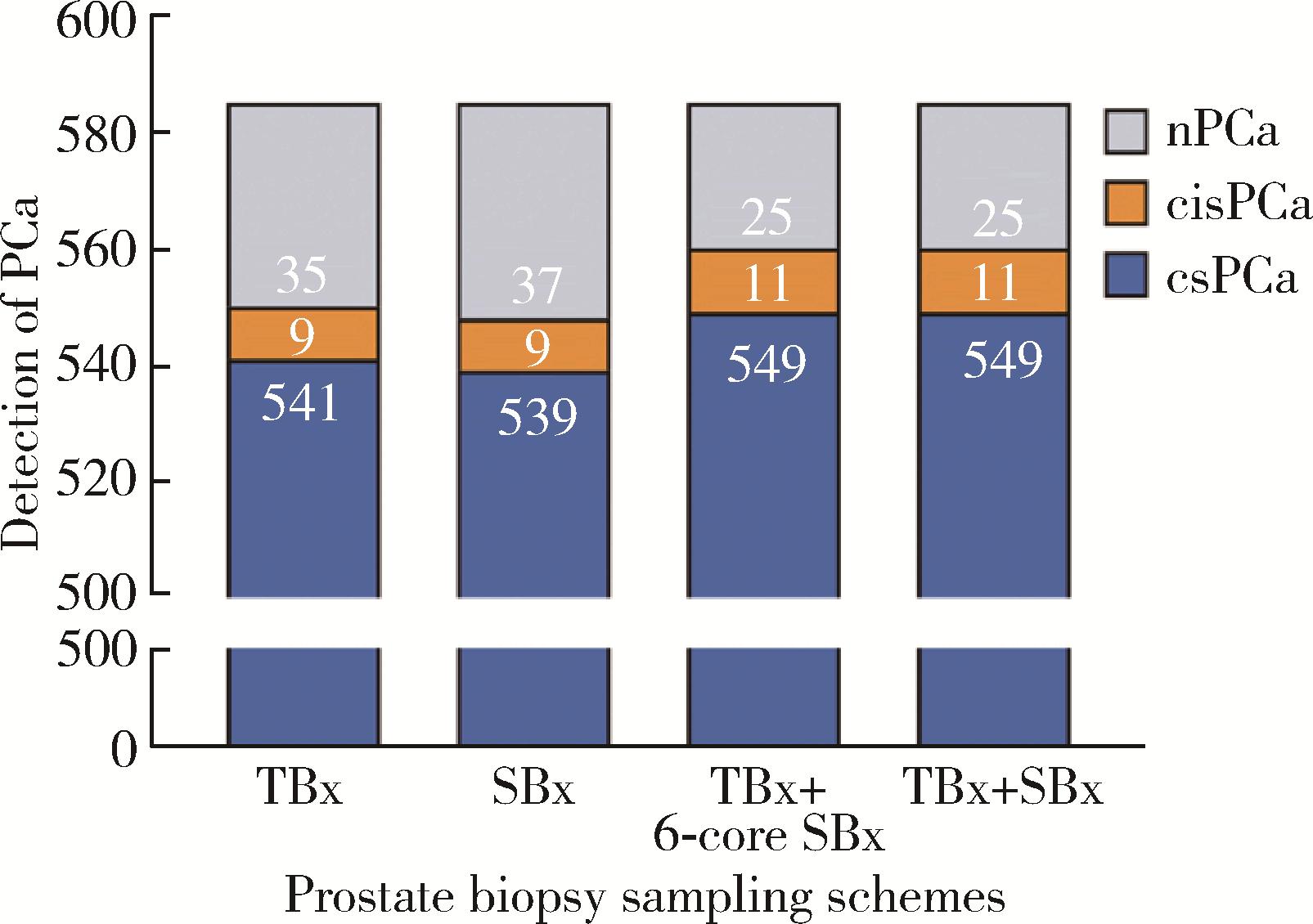
Diagnostic efficacy of prostate cancer using targeted biopsy with 6-core systematic biopsy for patients with PI-RADS 5
Yi LIU1,Chang-wei YUAN1,Jing-yun WU2,Qi SHEN1,Jiang-xi XIAO2,*( ),Zheng ZHAO1,*(
),Zheng ZHAO1,*( ),Xiao-ying WANG2,Xue-song LI1,Zhi-song HE1,Li-qun ZHOU1
),Xiao-ying WANG2,Xue-song LI1,Zhi-song HE1,Li-qun ZHOU1
- 1. Department of Urology, Peking University First Hospital; Institute of Urology, Peking University; National Urological Cancer Center, Beijing 100034, China
2. Department of Radiology, Peking University First Hospital, Beijing 100034, China
CLC Number:
- R737.25
| 1 |
Culp MB , Soerjomataram I , Efstathiou JA , et al. Recent global patterns in prostate cancer incidence and mortality rates[J]. Eur Urol, 2020, 77 (1): 38- 52.
doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2019.08.005 |
| 2 |
Shen WW , Cui LG , Ran WQ , et al. Targeted biopsy with reduced number of cores: Optimal sampling scheme in patients undergoing magnetic resonance imaging/transrectal ultrasound fusion prostate biopsy[J]. Ultrasound Med Biol, 2020, 46 (5): 1197- 1207.
doi: 10.1016/j.ultrasmedbio.2020.01.017 |
| 3 |
Raman AG , Sarma KV , Raman SS , et al. Optimizing spatial biopsy sampling for the detection of prostate cancer[J]. J Urol, 2021, 206 (3): 595- 603.
doi: 10.1097/JU.0000000000001832 |
| 4 |
Barkovich EJ , Shankar PR , Westphalen AC . A systematic review of the existing prostate imaging reporting and data system version 2 (PI-RADS v2) literature and subset meta-analysis of PI-RADSv2 categories stratified by Gleason scores[J]. AJR Am J Roentge-nol, 2019, 212 (4): 847- 854.
doi: 10.2214/AJR.18.20571 |
| 5 |
Stabile A , Giganti F , Kasivisvanathan V , et al. Factors influencing variability in the performance of multiparametric magnetic resonance imaging in detecting clinically significant prostate can-cer: A systematic literature review[J]. Eur Urol Oncol, 2020, 3 (2): 145- 167.
doi: 10.1016/j.euo.2020.02.005 |
| 6 |
Hansen NL , Barrett T , Lloyd T , et al. Optimising the number of cores for magnetic resonance imaging-guided targeted and systema-tic transperineal prostate biopsy[J]. BJU Int, 2020, 125 (2): 260- 269.
doi: 10.1111/bju.14865 |
| 7 | 涂祥, 熊性宇, 张驰宸, 等. 6针系统穿刺联合3针磁共振引导靶向穿刺对前列腺癌的检出效果[J]. 中华泌尿外科杂志, 2022, 43 (12): 914- 919. |
| 8 |
Aminsharifi A , Gupta RT , Tsivian E , et al. Reduced core targeted (RCT) biopsy: Combining multiparametric magnetic resonance imaging-transrectal ultrasound fusion targeted biopsy with laterally-directed sextant biopsies: An alternative template for prostate fusion biopsy[J]. Eur J Radiol, 2019, 110, 7- 13.
doi: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2018.11.006 |
| 9 |
Teraoka S , Honda M , Shimizu R , et al. Optimal number of systematic biopsy cores used in magnetic resonance imaging/transrectal ultrasound fusion targeted prostate biopsy[J]. Yonago Acta Med, 2021, 64 (3): 260- 268.
doi: 10.33160/yam.2021.08.004 |
| 10 |
Sigle A , Suarez-Ibarrola R , Benndorf M , et al. Individualized decision making in transperineal prostate biopsy: Should all men undergo an additional systematic biopsy?[J]. Cancers (Basel), 2022, 14 (21): 5230.
doi: 10.3390/cancers14215230 |
| [1] | Zhicun LI, Tianyu WU, Lei LIANG, Yu FAN, Yisen MENG, Qian ZHANG. Risk factors analysis and nomogram model construction of postoperative pathological upgrade of prostate cancer patients with single core positive biopsy [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(5): 896-901. |
| [2] | Yuxuan TIAN,Mingjian RUAN,Yi LIU,Derun LI,Jingyun WU,Qi SHEN,Yu FAN,Jie JIN. Predictive effect of the dual-parametric MRI modified maximum diameter of the lesions with PI-RADS 4 and 5 on the clinically significant prostate cancer [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(4): 567-574. |
| [3] | Kaifeng YAO,Mingjian RUAN,Derun LI,Yuxuan TIAN,Yuke CHEN,Yu FAN,Yi LIU. Diagnostic efficacy of targeted biopsy combined with regional systematic biopsy in prostate cancer in patients with PI-RADS 4-5 [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(4): 575-581. |
| [4] | Junyong OU,Kunming NI,Lulin MA,Guoliang WANG,Ye YAN,Bin YANG,Gengwu LI,Haodong SONG,Min LU,Jianfei YE,Shudong ZHANG. Prognostic factors of patients with muscle invasive bladder cancer with intermediate-to-high risk prostate cancer [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(4): 582-588. |
| [5] | Chang-wei YUAN,De-run LI,Zhi-hua LI,Yi LIU,Gang-zhi SHAN,Xue-song LI,Li-qun ZHOU. Application of dynamic contrast enhanced status in multiparametric magnetic resonance imaging for prostatic cancer with PI-RADS 4 lesion [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(5): 838-842. |
| [6] | Ying LIU,Ran HUO,Hui-min XU,Zheng WANG,Tao WANG,Hui-shu YUAN. Correlations between plaque characteristics and cerebral blood flow in patients with moderate to severe carotid stenosis using magnetic resonance vessel wall imaging [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(4): 646-651. |
| [7] | Qiang FU,Guan-ying GAO,Yan XU,Zhuo-hua LIN,You-jing SUN,Li-gang CUI. Comparative study of ultrasound and magnetic resonance imaging in the diagnosis of asymptomatic anterosuperior acetabular labrum tears [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(4): 665-669. |
| [8] | Yan XIONG,Xin LI,Li LIANG,Dong LI,Li-min YAN,Xue-ying LI,Ji-ting DI,Ting LI. Evaluation of accuracy of pathological diagnosis based on thyroid core needle biopsy [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(2): 234-242. |
| [9] | Dan-feng ZHENG,Jun-yu LI,Jia-xi LI,Ying-shuang ZHANG,Yan-feng ZHONG,Miao YU. Pathologic features of paraspinal muscle biopsies in patients with adolescent idiopathic scoliosis [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(2): 283-291. |
| [10] | Shan YE,Ping-ping JIN,Nan ZHANG,Hai-bo WU,Lin SHI,Qiang ZHAO,Kun YANG,Hui-shu YUAN,Dong-sheng FAN. Cortical thickness and cognitive impairment in patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(6): 1158-1162. |
| [11] | Ying CAI,Qiao-qin WAN,Xian-jie CAI,Ya-juan GAO,Hong-bin HAN. Epidural photobiomodulation accelerates the drainage of brain interstitial fluid and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(5): 1000-1005. |
| [12] | WANG Shu-lei,GAO Yang-xu,ZHANG Hong-wu,YANG Hai-bo,LI Hui,LI Yu,SHEN Li-xue,YAO Hong-xin. Clinical analysis of 30 cases of basal ganglia germinoma in children [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(2): 222-226. |
| [13] | ZHANG Fan,CHEN Qu,HAO Yi-chang,YAN Ye,LIU Cheng,HUANG Yi,MA Lu-lin. Relationship between recovery of urinary continence after laparoscopic radical prostatectomy and preoperative/postoperative membranous urethral length [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(2): 299-303. |
| [14] | Yi-fan WU,Xiao-yuan ZHANG,Shuang REN,Ying-xiang YU,Cui-qing CHANG. Measurement and evaluation of the quadriceps muscle mass in young men based on magnetic resonance imaging [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2021, 53(5): 843-849. |
| [15] | ZHOU Guang-ping,ZHOU Qian-yun,ZHU Ji-hong. A case report of TAFRO syndrome [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2021, 53(4): 814-817. |
|
||