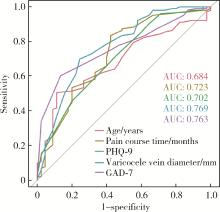
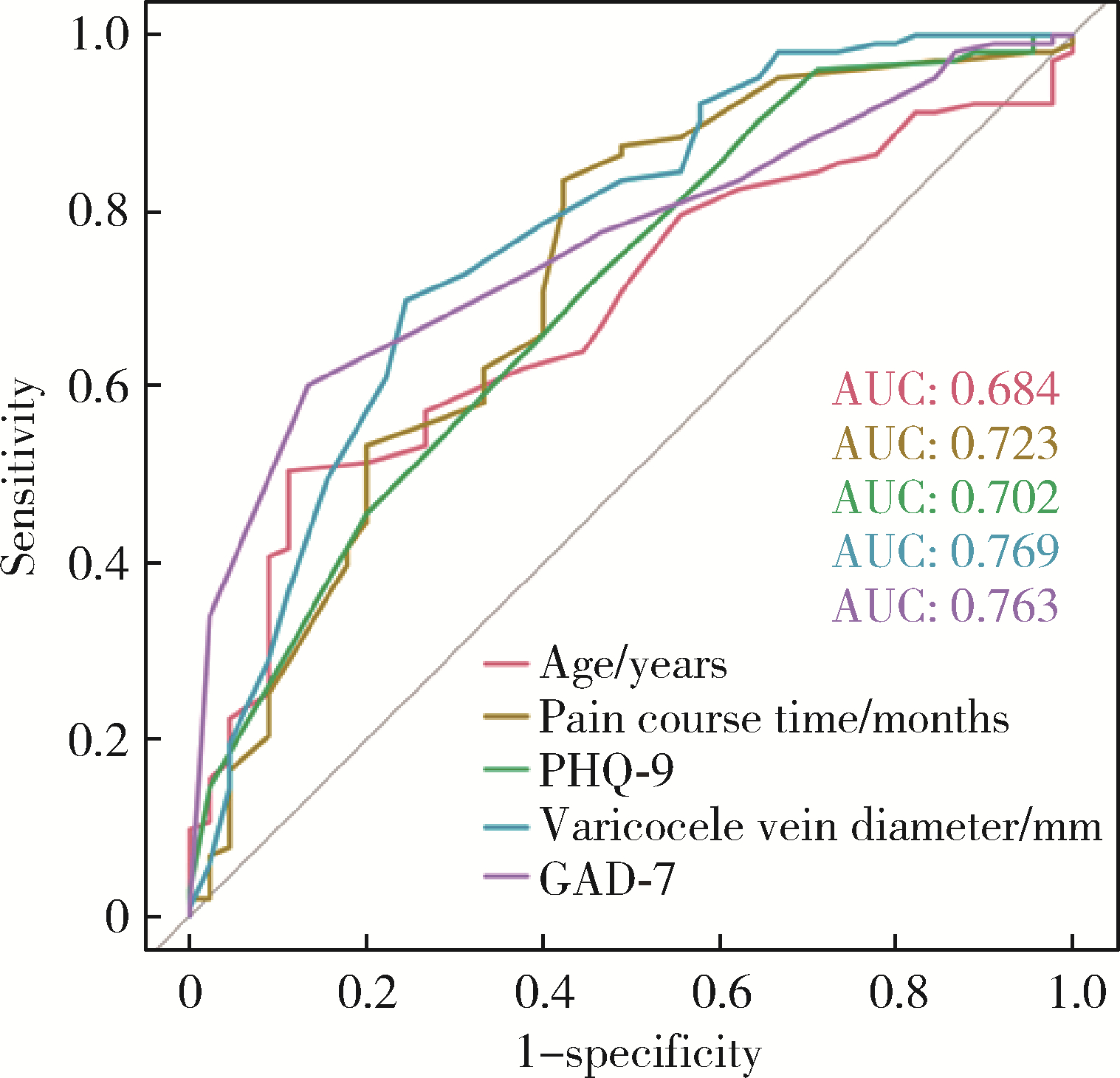
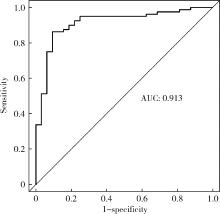
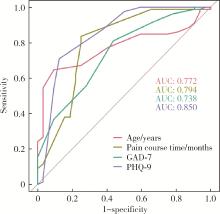
Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences) ›› 2024, Vol. 56 ›› Issue (4): 646-655. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2024.04.017
Previous Articles Next Articles
Construction of a predictive model for postoperative pain relief after microscopic spermatic cord surgery for spermatic cord pain
Hailong HE,Qing LI,Tao XU,Xiaowei ZHANG*( )
)
- Department of Urology, Peking University People' s Hospital; The Institute of Applied Lithotripsy Technology, Peking University, Beijing 100044, China
CLC Number:
- R697.24
| 1 |
Basal S , Ergin A , Yildirim I , et al. A novel treatment of chronic orchialgia[J]. J Androl, 2012, 33 (1): 22- 26.
doi: 10.2164/jandrol.110.010991 |
| 2 |
Calixte N , Brahmbhatt J , Parekattil S . Genital pain: Algorithm for management[J]. Transl Androl Urol, 2017, 6 (2): 252- 257.
doi: 10.21037/tau.2017.03.03 |
| 3 | Ziegelmann MJ , Farrell MR , Levine LA . Evaluation and management of chronic scrotal content pain: A common yet poorly understood condition[J]. Rev Urol, 2019, 21 (2/3): 74- 84. |
| 4 |
Rottenstreich M , Glick Y , Gofrit ON . Chronic scrotal pain in young adults[J]. BMC Res Notes, 2017, 10 (1): 241.
doi: 10.1186/s13104-017-2590-0 |
| 5 |
Wu C , Jarvi K . Chronic scrotal pain[J]. Curr Urol Rep, 2018, 19 (8): 59.
doi: 10.1007/s11934-018-0811-2 |
| 6 |
Shridharani A , Lockwood G , Sandlow J . Varicocelectomy in the treatment of testicular pain: A review[J]. Curr Opin Urol, 2012, 22 (6): 499- 506.
doi: 10.1097/MOU.0b013e328358f69f |
| 7 |
Lomboy JR , Coward RM . The varicocele: Clinical presentation, evaluation, and surgical management[J]. Semin Intervent Radiol, 2016, 33 (3): 163- 169.
doi: 10.1055/s-0036-1586143 |
| 8 |
Baigorri BF , Dixon RG . Varicocele: A review[J]. Semin Intervent Radiol, 2016, 33 (3): 170- 176.
doi: 10.1055/s-0036-1586147 |
| 9 |
Dewitt-Foy ME , Nickel JC , Shoskes DA . Management of chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome[J]. Eur Urol Focus, 2019, 5 (1): 2- 4.
doi: 10.1016/j.euf.2018.08.027 |
| 10 |
Zorn BH , Watson LR , Steers WD . Nerves from pelvic plexus contribute to chronic orchidalgia[J]. Lancet, 1994, 343 (8906): 1161.
doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(94)90266-6 |
| 11 | Patel AP . Anatomy and physiology of chronic scrotal pain[J]. Transl Androl Urol, 2017, 6 (Suppl 1): S51- S56. |
| 12 | Yi S , Tang X , Yu J , et al. Microarray and qPCR analyses of Wallerian degeneration in rat sciatic nerves[J]. Front Cell Neurosci, 2017, 11, 22. |
| 13 | Hunter CW , Stovall B , Chen G , et al. Anatomy, pathophysiology and interventional therapies for chronic pelvic pain: A review[J]. Pain Physician, 2018, 21 (2): 147- 167. |
| 14 |
Parekattil SJ , Gudeloglu A , Brahmbhatt JV , et al. Trifecta nerve complex: potential anatomical basis for microsurgical denervation of the spermatic cord for chronic orchialgia[J]. J Urol, 2013, 190 (1): 265- 270.
doi: 10.1016/j.juro.2013.01.045 |
| 15 | Zhuang J , Zhou M , Liao W , et al. Microvascular Doppler assisted microsurgical denervation of the spermatic cord in treating chronic orchialgia[J]. J Vis Exp, 2022, 25, 183. |
| 16 |
Sun HH , Tay KS , Jesse E , et al. Microsurgical denervation of the spermatic cord: A historical perspective and recent developments[J]. Sex Med Rev, 2022, 10 (4): 791- 799.
doi: 10.1016/j.sxmr.2021.11.005 |
| 17 |
Calixte N , Kartal IG , Tojuola B , et al. Salvage ultrasound-guided targeted cryoablation of the perispermatic cord for persistent chro-nic scrotal content pain after microsurgical denervation of the spermatic cord[J]. Urology, 2019, 130, 181- 185.
doi: 10.1016/j.urology.2019.04.027 |
| 18 |
Ho KY , Gwee KA , Cheng YK , et al. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in chronic pain: Implications of new data for clinical practice[J]. J Pain Res, 2018, 11, 1937- 1948.
doi: 10.2147/JPR.S168188 |
| 19 |
Long H , Bai W , Zhang X , et al. A clinical study on microsurgical denervation of spermatic cord for refractory chronic orchialgia[J]. Urol Int, 2019, 103 (1): 62- 67.
doi: 10.1159/000497281 |
| 20 |
Chaudhari R , Sharma S , Khant S , et al. Microsurgical denervation of spermatic cord for chronic idiopathic orchialgia: Long-term results from an institutional experience[J]. World J Mens Health, 2019, 37 (1): 78- 84.
doi: 10.5534/wjmh.180035 |
| 21 |
Choi Y , Mayer TG , Williams MJ , et al. What is the best scree-ning test for depression in chronic spinal pain patients?[J]. Spine J, 2014, 14 (7): 1175- 1182.
doi: 10.1016/j.spinee.2013.10.037 |
| 22 |
Kroenke K , Spitzer RL , Williams JB , et al. The patient health questionnaire somatic, anxiety, and depressive symptom scales: A systematic review[J]. Gen Hosp Psychiatry, 2010, 32 (4): 345- 359.
doi: 10.1016/j.genhosppsych.2010.03.006 |
| 23 |
Cavalheiro LM , Gil JA , Goncalves RS , et al. Measuring the pain impact in adults with a chronic pain condition: Adaptation and validation of the pain impact questionnaire (PIQ-6) to the Portuguese culture[J]. Pain Med, 2011, 12 (10): 1538- 1543.
doi: 10.1111/j.1526-4637.2011.01222.x |
| 24 |
Park HJ , Lee SS , Park NC . Predictors of pain resolution after varicocelectomy for painful varicocele[J]. Asian J Androl, 2011, 13 (5): 754- 758.
doi: 10.1038/aja.2010.87 |
| 25 | Punjani N , Wald G , Gaffney CD , et al. Predictors of varicocele-associated pain and its impact on semen parameters following microsurgical repair[J]. Andrologia, 2021, 53 (8): e14121. |
| 26 |
Abd Ellatif ME , Asker W , Abbas A , et al. Varicocelectomy to treat pain, and predictors of success: A prospective study[J]. Curr Urol, 2012, 6 (1): 33- 36.
doi: 10.1159/000338867 |
| 27 |
Yaman O , Ozdiler E , Anafarta K , et al. Effect of microsurgical subinguinal varicocele ligation to treat pain[J]. Urology, 2000, 55 (1): 107- 108.
doi: 10.1016/S0090-4295(99)00374-X |
| 28 |
Al-Gadheeb A , El-Tholoth HS , Albalawi A , et al. Microscopic subinguinal varicocelectomy for testicular pain: A retrospective study on outcomes and predictors of pain relief[J]. Basic Clin Androl, 2021, 31 (1): 1.
doi: 10.1186/s12610-020-00119-z |
| 29 |
Wilcox SL , Redmond S , Davis TL . Genital image, sexual anxiety, and erectile dysfunction among young male military personnel[J]. J Sex Med, 2015, 12 (6): 1389- 1397.
doi: 10.1111/jsm.12880 |
| 30 |
Hooten WM . Chronic pain and mental health disorders: Shared neural mechanisms, epidemiology, and treatment[J]. Mayo Clin Proc, 2016, 91 (7): 955- 970.
doi: 10.1016/j.mayocp.2016.04.029 |
| 31 |
Van Oudenhove L , Törnblom H , Störsrud S , et al. Depression and somatization are associated with increased postprandial symptoms in patients with irritable bowel syndrome[J]. Gastroenterology, 2016, 150 (4): 866- 874.
doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2015.11.010 |
| 32 |
Kim HT , Song PH , Moon KH . Microsurgical ligation for painful varicocele: Effectiveness and predictors of pain resolution[J]. Yonsei Med J, 2012, 53 (1): 145- 150.
doi: 10.3349/ymj.2012.53.1.145 |
| 33 |
Clemens JQ , Mullins C , Ackerman AL , et al. Urologic chronic pelvic pain syndrome: Insights from the MAPP Research Network[J]. Nat Rev Urol, 2019, 16 (3): 187- 200.
doi: 10.1038/s41585-018-0135-5 |
| [1] | Hanwei KE, Qi WANG, Kexin XU. Optimization study of an animal model for interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome based on the dose effect of cyclophosphamide [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(5): 908-912. |
| [2] | Silan AN,Qunyi ZHENG,Kai WANG,Shan GAO. Characteristics and influencing factors of early pain in patients after total knee arthroplasty [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(1): 167-173. |
| [3] | Hui-li LIU,Yan-han LV,Xiao-xiao WANG,Min LI. Factors influencing the chronic post-surgical pain after laparoscopic surgery for elderly patients with urinary tract tumors [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(5): 851-856. |
| [4] | Ci TIAN,Yi BAI,Qing-bian MA,Hong-xia GE. Clinical characteristics of 7 cases of hepatic portal venous gas [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(4): 743-747. |
| [5] | Zhan-peng SHANG,Yang YI,Rong YU,Jing-jing FAN,Yu-xi HUANG,Xue QIAO,Min YE. Bioactive compounds of Jingfang Granules against SARS-CoV-2 virus proteases 3CLpro and PLpro [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(5): 907-919. |
| [6] | Lin ZHU,Wei-yu ZHANG,Ke-xin XU. Urodynamic and histological evaluation of cyclophosphamide-induced bladder pain syndrome in SD rats [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(4): 735-740. |
| [7] | PENG Jing,FANG Dong,ZHANG Zhi-chao,GAO Bing,YUAN Yi-ming,TANG Yuan,SONG Wei-dong,CUI Wan-shou. Testosterone levels in patients with varicocele and azoospermia [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(2): 294-298. |
| [8] | Jing-xian ZHU,Sheng-nan LU,Yan-fang JIANG,Ling JIANG,Jian-quan WANG. Influencing factors of preoperative pulmonary function in elderly patients undergoing rotator cuff surgery [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2021, 53(5): 902-906. |
| [9] | Peng ZHANG,Bo JIA,Xiao-kun CHEN,Yu WANG,Wei HUANG,Ren-jie LAI,Zhi-wei WANG,Jian XIONG,Tian-bing WANG. Effects of ulnar styloid and sigmoid notch fractures on postoperative wrist function of patients with distal radius fracture [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2020, 52(3): 578-581. |
| [10] | Duan YI,Wei ZHU,Xiu-li MENG,Xiao-guang LIU,Shui-qing LI,Bin ZHU,Dong-lin JIA. Analysis of anxiety, depression and related factors in patients with chronic lumbocrural pain before minimally invasive surgery [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2020, 52(2): 285-289. |
| [11] | Shan-shan BAI,Si-yi MO,Xiao-xiang XU,Yun LIU,Qiu-fei XIE,Ye CAO. Characteristics of orofacial operant test for orofacial pain sensitivity caused by occlusal interference in rats [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2020, 52(1): 51-57. |
| [12] | Jiao HE,Ge-heng YUAN,Jun-qing ZHANG,Xiao-hui GUO. Approach to creating early diabetic peripheral neuropathy rat model [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2019, 51(6): 1150-1154. |
| [13] | Xue-hua ZHU,Ming-yu YANG,Hai-zhui XIA,Wei HE,Zhi-ying ZHANG,Yu-qing LIU,Chun-lei XIAO,Lu-lin MA,Jian LU. Application of machine learning models in predicting early stone-free rate after flexible ureteroscopic lithotripsy for renal stones [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2019, 51(4): 653-659. |
| [14] | Yi-chong ZHANG,Jian-hai CHEN,Yu DANG,Ming YANG,Zhong-guo FU,Dian-ying ZHANG,Pei-xun ZHANG,Bao-guo JIANG. Correlation analysis between rotator cuff tear and the superior migration of humeral head [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2019, 51(2): 273-276. |
| [15] | Shu-dong YAN,Guang-ju YANG,Si-yi MO,Yun LIU,Qiu-fei XIE. Effect of long-term resistance exercise on masseter muscle mechanical hyperalgesia in rats [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2019, 51(1): 21-27. |
|
||