北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2019, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (4): 689-693. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2019.04.016
肾嗜酸细胞瘤诊治的回顾性研究
邱敏1,张永旺2,费月阳3,刘承1,△( ),邓绍晖1,何为4,陆敏5,卢剑1,侯小飞1,马潞林1
),邓绍晖1,何为4,陆敏5,卢剑1,侯小飞1,马潞林1
- 1. 北京大学第三医院泌尿外科, 北京 100191
2. 太原市人民医院泌尿外科, 太原 030001
3. 鸡西鸡矿医院泌尿外科, 黑龙江鸡西 158100
4. 北京大学第三医院影像科, 北京 100191
5. 北京大学第三医院病理科, 北京 100191
Retrospective study of diagnosis and treatment of renal oncocytoma
Min QIU1,Yong-wang ZHANG2,Yue-yang FEI3,Cheng LIU1,△( ),Shao-hui DENG1,Wei HE4,Min LU5,Jian LU1,Xiao-fei HOU1,Lu-lin MA1
),Shao-hui DENG1,Wei HE4,Min LU5,Jian LU1,Xiao-fei HOU1,Lu-lin MA1
- 1. Department of Urology, Peking University Third Hospital, Beijing 100191, China
2. Department of Urology, Taiyuan People’s Hospital, Taiyuan 030001, China
3. Department of Urology, Jixi Jikuang Hospital, Jixi 158100, Heilongjiang, China
4. Department of Radiology, Peking University Third Hospital, Beijing 100191, China
5. Department of Pathology, Peking University Third Hospital, Beijing 100191, China
摘要:
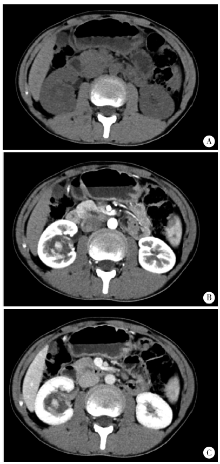
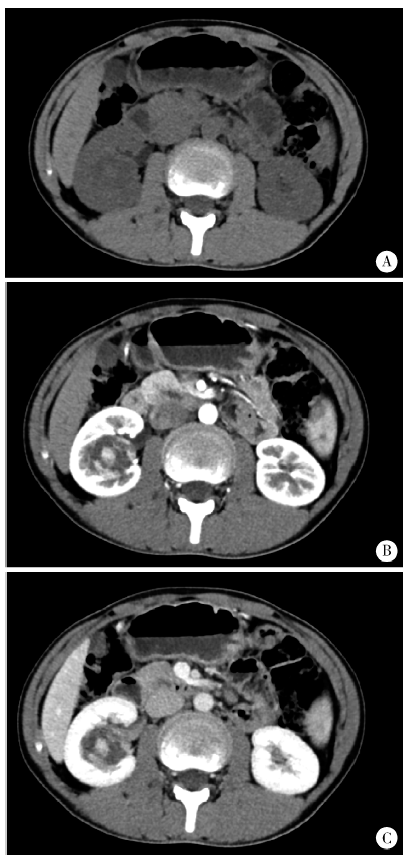
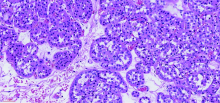
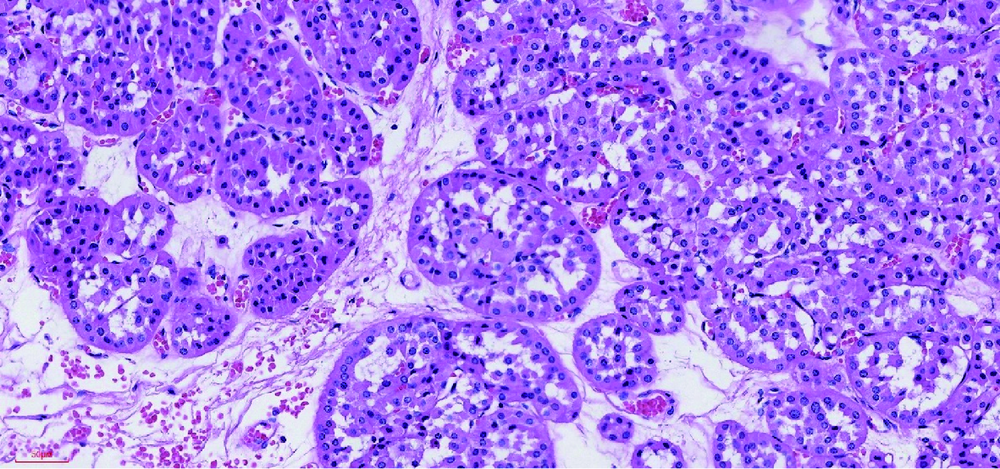
目的:总结肾嗜酸细胞瘤的诊断及手术治疗经验,根据随访结果评价手术效果,研究最佳策略。方法:回顾性分析2003年12月至2016年4月的21例肾嗜酸细胞瘤患者,其中男4例、女17例,右侧10例、左侧11例,年龄15~80岁(平均58岁),肿物大小1.5~6.5 cm(平均3.3 cm),完善检查后根据肿物的大小及位置,分别采用腹腔镜肾部分切除术或腹腔镜根治性肾切除术。结果:所有患者手术顺利,17例行腹腔镜肾部分切除术(其中3例中转开放手术),4例行腹腔镜根治性肾切除术。手术时间75~275 min(平均144 min),出血量10~1 000 mL(平均115 mL),术后住院时间6~13 d(平均8.2 d),组织病理检查结果为肾嗜酸细胞瘤。术后有17例获得随访,4例失访,随访时间12~175个月,平均44个月,有1例术后20个月去世,原因不详,其余16例随访无复发。结论:肾嗜酸细胞瘤为良性肿瘤,预后较好,增强CT是较为有效的诊断方法,通过影像归档和通信系统(picture archiving and communication systems,PACS)对肿瘤不同时期CT值的测量及与肿瘤旁肾组织CT值的比较,可能提高CT的诊断效能。腹腔镜手术是治疗肾嗜酸细胞瘤的有效方式,如条件允许,尽量选择肾部分切除术。
中图分类号:
- R737.11
| [1] | Zippel L . Zur kenntnis der onkocyten[J]. Virchows Arch Pathol, 1942,308:360-382. |
| [2] | Kay FU, Pedrosa I . Imaging of solid renal masses[J]. Urol Clin North Am, 2018,45(3):311-330. |
| [3] | Neves JB, Withington J, Fowler S , et al. Contemporary surgical management of renal oncocytoma: a nation’s outcome[J]. BJU Int, 2018,121(6):893-899. |
| [4] | 李保国, 陆敏, 王国良 , 等. 619例肾脏肿瘤的临床病理特征分析[J]. 中国微创外科杂志, 2018,18(5):445-449. |
| [5] | Bhatt NR, Davis NF, Flynn R , et al. Dilemmas in diagnosis and natural history of renal oncocytoma and implications for management[J]. Can Urol Assoc J, 2015,9(9-10):E709-E712. |
| [6] | Wentzel SW, Vermeulen LP . Bilateral multifocal renal oncocytoma in pregnancy[J]. Rare Tumors, 2012,4(4):e54. |
| [7] | Pagano D, di Francesco F, Rosa L , et al. Oncocytoma managed by active surveillance in a transplant allograft kidney: a case report[J]. World J Surg Oncol, 2018,16(1):123. |
| [8] | Wu Y, Du L, Li F , et al. Renal oncocytoma: contrast-enhanced sonographic features[J]. J Ultrasound Med, 2013,32(3):441-448. |
| [9] | Ren A, Cai F, Shang YN , et al. Differentiation of renal oncocytoma and renal clear cell carcinoma using relative CT enhancement ratio[J]. Chin Med J (Engl), 2015,128(2):175-179. |
| [10] | Kang SH, Seo WT, Kang PM , et al. A back-to-back tumor composed of papillary renal cell carcinoma and oncocytoma treated by laparoscopic partial nephrectomy: a case report[J]. J Med Case Rep, 2018,12(1):146. |
| [11] | Kocher NJ, Rjepaj C, Lehman E , et al. Incidence and histologic features of mixed renal tumors[J]. J Surg Oncol, 2018,117(3):430-433. |
| [12] | von Brandenstein M, Schlosser M, Herden J , et al. MicroRNAs as urinary biomarker for oncocytoma[J]. Dis Markers, 2018,2018:6979073. |
| [13] | Wobker SE, Williamson SR . Modern pathologic diagnosis of renal oncocytoma[J]. J Kidney Cancer VHL, 2017,4(4):1-12. |
| [14] | Liu S, Lee S, Rashid P , et al. Active surveillance is suitable for intermediate term follow-up of renal oncocytoma diagnosed by percutaneous core biopsy[J]. BJU Int, 2016,118(Suppl 3):30-34. |
| [15] | 邱敏, 向军吉, 马潞林 , 等. 实时超声监测后腹腔镜下肾部分切除术治疗完全内生型肾肿瘤的疗效分析[J]. 中华泌尿外科杂志, 2016,37(10):730-734. |
| [16] | Trivedi PP, Kriplani D, Gami A , et al. Small cell variant of renal oncocytoma with liver metastases[J]. Int J Surg Pathol, 2013,21(6):615-617. |
| [17] | Cacciamani G, Cima L, Ficial M , et al. Liver metastases from renal oncocytoma with vascular extension[J]. Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol, 2017,27(5):e48-e53 |
| [18] | Wobker SE, Przybycin CG, Sircar K , et al. Renal oncocytoma with vascular invasion: a series of 22 cases[J]. Hum Pathol, 2016,58:1-6. |
| [1] | 陈心心, 唐哲, 乔艳春, 荣文笙. 北京市密云区4岁儿童患龋状况及其与龋活跃性检测的相关性[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(5): 833-838. |
| [2] | 钟华, 李原, 徐丽玲, 白明欣, 苏茵. 18F-FDG PET/CT在风湿免疫病中的应用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(5): 853-859. |
| [3] | 丁汉东, 王琴, 廖贵益, 郝宗耀. 肾移植术后并发消化道出血的诊治[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(5): 902-907. |
| [4] | 陈思鹭, 王海菊, 吴宇财, 李志华, 黄燕波, 何宇辉, 许洋洋, 李学松, 贯华. 成人肾积水病因分析:一项单中心横断面研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(5): 913-918. |
| [5] | 王明瑞, 王起, 胡浩, 赖金惠, 唐鑫伟, 万春艳, 许克新, 徐涛. 覆膜金属输尿管支架治疗盆腔脂肪增多症所致肾积水的疗效[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(5): 919-922. |
| [6] | 张树栋,谢睿扬. 机器人手术时代的肾癌合并腔静脉瘤栓治疗策略[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 562-564. |
| [7] | 王明瑞,刘军,熊六林,于路平,胡浩,许克新,徐涛. 经皮微通道-微电子肾镜-微超声探针碎石术治疗1.5~2.5 cm肾结石的疗效和安全性[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 605-609. |
| [8] | 郑生旗,花天池,殷桂草,张伟,姚曳,李一帆. 甘油三酯葡萄糖指数与男性肾结石风险的关联[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 610-616. |
| [9] | 陈克伟,刘茁,邓绍晖,张帆,叶剑飞,王国良,张树栋. 肾血管平滑肌脂肪瘤伴下腔静脉瘤栓的临床诊治[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 617-623. |
| [10] | 刘帅,刘磊,刘茁,张帆,马潞林,田晓军,侯小飞,王国良,赵磊,张树栋. 伴静脉癌栓的肾上腺皮质癌的临床治疗及预后[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 624-630. |
| [11] | 杨捷,冯杰莉,张树栋,马潞林,郑清. 经食管超声心动图在肾切除术联合Mayo Ⅲ~Ⅳ级静脉瘤栓取栓术不同手术方式中的临床作用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 631-635. |
| [12] | 王滨帅,邱敏,张前进,田茂锋,刘磊,王国良,陆敏,田晓军,张树栋. 6例肾尤文肉瘤伴静脉瘤栓的诊治[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 636-639. |
| [13] | 杨文博,余磊,张维宇,徐涛,王强. 带线输尿管支架自排技术在肾移植受者中的效果及安全性[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 656-660. |
| [14] | 虞乐,邓绍晖,张帆,颜野,叶剑飞,张树栋. 具有低度恶性潜能的多房囊性肾肿瘤的临床病理特征及预后[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 661-666. |
| [15] | 舒帆,郝一昌,张展奕,邓绍晖,张洪宪,刘磊,王国良,田晓军,赵磊,马潞林,张树栋. 肾部分切除术治疗囊性肾癌的功能学和肿瘤学结果:单中心回顾性研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 667-672. |
|
||