北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2024, Vol. 56 ›› Issue (4): 610-616. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2024.04.011
甘油三酯葡萄糖指数与男性肾结石风险的关联
郑生旗1,花天池1,殷桂草1,张伟1,姚曳2,*( ),李一帆1,*(
),李一帆1,*( )
)
- 1. 扬州大学附属医院泌尿外科, 江苏扬州 225001
2. 苏北人民医院疝儿外科, 江苏扬州 225001
Association between the triglyceride-glucose index and the incidence of nephrolithiasis in male individuals
Shengqi ZHENG1,Tianchi HUA1,Guicao YIN1,Wei ZHANG1,Ye YAO2,*( ),Yifan LI1,*(
),Yifan LI1,*( )
)
- 1. Department of Urology, Affiliated Hospital of Yangzhou University, Yangzhou 225001, Jiangsu, China
2. Department of Hernia and Pediatric Surgery, Northern Jiangsu People's Hospital, Yangzhou 225001, Jiangsu, China
摘要:
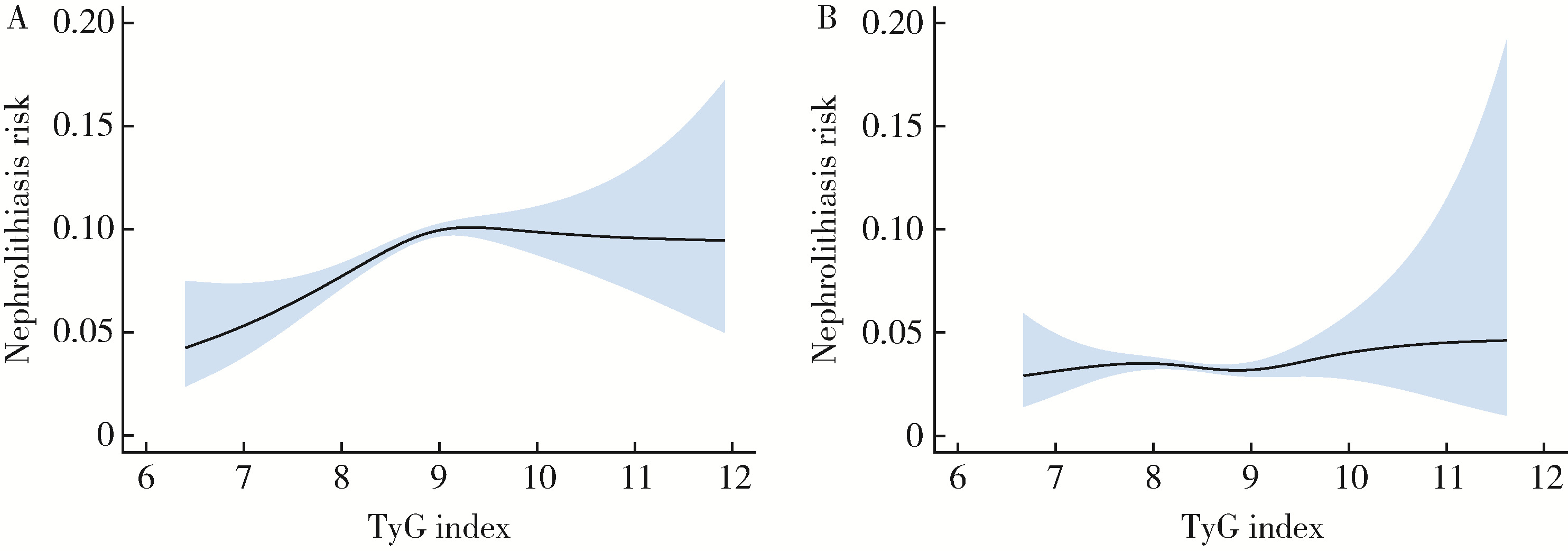
目的: 评估甘油三酯葡萄糖(triglyceride-glucose,TyG)指数与肾结石风险间的关联性,并探讨在不同人群中的效应差异。方法: 通过横断面研究分析84 968名成年体检者的受检记录,将体检者根据TyG指数分为三个分位组(低、中、高)。采用多因素Logistic回归模型评估TyG指数与肾结石风险之间的关联,使用分段线性回归模型探讨TyG指数与肾结石风险之间的非线性剂量-反应关系,并进行亚组分析以探究不同人群中的效应差异。结果: 随着TyG指数的增加,肾结石的患病率呈上升趋势,从低TyG指数组的4.36%增加到高TyG指数组的8.96%(P < 0.001)。在调整了多种因素后,中、高TyG指数组的男性与低TyG指数组男性相比,肾结石的风险分别增加了1.18倍(95%CI: 1.07~1.31,P=0.002)和1.29倍(95%CI: 2.08~2.47,P < 0.001)。然而,在女性中,这一关联在调整后并不显著(OR=0.98,95%CI: 0.82~1.16,P=0.778)。非线性分析显示,在男性中,TyG指数在8.98的折点以下存在显著关联(OR=1.40,95%CI: 1.24~1.58,P < 0.001),而在该折点及以上则不显著(OR=0.91,95%CI: 0.78~1.06,P=0.24)。亚组分析表明,TyG指数与肾结石风险之间的关系在不同年龄、不同BMI和高血压状态下均较为稳定。结论: TyG指数与男性肾结石风险呈正相关,且这种关系表现为非线性剂量-反应关系; TyG指数有助于识别高风险的肾结石男性患者,但需进一步探讨其潜在机制及在不同人群的普遍性。
中图分类号:
- R692.4
| 1 |
Hill AJ , Basourakos SP , Lewicki P , et al. Incidence of kidney stones in the united states: The continuous national health and nutrition examination survey[J]. J Urol, 2022, 207 (4): 851- 856.
doi: 10.1097/JU.0000000000002331 |
| 2 |
Haas CR , Li G , Hyams ES , et al. Delayed decompression of obstructing stones with urinary tract infection is associated with increased odds of death[J]. J Urol, 2020, 204 (6): 1256- 1262.
doi: 10.1097/JU.0000000000001182 |
| 3 |
Khan SR , Pearle MS , Robertson WG , et al. Kidney stones[J]. Nat Rev Dis Primers, 2016, 2, 16008.
doi: 10.1038/nrdp.2016.8 |
| 4 |
Peerapen P , Thongboonkerd V . Kidney stone prevention[J]. Adv Nutr, 2023, 14 (3): 555- 569.
doi: 10.1016/j.advnut.2023.03.002 |
| 5 |
Fritz J , Bjørge T , Nagel G , et al. The triglyceride-glucose index as a measure of insulin resistance and risk of obesity-related cancers[J]. Int J Epidemiol, 2020, 49 (1): 193- 204.
doi: 10.1093/ije/dyz053 |
| 6 |
Lee SH , Park SY , Choi CS . Insulin resistance: From mechanisms to therapeutic strategies[J]. Diabetes Metab J, 2022, 46 (1): 15- 37.
doi: 10.4093/dmj.2021.0280 |
| 7 |
Kim S , Chang Y , Jung HS , et al. Glycemic status, insulin resistance, and the risk of nephrolithiasis: A cohort study[J]. Am J Kidney Dis, 2020, 76 (5): 658- 668. e1.
doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2020.03.013 |
| 8 |
Huo RR , Liao Q , Zhai L , et al. Interacting and joint effects of triglyceride-glucose index (TyG) and body mass index on stroke risk and the mediating role of TyG in middle-aged and older Chinese adults: A nationwide prospective cohort study[J]. Cardiovasc Diabetol, 2024, 23 (1): 30.
doi: 10.1186/s12933-024-02122-4 |
| 9 |
Xu L , Wu M , Chen S , et al. Triglyceride-glucose index associates with incident heart failure: A cohort study[J]. Diabetes Metab, 2022, 48 (6): 101365.
doi: 10.1016/j.diabet.2022.101365 |
| 10 |
Tao LC , Xu JN , Wang TT , et al. Triglyceride-glucose index as a marker in cardiovascular diseases: Landscape and limitations[J]. Cardiovasc Diabetol, 2022, 21 (1): 68.
doi: 10.1186/s12933-022-01511-x |
| 11 |
Xiang Q , Xu H , Zhan J , et al. Association between the trigly-ceride-glucose index and vitamin d status in type 2 diabetes mellitus[J]. Nutrients, 2023, 15 (3): 639.
doi: 10.3390/nu15030639 |
| 12 |
Wang S , Shi J , Peng Y , et al. Stronger association of triglyceride glucose index than the HOMA-IR with arterial stiffness in patients with type 2 diabetes: A real-world single-centre study[J]. Cardiovasc Diabetol, 2021, 20 (1): 82.
doi: 10.1186/s12933-021-01274-x |
| 13 |
Zhang Q , Xiao S , Jiao X , et al. The triglyceride-glucose index is a predictor for cardiovascular and all-cause mortality in CVD patients with diabetes or pre-diabetes: Evidence from NHANES 2001-2018[J]. Cardiovasc Diabetol, 2023, 22 (1): 279.
doi: 10.1186/s12933-023-02030-z |
| 14 | 艾比班木·艾则孜, 马依彤. 甘油三酯葡萄糖指数与心血管疾病及代谢综合征相关性的研究进展[J]. 中华老年多器官疾病杂志, 2022, 21 (4): 317- 320. |
| 15 |
Jiang H , Li L , Liu J , et al. Triglyceride-glucose index as a novel biomarker in the occurrence of kidney stones: A cross-sectional population-based study[J]. Int J Gen Med, 2021, 14, 6233- 6244.
doi: 10.2147/IJGM.S334821 |
| 16 |
Qin Z , Zhao J , Geng J , et al. Higher triglyceride-glucose index is associated with increased likelihood of kidney stones[J]. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne), 2021, 12, 774567.
doi: 10.3389/fendo.2021.774567 |
| 17 |
Chen L , Zhang J , Shen K , et al. Kidney stones are associated with metabolic syndrome in a health screening population: A cross-sectional study[J]. Transl Androl Urol, 2023, 12 (6): 967- 976.
doi: 10.21037/tau-23-51 |
| 18 |
Ye Z , Wu C , Xiong Y , et al. Obesity, metabolic dysfunction, and risk of kidney stone disease: A national cross-sectional study[J]. Aging Male, 2023, 26 (1): 2195932.
doi: 10.1080/13685538.2023.2195932 |
| 19 | Yuan S , Larsson SC . Assessing causal associations of obesity and diabetes with kidney stones using Mendelian randomization analysis[J]. Mol Genet Metab, 2021, 134 (1/2): 212- 215. |
| 20 | 王昱, 张慧敏, 邓雪蓉, 等. 尿枸橼酸定量检测在原发性痛风患者肾结石诊断中的应用价值[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54 (6): 1134- 1140. |
| 21 |
Xu Z , Yao X , Duan C , et al. Metabolic changes in kidney stone disease[J]. Front Immunol, 2023, 14, 1142207.
doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1142207 |
| 22 |
Deng J , Yu B , Chang Z , et al. Cerium oxide-based nanozyme suppresses kidney calcium oxalate crystal depositions via reversing hyperoxaluria-induced oxidative stress damage[J]. J Nanobiotechnology, 2022, 20 (1): 516.
doi: 10.1186/s12951-022-01726-w |
| 23 |
Khan SR , Canales BK , Dominguez-Gutierrez PR . Randall's plaque and calcium oxalate stone formation: Role for immunity and inflammation[J]. Nat Rev Nephrol, 2021, 17 (6): 417- 433.
doi: 10.1038/s41581-020-00392-1 |
| 24 |
Flisiński M , Brymora A , Skoczylas-Makowska N , et al. Fructose-rich diet is a risk factor for metabolic syndrome, proximal tubule injury and urolithiasis in rats[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2021, 23 (1): 203.
doi: 10.3390/ijms23010203 |
| 25 |
Xu JZ , Li C , Xia QD , et al. Sex disparities and the risk of urolithiasis: A large cross-sectional study[J]. Ann Med, 2022, 54 (1): 1627- 1635.
doi: 10.1080/07853890.2022.2085882 |
| 26 |
Zhao JV , Schooling CM . Sex-specific associations of insulin resistance with chronic kidney disease and kidney function: A bi-directional Mendelian randomisation study[J]. Diabetologia, 2020, 63 (8): 1554- 1563.
doi: 10.1007/s00125-020-05163-y |
| 27 | Emami E , Heidari-Soureshjani S , Mohammadjavad AO , et al. Obesity and the risk of developing kidney stones: A systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Iran J Kidney Dis, 2023, 1 (2): 63- 72. |
| 28 |
Inci M , Demirtas A , Sarli B , et al. Association between body mass index, lipid profiles, and types of urinary stones[J]. Ren Fail, 2012, 34 (9): 1140- 1143.
doi: 10.3109/0886022X.2012.713298 |
| 29 |
Kittanamongkolchai W , Mara KC , Mehta RA , et al. Risk of hypertension among first-time symptomatic kidney stone formers[J]. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol, 2017, 12 (3): 476- 482.
doi: 10.2215/CJN.06600616 |
| 30 |
Stamatelou K , Goldfarb DS . Epidemiology of kidney stones[J]. Healthcare, 2023, 11 (3): 424.
doi: 10.3390/healthcare11030424 |
| [1] | 王明瑞,刘军,熊六林,于路平,胡浩,许克新,徐涛. 经皮微通道-微电子肾镜-微超声探针碎石术治疗1.5~2.5 cm肾结石的疗效和安全性[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 605-609. |
| [2] | 田聪,刘军,杨波,乔佳佳,黄晓波,许清泉. 经皮肾镜取石术中异常肾盂黏膜活检结果分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(5): 948-952. |
| [3] | 崔孟杰,马奇,陈曼曼,马涛,王鑫鑫,刘婕妤,张奕,陈力,蒋家诺,袁雯,郭桐君,董彦会,马军,星一. 不同生长模式与7~17岁儿童青少年代谢综合征的关系[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(3): 415-420. |
| [4] | 王昱,张慧敏,邓雪蓉,刘伟伟,陈璐,赵宁,张晓慧,宋志博,耿研,季兰岚,王玉,张卓莉. 尿枸橼酸定量检测在原发性痛风患者肾结石诊断中的应用价值[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(6): 1134-1140. |
| [5] | 左美妮,杜依青,于路平,戴翔,徐涛. 代谢综合征与肾透明细胞癌患者预后的相关性[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(4): 636-643. |
| [6] | 安立哲,熊六林,陈亮,王焕瑞,陈伟男,黄晓波. 腹腔镜肾盂成形术联合肾盂镜超声碎石取石术治疗肾盂输尿管连接部梗阻合并肾结石[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(4): 746-750. |
| [7] | 王明瑞,王起,胡浩,赖金惠,贺永新,熊杰,刘献辉,刘士军,许克新,徐涛. 标准通道经皮肾镜取石术治疗孤立肾肾结石的长期安全性和有效性[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2020, 52(4): 663-666. |
| [8] | 康宁,蒋一航,蒋宇光,吴栗洋,张际青,牛亦农,张军晖. 内镜联合超声与单纯超声引导建立皮肾通道在多镜联合术中的应用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2020, 52(4): 692-696. |
| [9] | 张晓圆,郭成成,玉应香,谢岚,常翠青. 高脂饲料诱导肥胖胰岛素抵抗大鼠模型的建立[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2020, 52(3): 557-563. |
| [10] | 张勇,刘畅,陈彬,陈帆,段晋瑜,张孟钧,焦剑. 糖尿病前期患者糖代谢异常与慢性牙周炎的相关性[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2020, 52(1): 71-76. |
| [11] | 朱学华,杨明钰,夏海缀,何为,张智荧,刘余庆,肖春雷,马潞林,卢剑. 机器学习模型在预测肾结石输尿管软镜碎石术后早期结石清除率中的应用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2019, 51(4): 653-659. |
| [12] | 谌诚,张博,韩文科,林健,王刚,张晓春,宋毅,赵峥,张中元,金杰,虞巍. 超声造影技术引导下经皮肾穿刺应用于经皮肾镜取石术的单中心初步经验[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2017, 49(6): 1071-1075. |
| [13] | 王少刚, 余虓. 经皮肾镜碎石术——日间手术新探索[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2017, 49(5): 753-755. |
| [14] | 刘可, 肖春雷, 刘余庆, 郝一昌, 张树栋, 田雨, 马潞林. 输尿管软镜下钬激光憩室颈部切开及碎石治疗微小出口肾盏憩室结石[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2015, 47(4): 618-621. |
| [15] | 杨波, 胡卫国, 胡浩, 陈亮, 李建兴, 王晓峰. 逆行肾内手术治疗肾结石失败的原因分析及其对策[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2014, 46(5): 794-797. |
|
||