北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2022, Vol. 54 ›› Issue (4): 636-643. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2022.04.009
代谢综合征与肾透明细胞癌患者预后的相关性
- 北京大学人民医院泌尿外科,北京 10044
Correlation between metabolic syndrome and prognosis of patients with clear cell renal cell carcinoma
Mei-ni ZUO,Yi-qing DU,Lu-ping YU,Xiang DAI,Tao XU*( )
)
- Department of Urology, Peking University People's Hospital, Beijing 100044, China
摘要:
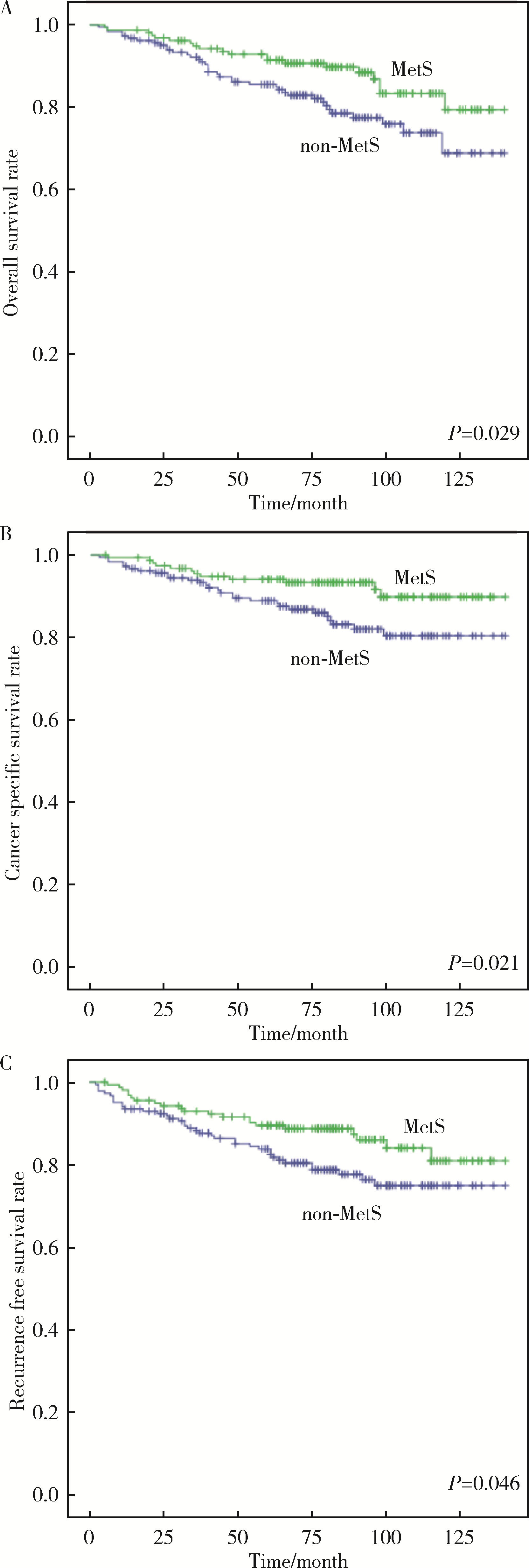
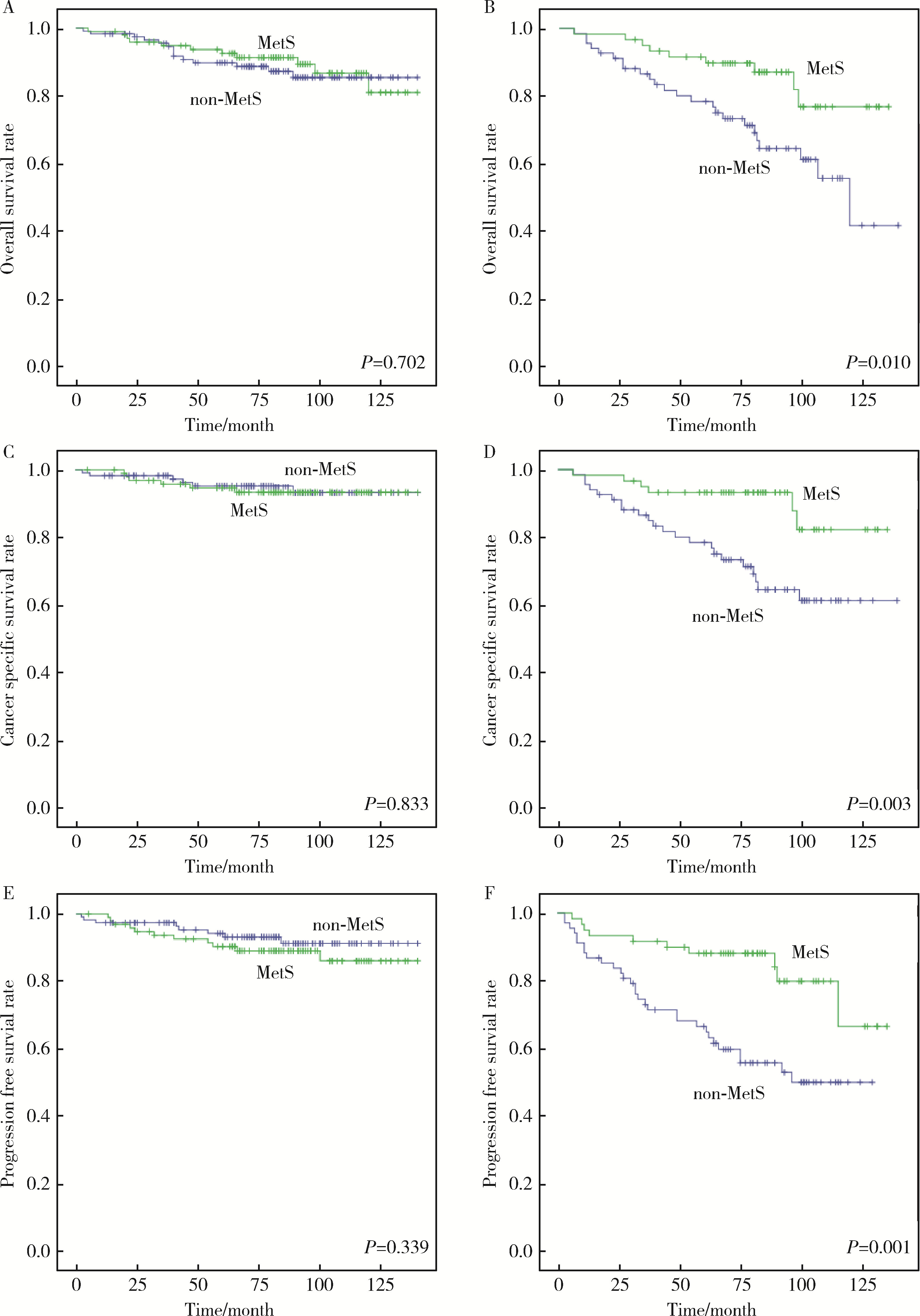
目的: 探讨肾透明细胞癌(clear cell renal cell carcinoma,ccRCC)手术后患者中代谢综合征(metabolic syndrome,MetS)与ccRCC预后的相关性。方法: 选择2009年1月—2014年11月于北京大学人民医院行根治性肾切除术或部分肾切除术患者的病例资料进行回顾性分析,共收集到342例ccRCC患者,记录患者的临床资料和病理资料,以及治疗前的实验室检查结果。将患者分为合并MetS组及未合并MetS组,对两组患者的总生存期(overall survival,OS)、肿瘤特异性生存期(cancer-specific survival,CSS)和无进展生存期(progression-free survival,PFS)进行单变量Cox回归分析与亚组分析。对两组患者以及各亚组的OS、CSS以及PFS使用Kaplan-Meier法绘制生存曲线进行生存分析。结果: 单变量Cox回归分析发现,MetS是ccRCC术后OS [风险比(hazard ratio,HR)=0.551,95%CI:0.321~0.949,P=0.031]、CSS(HR=0.460,95%CI 0.234~0.905,P=0.025)以及PFS(HR=0.585,95%CI:0.343~0.998,P=0.049)的保护因素。在肿瘤直径≤4 cm的亚组,MetS与术后OS(HR= 0.857,95%CI:0.389~1.890,P=0.702)、CSS(HR=1.129,95%CI:0.364~3.502,P=0.833)以及PFS(HR=1.554,95%CI:0.625~3.864,P=0.343)无明显相关性。在肿瘤直径>4 cm的亚组,MetS是ccRCC术后OS(HR=0.377,95%CI:0.175~0.812,P=0.013)、CSS(HR=0.280,95%CI:0.113~0.690,P=0.006)以及PFS(HR=0.332,95%CI:0.157~0.659,P=0.002)的保护因素;肥胖是术后CSS(HR=0.464,95%CI:0.219~0.981,P=0.044)和PFS(HR=0.445,95%CI:0.238~0.833,P=0.011)的保护因素。Kaplan-Meier生存分析显示,合并MetS较未合并MetS的患者术后远期生存更佳,二者OS(P=0.029)、CSS(P=0.021)以及PFS(P=0.046)差异均具有统计学意义;对肿瘤直径≤4 cm的亚组,合并MetS与未合并MetS的ccRCC患者术后OS(P=0.702)、CSS(P=0.833)以及PFS(P=0.339)差异均无统计学意义;对肿瘤直径> 4 cm的亚组,合并MetS的患者OS(P=0.010)、CSS(P=0.003)以及PFS(P=0.001)均高于未合并MetS的患者。结论: MetS是ccRCC患者术后OS、CSS和PFS的保护因素,该现象在肿瘤直径>4 cm亚组中更为显著;MetS的组分中肥胖与ccRCC术后OS以及CSS相关。
中图分类号:
- R737
| 1 |
Bray F , Ferlay J , Soerjomataram I , et al. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2018, 68 (6): 394- 424.
doi: 10.3322/caac.21492 |
| 2 |
Ozbek E , Otunctemur A , Sahin S , et al. Renal cell carcinoma is more aggressive in Turkish patients with the metabolic syndrome[J]. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev, 2013, 14 (12): 7351- 7354.
doi: 10.7314/APJCP.2013.14.12.7351 |
| 3 | Chakiryan NH, Jiang DD, Gillis KA, et al. Real-world survival outcomes associated with first-line immunotherapy, targeted therapy, and combination therapy for metastatic clear cell renal cell carcinoma[J]. JAMA Netw Open, 2021, 4(5): e2111329[2022-03-01]. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8150693/. |
| 4 |
Jonasch E , Walker CL , Rathmell WK . Clear cell renal cell carcinoma ontogeny and mechanisms of lethality[J]. Nat Rev Nephrol, 2021, 17 (4): 245- 261.
doi: 10.1038/s41581-020-00359-2 |
| 5 |
Zhang GM , Zhu Y , Ye DW . Metabolic syndrome and renal cell carcinoma[J]. World J Surg Oncol, 2014, 12, 236.
doi: 10.1186/1477-7819-12-236 |
| 6 |
Yao F , Bo Y , Zhao L , et al. Prevalence and influencing factors of metabolic syndrome among adults in China from 2015 to 2017[J]. Nutrients, 2021, 13 (12): 4475.
doi: 10.3390/nu13124475 |
| 7 |
Bovolini A , Garcia J , Andrade MA , et al. Metabolic syndrome pathophysiology and predisposing factors[J]. Int J Sports Med, 2021, 42 (3): 199- 214.
doi: 10.1055/a-1263-0898 |
| 8 |
Ewertz M , Jensen MB , Gunnarsdóttir K , et al. Effect of obesity on prognosis after early-stage breast cancer[J]. J Clin Oncol, 2011, 29 (1): 25- 31.
doi: 10.1200/JCO.2010.29.7614 |
| 9 |
Qi J , An R , Bhatti P , et al. Anti-hypertensive medications and risk of colorectal cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Cancer Causes Control, 2022, 33 (6): 801- 812.
doi: 10.1007/s10552-022-01570-1 |
| 10 | Yang X, Li X, Dong Y, et al. Effects of metabolic syndrome and its components on the prognosis of endometrial cancer[J]. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne), 2021, 12: 780769[2022-03-01]. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8717682/. |
| 11 |
Bulut S , Aktas BK , Erkmen AE , et al. Metabolic syndrome prevalence in renal cell cancer patients[J]. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev, 2014, 15 (18): 7925- 7928.
doi: 10.7314/APJCP.2014.15.18.7925 |
| 12 |
Yu Y , Gong L , Ye J . The role of aberrant metabolism in cancer: Insights into the interplay between cell metabolic reprogramming, metabolic syndrome, and cancer[J]. Front Oncol, 2020, 10, 942.
doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.00942 |
| 13 |
Luzzago S , Palumbo C , Rosiello G , et al. Metabolic syndrome predicts worse perioperative outcomes in patients treated with partial nephrectomy for renal cell carcinoma[J]. Urology, 2020, 140, 91- 97.
doi: 10.1016/j.urology.2020.02.019 |
| 14 |
Zhang Y , Wu T , Xie J , et al. Effects of metabolic syndrome on renal function after radical nephrectomy in patients with renal cell carcinoma[J]. Int Urol Nephrol, 2021, 53 (10): 2127- 2135.
doi: 10.1007/s11255-020-02759-6 |
| 15 |
Kriegmair MC , Mandel P , Porubsky S , et al. Metabolic syndrome negatively impacts the outcome of localized renal cell carcinoma[J]. Horm Cancer, 2017, 8 (2): 127- 134.
doi: 10.1007/s12672-017-0289-2 |
| 16 |
Liu Z , Wang H , Zhang L , et al. Metabolic syndrome is associated with improved cancer-specific survival in patients with localized clear cell renal cell carcinoma[J]. Transl Androl Urol, 2019, 8 (5): 507- 518.
doi: 10.21037/tau.2019.10.04 |
| 17 |
Eskelinen TJ , Kotsar A , Tammela TLJ , et al. Components of metabolic syndrome and prognosis of renal cell cancer[J]. Scand J Urol, 2017, 51 (6): 435- 441.
doi: 10.1080/21681805.2017.1352616 |
| 18 |
Du Y , Yang W , Liu H , et al. Perirenal fat as a new independent prognostic factor in patients with surgically treated clear cell renal cell carcinoma[J]. Clin Genitourin Cancer, 2022, 20 (1): e75- e80.
doi: 10.1016/j.clgc.2021.10.006 |
| 19 |
Ford E S . Prevalence of the metabolic syndrome defined by the International Diabetes Federation among adults in the U.S[J]. Diabetes Care, 2005, 28 (11): 2745- 2749.
doi: 10.2337/diacare.28.11.2745 |
| 20 |
Liu M , Wang J , Jiang B , et al. Increasing prevalence of metabolic syndrome in a Chinese elderly population: 2001-2010[J]. PLoS One, 2013, 8 (6): e66233.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0066233 |
| 21 |
Capitanio U , Bensalah K , Bex A , et al. Epidemiology of renal cell carcinoma[J]. Eur Urol, 2019, 75 (1): 74- 84.
doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2018.08.036 |
| 22 |
Miricescu D , Balan DG , Tulin A , et al. PI3K/AKT/mTOR signalling pathway involvement in renal cell carcinoma pathogenesis (Review)[J]. Exp Ther Med, 2021, 21 (5): 540.
doi: 10.3892/etm.2021.9972 |
| 23 |
Silva A , Pereira SS , Monteiro MP , et al. Effect of metabolic syndrome and individual components on colon cancer characteristics and prognosis[J]. Front Oncol, 2021, 11, 631257.
doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.631257 |
| 24 |
Mallik R , Chowdhury TA . Metformin in cancer[J]. Diabetes Res Clin Pract, 2018, 143, 409- 419.
doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2018.05.023 |
| 25 |
Parker AS , Lohse CM , Cheville JC , et al. Greater body mass index is associated with better pathologic features and improved outcome among patients treated surgically for clear cell renal cell carcinoma[J]. Urology, 2006, 68 (4): 741- 746.
doi: 10.1016/j.urology.2006.05.024 |
| 26 |
Wu X , Wang Q , Wang Z , et al. Association of extrarenal invasion patterns and tumor size with the differences in survival outcomes of t3a renal cell carcinoma: a proposal modified T3a stage system is needed[J]. Int J Gen Med, 2022, 15, 367- 378.
doi: 10.2147/IJGM.S344215 |
| 27 |
Dinatale RG , Xie W , Becerra MF , et al. The association between small primary tumor size and prognosis in metastatic renal cell carcinoma: Insights from two independent cohorts of patients who underwent cytoreductive nephrectomy[J]. Eur Urol Oncol, 2020, 3 (1): 47- 56.
doi: 10.1016/j.euo.2019.10.002 |
| [1] | 郑生旗,花天池,殷桂草,张伟,姚曳,李一帆. 甘油三酯葡萄糖指数与男性肾结石风险的关联[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 610-616. |
| [2] | 苏俊琪,王晓颖,孙志强. 舌鳞状细胞癌根治性切除术后患者预后预测列线图的构建与验证[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(1): 120-130. |
| [3] | 刘耘充,吴宗龙,葛力源,杜坦,吴雅倩,宋一萌,刘承,马潞林. 肾透明细胞癌中核蛋白1对阿昔替尼耐药的作用及机制[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(5): 781-792. |
| [4] | 崔孟杰,马奇,陈曼曼,马涛,王鑫鑫,刘婕妤,张奕,陈力,蒋家诺,袁雯,郭桐君,董彦会,马军,星一. 不同生长模式与7~17岁儿童青少年代谢综合征的关系[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(3): 415-420. |
| [5] | 蔡天玉,朱振鹏,徐纯如,吉星,吕同德,郭振可,林健. 成纤维细胞生长因子受体2在肾透明细胞癌中的表达及意义[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(4): 628-635. |
| [6] | 刘淼, 何耀, 姜斌, 吴蕾, 王建华, 杨姗姗, 王义艳, 李小鹰. 北京某社区老年人群肱踝脉搏波传导速度与代谢综合征的现况研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2014, 46(3): 429-434. |
| [7] | 闫睿, 栾庆先, 刘力笙, 王兴宇, 李蓬, 沙月琴. 代谢综合征相关线粒体基因单核苷酸多态性与慢性牙周炎的关系[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2014, 46(2): 264-268. |
| [8] | 陶庆梅, 王胜锋, 孙凤, 陶秋山, 曹纯铿, 詹思延. 北京健康体检人群γ-谷氨酰转肽酶水平与代谢综合征的关联分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2013, 45(03): 364-369. |
| [9] | 于卓人*, 刘丽笙, 栾庆先, 王兴宇, 李蓬, 沙月琴, 刘曦. 北京石景山区老年人群牙周炎与代谢综合征的相关性探讨[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2012, 44(4): 633-638. |
| [10] | 陈天娇, 季成叶. 北京市中学生腰围与体质指数及代谢综合征相关性状分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2012, 44(3): 355-358. |
| [11] | 李蓬, 张大鹍, 张继睿, 陈力. 伴牙周炎的代谢综合征者动脉硬化早期指标的检测[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2011, 43(1): 34-39. |
| [12] | 和璐. 牙周炎和代谢综合征[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2011, 43(1): 13-17. |
| [13] | 胡卫红, 乔杰, 王黎娜, 同军. 多囊卵巢综合征患者代谢综合征的发生及临床特征的相关性[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2010, 42(2): 159-163. |
| [14] | 刘靖, 杨靓, 孙宁玲, 马济顺, 胡大一. 微量白蛋白尿及假性血友病因子与高血压代谢综合征的关系[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2007, 39(6): 587-590. |
| Viewed | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Full text 98
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Abstract 463
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Cited |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Shared | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Discussed | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||