北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2024, Vol. 56 ›› Issue (2): 253-259. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2024.02.008
乌司奴单抗对克罗恩病临床缓解及透壁愈合的疗效
吴芸,徐亚兰,张国艳,张媛媛,王峻瑶,尤鹏,彭涛,刘玉兰,陈宁*( )
)
- 北京大学人民医院消化内科,北京 100044
Clinical remission and transmural healing of ustekinumab in patients with Crohn's disease
Yun WU,Yalan XU,Guoyan ZHANG,Yuanyuan ZHANG,Junyao WANG,Peng YOU,Tao PENG,Yulan LIU,Ning CHEN*( )
)
- Department of Gastroenterology, Peking University People's Hospital, Beijing 100044, China
摘要:
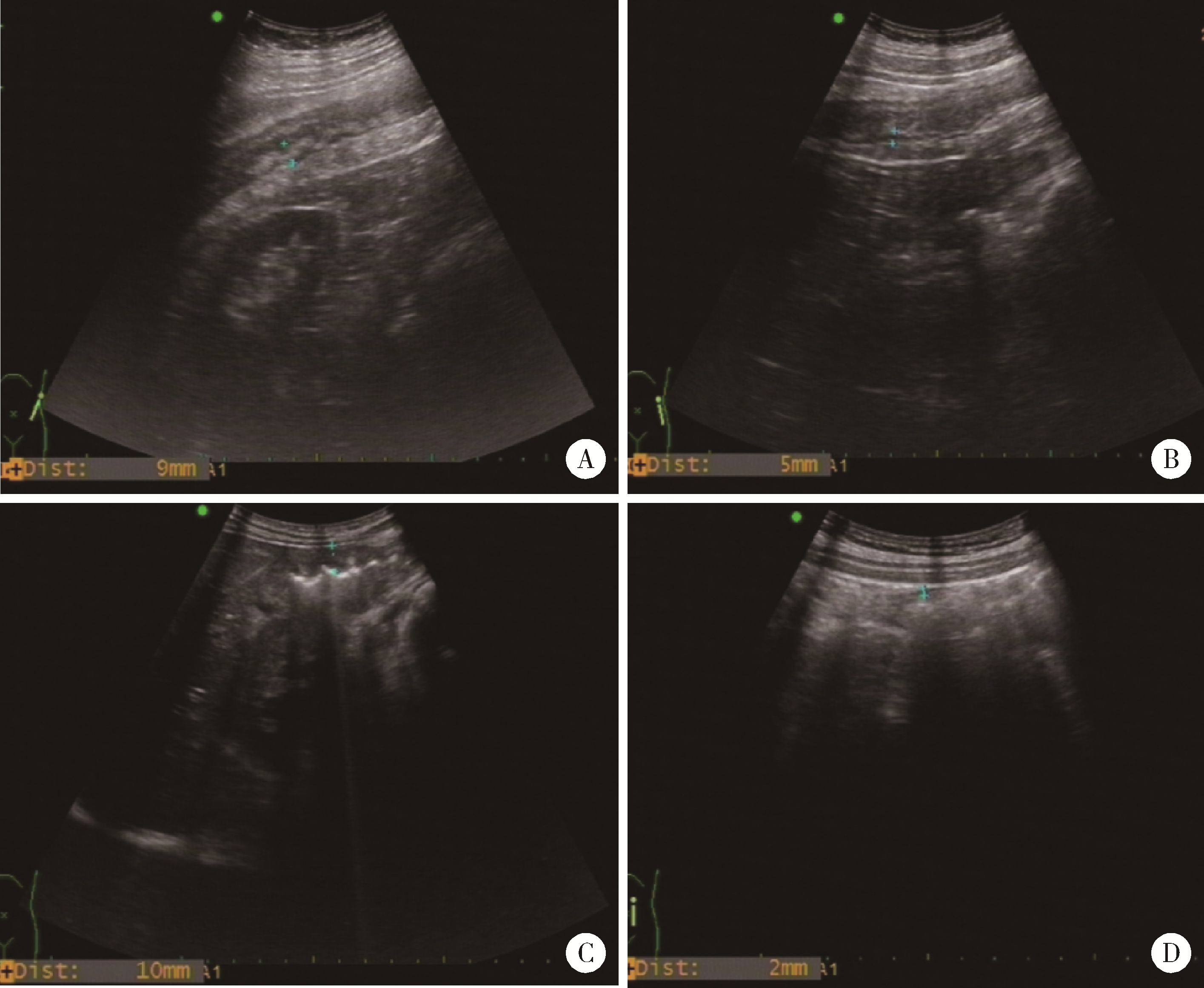
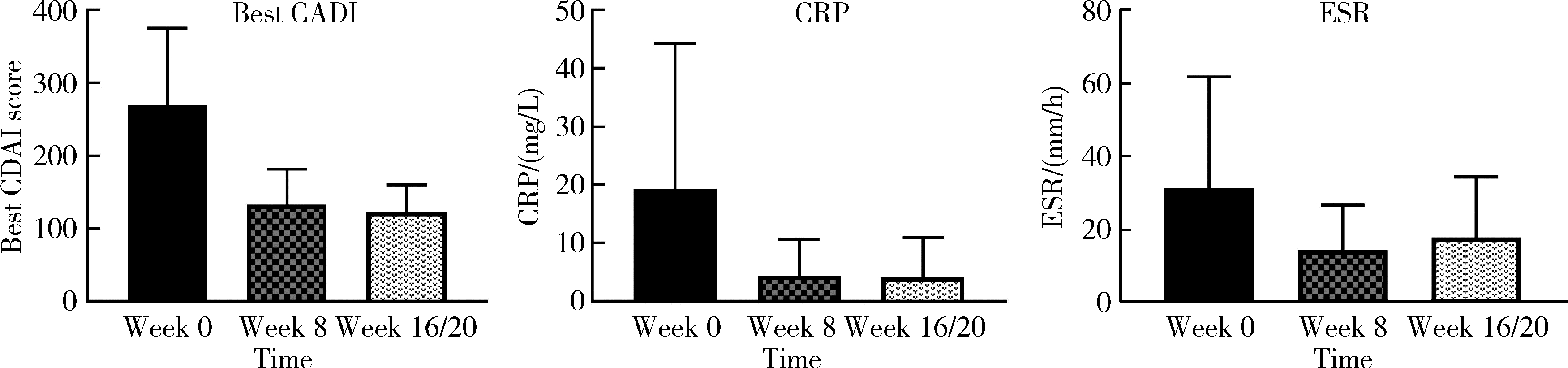
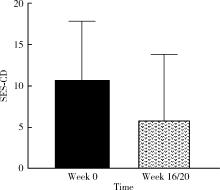
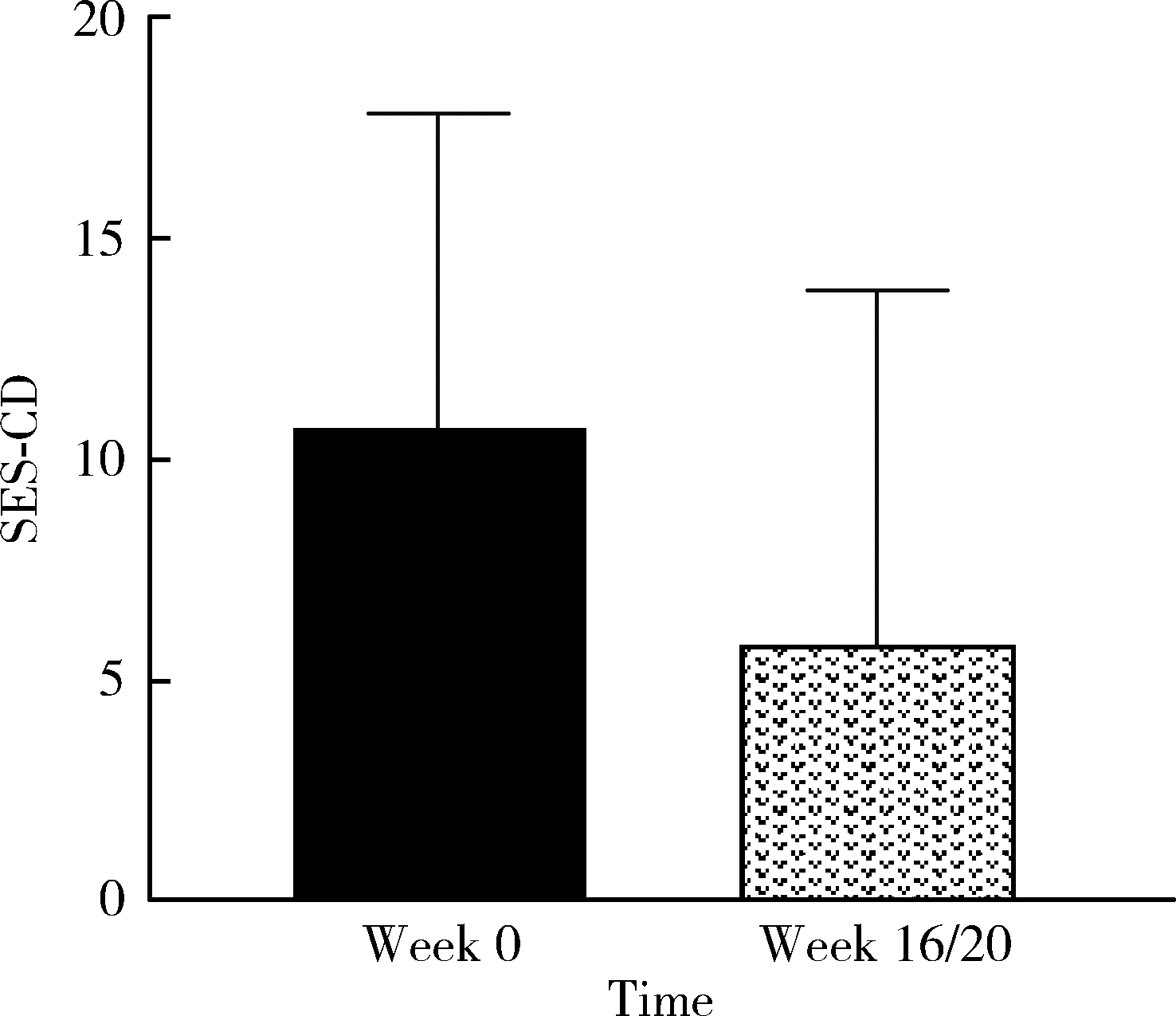
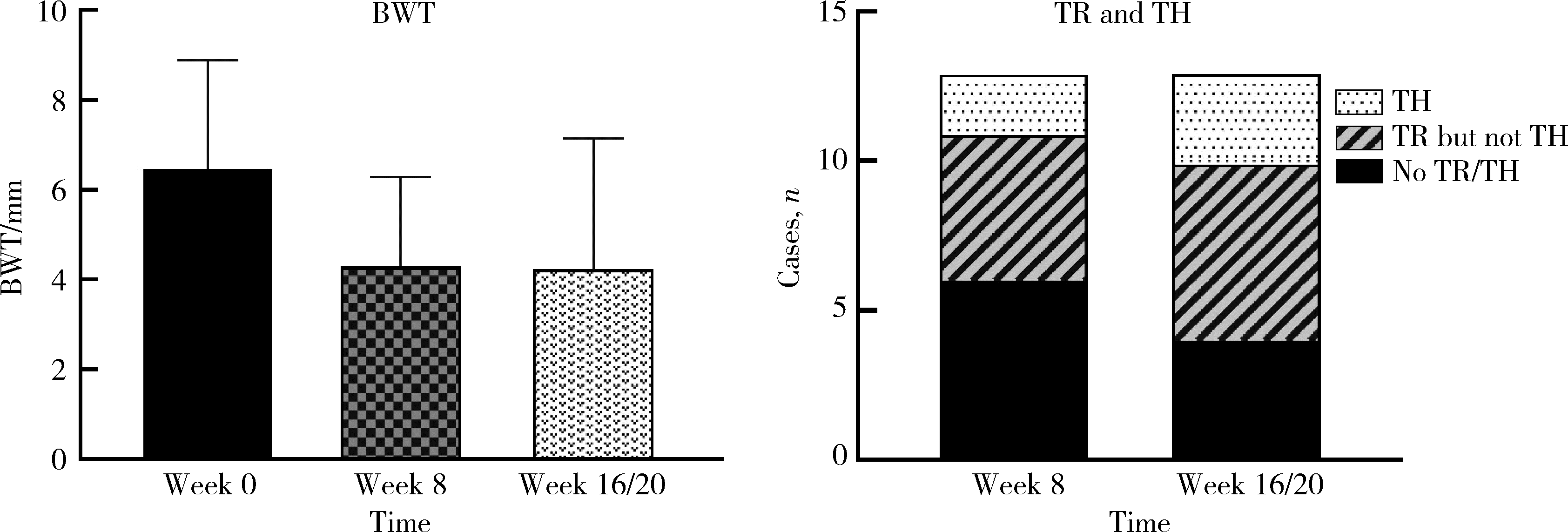
目的: 应用乌司奴单抗(ustekinumab, UST)治疗克罗恩病(Crohn’s disease, CD)患者,评估临床及内镜缓解情况,采用肠道超声(intestinal ultrasonography, IUS)评估透壁应答(transmural response, TR)与透壁愈合(transmural healing, TH)情况。方法: 回顾性分析2020年1月到2022年8月北京大学人民医院所有确诊应用UST进行治疗的CD患者,分别于治疗后8周、治疗后16/20周进行评估,包括临床、生化学指标、结肠镜及IUS检查。结果: 共纳入患者13例,其中男性11例,女性2例,平均年龄36.92岁,治疗前Best克罗恩病活动指数(Best Crohn’s disease activity index, Best CDAI)平均值为270.12±105.55。在治疗8周时,患者的Best CDAI评分下降至133.16± 48.66 (t=4.977,P<0.001),8例患者达到临床缓解,5例未达到临床缓解。共有9例患者治疗前后进行结肠镜检查评估,治疗前进行简化克罗恩病内镜下评分(simple endoscopic score for Crohn’s disease,SES-CD),评分为10.71± 7.14,16/20周复查SES-CD下降至6.00±7.81(t=2.483,P=0.048),其中4例患者达到内镜缓解,5例患者未达到内镜缓解。在8周时,13例患者中有5例达到TR,2例达到TH,6例未达到TR或TH。16/20周时,6例患者达到TR,3例达到TH,4例未达到TR或TH。UST对于小肠和结肠病变的TR效果差异无统计学意义(Fisher精确概率检验,P>0.999)。既往应用过其他生物制剂的患者中UST的TR偏低,但差异无统计学意义(Fisher精确概率检验,P=0.491)。结论: 应用UST 16/20周后患者的临床情况及内镜下评估均有改善,部分患者可以达到临床缓解及内镜缓解;UST对CD患者具有较好的TR效果,在8周即出现TR,16/20周TR有所增加;UST对小肠和结肠病变的TR效果差异无统计学意义;既往未应用过其他生物制剂的患者UST的TR较既往使用过生物制剂的患者效果更好,但差异无统计学意义。
中图分类号:
- R574.1
| 1 |
Torres J , Mehandru S , Colombel JF , et al. Crohn's disease[J]. Lancet, 2017, 389 (10080): 1741- 1755.
doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(16)31711-1 |
| 2 |
Geyl S , Guillo L , Laurent V , et al. Transmural healing as a therapeutic goal in Crohn's disease: A systematic review[J]. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2021, 6 (8): 659- 667.
doi: 10.1016/S2468-1253(21)00096-0 |
| 3 |
Helwig U , Fischer I , Hammer L , et al. Transmural response and transmural healing defined by intestinal ultrasound: New potential therapeutic targets?[J]. J Crohns Colitis, 2022, 16 (1): 57- 67.
doi: 10.1093/ecco-jcc/jjab106 |
| 4 |
Best WR , Becktel JM , Singleton JW , et al. Development of a Crohn's disease activity index. National cooperative Crohn's disease study[J]. Gastroenterology, 1976, 70 (3): 439- 444.
doi: 10.1016/S0016-5085(76)80163-1 |
| 5 |
Lu C , Merrill C , Medellin A , et al. Bowel ultrasound state of the art: Grayscale and doppler ultrasound, contrast enhancement, and elastography in Crohn disease[J]. J Ultrasound Med, 2019, 38 (2): 271- 288.
doi: 10.1002/jum.14920 |
| 6 |
Laserna-Mendieta EJ , Lucendo J . Faecal calprotectin in inflammatory bowel diseases: A review focused on meta-analyses and routine usage limitations[J]. Clin Chem Lab Med, 2019, 57 (9): 1295- 1307.
doi: 10.1515/cclm-2018-1063 |
| 7 |
Solem CA , Loftus EJ , Tremaine WJ , et al. Correlation of C-reactive protein with clinical, endoscopic, histologic, and radiographic activity in inflammatory bowel disease[J]. Inflamm Bowel Dis, 2005, 11 (8): 707- 712.
doi: 10.1097/01.MIB.0000173271.18319.53 |
| 8 |
Schnitzler F , Fidder H , Ferrante M , et al. Mucosal healing predicts long-term outcome of maintenance therapy with infliximab in Crohn's disease[J]. Inflamm Bowel Dis, 2009, 15 (9): 1295- 1301.
doi: 10.1002/ibd.20927 |
| 9 |
Turner D , Ricciuto A , Lewis A , et al. STRIDE-Ⅱ: An update on the selecting therapeutic targets in inflammatory bowel disease (STRIDE) initiative of the international organization for the study of IBD (IOIBD): Determining therapeutic goals for treat-to-target strategies in IBD[J]. Gastroenterology, 2021, 160 (5): 1570- 1583.
doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2020.12.031 |
| 10 |
Mazzuoli S , Guglielmi FW , Antonelli E , et al. Definition and evaluation of mucosal healing in clinical practice[J]. Dig Liver Dis, 2013, 45 (12): 969- 977.
doi: 10.1016/j.dld.2013.06.010 |
| 11 |
Civitelli F , Nuti F , Oliva S , et al. Looking beyond mucosal hea-ling: Effect of biologic therapy on transmural healing in pediatric Crohn's disease[J]. Inflamm Bowel Dis, 2016, 22 (10): 2418- 2424.
doi: 10.1097/MIB.0000000000000897 |
| 12 |
Zacharopoulou E , Craviotto V , Fiorino G , et al. Targeting the gut layers in Crohn's disease: Mucosal or transmural healing?[J]. Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2020, 14 (9): 775- 787.
doi: 10.1080/17474124.2020.1780914 |
| 13 |
Lafeuille P , Hordonneau C , Vignette J , et al. Transmural healing and MRI healing are associated with lower risk of bowel damage progression than endoscopic mucosal healing in Crohn's disease[J]. Aliment Pharmacol Ther, 2021, 53 (5): 577- 586.
doi: 10.1111/apt.16232 |
| 14 |
Sandborn WJ , Rebuck R , Wang Y , et al. Five-year efficacy and safety of ustekinumab treatment in Crohn's disease: The IMUNITI trial[J]. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2022, 20 (3): 578- 590.
doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2021.02.025 |
| 15 |
Yao J Y , Zhang M , Wang W , et al. Ustekinumab trough concentration affects clinical and endoscopic outcomes in patients with refractory Crohn's disease: A Chinese real-world study[J]. BMC Gastroenterol, 2021, 21 (1): 380.
doi: 10.1186/s12876-021-01946-8 |
| 16 |
Kucharzik T , Wilkens R , D'Agostino MA , et al. Early ultrasound response and progressive transmural remission after treatment with ustekinumab in Crohn's disease[J]. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2023, 21 (1): 153- 163.
doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2022.05.055 |
| 17 |
Calabrese E , Rispo A , Zorzi F , et al. Ultrasonography tight control and monitoring in Crohn's disease during different biological therapies: A multicenter study[J]. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2022, 20 (4): e711- e722.
doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2021.03.030 |
| 18 |
Feagan BG , Rubin DT , Danese S , et al. Efficacy of vedolizumab induction and maintenance therapy in patients with ulcerative colitis, regardless of prior exposure to tumor necrosis factor antagonists[J]. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2017, 15 (2): 229- 239.
doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2016.08.044 |
| 19 |
Hanauer SB , Sandborn WJ , Feagan BG , et al. IM-UNITI: Three-year efficacy, safety, and immunogenicity of ustekinumab treatment of Crohn's disease[J]. J Crohns Colitis, 2020, 14 (1): 23- 32.
doi: 10.1093/ecco-jcc/jjz110 |
| 20 |
Ghosh S , Gensler LS , Yang Z , et al. Ustekinumab safety in psoriasis, psoriatic arthritis, and Crohn's disease: An integrated analysis of phase Ⅱ/Ⅲ clinical development programs[J]. Drug Saf, 2019, 42 (6): 751- 768.
doi: 10.1007/s40264-019-00797-3 |
| [1] | 贺冰洁,刘志科,沈鹏,孙烨祥,陈彬,詹思延,林鸿波. 2011—2020年宁波市鄞州区炎症性肠病发病的流行病学研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(3): 511-519. |
| [2] | 周吴平,穆楠,简伟研,王化虹. 克罗恩病患者疾病经济负担现状与相关因素[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(3): 555-559. |
|
||