北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2018, Vol. 50 ›› Issue (6): 1039-1043. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2018.06.017
免疫球蛋白G4相关疾病患者发病形式及就诊行为特征分析
朱星昀1,刘燕鹰1,△( ),孙学娟2,于萍3,刘爽4,付美艳5,刘栩1,任立敏1,栗占国1
),孙学娟2,于萍3,刘爽4,付美艳5,刘栩1,任立敏1,栗占国1
- 1. 北京大学人民医院风湿免疫科, 北京 100044
2. 廊坊市人民医院风湿免疫科, 河北廊坊 065000
3. 唐山开滦总医院风湿免疫科, 河北唐山 063000
4. 昆明医科大学第一附属医院风湿免疫科, 昆明 650032
5. 乌鲁木齐市友谊医院风湿免疫科, 乌鲁木齐 830049
A cross-sectional study of the clinical features and physician visit patterns at onset of immunoglobulin G4 related disease
Xing-yun ZHU1,Yan-ying LIU1,△( ),Xue-juan SUN2,Ping YU3,Shuang LIU4,Mei-yan FU5,Xu LIU1,Li-min REN1,Zhan-guo LI1
),Xue-juan SUN2,Ping YU3,Shuang LIU4,Mei-yan FU5,Xu LIU1,Li-min REN1,Zhan-guo LI1
- 1. Department of Rheumatology and Immunology, Peking University People’s Hospital, Beijing 100044, China
2. Department of Rheumatology and Immunology, The People’s Hospital of Langfang City, Langfang 065000, Hebei, China
3. Department of Rheumatology and Immunology, Kailuan General Hospital, Tangshan 063000, Hebei, China
4. Department of Rheumatology and Immunology, First Affiliated Hospital of Kuiming Medical University, Kunming 650032, China
5. Department of Rheumatology and Immunology, Urumuqi Youyi Hospital, Urumuqi 830049, China
摘要:
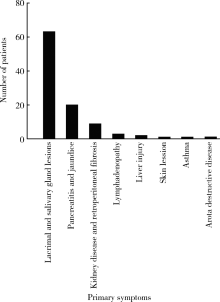
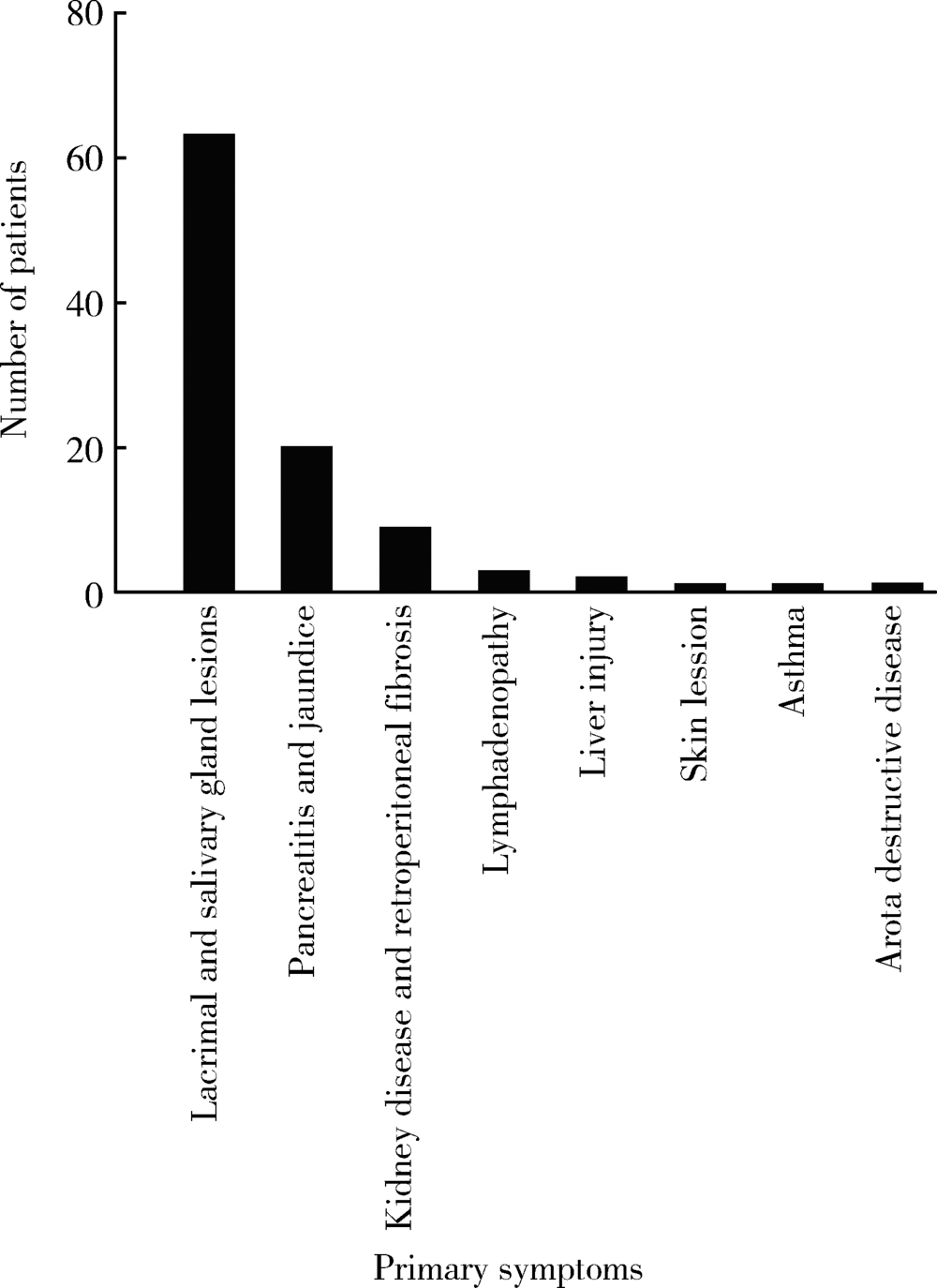
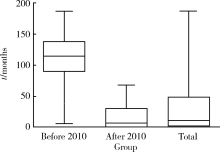
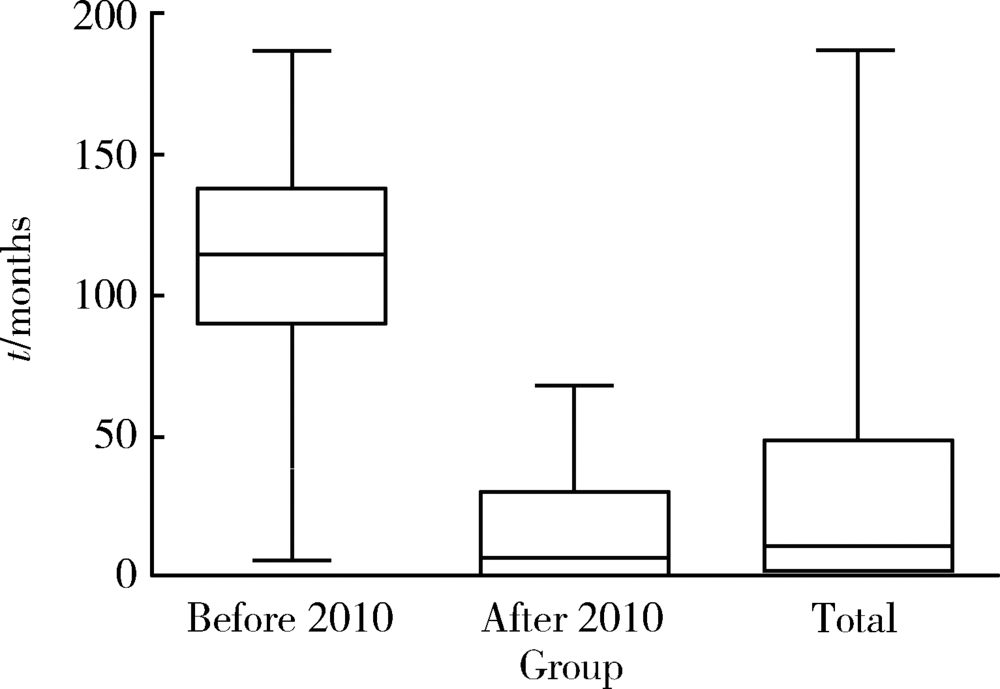
目的: 了解免疫球蛋白G4相关疾病(immunoglobulin G4-related disease,IgG4RD)患者的起病形式和就诊行为现况。方法: 采用流行病学研究方法,对在北京大学人民医院就诊的112例IgG4RD患者进行调查,其中资料完整者100例,内容包括患者的性别、年龄、身高、体重、病史、就诊过程及患病对工作的影响等。结果: 本组IgG4RD患者平均发病年龄为(51.51±12.9)岁,男女患病比为1 :0.75,女性发病年龄显著早于男性(P<0.001)。IgG4RD患者常见受累器官比例依次是颌下腺69%、泪腺59%、胰腺28%、腮腺28%,女性患者泪腺受累较多(P<0.05)。62%的患者合并有过敏性疾病。IgG4RD患者首诊科室主要为普通外科(9/100)、口腔及颌面外科(17/100)、风湿免疫科(16/100),确诊科室集中在风湿免疫科(67/100)、口腔颌面外科(16/100)和消化内科(7/100)。2010年后发病的患者平均发病到确诊月数较2010年前显著降低(P<0.01)。未明确诊断前接受过手术的患者有43例,首诊于外科的患者更易接受手术(P<0.01)。18%的患者因患病影响了工作。结论: IgG4RD女性患者并不少见,且发病年龄多早于男性,唾液腺、泪腺为最常见受累器官,且多为首发。过敏性疾病为IgG4RD常见的临床表现。临床漏诊、误诊普遍,近半数患者在诊断前接受了不必要的手术治疗,近年来延误诊断的情况略有改善,但仍应引起临床医师更多重视。
中图分类号:
- R593.2
| [1] |
Kamisawa T, Funata N, Hayashi Y , et al. A new clinicopatholo-gical entity of IgG4-related autoimmune disease[J]. J Gastroenterol, 2003,38(10):982-984.
doi: 10.1007/s00535-003-1175-y pmid: 14614606 |
| [2] |
Umehara H, Nakajima A, Nakamura T , et al. IgG4-related di-sease and its pathogenesis-cross-talk between innate and acquired immunity[J]. Int Immunol, 2014,26(11):585-595.
doi: 10.1093/intimm/dxu074 pmid: 4201844 |
| [3] |
Su Y, Sun W, Wang C , et al. Detection of serum IgG4 levels in patients with IgG4-related disease and other disorders[J]. PLoS One, 2015,10(4):e0124233.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0124233 pmid: 4401680 |
| [4] |
Inoue D, Yoshida K, Yoneda N , et al. IgG4-related disease: dataset of 235 consecutive patients[J]. Medicine (Baltimore), 2015,94(15):e680.
doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000000680 |
| [5] |
Lin W, Lu S, Chen H , et al. Clinical characteristics of immunoglobulin G4-related disease: a prospective study of 118 Chinese patients[J]. Rheumatology (Oxford), 2015,54(11):1982-1990.
doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/kev203 pmid: 26106212 |
| [6] |
Zhang J, Chen H, Ma Y , et al. Characterizing IgG4-related di-sease with 18F-FDG PET/CT: a prospective cohort study [J]. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging, 2014,41(8):1624-1634.
doi: 10.1007/s00259-014-2729-3 pmid: 4089015 |
| [7] |
Uchida K, Masamune A, Shimosegawa T , et al. Prevalence of IgG4-related disease in Japan based on nationwide survey in 2009[J]. Int J Rheumatol, 2012,2012:358371.
doi: 10.1155/2012/358371 pmid: 22899936 |
| [8] |
Takahashi H, Yamamoto M, Suzuki C , et al. The birthday of a new syndrome: IgG4-related diseases constitute a clinical entity[J]. Autoimmun Rev, 2010,9(9):591-594.
doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2010.05.003 pmid: 20457280 |
| [9] |
Umehara H, Okazaki K, Masaki Y , et al. Comprehensive diagnostic criteria for IgG4-related disease (IgG4-RD), 2011[J]. Mod Rheumatol, 2012,22(1):21-30.
doi: 10.3109/s10165-011-0571-z |
| [10] |
Kamisawa T, Zen Y, Pillai S , et al. IgG4-related disease[J]. Lancet, 2015,385(9976):1460-1471.
doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(14)60720-0 |
| [11] |
Masaki Y, Dong L, Kurose N , et al. Proposal for a new clinical entity, IgG4-positive multiorgan lymphoproliferative syndrome: analysis of 64 cases of IgG4-related disorders[J]. Ann Rheum Dis, 2009,68(8):1310-1315.
doi: 10.1136/ard.2008.089169 pmid: 18701557 |
| [12] |
Zen Y, Nakanuma Y . IgG4-related disease: a cross-sectional study of 114 cases[J]. Am J Surg Pathol, 2010,34(12):1812-1819.
doi: 10.1097/PAS.0b013e3181f7266b |
| [13] |
Fong W, Liew I, Tan D , et al. IgG4-related disease: features and treatment response in a multi-ethnic cohort in Singapore[J]. Clin Exp Rheumatol, 2018,36(Suppl. 112):89-93.
pmid: 29846168 |
| [14] |
Finkelman FD, Boyce JA, Vercelli D , et al. Key advances in mechanisms of asthma, allergy, and immunology in 2009[J]. J Allergy Clin Immunol, 2010,125(2):312-318.
doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2011.12.968 pmid: 2671063 |
| [15] |
Gao Y, Zheng M, Cui L , et al. IgG4-related disease: association between chronic rhino-sinusitis and systemic symptoms[J]. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol, 2018,275(8):2013-2019.
doi: 10.1007/s00405-018-5013-5 |
| [16] |
Hirano K, Tada M, Isayama H , et al. Long-term prognosis of autoimmune pancreatitis with and without corticosteroid treatment[J]. Gut, 2007,56(12):1719-1724.
doi: 10.1136/gut.2006.115246 pmid: 2095691 |
| [17] |
Hong X, Zhang YY, Li W , et al. Treatment of immunoglobulin G4-related sialadenitis: outcomes of glucocorticoid therapy combined with steroid-sparing agents[J]. Arthritis Res Ther, 2018,20(1):12.
doi: 10.1186/s13075-017-1507-6 pmid: 5791187 |
| [1] | 俞光岩,苏家增,柳登高,吴立玲,丛馨. 下颌下腺保存治疗新技术体系的建立与应用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(5): 842-845. |
| [2] | 杨红霞,田小兰,江薇,李文丽,刘青艳,彭清林,王国春,卢昕. 免疫介导坏死性肌病的临床和病理特征分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2019, 51(6): 989-995. |
| [3] | 宁晓然,王子乔,张珊珊,张霞,唐素玫,刘燕鹰. 超声评分系统在IgG4相关涎腺炎评估中的应用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2019, 51(6): 1032-1035. |
| [4] | 刘恩阳, 刘静芳, 邵文威, 肖琳, 李国辉, 昌晓红, 邱晓彦. 肿瘤来源的IgG抑制脐带血中T细胞的增殖[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2017, 49(5): 824-828. |
| [5] | 冯向辉, 张立, 徐莉, 孟焕新, 陈智滨, 释栋, 路瑞芳. 侵袭性牙周炎患者抗伴放线聚集杆菌血清c型IgG滴度分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2015, 47(5): 820-824. |
| [6] | 刘丹, 李茹, 刘佳钰, 姚海红, 陈庆平, 贾园, 苏茵 . 显微镜下多血管炎合并自身免疫性溶血性贫血的临床特点及治疗转归[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2015, 47(4): 657-660. |
| [7] | 顿耀军, 于路平, 杜依青, 盛正祚, 王功伟, 李雪, 杨冰, 徐涛, 黄晓波, 王晓峰. IgG4相关性腹膜后纤维化5例临床特征及文献回顾[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2015, 47(4): 622-627. |
| [8] | 朱一丹, 魏建荣, 黄露, 王绍华, 田寒梅, 郭新彪. 不同大气污染程度地区学龄儿童呼吸系统疾病及症状发生的比较[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2015, 47(3): 395-399. |
| [9] | 王琳琳, 杨娜, 袁悦, 任爱国. 人叶酸受体自身抗体IgG酶联免疫吸附试验检测方法的建立及评价[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2014, 46(3): 483-487. |
| [10] | 张颖健, 赵金霞, 刘蕊, 刘湘源. 肺受累的IgG4相关硬化性疾病1例[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2012, 44(2): 311-315. |
| [11] | 石宇红, 李茹 , 陈适 , 苏茵 , 贾园. 91例混合性结缔组织病患者的临床特点及转归[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2012, 44(2): 270-274. |
| [12] | 王欣, 邓芙蓉, 吕海波, 吴少伟, 郭新彪. 北京市大气污染对成人呼吸系统症状发生的长期影响 [J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2011, 43(3): 356-359. |
| [13] | 李珺, 曲贞, 张宜苗, 于峰, 黄婧, 杨瑞, 赵明辉, 刘刚. 检测血、尿IgG4在特发性膜性肾病中的临床意义[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2010, 42(6): 671-674. |
| [14] | 冯向辉, 徐莉, 孟焕新, 张立, 陈智滨, 释栋. 慢性牙周炎患者抗伴放线放线杆菌IgG滴度改变的临床意义[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2010, 42(2): 207-210. |
| [15] | 安媛, 张学武, 栗占国. 青年发病的原发性干燥综合征发病形式和临床特点研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2009, 41(3): 324-327. |
|
||