北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2025, Vol. 57 ›› Issue (5): 980-988. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2025.05.025
上颌骨前部和整体顺时针旋转改善骨性Ⅲ类牙颌面畸形患者鼻旁凹陷的对比
- 北京大学口腔医学院·口腔医院口腔颌面外科,国家口腔医学中心,国家口腔疾病临床医学研究中心,口腔生物材料和数字诊疗装备国家工程研究中心,北京 100081
Comparation of anterior maxilla and whole maxilla clockwise rotation to improve paranasal aesthetic defects of skeletal Class Ⅲ maxillofacial deformity
Fengqi SONG, Xinyu XU, Xiaojing LIU, Zili LI*( )
)
- Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Peking University School and Hospital of Stomatology & National Center of Stomatology & National Clinical Research Center for Oral Diseases & National Engineering Research Center of Oral Biomaterials and Digital Medical Devices, Beijing 100081, China
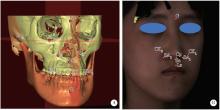
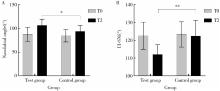
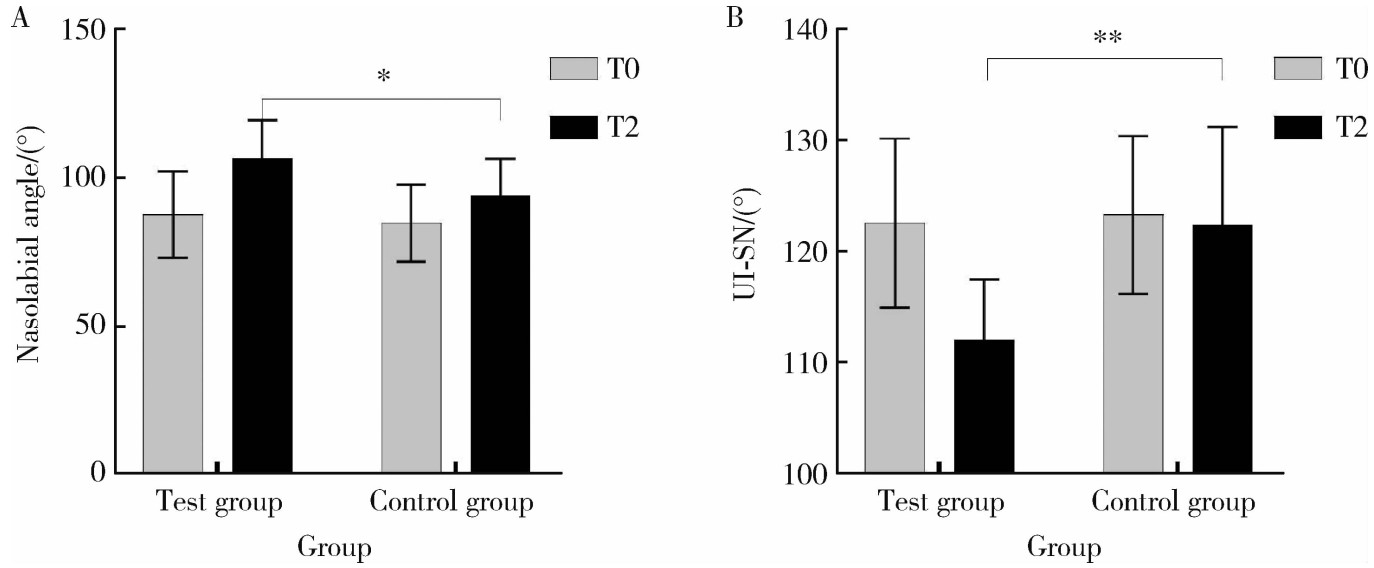
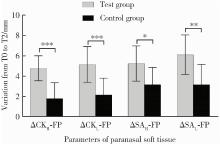
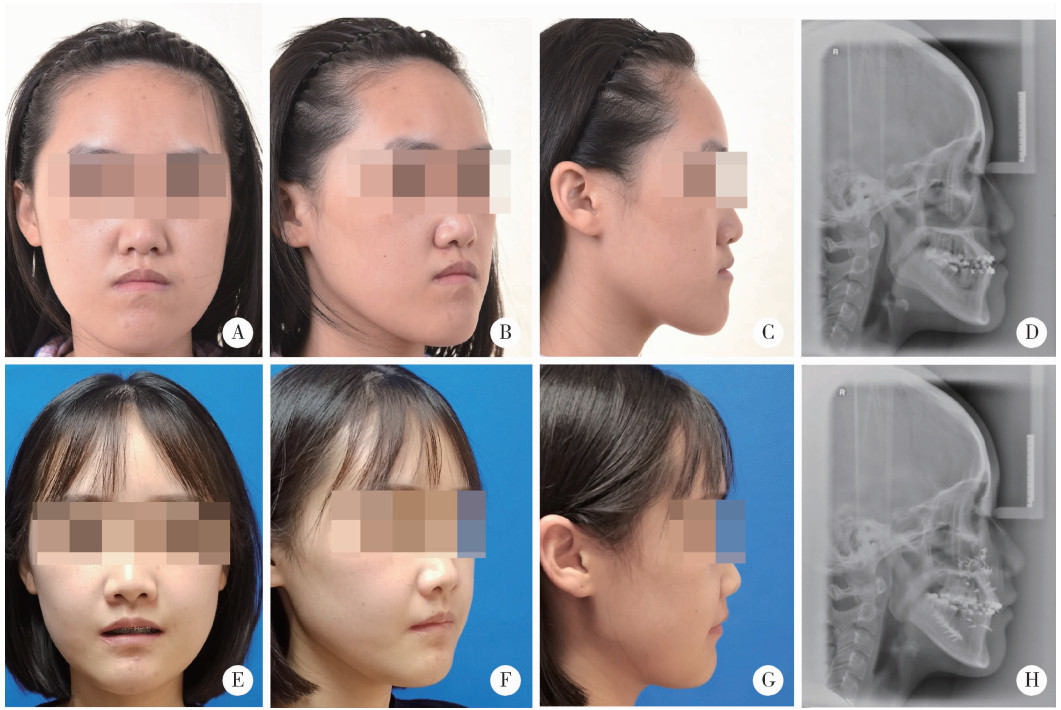
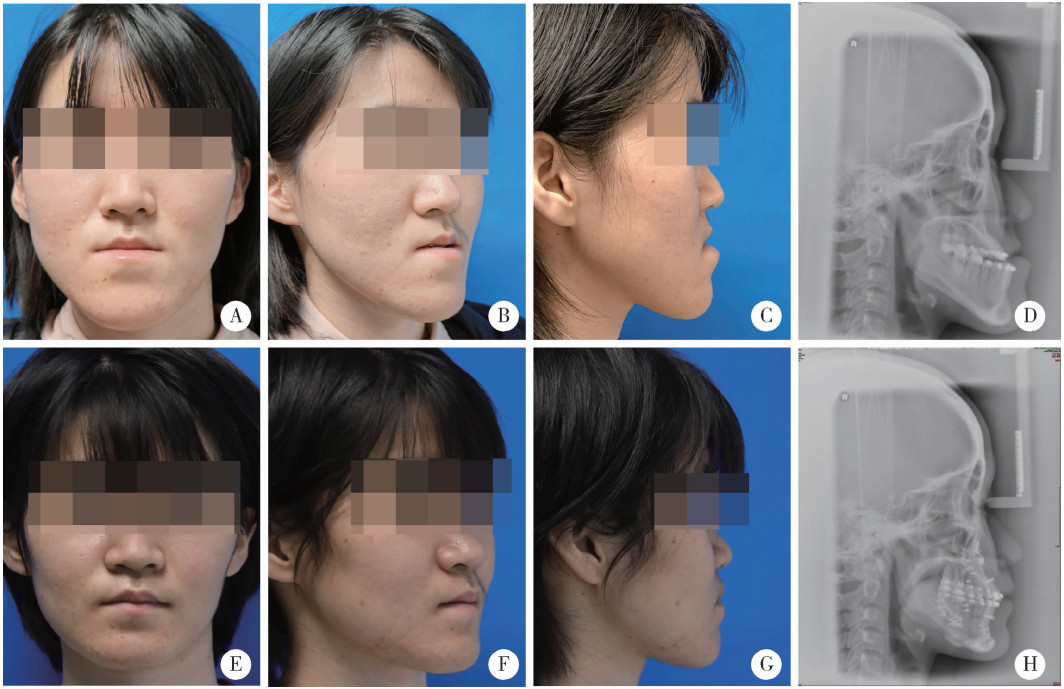
摘要: 目的: 比较上颌骨前部顺时针旋转与整体顺时针旋转两种手术方式改善骨性Ⅲ类牙颌面畸形患者鼻旁凹陷的美学效果,为临床手术方式的选择提供参考依据。方法: 设计非随机临床对照试验,纳入骨性Ⅲ类牙颌面畸形患者21例(试验组11例,对照组10例),试验组采用上颌Le Fort Ⅰ型分块截骨术配合上颌前部顺时针旋转,对照组采用上颌整体顺时针旋转。分别采集术前(T0期)、术后2周(T1期)、术后6个月(T2期)的大视野锥形束CT(cone beam computered tomography, CBCT)和三维面相,进行三维软硬组织测量,测量指标包括颊凸点(cheek mass, CK)和鼻翼基点(subalare, SA)的矢状向位移量、鼻唇角、咬合平面角、上前牙唇倾角等。采用独立样本t检验对比不同时间节点测量指标的组间差异。结果: T0期两组三维头影测量指标的差异无统计学意义,术中试验组上颌平均前徙距离为(-0.71±1.67) mm,明显小于对照组(2.26±1.68) mm,t=-4.052,P<0.05;试验组咬合平面顺时针旋转角度1.46°±2.38°,明显小于对照组4.31°±1.83°,t=-3.047,P<0.05。T0到T2期试验组CK点和SA点的矢状向前移距离分别为(4.96±1.18) mm和(5.19±1.17) mm,对照组分别为(2.01±1.50) mm和(2.69±1.45) mm,组间差异具有统计学意义(P<0.05)。T2期试验组的上前牙唇倾角度为112.15°±5.40°,显著小于对照组122.38°±8.83°(t=-3.237,P<0.05);鼻唇角为106.54°±12.82°,显著大于对照组93.90°±12.46°(t=2.288,P<0.05)。结论: 相较于上颌整体顺时针旋转,上颌Le Fort Ⅰ型分块截骨术后顺时针旋转上颌前部,可以在不改变上颌切牙矢状向位置和咬合平面角的前提下,增大鼻旁区软硬组织的前徙距离,纠正上前牙唇倾及鼻唇角过锐,更好地改善骨性Ⅲ类牙颌面畸形患者的鼻旁美学缺陷。
中图分类号:
- R782.1
| 1 |
|
| 2 |
doi: 10.1016/j.jormas.2019.07.003 |
| 3 |
doi: 10.1093/asj/sjz103 |
| 4 |
doi: 10.2319/072113-529.1 |
| 5 |
doi: 10.1016/j.ajodo.2012.10.014 |
| 6 |
doi: 10.1016/j.jcms.2013.05.004 |
| 7 |
doi: 10.1016/S0889-5406(94)70066-4 |
| 8 |
doi: 10.1016/S0889-5406(94)70051-6 |
| 9 |
林广贤, 宋震, 范飞. 鼻基底填充术矫正鼻翼基底凹陷的临床应用进展[J]. 中国美容整形外科杂志, 2022, 33 (5): 312- 314.
|
| 10 |
王兴. 正颌外科手术学[M]. 济南: 山东科学技术出版社, 1999: 199- 201.
|
| 11 |
doi: 10.1097/00006534-199908000-00009 |
| 12 |
doi: 10.1016/j.ajodo.2015.01.016 |
| 13 |
doi: 10.1016/j.ijom.2011.03.011 |
| 14 |
doi: 10.3390/jcm8122106 |
| 15 |
doi: 10.1016/j.bjps.2015.03.023 |
| 16 |
doi: 10.3390/jcm9010262 |
| 17 |
doi: 10.1016/j.ajodo.2018.09.018 |
| 18 |
doi: 10.1097/PRS.0000000000006248 |
| 19 |
doi: 10.1016/j.ijom.2018.05.002 |
| 20 |
doi: 10.1016/j.ijom.2014.02.007 |
| 21 |
doi: 10.1016/j.joms.2010.07.022 |
| 22 |
doi: 10.1097/PRS.0000000000004988 |
| [1] | 金珉廷,刘怡. 三维颅面水平参考平面的确定方法[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2019, 51(5): 937-943. |
|
||