北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2025, Vol. 57 ›› Issue (5): 989-995. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2025.05.026
姿势性微笑的三维形态学研究
- 北京大学口腔医学院·口腔医院正畸科,国家口腔医学中心,国家口腔疾病临床医学研究中心,口腔生物材料和数字诊疗装备国家工程研究中心,口腔数字医学北京市重点实验室,国家卫生健康委员会口腔医学计算机应用工程技术研究中心,国家药品监督管理局口腔生物材料重点实验室,北京 100081
Three-dimensional morphological analysis of posed smile
Yujia XIAO, Bochun MAO, Yanheng ZHOU*( )
)
- Department of Orthodontics, Peking University School and Hospital of Stomatology & National Center of Stomatology & National Clinical Research Center for Oral Diseases & National Engineering Research Center of Oral Biomaterials and Digital Medical Devices & Beijing Key Laboratory of Digital Stomatology & NHC Research Center of Engineering and Technology for Computerized Dentistry & NMPA Key Laboratory for Dental Materials, Beijing 100081, China
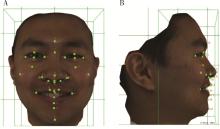
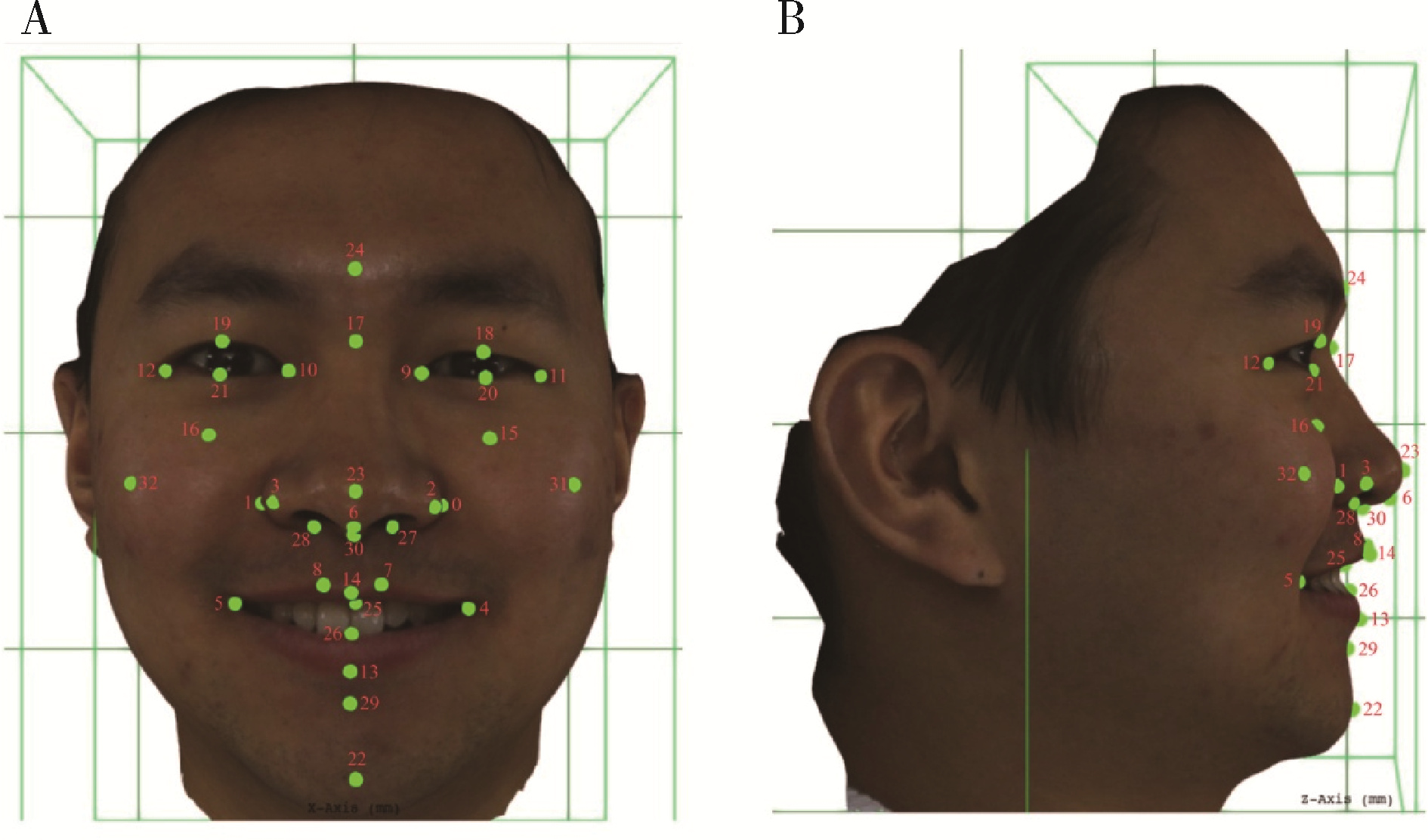
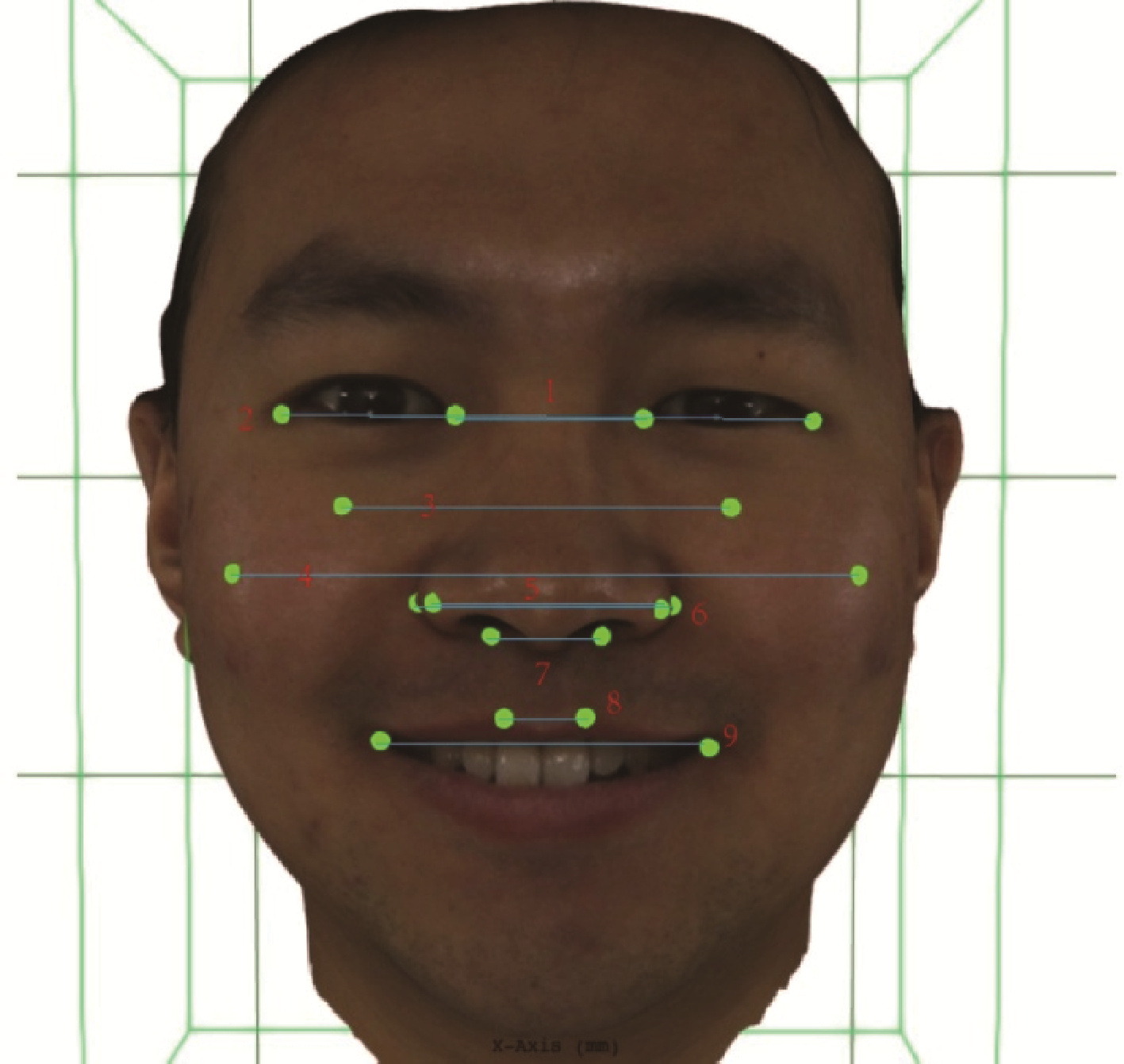
摘要: 目的: 研究姿势性微笑时三维面部软组织变化和对称性,并分析姿势性微笑的性别差异,同时验证姿势性微笑的一致性。方法: 应用光学面部三维扫描设备获取41名成年志愿者每一张休息位和两张姿势位的面部软组织图像,其中男性16人,女性25人,年龄(26.76±2.70)岁。将面部图像数据导入三维分析软件进行模型定位后应用三维可变模型(3-dimensional morphable face model method, 3DMM)标定软组织特征点,选取眼部、面颊部、鼻部及口周测量指标进行软组织分析,比较两种表情状态下的面中下部软组织变化情况和对称性,并分析男女差异,同时对两次姿势性微笑的测量结果进行统计学检验。结果: 与休息位相比,除鼻唇角变化量(1.45°±7.65°)差异无统计学意义外,姿势性微笑时其余软组织测量值均有改变,且眼部区域也有显著变化(P < 0.001)。面下部软组织主要表现为鼻基底变宽,上下唇区域后向运动,颏部前移,唇红变窄变薄,颏唇沟变浅;姿势性微笑时不对称性以口角点[2.78 (1.73,3.49) mm]、眶下中点[2.36 (1.22, 3.27) mm]和外眼角点[2.31(1.29,2.80) mm]最为显著,另外与休息位相比,除口角点和鼻翼基部外不对称性变化差异无统计学意义(P>0.05);姿势性微笑时,男性右眼高和下唇红深度变化量大于女性(P < 0.05),外眼角点和脸颊点的不对称性增加程度较女性大(P < 0.05);两次姿势性微笑的一致性较好。结论: 姿势性微笑时眼部、面颊部、鼻部及口周软组织存在不同程度的变化,且口角和鼻翼基部不对称性较休息位增加;另外,姿势性微笑时面部软组织的一致性较好,可为临床面部微笑美学研究提供参考。
中图分类号:
- R782
| 1 |
doi: 10.1111/ocr.1998.1.1.2 |
| 2 |
|
| 3 |
doi: 10.1016/j.prosdent.2017.04.002 |
| 4 |
doi: 10.1186/s12903-018-0673-5 |
| 5 |
doi: 10.1016/j.cden.2019.12.003 |
| 6 |
doi: 10.1016/j.ijom.2017.08.005 |
| 7 |
doi: 10.1007/s00266-017-1028-3 |
| 8 |
doi: 10.1016/j.jobcr.2021.01.001 |
| 9 |
doi: 10.1111/j.1469-7580.2012.01528.x |
| 10 |
邱淑婷, 朱玉佳, 王时敏, 等. 姿势微笑位口唇对称参考平面的数字化构建及初步应用验证[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54 (1): 193- 199.
doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2022.01.031 |
| 11 |
doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-42533-y |
| 12 |
doi: 10.1196/annals.1280.010 |
| 13 |
|
| 14 |
doi: 10.31729/jnma.7072 |
| 15 |
doi: 10.3390/s20247184 |
| 16 |
doi: 10.1007/s10919-005-0003-x |
| 17 |
doi: 10.3390/s20041199 |
| 18 |
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0244647 |
| 19 |
doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2018.00202 |
| 20 |
doi: 10.1097/SCS.0000000000005969 |
| 21 |
|
| 22 |
doi: 10.1007/s10919-012-0139-4 |
| 23 |
doi: 10.4067/S0717-95022019000100232 |
| 24 |
doi: 10.1097/00006534-198901000-00001 |
| 25 |
doi: 10.1093/asj/sjab152 |
| 26 |
|
| 27 |
doi: 10.2319/062617-425.1 |
| [1] | 陈逸凡,刘中砥,张鹏,黄伟. 严重创伤患者损伤严重度评分的一致性[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(1): 157-160. |
| [2] | 何颖, 郭传瑸, 邓旭亮, 王兴, 王晓霞. 北方正常人群颅颌面三维比例测量及面部对称性分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2015, 47(4): 708-713. |
|
||