北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2018, Vol. 50 ›› Issue (6): 991-997. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2018.06.009
功能锻炼对类风湿关节炎患者效果评价的meta分析
- 北京大学人民医院风湿免疫科, 北京 100044
Effect of functional exercises on patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a meta-analysis
Li WANG,Chao GAO,Di ZHU,Li-hong CHEN( )
)
- Department of Rheumatology and Immunology, Peking University People’s Hospital, Beijing 100044, China
摘要:
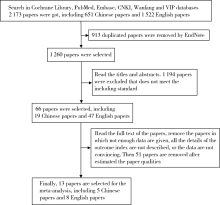
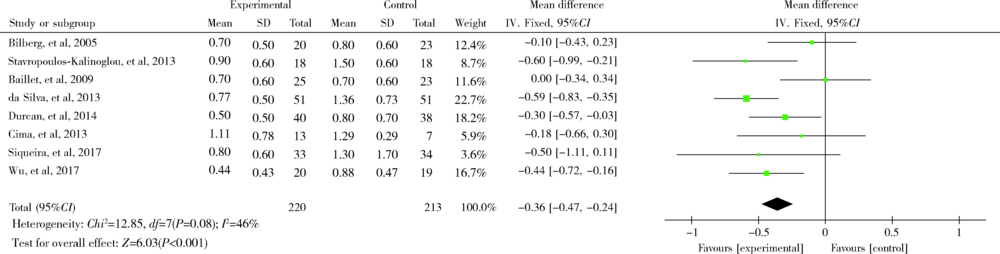
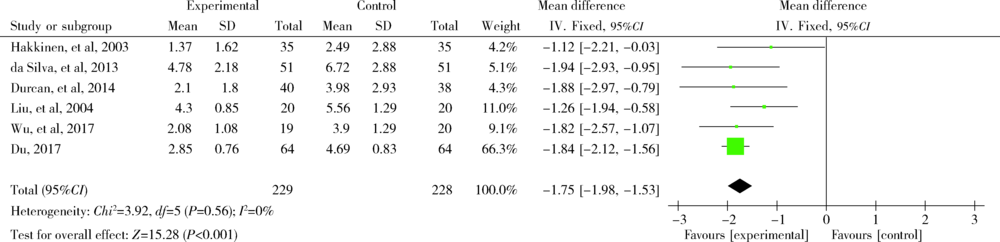
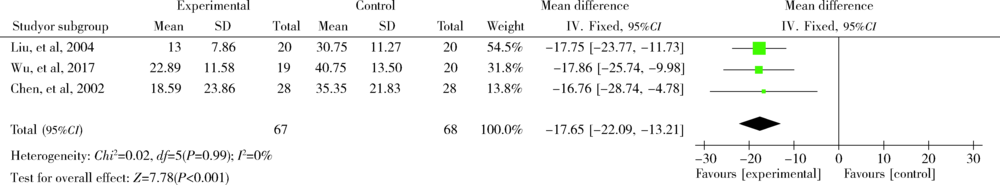
目的: 评价功能锻炼对改善类风湿关节炎(rheumatoid arthritis, RA)患者的疾病活动度、关节功能、生活质量等方面的效果。方法: 计算机检索Cochrane Library、PubMed、中国知网(China National Knowledge Infrastructure,CNKI)、维普、万方数据库中符合标准的随机对照试验(randomized controlled trials,RCTs),根据纳入与排除标准,由两人对上述数据库分别进行文献筛选、提取及文献质量评价后,采用Review Manager 5.3软件对结局指标进行meta分析。结果: 初步检索获得文献2 173篇(英文1 522篇,中文651篇),经过EndNote软件去除重复文献913篇,通过阅读文题和摘要排除不符合纳入标准的文献1 194篇,经过阅读全文、剔除数据不全等最终纳入13篇文献(英文8篇,中文5篇),纳入的总样本数812例,其中实验组426例,常规组386例。13篇文献中5篇文献采用疾病活动评分(disease activity score 28, DAS28)作为其中的结局指标,8篇文献采用健康评定调查表(health assessment questionnaire,HAQ)作为其中的结局指标,6篇文献采用视觉模拟疼痛评分(visual analogue score,VAS)作为其中的结局指标,3篇文献采用晨僵时间作为其中的结局指标。meta分析结果显示,功能锻炼在一定程度上能够缓解RA患者的疾病活动度(mean difference=-0.76;95%CI:-1.13,-0.38;P<0.001),改善患者关节功能(mean difference=-0.36;95%CI:-0.47,-0.24;P<0.001),降低关节疼痛感(mean difference=-1.75;95%CI:-1.98,-1.53;P<0.001)以及减少关节晨僵时间(mean difference=-17.65;95%CI:-22.09,-13.21;P<0.001)。结论: 功能锻炼可以降低RA患者的关节疼痛感,减少晨僵时间,缓解患者病情,对改善关节功能、提高患者生存质量有积极作用。
中图分类号:
- R593.22
| [1] |
Smolen JS, Landewé R, Breedveld FC , et al. EULAR recommendations for the management of rheumatoid arthritis with synthetic and biological disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs[J]. Ann Rheum Dis, 2010,69(6):964-975.
doi: 10.1136/ard.2009.126532 |
| [2] |
McInnes IB, Schett G . Pathogenetic insights from the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis[J]. Lancet, 2017,389(10086):2328-2337.
doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(17)31472-1 pmid: 28612747 |
| [3] |
曾小峰, 朱松林, 谭爱春 , 等. 我国类风湿关节炎疾病负担和生存质量研究的系统评价[J]. 中国循证医学杂志, 2013,13(3):300-307.
doi: 10.7507/1672-2531.20130052 |
| [4] |
周云杉, 王秀茹, 安媛 , 等. 全国多中心类风湿关节炎患者残疾及功能受限情况的调查[J]. 中华风湿病学杂志, 2013,17(8):526-532.
doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1007-7480.2013.08.006 |
| [5] |
王秀丽, 唐玉萍, 孙树萍 , 等. 类风湿关节炎患者功能锻炼现状及影响因素分析[J]. 护理进修杂志, 2016,31(5):442-444.
doi: 10.16821/j.cnki.hsjx.2016.05.020 |
| [6] | 王庆, 徐桂华, 周学平 , 等. 功能锻炼在类风湿关节炎患者康复中的作用研究近况[J]. 风湿病与关节炎, 2013,2(5):46-48. |
| [7] |
风湿免疫疾病慢病管理全国护理协作组. 类风湿关节炎患者的慢病管理专家共识(2014版)[J]. 中华风湿病学杂志, 2016,20(2):127-130.
doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1007-7480.2016.02.013 |
| [8] |
Arnett FC, Edworthy SM, Bloch DA , et al. The American rheumatism association 1987 revised criteria for the classification of rheumatoid arthritis[J]. Arthritis Rheum, 1988,31(3):315-324.
doi: 10.1002/art.1780310302 pmid: 3358796 |
| [9] | Higgins JPT , Green S. Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions version 5.1.0 [EB/OL]. ( 2011 -04-10) (2015-07-05). |
| [10] |
Baillet A, Payraud E, Niderprim VA , et al. A dynamic exercise programme to improve patients’ disability in rheumatoid arthritis: A prospective randomized controlled trial[J]. Rheumatology, 2009,48(4):410-415.
doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/ken511 pmid: 19211654 |
| [11] |
da Silva KN, Teixeira LE, Imoto AM , et al. Effectiveness of sensorimotor training in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a rando-mized controlled trial[J]. Rheumatol Int, 2013,33(9):2269-2275.
doi: 10.1007/s00296-013-2706-3 pmid: 23455663 |
| [12] |
Siqueira US , Orsini Valente LG, de Mello MT, et al. Effectiveness of aquatic exercises in women with rheumatoid arthritis: a rando-mized, controlled, 16-week intervention-the HydRA trial[J]. Am J Phys Med Rehabil, 2017,96(3):167-175.
doi: 10.1097/PHM.0000000000000564 |
| [13] | 陈立红, 杨玉琴, 吴鸥 , 等. 手腕部锻炼对类风湿关节炎手功能恢复的影响[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2002,37(9):668-669. |
| [14] | 刘启华, 王玉玲, 孙美红 , 等. 手腕部关节功能操减轻类风湿关节炎局部症状的观察[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2004,39(7):508-510. |
| [15] |
Cima SR, Barone A, Porto JM , et al. Strengthening exercises to improve hand strength and functionality in rheumatoid arthritis with hand deformities: a randomized, controlled trial[J]. Rheumatol Int, 2013,33(3):725-732.
doi: 10.1007/s00296-012-2447-8 pmid: 22565655 |
| [16] |
张标新, 朱庆云 . 个体化系统锻炼对类风湿关节炎患者活动能力的影响[J]. 护士进修杂志, 2008,23(22):2029-2030.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-6975.2008.22.005 |
| [17] | 杜晓云 . 功能锻炼及个性化运动对类风湿关节炎患者预后及生活质量的影响[J]. 当代护士, 2017(6):31-33. |
| [18] |
吴莉萍, 张子云, 李晓倩 , 等. 活动期类风湿关节炎患者关节功能锻炼的延续护理[J]. 护理学杂志, 2017,32(4):83-85.
doi: 10.3870/j.issn.1001-4152.2017.07.083 |
| [19] |
Durcan L, Wilson F, Cunnane G . The effect of exercise on sleep and fatigue in rheumatoid arthritis: a randomized controlled study[J]. J Rheumatol, 2014,41(10):1966-1973.
doi: 10.3899/jrheum.131282 pmid: 25128510 |
| [20] |
Stavropoulos-Kalinoglou A, Metsios GS , Veldhuijzen van Zanten JJ, et al. Individualised aerobic and resistance exercise training improves cardiorespiratory fitness and reduces cardiovascular risk in patients with rheumatoid arthritis[J]. Ann Rheum Dis, 2013,72(11):1819-1825.
doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2012-202075 pmid: 23155222 |
| [21] |
Häkkinen A, Sokka T, Lietsalmi AM , et al. Effects of dynamic strength training on physical function, Valpar 9 work sample test, and working capacity in patients with recent-onset rheumatoid arthritis[J]. Arthritis Rheum, 2003,49(1):71-77.
doi: 10.1002/art.10902 pmid: 12579596 |
| [22] |
Bilberg A, Ahlmén M, Mannerkorpi K . Moderately intensive exercise in a temperate pool for patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a randomized controlled study[J]. Rheumatology, 2005,44(4):502-508.
doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/keh528 pmid: 15728422 |
| [23] |
Prioreschi A, Makda MA, Tikly M , et al. In patients with established RA, positive effects of a randomised three month WBV therapy intervention on functional ability, bone mineral density and fatigue are sustained for up to six months[J]. PLoS One, 2016,11(4):e0153470.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0153470 pmid: 27073832 |
| [24] |
McKenna S, Tierney M, O’Neill A , et al. Sleep and physical activity: a cross-sectional objective profile of people with rheumatoid arthritis[J]. Rheumatol Int, 2018,38(5):845-853.
doi: 10.1007/s00296-018-4009-1 pmid: 29541902 |
| [25] |
Agca R, Heslinga SC, Rollefstad S , et al. EULAR recommendations for cardiovascular disease risk management in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and other forms of inflammatory joint disorders: 2015/2016 update[J]. Ann Rheum Dis, 2017,76(1):17-28.
doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2016-209775 |
| [26] | 中华医学会风湿病学分会. 2018中国类风湿关节炎诊疗指南[J]. 中华内科杂志, 2018,57(4):242-251. |
| [1] | 刘东武, 陈杰, 高明利, 于静. 类风湿关节炎伴发淋巴结Castleman样病理改变1例[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(5): 928-931. |
| [2] | 黄会娜,赵静,赵祥格,白自然,李霞,王冠. 乳酸对类风湿关节炎患者外周血CD4+T细胞亚群的调控作用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(3): 519-525. |
| [3] | 汤晓菲,李永红,丁秋玲,孙卓,张阳,王育梅,田美伊,刘坚. 类风湿关节炎患者下肢深静脉血栓发病率及危险因素[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(2): 279-283. |
| [4] | 邹雪,白小娟,张丽卿. 艾拉莫德联合托法替布治疗难治性中重度类风湿关节炎的疗效[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(6): 1013-1021. |
| [5] | 吴琦,蔡月明,何娟,黄文蒂,王庆文. 血脂异常与类风湿关节炎肺间质病变的相关性分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(6): 982-992. |
| [6] | 张警丰,金银姬,魏慧,姚中强,赵金霞. 体重指数与类风湿关节炎临床特征的相关性分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(6): 993-999. |
| [7] | 赖金惠,王起,姬家祥,王明瑞,唐鑫伟,许克新,徐涛,胡浩. 新型冠状病毒肺炎疫情期间延迟拔除输尿管支架对泌尿系结石术后患者生活质量和心理状态的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(5): 857-864. |
| [8] | 金银姬,孙琳,赵金霞,刘湘源. 血清IgA型抗鼠科肉瘤病毒癌基因同源物B1抗体在类风湿关节炎中的意义[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(4): 631-635. |
| [9] | 李志华,黄燕波,庞秋颖,于书慧,陈宇珂,李德润. 膀胱阴道瘘修补术后患者生存质量和心理状态调查[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(1): 190-193. |
| [10] | 蔡文心,李仕成,刘一鸣,梁如玉,李静,郭建萍,胡凡磊,孙晓麟,李春,刘栩,叶华,邓立宗,李茹,栗占国. 类风湿关节炎临床分层及其特征的横断面研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(6): 1068-1073. |
| [11] | 程昉,杨邵英,房星星,王璇,赵福涛. CCL28-CCR10通路在类风湿关节炎单核细胞迁移中的作用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(6): 1074-1078. |
| [12] | 刘蕊,赵金霞,闫良. 类风湿关节炎合并下肢静脉血栓患者的临床特点[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(6): 1079-1085. |
| [13] | 张警丰,金银姬,魏慧,姚中强,赵金霞. 类风湿关节炎患者生活质量与疾病活动度的横断面研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(6): 1086-1093. |
| [14] | 高超,陈立红,王莉,姚鸿,黄晓玮,贾语博,刘田. 类风湿关节炎合并纤维肌痛简易分类标准的临床验证[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(2): 278-282. |
| [15] | 娄雪,廖莉,李兴珺,王楠,刘爽,崔若玫,徐健. 类风湿关节炎患者外周血TWEAK基因启动子区甲基化状态及其表达[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(6): 1020-1025. |
|
||