北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2019, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (3): 459-466. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2019.03.013
IgA肾病易感基因遗传多态性的种族差异分析
康玉琦1,2,张月苗1△( ),侯平1,师素芳1,刘立军1,周绪杰1,吕继成1,张宏1
),侯平1,师素芳1,刘立军1,周绪杰1,吕继成1,张宏1
Trans-ethnic analysis of susceptibility variants in IgA nephropathy
Yu-qi KANG1,2,Yue-miao ZHANG1△( ),Ping HOU1,Su-fang SHI1,Li-jun LIU1,Xu-jie ZHOU1,Ji-cheng LV1,Hong ZHANG1
),Ping HOU1,Su-fang SHI1,Li-jun LIU1,Xu-jie ZHOU1,Ji-cheng LV1,Hong ZHANG1
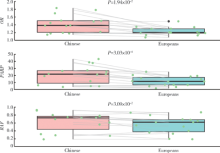
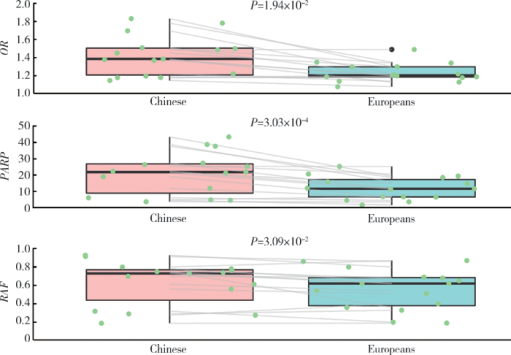
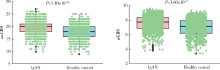
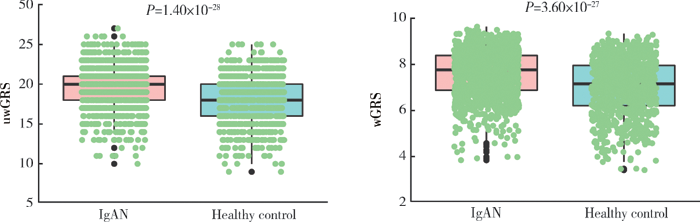
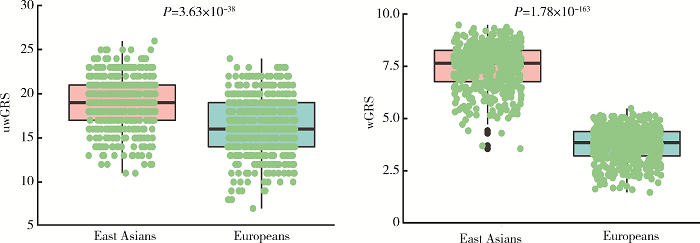
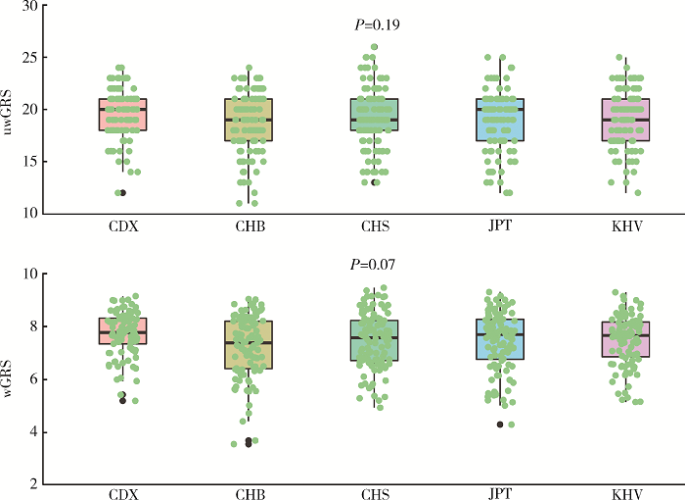
摘要: 目的 在中国和欧洲人群中比较IgA肾病易感基因遗传多态性的种族差异。方法 检索欧洲人群中已报道的IgA肾病易感基因遗传位点,验证其在中国人群(1 194例患者和902例对照)中的关联性,比较两个人群中显著相关位点的危险等位基因型及其基因型频率、效应OR值、人群归因风险百分比之间的差异。利用所有相关位点计算遗传危险度评分,比较其在亚欧人群中的分布,分析其与临床表型的关联。结果 共有11个遗传座位上16个独立相关遗传位点与欧洲人群中IgA肾病的遗传易感性显著相关。93.75%(15/16)欧洲人相关遗传位点在中国人群中得到独立验证(P<0.05),且危险等位基因型在两个人群中一致。与欧洲人群相比,中国人群遗传位点拥有更高的危险等位基因型频率(P=3.09×10 -2)、OR值(P=1.94×10 -2)和人群归因风险百分比(P=3.03×10 -4)。中国人群IgA肾病患者与健康对照、东亚人群与欧洲人群相比遗传危险度评分更高(P值分别为3.60×10 -27和1.78×10 -163),东亚人群和欧洲人群各亚组之间差异无统计学意义。研究人群中IgA肾病遗传危险度评分与血浆IgA1水平、慢性肾脏病(chronic kidney disease,CKD)分期和Hass分级显著相关。 结论 IgA肾病相关易感基因在欧洲人群和中国人群相似,中国人群有更高遗传风险,提示亚洲人群中IgA肾病高患病率具有遗传基础。
中图分类号:
- R692.31
| [1] | Scolari F . Familial IgA nephropathy[J]. J Nephrol, 1999,12(4):213-219. |
| [2] |
Scolari F, Amoroso A, Savoldi S , et al. Familial clustering of IgA nephropathy: further evidence in an Italian population[J]. Am J Kidney Dis, 1999,33(5):857-865.
doi: 10.1016/S0272-6386(99)70417-8 |
| [3] |
Kiryluk K, Li Y, Sanna-Cherchi S , et al. Geographic differences in genetic susceptibility to IgA nephropathy: GWAS replication study and geospatial risk analysis[J]. PLoS Genet, 2012,8(6):e1002765.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1002765 |
| [4] |
Feehally J, Farrall M, Boland A , et al. HLA has strongest association with IgA nephropathy in genome-wide analysis[J]. J Am Soc Nephrol, 2010,21(10):1791-1797.
doi: 10.1681/ASN.2010010076 |
| [5] |
Gharavi AG, Kiryluk K, Choi M , et al. Genome-wide association study identifies susceptibility loci for IgA nephropathy[J]. Nat Genet, 2011,43(4):321-327.
doi: 10.1038/ng.787 |
| [6] |
Yu XQ, Li M, Zhang H , et al. A genome-wide association study in Han Chinese identifies multiple susceptibility loci for IgA nephropathy[J]. Nat Genet, 2012,44(2):178-182.
doi: 10.1038/ng.1047 |
| [7] |
Kiryluk K, Li Y, Scolari F , et al. Discovery of new risk loci for IgA nephropathy implicates genes involved in immunity against intestinal pathogens[J]. Nat Genet, 2014,46(11):1187-1196.
doi: 10.1038/ng.3118 |
| [8] |
Li M, Foo JN, Wang JQ , et al. Identification of new susceptibility loci for IgA nephropathy in Han Chinese[J]. Nat Commun, 2015,6:7270.
doi: 10.1038/ncomms8270 |
| [9] |
Fu J, Festen EA, Wijmenga C . Multi-ethnic studies in complex traits[J]. Hum Mol Genet, 2011,20(R2):R206-R213.
doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddr386 |
| [10] | Cole P , MacMahon B. Attributable risk percent in case-control studies[J]. Br J Prev Soc Med, 1971,25(4):242-244. |
| [11] |
Prahalad S, Conneely KN, Jiang Y , et al. Susceptibility to childhood-onset rheumatoid arthritis: investigation of a weighted genetic risk score that integrates cumulative effects of variants at five genetic loci[J]. Arthritis Rheum, 2013,65(6):1663-1667.
doi: 10.1002/art.37913 |
| [12] |
Karlson EW, Chibnik LB, Kraft P , et al. Cumulative association of 22 genetic variants with seropositive rheumatoid arthritis risk[J]. Ann Rheum Dis, 2010,69(6):1077-1085.
doi: 10.1136/ard.2009.120170 |
| [13] |
Meguid El Nahas A, Bello AK . Chronic kidney disease: the global challenge[J]. Lancet, 2005,365(9456):331-340.
doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(05)70199-9 |
| [14] |
Zhang L, Wang F, Wang L , et al. Prevalence of chronic kidney disease in China: a cross-sectional survey[J]. Lancet, 2012,379(9818):815-822.
doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(12)60033-6 |
| [15] |
Morris DL, Sheng Y, Zhang Y , et al. Genome-wide association meta-analysis in Chinese and European individuals identifies ten new loci associated with systemic lupus erythematosus[J]. Nat Genet, 2016,48(8):940-946.
doi: 10.1038/ng.3603 |
| [16] |
Wang C, Ahlford A, Jarvinen TM , et al. Genes identified in Asian SLE GWASs are also associated with SLE in Caucasian populations[J]. Eur J Hum Genet, 2013,21(9):994-999.
doi: 10.1038/ejhg.2012.277 |
| [17] |
Morris AP, Le TH, Wu H , et al. Trans-ethnic kidney function association study reveals putative causal genes and effects on kidney-specific disease aetiologies[J]. Nat Commun, 2019,10(1):29.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-07867-7 |
| [18] |
Zhao N, Hou P, Lv J , et al. The level of galactose-deficient IgA1 in the sera of patients with IgA nephropathy is associated with di-sease progression[J]. Kidney Int, 2012,82(7):790-796.
doi: 10.1038/ki.2012.197 |
| [19] |
Wyatt RJ, Julian BA . IgA nephropathy[J]. N Engl J Med, 2013,368(25):2402-2414.
doi: 10.1056/NEJMra1206793 |
| [20] |
Zhu L, Zhai YL, Wang FM , et al. Variants in complement factor H and complement factor H-related protein genes, CFHR3 and CFHR1, affect complement activation in IgA nephropathy[J]. J Am Soc Nephrol, 2015,26(5):1195-1204.
doi: 10.1681/ASN.2014010096 |
| [21] |
Zhai YL, Meng SJ, Zhu L , et al. Rare variants in the complement factor H-related protein 5 gene contribute to genetic susceptibility to IgA nephropathy[J]. J Am Soc Nephrol, 2016,27(9):2894-2905.
doi: 10.1681/ASN.2015010012 |
| [22] |
Zhu L, Guo WY, Shi SF , et al. Circulating complement factor H-related protein 5 levels contribute to development and progression of IgA nephropathy[J]. Kidney Int, 2018,94(1):150-158.
doi: 10.1016/j.kint.2018.02.023 |
| [1] | 薛恩慈, 陈曦, 王雪珩, 王斯悦, 王梦莹, 李劲, 秦雪英, 武轶群, 李楠, 李静, 周治波, 朱洪平, 吴涛, 陈大方, 胡永华. 中国人群非综合征型唇裂伴或不伴腭裂的单核苷酸多态性遗传度[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(5): 775-780. |
| [2] | 陈敬,肖伍才,单蕊,宋洁云,刘峥. DRD2基因rs2587552多态性对儿童肥胖干预效果的影响:一项前瞻性、平行对照试验[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(3): 436-441. |
| [3] | 王梓,张军军,左力,王悦,李文歌,程虹,蔡广研,裴华颖,王利华,周绪杰,师素芳,刘立军,吕继成,张宏. 血浆置换治疗新月体型IgA肾病的有效性分析: 多中心队列研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(5): 1038-1046. |
| [4] | 方伟岗,田新霞,解云涛. 基因多态性对中国汉族女性乳腺癌遗传易感性的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(5): 822-828. |
| [5] | 朱小玲,李文静,王宪娥,宋文莉,徐莉,张立,冯向辉,路瑞芳,释栋,孟焕新. 细胞色素B-245α链及胆固醇酯转运蛋白基因多态性与广泛型侵袭性牙周炎易感性的关系[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(1): 18-22. |
| [6] | 刘建,王宪娥,吕达,乔敏,张立,孟焕新,徐莉,毛铭馨. 广泛型侵袭性牙周炎患者牙根形态异常与相关致病基因的关联[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(1): 16-23. |
| [7] | 田艳,朱军. p53 rs1625895基因多态性与弥漫大B细胞淋巴瘤预后相关性分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2019, 51(5): 791-796. |
| [8] | 张杰铌,宋凤岐,周绍楠,郑晖,彭丽颖,张倩,赵望泓,张韬文,李巍然,周治波,林久祥,陈峰. 中国唇腭裂患者Sonic hedgehog信号通路相关单核苷酸多态性的分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2019, 51(3): 556-563. |
| [9] | 王丹丹,甘业华,马绪臣,孟娟红. ADAMTS14基因单核苷酸多态性与汉族女性颞下颌关节骨关节炎的相关性研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2018, 50(2): 279-283. |
| [10] | 刘凯宁,孟焕新,侯建霞. 维生素D受体FokⅠ多态性对牙周组织细胞CYP24A1表达的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2018, 50(1): 13-19. |
| [11] | 刘艳霞,杨雪松,付卫,姚宏伟. 单核苷酸多态性位点rs6983267与溃疡性结肠炎及大肠癌的相关性[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2016, 48(6): 994-999. |
| [12] | 刘滕飞,张婧薇,陈夏欢,冯雪茹,柏中胜,刘梅林. CMTM5基因rs723840单核苷酸多态性与阿司匹林治疗下血小板高反应性的相关性研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2015, 47(6): 905-909. |
| [13] | 池里群, 卢新, 王雷, 刘叔平, 丁楠, 张洪影, 鄂文. 细胞色素P450 3A4基因多态性分子检测指导分娩镇痛舒芬太尼用药[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2015, 47(4): 653-656. |
| [14] | 常亮, 赵楠, 魏媛, 钟粟, 刘平, 乔杰. 单核苷酸多态性微阵列与染色体核型分析的产前诊断意义比较[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2014, 46(5): 676-680. |
| [15] | 岳青, 王红, 张博, 赵凯平. SUMO1基因单核苷酸多态性分析及rs7599810多态性与非综合征型唇/腭裂的关联研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2014, 46(2): 258-263. |
|
||