北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2019, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (6): 1165-1168. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2019.06.033
腺泡状横纹肌肉瘤椎管内转移1例
- 1. 北京大学第三医院 神经外科,北京 100191
2. 北京大学第三医院 病理科,北京 100191
Intraspinal metastasis of alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma: A case report
Guo-zhong LIN,Zhen-yu WANG1,△( ),Bin LIU1,Shao-min YANG2
),Bin LIU1,Shao-min YANG2
- 1. Department of Neurosurgery, Peking University Third Hospital, Beijing 100191, China
2. Department of Pathology, Peking University Third Hospital, Beijing 100191, China
摘要:
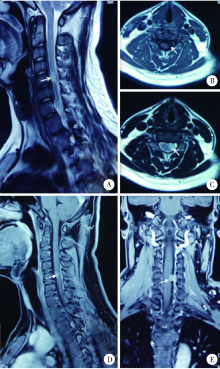
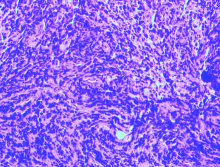
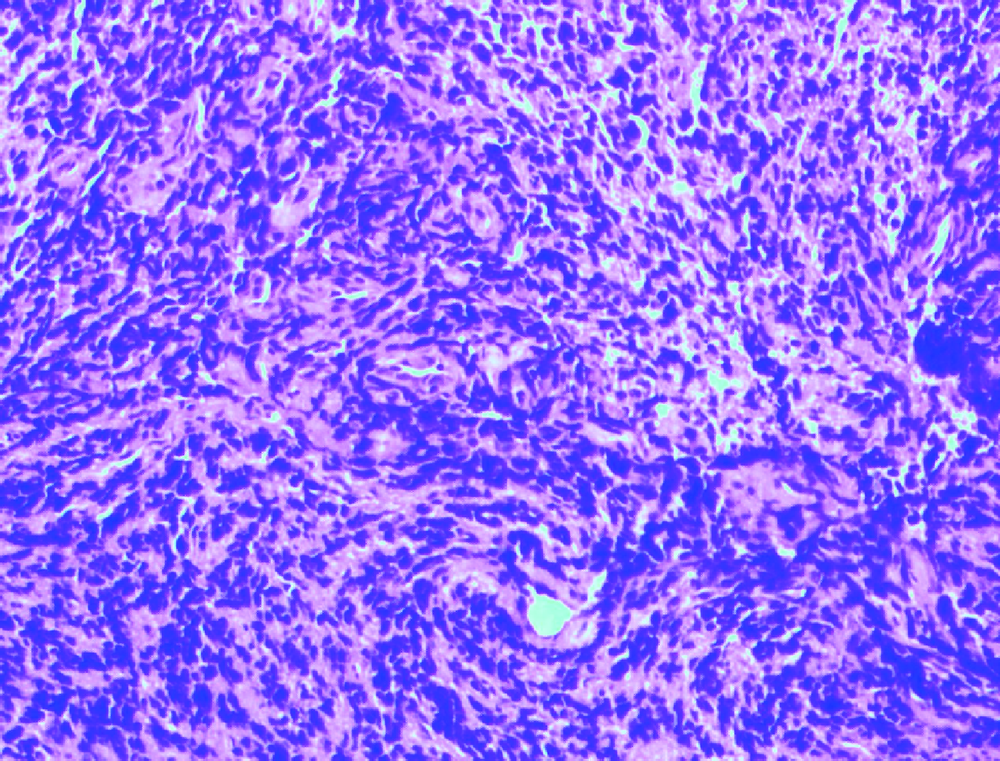
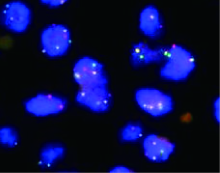
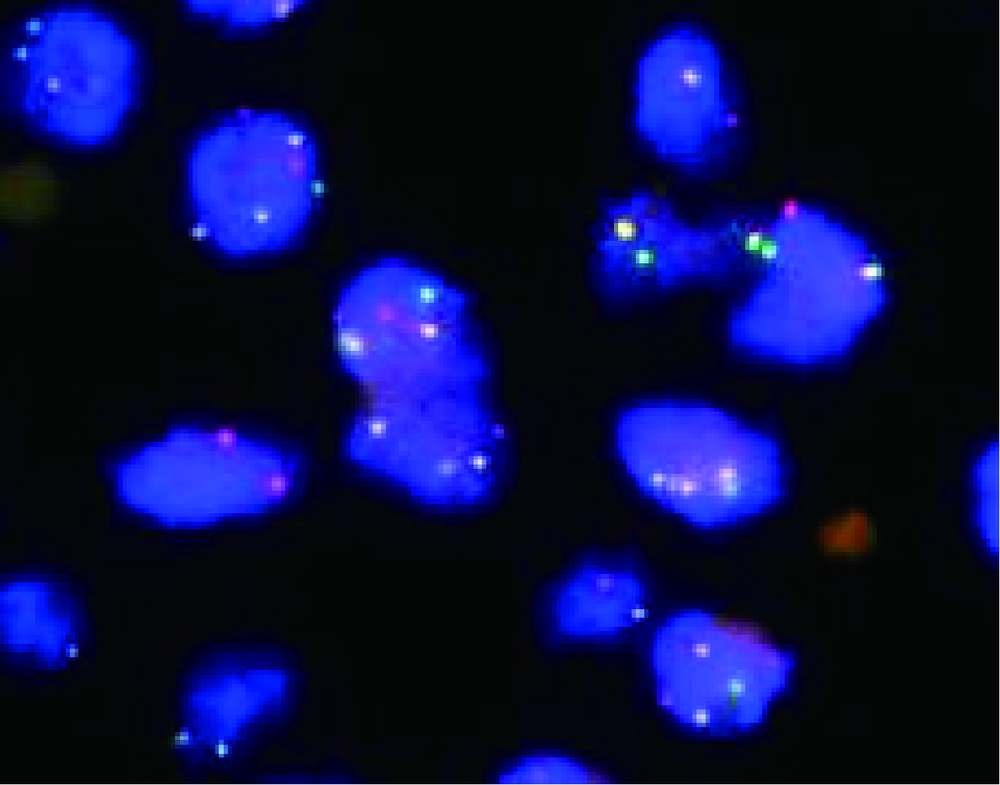
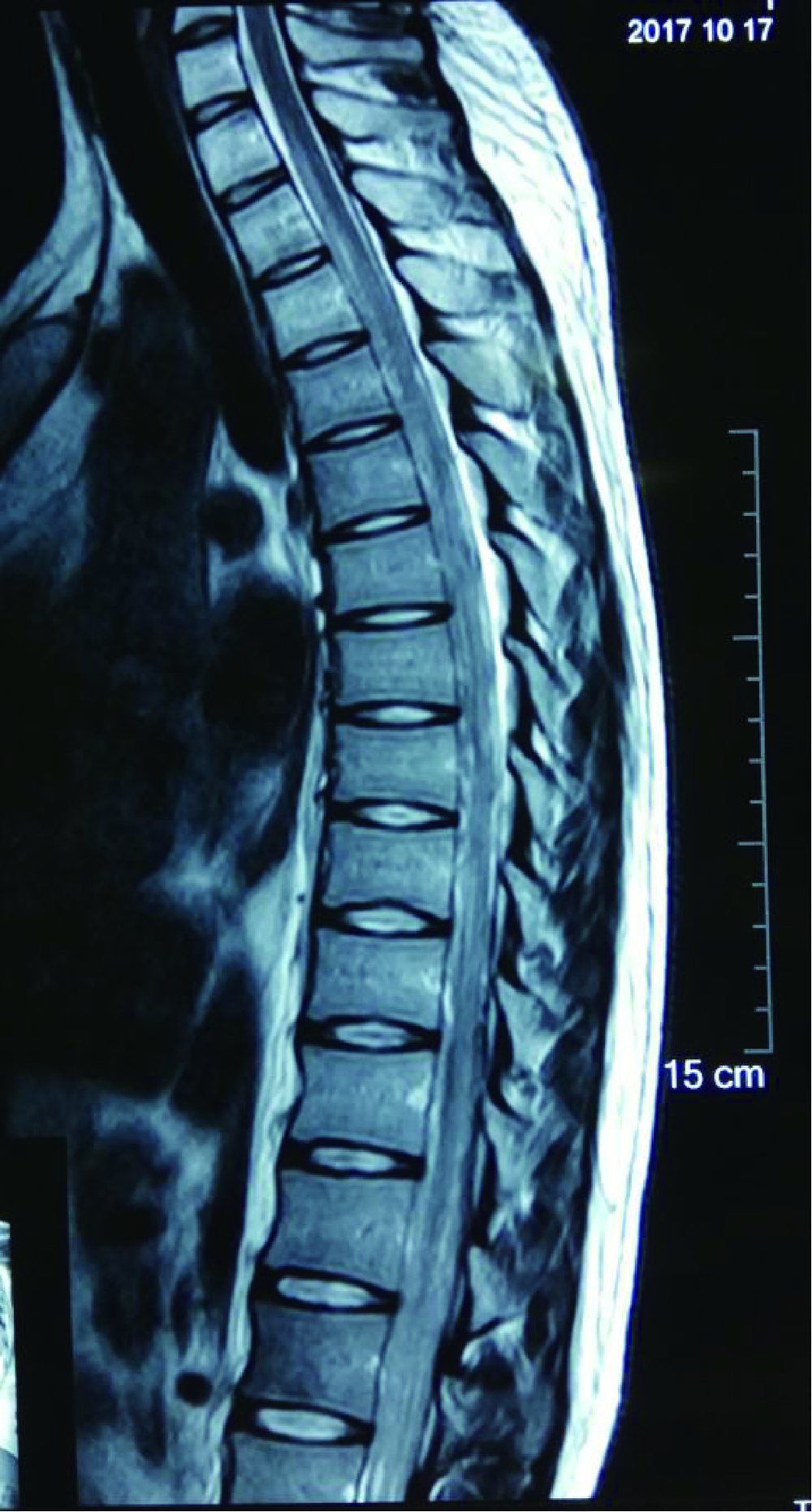
北京大学第三医院神经外科2017年收治1例颈椎管内腺泡状横纹肌肉瘤(alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma,ARMS)转移病例,回顾其临床病理特征,手术治疗、化疗及预后情况,并复习国内外文献报道,对该病的诊断、鉴别诊断以及治疗预后进行综合分析,以提高临床医生对这一罕见疾病的认识。本例患者病情发展快,原发病灶为无痛性包块,1年余出现椎管内转移,有明显的疼痛。给予手术切除,病理诊断为小细胞恶性肿瘤,免疫组织化学Myogenin(+)、MyoD1(+)。FOXO1基因FISH检测阳性,>50%的细胞核显示红绿信号分离,且红绿信号之间的距离大于两个信号点的直径,支持腺泡状横纹肌肉瘤的诊断。全切椎管内肿瘤并术后化疗,但肿瘤药物反应差,病情进展快,迅速出现椎管内播散转移。ARMS少见,侵袭性强,预后不佳,硬膜下转移罕见,临床医生要充分利用现代分子生物学诊断方法,做出正确的诊断和分型,才能有效指导治疗。
中图分类号:
- R739.4
| [1] | Paulino AC, Okcu MF . Rhabdomyosarcoma[J]. Curr Probl Can-cer, 2008,32(1):7-34. |
| [2] | Egas-Bejar D, Huh WW . Rhabdomyosarcoma in adolescent and young adult patients: current perspectives[J]. Adolesc Health Med Ther, 2014,5:115-125. |
| [3] | Parham DM, Barr FG . Classification of rhabdomyosarcoma and its molecular basis[J]. Adv Anat Pathol, 2013,20(6):387-397. |
| [4] | Fletcher CD . The evolving classification of soft tissue tumours:an update based on the new 2013 WHO classification[J]. Histopathology, 2013,64(1):2-11. |
| [5] | Sarkar D, Ray S, Saha M , et al. Alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma with multiple distal metastases. A case report and review of literature[J]. BMJ Case Rep, 2012,2012(968):382. |
| [6] | Eftekhari K, Chambers CB, Goldstein SM , et al. Alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma masquerading as embryonal subtype: the value of modern molecular diagnostic testing[J]. Ophthal Plast Reconstr Surg, 2015,31(2):e43-e45. |
| [7] | La Starza R, Nofrini V, Pierini T , et al. Molecular cytogenetics detect an unbalanced t(2;13)(q36;q14) and PAX3-FOXO1 fusion in rhabdomyosarcoma with mixed embryonal/alveolar features[J]. Pediatr Blood Cancer, 2015,62(12):2238-2241. |
| [8] | Mercado GE, Barr FG . Fusions involving PAX and FOX genes in the molecular pathogenesis of alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma: recent advances[J]. Curr Mol Med, 2007,7(1):47-61. |
| [9] | Sullivan LM, Atkins KA, LeGallo RD . PAX immunoreactivity identifies alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma[J]. Am J Surg Pathol, 2009,33(5):775-780. |
| [1] | 叶剑飞,赵磊,王国良,洪锴,马潞林. 睾丸横纹肌肉瘤的诊治分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(6): 1178-1182. |
|
||