北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2020, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (5): 952-958. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2020.05.027
猪小肠黏膜下层海绵的制备及促成骨作用
- 1.北京大学口腔医学院·口腔医院,修复科 国家口腔疾病临床医学研究中心 口腔数字化医疗技术和材料国家工程实验室 口腔数字医学北京市重点实验室,北京 100081
2.同济大学附属口腔医院修复教研室,上海 200072
Preparation and osteogenic effect study of small intestinal submucosa sponge
Mei WANG1*,Bo-wen LI1*,Si-wen WANG2,Yu-hua LIU1,∆( )
)
- 1. Department of Prosthodontics, Peking University School and Hospital of Stomatology & National Clinical Research Center for Oral Diseases & National Engineering Laboratory for Digital and Material Technology of Stomatology & Beijing Key Laboratory of Digital Stomatology, Beijing 100081, China
2. Department of Prosthodontics, Tongji University School and Hospital of Stomatology, Shanghai 200072, China
摘要:
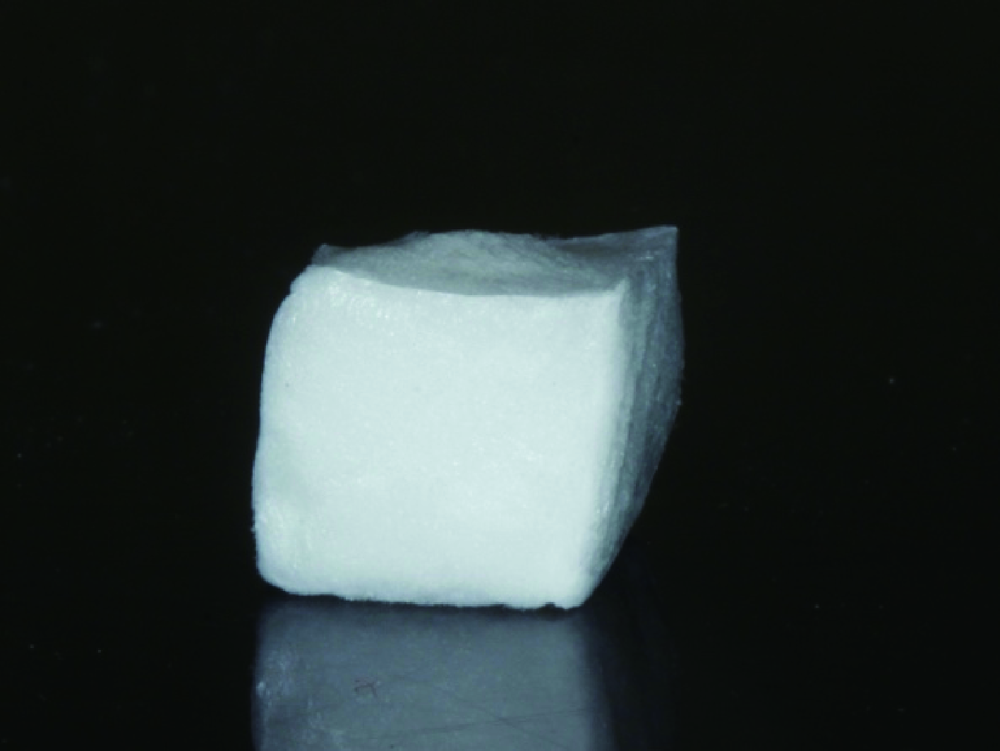
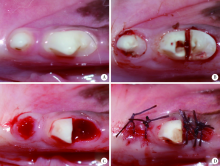
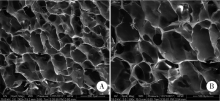
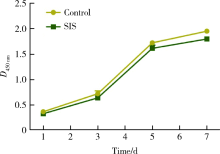
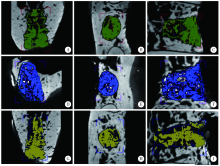
目的:制备并通过体外实验评价一种新型猪小肠黏膜下层(small intestinal submucosa, SIS)海绵的基本性能,建立动物模型评价其体内促成骨能力。方法:采用冷冻干燥法制备SIS海绵,通过环境扫描电镜观察微观结构和孔径大小,比重法检测孔隙率和吸水率,万能力学试验机测试其机械性能,细胞增殖-毒性检测评估其生物相容性。通过建立比格犬动物模型评价其体内促成骨作用,将3只比格犬前磨牙拔牙窝共计18个位点随机分为3组,放置SIS海绵作为SIS海绵组、放置Bio-Oss骨粉并覆盖Bio-Gide膜作为阳性对照组,不做处理作为空白对照组,术后分别于4周和12周取材行微计算机断层扫描技术(micro computed tomography, Micro-CT)检测,采用单因素方差分析法对数据进行统计学分析,以评估SIS海绵的促成骨效果。结果:SIS海绵的平均孔径为(194.90±30.39) μm,孔隙率为92.31%±0.24%,吸水率为771.50%±40.90%,压缩弹性模量为(2.20±0.19) kPa。细胞增殖-毒性检测结果显示SIS海绵不会影响人骨髓间充质干细胞的早期增殖,Micro-CT结果显示术后4周时SIS海绵组骨体积分数(bone volume fraction, BV/TV, 52.81%±3.21%)和阳性对照组(58.30%±9.36%)显著高于空白对照组(38.65%±4.80%,P <0.05),SIS海绵组骨密度[bone mineralized density, BMD, (887.09±61.02) mg/cm3]、阳性对照组[(952.05±132.78) mg/cm3]和空白对照组[(879.29±74.27) mg/cm3] 差异无统计学意义(P >0.05);术后12周时SIS海绵组BV/TV(47.89%±3.59%)显著低于阳性对照组(60.57%±6.56%, P <0.05),与空白对照组(42.99%±2.54%)差异无统计学(P >0.05),SIS海绵组BMD[(1047±89.95) mg/cm3]和阳性对照组[(1101.37±98.85) mg/cm3]显著高于空白对照组[(890.36±79.79) mg/cm3,P <0.05]。结论:SIS海绵具有良好的理化性能和生物相容性,在犬拔牙窝成骨早期(4周)能提高新生BV/TV,在犬拔牙窝成骨后期(12周)可提高新生BMD,具有潜在促成骨应用前景。
中图分类号:
- R783.3
| [1] |
Avilaortiz G, Elangovan S, Kramer KWO, et al. Effect of alveolar ridge preservation after tooth extraction: A systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. J Dent Res, 2014,93(10):950-958.
doi: 10.1177/0022034514541127 |
| [2] |
López M, Fanny, Gómez M, et al. Implants failures related to endodontic treatment. An observational retrospective study[J]. Clin Oral Implant Res, 2015,26(9):992-995.
doi: 10.1111/clr.2015.26.issue-9 |
| [3] |
Horváth A, Mardas N, Mezzomo LA, et al. Alveolar ridge preservation. A systematic review[J]. Clin Oral Investig, 2013,17(2):341-363.
doi: 10.1007/s00784-012-0758-5 pmid: 22814758 |
| [4] |
Bose S, Roy M, Bandyopadhyay A. Recent advances in bone tissue engineering scaffolds[J]. Trends Biotechnol, 2012,30(10):546-554.
doi: 10.1016/j.tibtech.2012.07.005 |
| [5] | 蒋欣泉. 骨缺损修复生物材料与骨再生[J]. 中华口腔医学杂志, 2017,52(10):600-604. |
| [6] |
Andrée B, Bär A, Haverich A, et al. Small intestinal submucosa segments as matrix for tissue engineering: review[J]. Tissue Eng Part B, 2013,19(4):279-291.
doi: 10.1089/ten.teb.2012.0583 |
| [7] |
Nezhad ZM, Poncelet A, Kerchove LD, et al. Small intestinal submucosa extracellular matrix (CorMatrix®) in cardiovascular surgery: A systematic review [J]. Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg, 2016,22(6):839-850.
doi: 10.1093/icvts/ivw020 pmid: 26912574 |
| [8] |
Li M, Zhang C, Mao Y, et al. A cell-engineered small intestinal submucosa-based bone mimetic construct for bone regeneration[J]. Tissue Eng Part A, 2018,24(13):1099-1111.
doi: 10.1089/ten.tea.2017.0407 |
| [9] | 房艳, 倪伟民, 单伟, 等. 海绵状的小肠粘膜下层促进成骨样细胞增殖分化[J]. 中国生物工程杂志, 2013,33(6):18-23. |
| [10] |
Kim KS, Lee J Y, Kang YM, et al. Small intestine submucosa sponge for in vivo support of tissue-engineered bone formation in the presence of rat bone marrow stem cells[J]. Biomaterials, 2010,31(6):1104-1113.
doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2009.10.020 |
| [11] |
Lin X, Chen J, Qiu P, et al. Biphasic hierarchical extracellular matrix scaffold for osteochondral defect regeneration[J]. Osteoarthritis Cartilage, 2018,26(3):433-444.
doi: 10.1016/j.joca.2017.12.001 pmid: 29233641 |
| [12] | Cunniffe GM, Díazpayno PJ, Ramey JS, et al. Growth plate extracellular matrix-derived scaffolds for large bone defect healing[J]. Eur Cells Mater, 2017,33(1):130-142. |
| [13] |
Wang W, Zhang X, Chao NN, et al. Preparation and charac-terization of proangiogenic gel derived from small intestinal submucosa[J]. Acta Biomaterialia, 2016,29(1):135-148.
doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2015.10.013 |
| [14] |
Lin X, Robinson M, Petrie T, et al. Small intestinal submucosa-derived extracellular matrix bioscaffold significantly enhances angiogenic factor secretion from human mesenchymal stromal cells[J]. Stem Cell Res Ther, 2015,6(1):164-176.
doi: 10.1186/s13287-015-0165-3 |
| [15] |
Kim MS, Hong KD, Shin HW, et al. Preparation of porcine small intestinal submucosa sponge and their application as a wound dressing in full-thickness skin defect of rat[J]. Int J Biol Macromol, 2005,36(1/2):54-60.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2005.03.013 |
| [16] |
Li M, Zhang C, Cheng M, et al. Small intestinal submucosa: A potential osteoconductive and osteoinductive biomaterial for bone tissue engineering[J]. Mater Sci Eng C Biomim Supramol Syst, 2017,75(6):149-156.
doi: 10.1016/j.msec.2017.02.042 |
| [17] |
Dimitriou R, Mataliotakis GI, Calori GM, et al. The role of barrier membranes for guided bone regeneration and restoration of large bone defects: current experimental and clinical evidence[J]. BMC Med, 2012,10(1):81-105.
doi: 10.1186/1741-7015-10-81 |
| [18] |
Rouwkema J, Rivron NC, Blitterswijk CAV. Vascularization in tissue engineering[J]. Trends Biotechnol, 2008,26(8):434-441.
doi: 10.1016/j.tibtech.2008.04.009 |
| [19] |
Bolaños MAC, Buttigieg J, Triana JCB. Development and characterization of a novel porous small intestine submucosa-hydroxyapatite scaffold for bone regeneration[J]. Mater Sci Eng C Biomim Supramol Syst, 2017,72(3):519-525.
doi: 10.1016/j.msec.2016.11.113 |
| [20] | 孙慧哲, 田伟, 曾亮, 等. 猪小肠黏膜下基质海绵的制备[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2016,20(21):3110-3116. |
| [21] |
Sarkar AD, Singhvi N, Shetty JN, et al. The local effect of alendronate with intra-alveolar collagen sponges on post extraction alveolar ridge resorption: A clinical trial[J]. J Oral Maxillofac Surg, 2015,14(2):344-356.
doi: 10.1007/s12663-014-0633-9 |
| [22] |
Gilbert TW, Stewartakers AM, Simmonsbyrd A, et al. Degradation and remodeling of small intestinal submucosa in canine achilles tendon repair[J]. J Bone Joint Surg Am, 2007,89(3):621-630.
doi: 10.2106/JBJS.E.00742 pmid: 17332112 |
| [23] | Wu W, Li B, Liu Y, et al. Effect of multilaminate small intestinal submucosa as a barrier membrane on bone formation in a rabbit mandible defect model[J]. Biomed Res Int, 2018(2):1-11. |
| [24] | Kim JJ, Schwarz F, Song HY, et al. Ridge preservation of extraction sockets with chronic pathology using Bio-Oss Collagen with or without collagen membrane: An experimental study in dogs[J]. Clin Oral Implant Res, 2017(28):727-733. |
| [25] |
Wang F, Li Q, Wang Z. A comparative study of the effect of Bio-Oss® in combination with concentrated growth factors or bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells in canine sinus grafting [J]. J Oral Pathol Med, 2017,46(7):528-536.
doi: 10.1111/jop.12507 pmid: 27682609 |
| [1] | 李榕,陈科龙,王勇,刘云松,周永胜,孙玉春. 骨组织工程支架3D打印系统的建立与支架宏微结构精度的可控性评价[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2019, 51(1): 115-119. |
|
||