北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2022, Vol. 54 ›› Issue (5): 863-873. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2022.05.014
首发精神分裂症肠道微生物多态性与临床症状及血清代谢组学的关联
王雪萍,张于亚楠,卢天兰,卢喆,康哲维,孙瑶瑶,岳伟华*( )
)
- 北京大学第六医院,北京大学精神卫生研究所,国家卫生健康委员会精神卫生学重点实验室(北京大学),国家精神心理疾病临床医学研究中心(北京大学第六医院),北京 100191
Variations in fecal microbiota of first episode schizophrenia associated with clinical assessment and serum metabolomics
Xue-ping WANG,Yu-ya-nan ZHANG,Tian-lan LU,Zhe LU,Zhe-wei KANG,Yao-yao SUN,Wei-hua YUE*( )
)
- Peking University Sixth Hospital, Peking University Institute of Mental Health, NHC Key Laboratory of Mental Health (Peking University), National Clinical Research Center for Mental Disorders (Peking University Sixth Hospital), Beijing 100191, China
摘要:
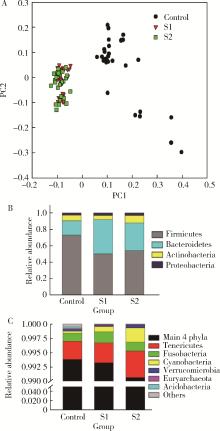
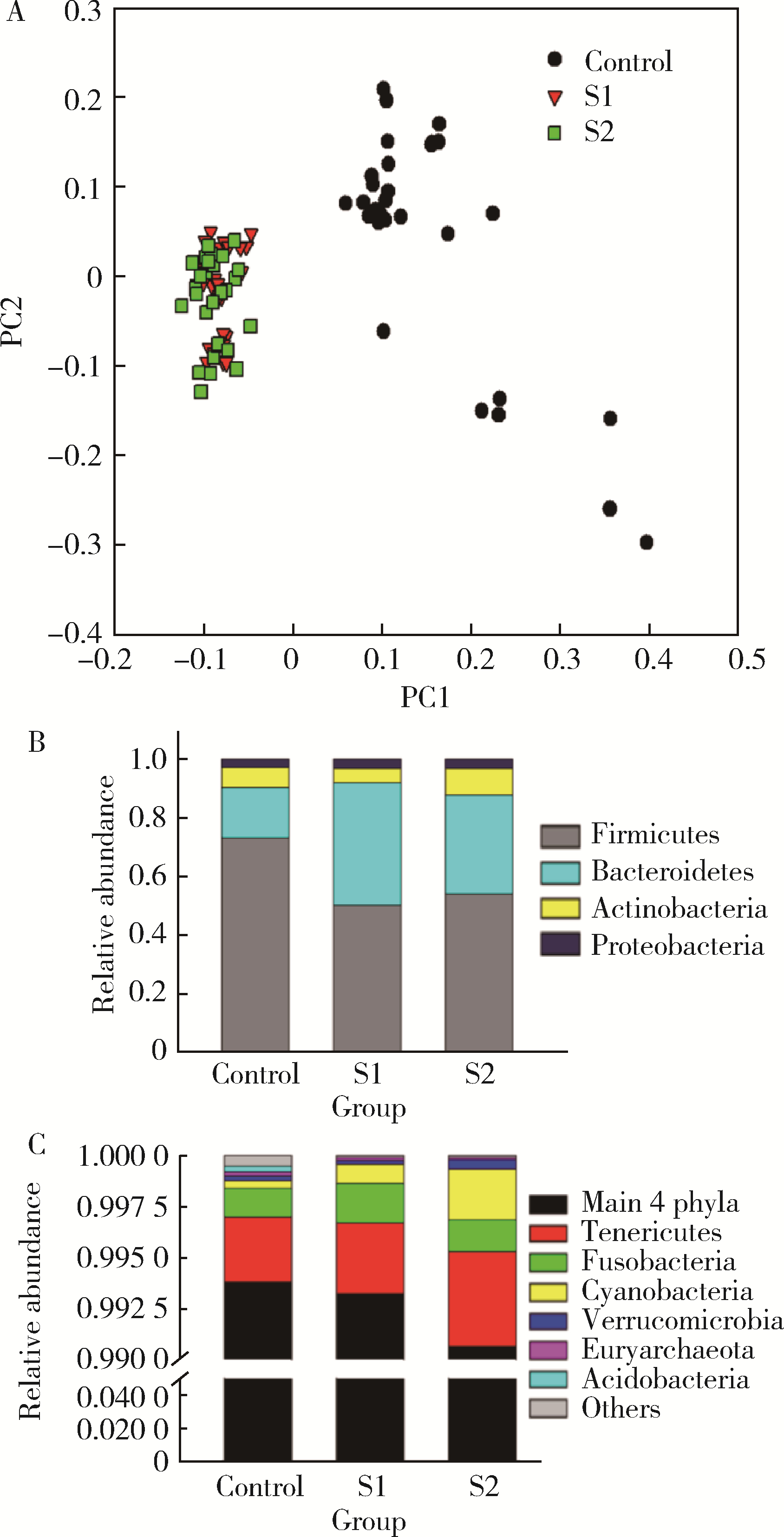
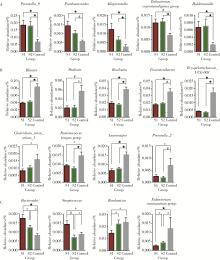
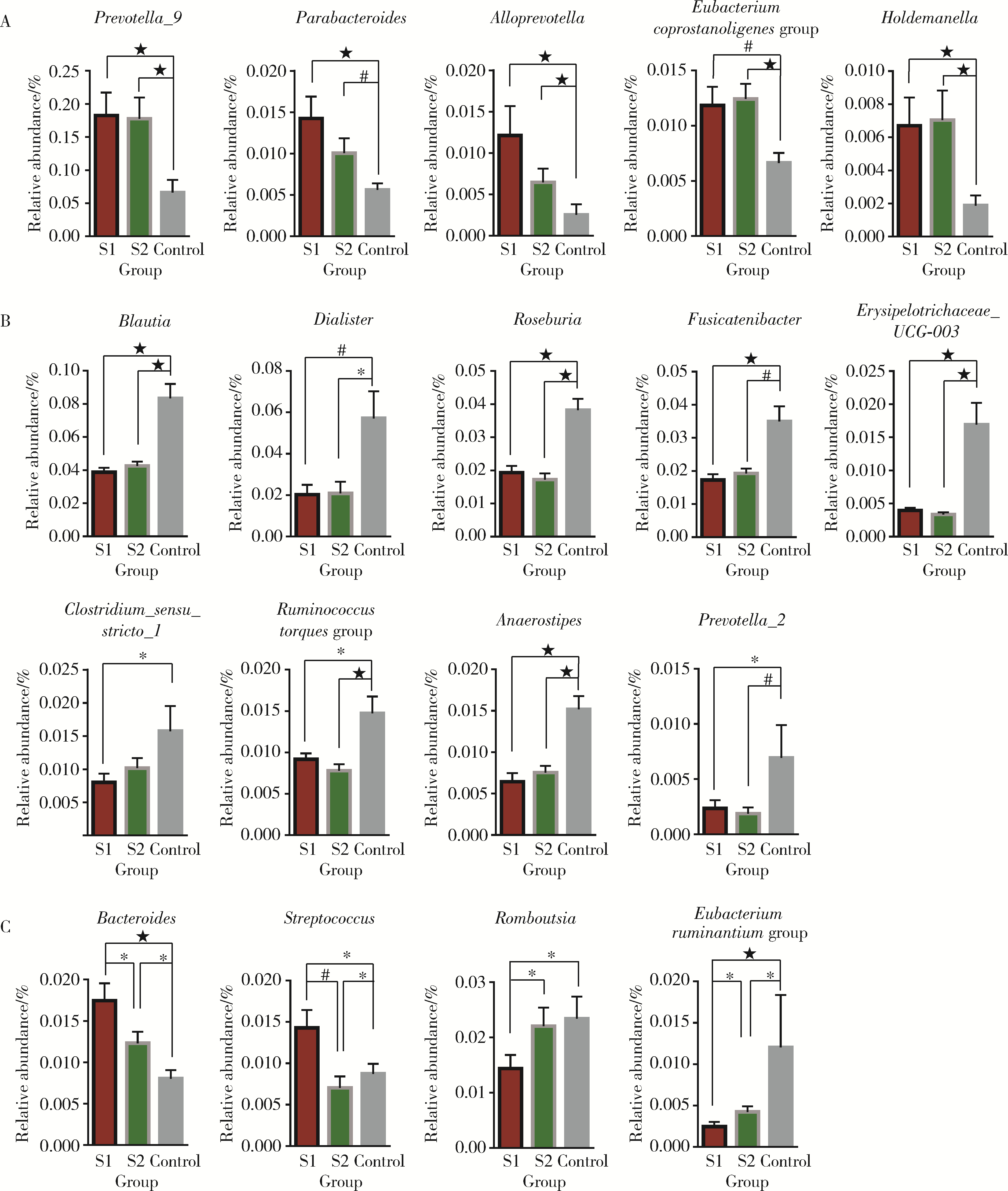
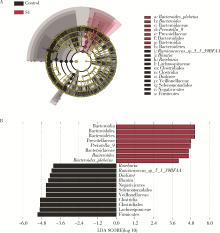
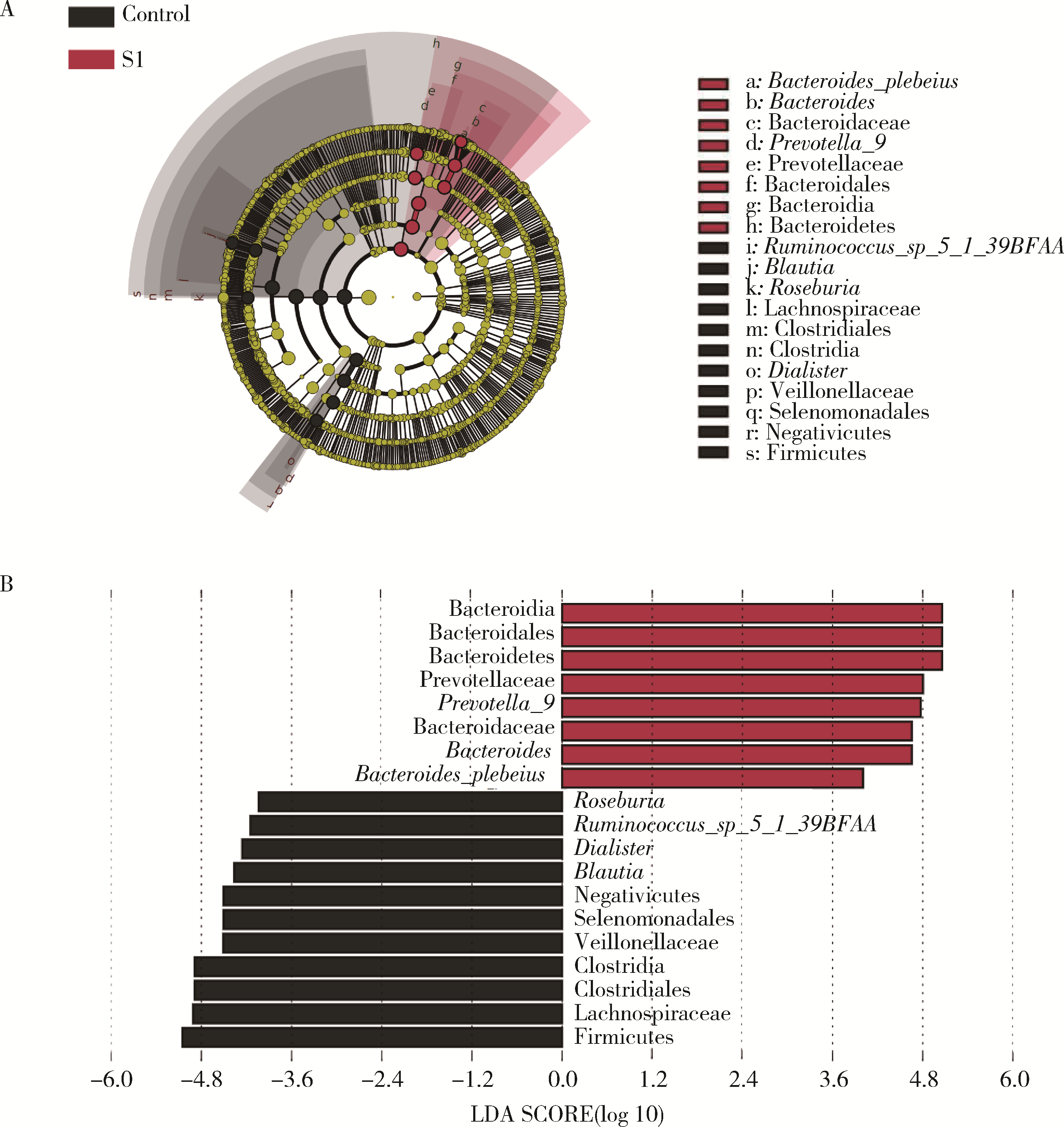
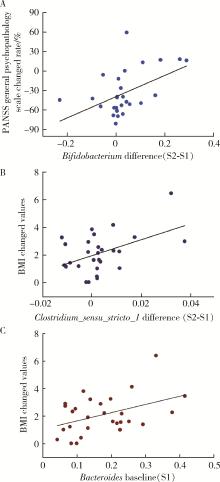
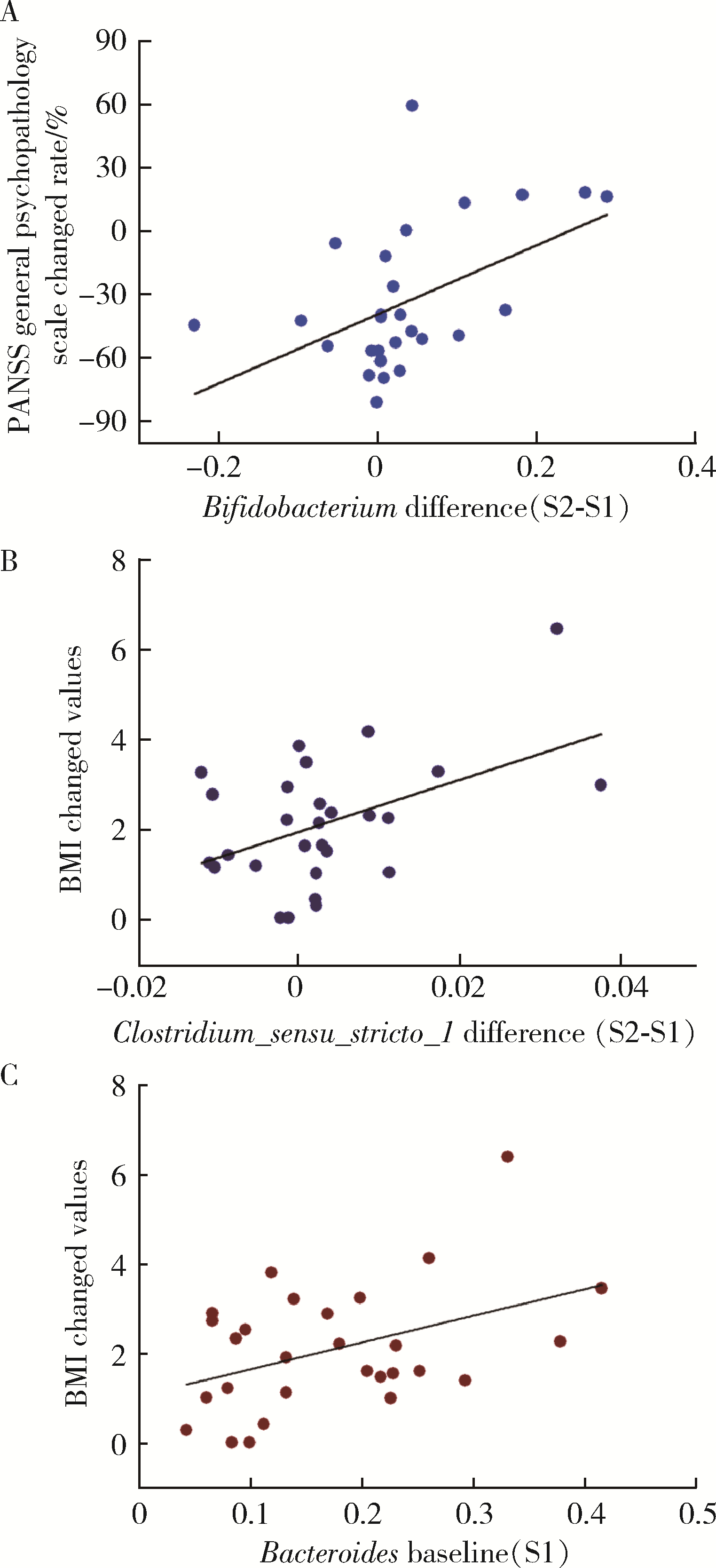
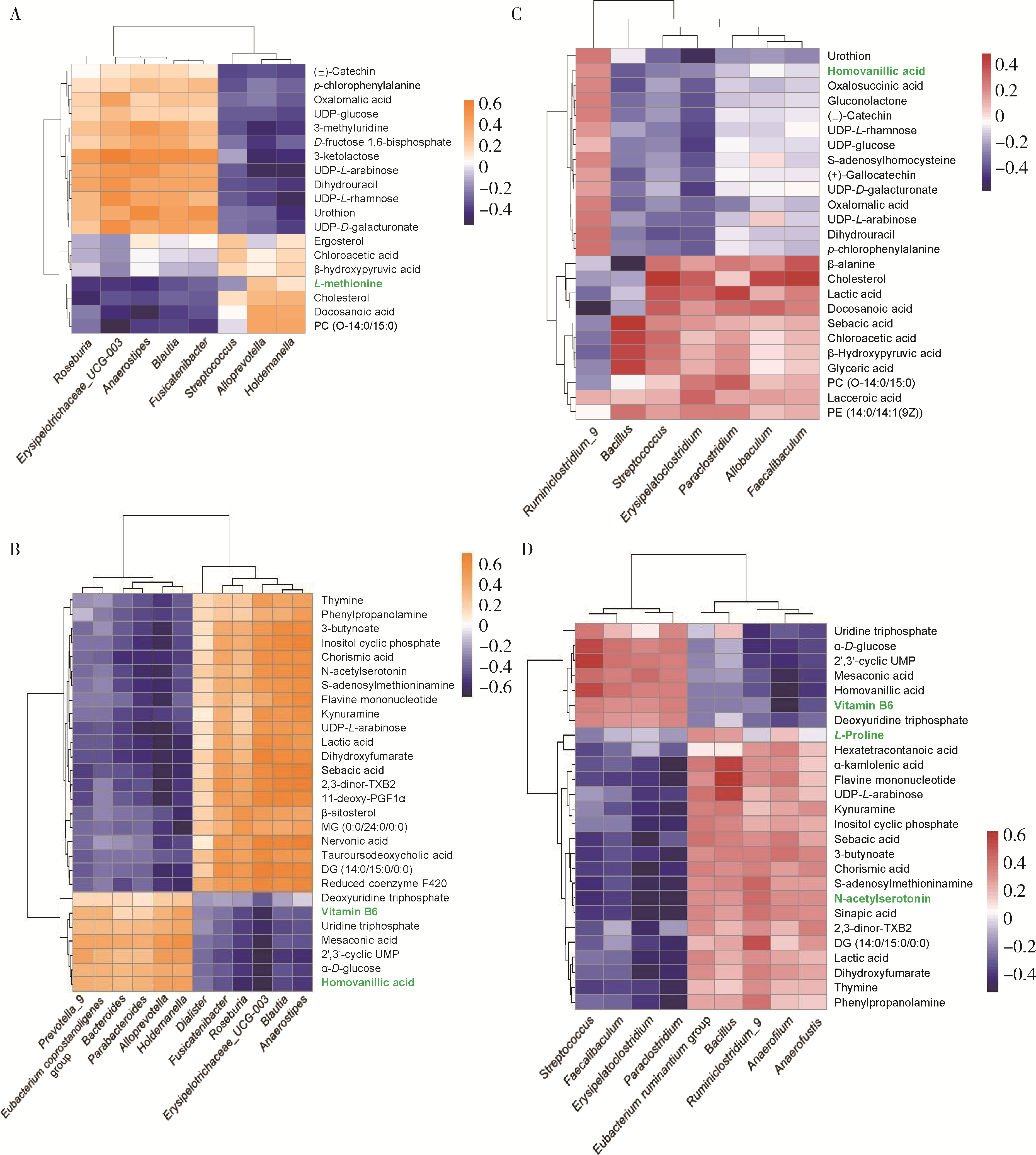
目的: 探索肠道微生物在首发未用药精神分裂症患者与健康对照者间的差异,多维度纵向分析探索抗精神病药物(antipsychotic drugs, APDs)治疗后肠道微生物与临床表型及血清代谢组学的关联。方法: 选择2017年6—12月于北京大学第六医院门诊就诊的28例首发未用药的精神分裂症患者(病例组)及同期性别、年龄、受教育程度相匹配的29例健康志愿者(对照组)为研究对象,其中病例组接受了APDs治疗。研究采集病例组入组基线和治疗6周后的粪便和血清样本,并对粪便样本微生物种类和临床症状及血清代谢物进行了检测和分析。结果: 菌群多样性分析发现,病例组alpha多样性指数(chao1、ACE、goods_coverage)低于对照组,并且组间差异有统计学意义,病例组与对照组在beta多样性方面有明显的区分。菌群组成分析结果显示Bacteroides、Streptococcus、Romboutsia、Eubacterium ruminantium group在病例组患者接受治疗前后发生变化,且差异具有统计学意义,这些菌群可能反映了APDs治疗的影响。病例组与对照组相比,有更多的微生物种属发生变化。LEfSe种群丰度差异分析显示Prevotel-la_9和Bacteroides在病例组富集,而Blautia、Dialister、Roseburia在对照组富集。肠道微生物与临床症状的关联分析显示,Bifidobacterium在病例组患者中与PANSS (positive and negative syndrome scale)量表中一般精神病理学症状分量表的减分率呈正相关。体重指数的增加与药物治疗前后Clostridium_sensu_stricto_1的变化呈正相关,与基线Bacteroides也呈正相关。进一步的代谢组学分析显示,某些菌属的差异与特定代谢物,如L-甲硫氨酸、L-脯氨酸、高香草酸、N-乙酰血清素和维生素B6的相关性具有统计学意义。结论: 在精神分裂症患者和正常对照之间存在一些微生物群体特征差异且组间差异具有统计学意义,一些菌种与抗精神病药物疗效相关。结合代谢组学结果分析,提示微生物种群可能在抗精神病药物疗效和血清代谢物之间发挥中介作用,为解析抗精神病药物治疗前后肠道微生物对疾病的影响提供了新的证据。
中图分类号:
- R749.3
| 1 |
Samochowiec J , Misiak B . Gut microbiota and microbiome in schizophrenia[J]. Curr Opin Psychiatry, 2021, 34 (5): 503- 507.
doi: 10.1097/YCO.0000000000000733 |
| 2 |
Eckburg PB , Bik EM , Bernstein CN , et al. Diversity of the human intestinal microbial flora[J]. Science, 2005, 308 (5728): 1635- 1638.
doi: 10.1126/science.1110591 |
| 3 |
Gill SR , Pop M , Deboy RT , et al. Metagenomic analysis of the human distal gut microbiome[J]. Science, 2006, 312 (5778): 1355- 1359.
doi: 10.1126/science.1124234 |
| 4 |
Collins SM , Surette M , Bercik P . The interplay between the intestinal microbiota and the brain[J]. Nat Rev Microbiol, 2012, 10 (11): 735- 742.
doi: 10.1038/nrmicro2876 |
| 5 |
Kanji S , Fonseka TM , Marshe VS , et al. The microbiome-gut-brain axis: Implications for schizophrenia and antipsychotic induced weight gain[J]. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci, 2018, 268 (1): 3- 15.
doi: 10.1007/s00406-017-0820-z |
| 6 |
Arneth BM . Gut-brain axis biochemical signalling from the gastrointestinal tract to the central nervous system: gut dysbiosis and altered brain function[J]. Postgrad Med J, 2018, 94 (1114): 446- 452.
doi: 10.1136/postgradmedj-2017-135424 |
| 7 |
Thaker GK , Carpenter WT . Advances in schizophrenia[J]. Nat Med, 2001, 7 (6): 667- 671.
doi: 10.1038/89040 |
| 8 | He Y, Kosciolek T, Tang J, et al. Gut microbiome and magnetic resonance spectroscopy study of subjects at ultra-high risk for psychosis may support the membrane hypothesis[J/OL]. Eur Psychiatry, 2018, 53: 37-45(2018-06-02)[2022-06-01]. https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0924-9338(18)30106-8. |
| 9 | Ma X, Asif H, Dai L, et al. Alteration of the gut microbiome in first-episode drug-naive and chronic medicated schizophrenia correlate with regional brain volumes[J/OL]. J Psychiatr Res, 2020, 123: 136-144(2020-02-08)[2022-06-01]. https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0022-3956(19)31162-8. |
| 10 | Nguyen TT, Kosciolek T, Maldonado Y, et al. Differences in gut microbiome composition between persons with chronic schizophrenia and healthy comparison subjects[J/OL]. Schizophr Res, 2019, 204: 23-29(2018-09-26)[2022-06-01]. https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0920-9964(18)30572-3. |
| 11 | Schwarz E, Maukonen J, Hyytiainen T, et al. Analysis of microbiota in first episode psychosis identifies preliminary associations with symptom severity and treatment response[J/OL]. Schizophr Res, 2018, 192: 398-403[2022-06-01]. https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0920-9964(17)30204-9. |
| 12 | Yuan X, Zhang P, Wang Y, et al. Changes in metabolism and microbiota after 24-week risperidone treatment in drug naive, normal weight patients with first episode schizophrenia[J/OL]. Schizophr Res, 2018, 201: 299-306(2018-05-30)[2022-06-01]. https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0920-9964(18)30274-3. |
| 13 |
Nicholson JK , Holmes E , Kinross J , et al. Host-gut microbiota metabolic interactions[J]. Science, 2012, 336 (6086): 1262- 1267.
doi: 10.1126/science.1223813 |
| 14 | Vernocchi P, Chierico F, Putignani L. Gut microbiota profiling: Metabolomics based approach to unravel compounds affecting human health[J/OL]. Front Microbiol, 2016, 7: 1144(2016-07-26)[2022-06-01]. https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fmicb.2016.01144/full |
| 15 | Swann JR , Want EJ , Geier FM , et al. Systemic gut microbial modulation of bile acid metabolism in host tissue compartments[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2011, 108 (Suppl 1): 4523- 4530. |
| 16 |
Zhu F , Guo R , Wang W , et al. Transplantation of microbiota from drug-free patients with schizophrenia causes schizophrenia-like abnormal behaviors and dysregulated kynurenine metabolism in mice[J]. Mol Psychiatry, 2020, 25 (11): 2905- 2918.
doi: 10.1038/s41380-019-0475-4 |
| 17 | Shen Y, Xu J, Li Z, et al. Analysis of gut microbiota diversity and auxiliary diagnosis as a biomarker in patients with schizophrenia: A cross-sectional study[J/OL]. Schizophr Res, 2018, 197: 470-477(2018-01-17)[2022-06-01]. https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0920-9964(18)30002-1. |
| 18 | Reiterer M , Schmidt-Kastner R , Milton SL . Methionine sulfoxide reductase (Msr) dysfunction in human brain disease[J]. Free radical research, 2019, 53 (11/12): 1144- 1154. |
| 19 | Wang L , Alachkar A , Sanathara N , et al. A Methionine-induced animal model of schizophrenia: Face and predictive validity[J]. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol, 2015, 18 (12): 1- 11. |
| 20 |
Crabtree GW , Park AJ , Gordon JA , et al. Cytosolic accumulation of L-proline disrupts GABA-ergic transmission through GAD blockade[J]. Cell Rep, 2016, 17 (2): 570- 582.
doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2016.09.029 |
| 21 |
Ghasemvand F , Omidinia E , Salehi Z , et al. Relationship between polymorphisms in the proline dehydrogenase gene and schizophrenia risk[J]. Genet Mol Res, 2015, 14 (4): 11681- 11691.
doi: 10.4238/2015.October.2.1 |
| 22 |
Clelland CL , Drouet V , Rilett KC , et al. Evidence that COMT genotype and proline interact on negative-symptom outcomes in schizophrenia and bipolar disorder[J]. Transl Psychiatry, 2016, 6 (9): e891.
doi: 10.1038/tp.2016.157 |
| 23 | Pickar D , Breier A , Kelsoe J . Plasma homovanillic acid as an index of central dopaminergic activity: Studies in schizophrenic patients[J]. Ann N Y Acad Sci, 1988, 537 (1): 339- 346. |
| 24 |
Yao JK , Dougherty GG , Reddy RD , et al. Altered interactions of tryptophan metabolites in first-episode neuroleptic-naive patients with schizophrenia[J]. Mol Psychiatry, 2010, 15 (9): 938- 953.
doi: 10.1038/mp.2009.33 |
| 25 |
Firth J , Stubbs B , Sarris J , et al. The effects of vitamin and mineral supplementation on symptoms of schizophrenia: A systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Psychol Med, 2017, 47 (9): 1515- 1527.
doi: 10.1017/S0033291717000022 |
| 26 |
Tomioka Y , Numata S , Kinoshita M , et al. Decreased serum pyridoxal levels in schizophrenia: Meta-analysis and Mendelian randomization analysis[J]. J Psychiatry Neurosci, 2018, 43 (3): 194- 200.
doi: 10.1503/jpn.170053 |
| [1] | 龙仁,毛鑫,高天姿,解倩,谈瀚博,李子寅,韩鸿宾,袁兰. 熊果酸改善精神分裂症小鼠脱髓鞘和脑组织间液引流紊乱[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(3): 487-494. |
| [2] | 任军,杨朵. 提高过继性T细胞免疫治疗临床疗效的新思考----肠道菌群与肿瘤免疫[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2020, 52(2): 204-206. |
| [3] | 白宁,杨凌飞,安丽华,王雯,李昀倩,盛荟,王彤,李华侃,袁兰. 精神分裂症模型鼠腹腔中的中性粒细胞趋化运动的动态可视化分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2018, 50(2): 226-230. |
| [4] | 郑丽娜, 郭茜, 李惠, 李春波, 王继军. 不同重复经颅磁刺激模式对精神分裂症认知功能和精神症状的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2012, 44(5): 732-736. |
| [5] | 韩雪, 杨磊, 程章, 张涛, 原岩波, 于欣. 首次发作精神分裂症患者及独立样本未患病一级亲属的神经认知功能:横断面研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2010, 42(6): 681-686. |
| [6] | 汤宜朗, 王玉凤, 蔡焯基, 周儒伦, 汪冰, 周朝凤. 儿茶酚-○-甲基转移酶基因多态性与精神分裂症发病特点的关系[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2002, 34(4): 342-344. |
|
||