北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2025, Vol. 57 ›› Issue (2): 360-368. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2025.02.022
基于下颌骨数据库和全连接神经网络的三维检索模型辅助下的下颌骨个性化重建
仇师禹1, 练洋2, 康一帆1, 张雷1, 蔡义望2, 单小峰1,*( ), 蔡志刚1,*(
), 蔡志刚1,*( )
)
- 1. 北京大学口腔医学院·口腔医院口腔颌面外科,国家口腔医学中心,国家口腔疾病临床医学研究中心,口腔生物材料和数字诊疗装备国家工程研究中心,口腔数字医学北京市重点实验室,北京 100081
2. 北京百特康科技有限公司,北京 102629
Personalized mandibular reconstruction assisted by three-dimensional retrieval model based on fully connected neural network and a database of mandibles
Shiyu QIU1, Yang LIAN2, Yifan KANG1, Lei ZHANG1, Yiwang CAI2, Xiaofeng SHAN1,*( ), Zhigang CAI1,*(
), Zhigang CAI1,*( )
)
- 1. Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Peking University School and Hospital of Stomatology & National Center for Stomatology & National Clinical Research Center for Oral Diseases & National Engineering Research Center of Oral Biomaterials and Digital Medical Devices & Beijing Key Laboratory of Digital Stomatology, Beijing 100081, China
2. Byte-king Technology, Beijing 102629, China
摘要:
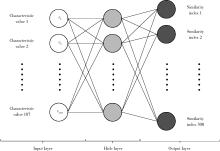
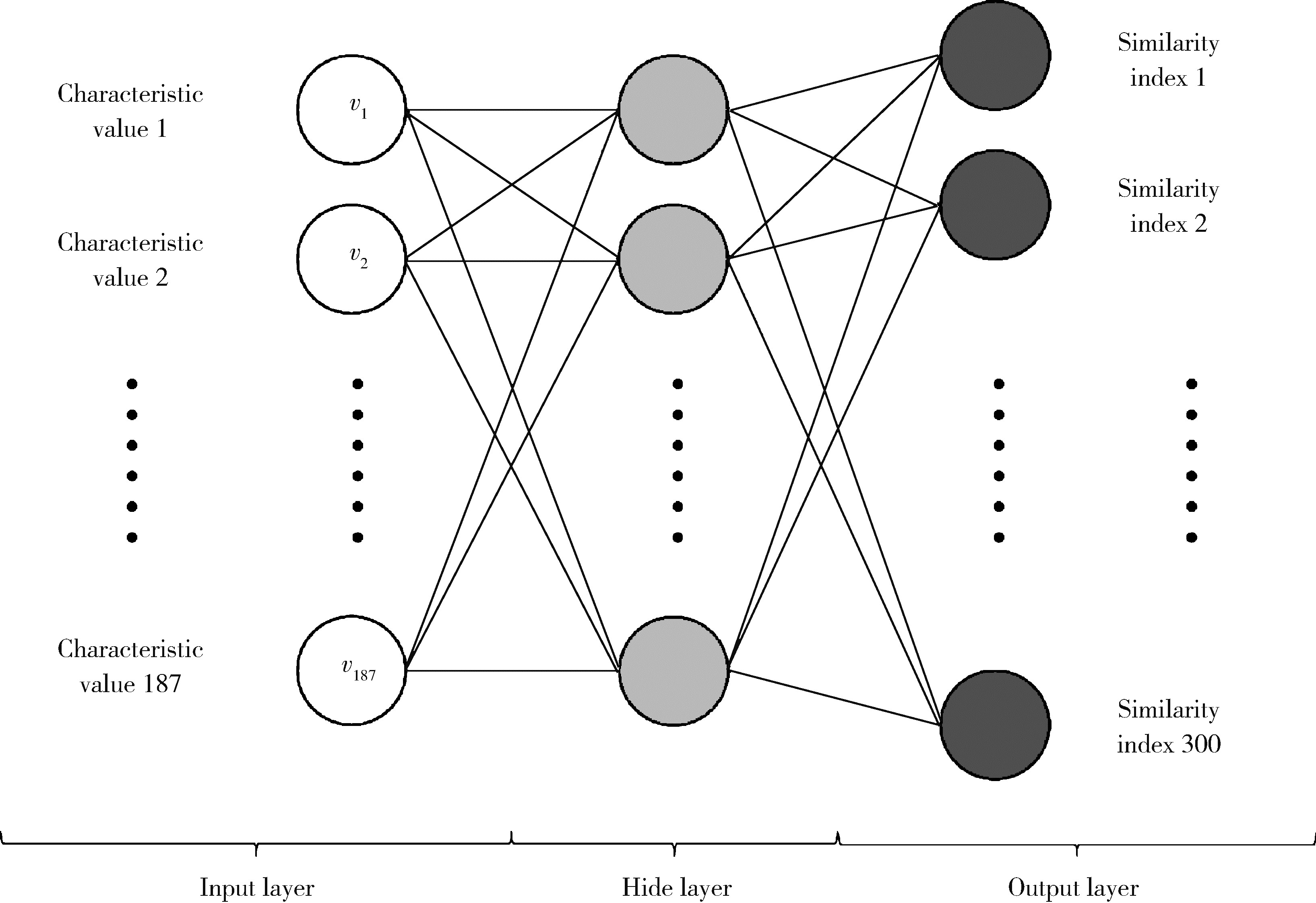
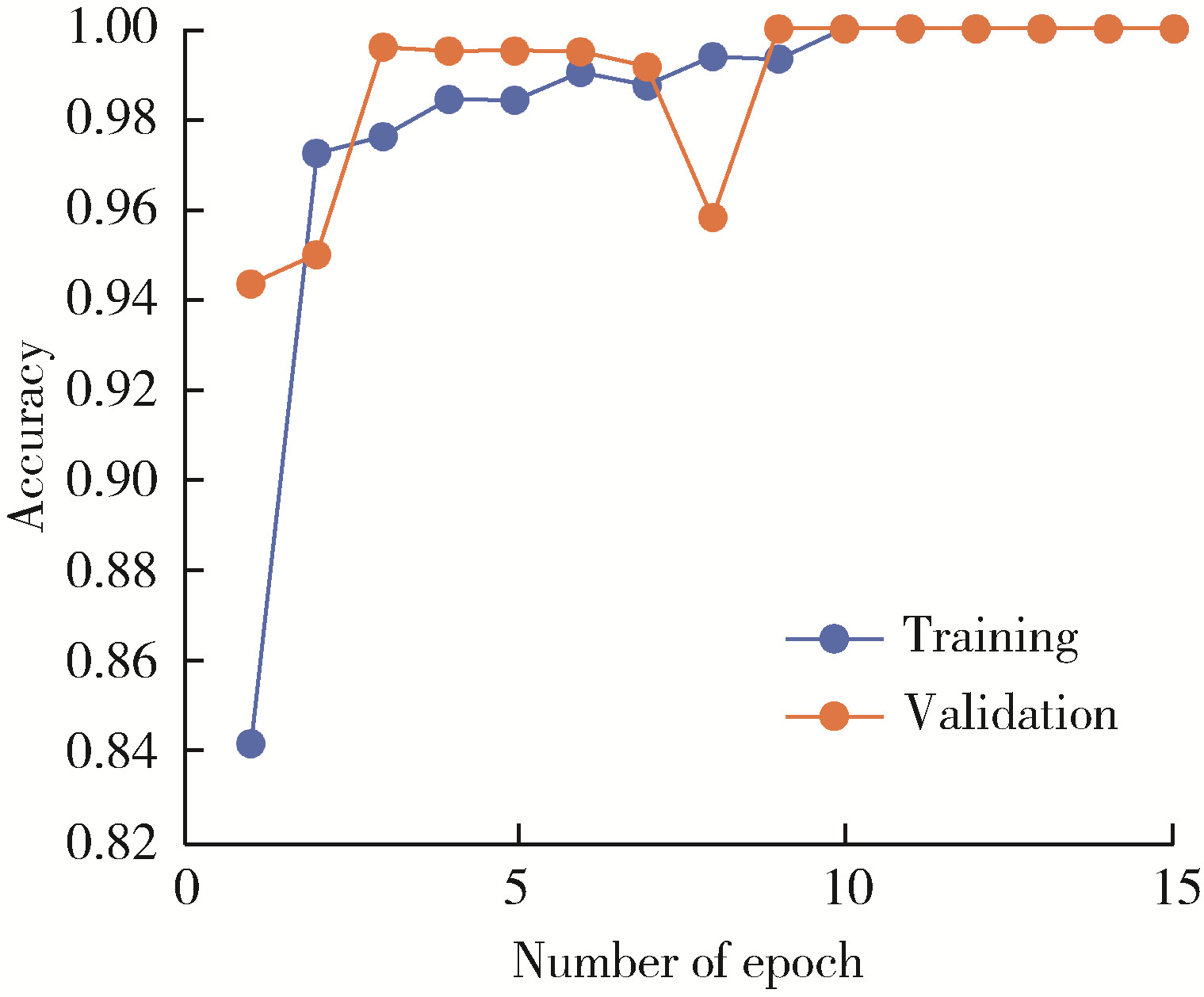
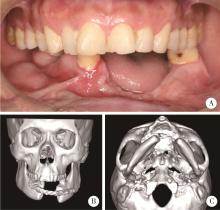
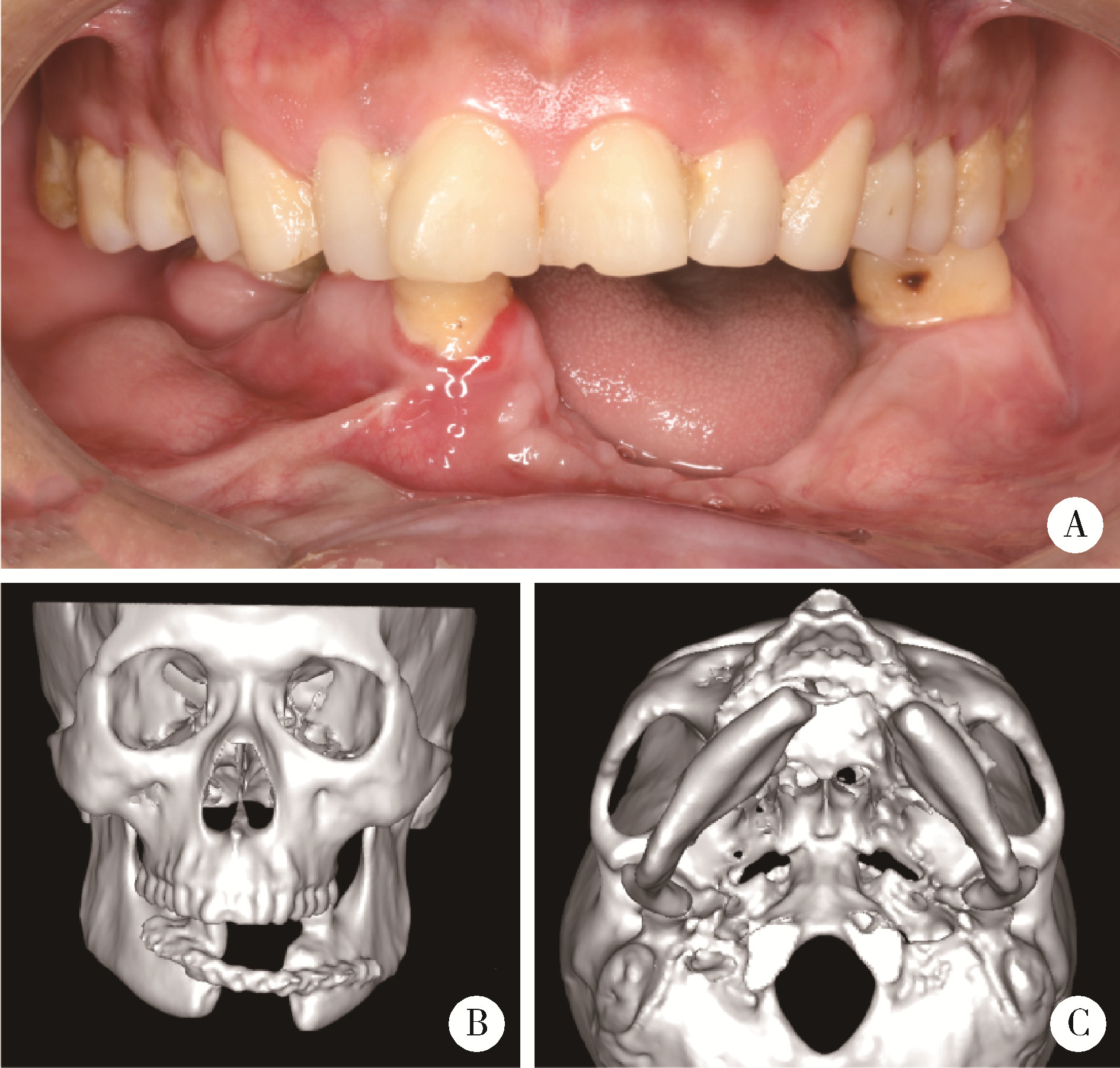
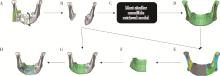
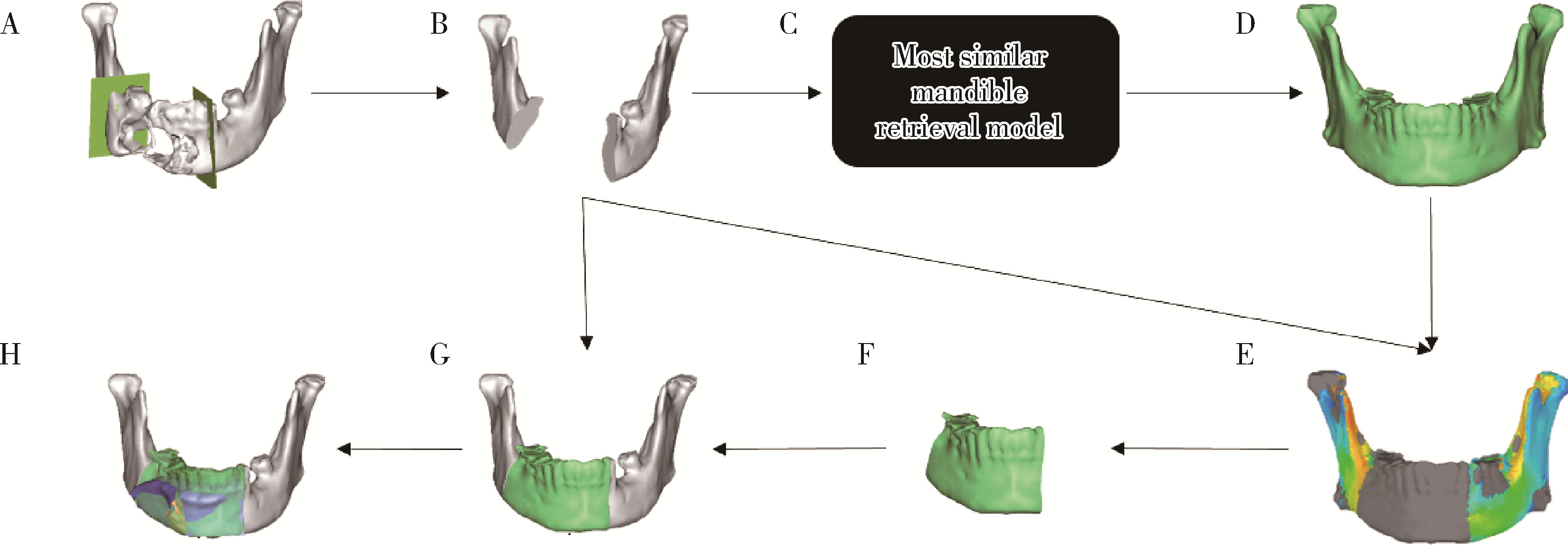
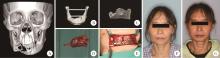
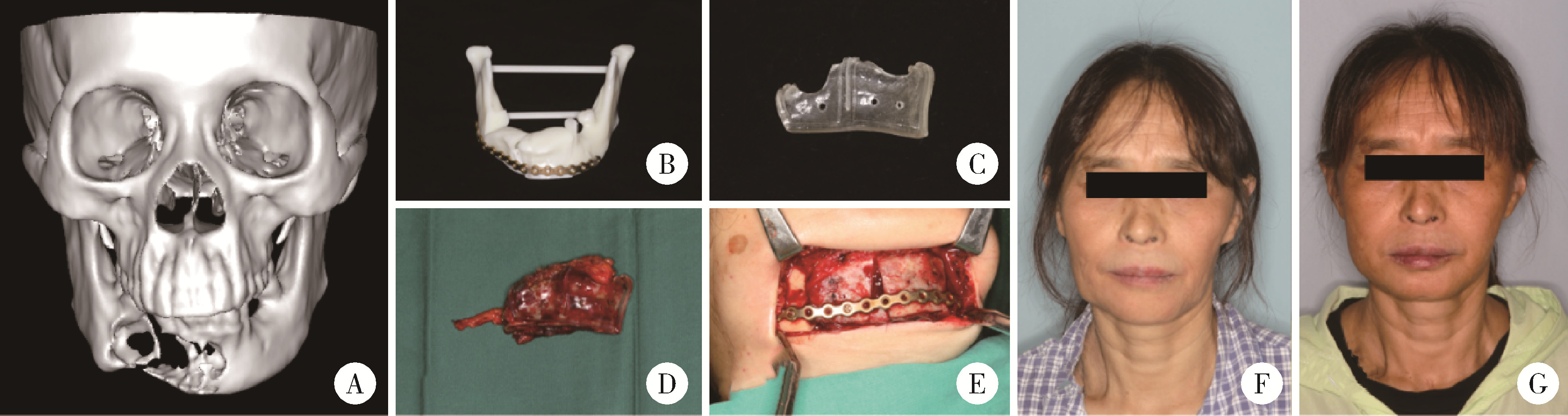
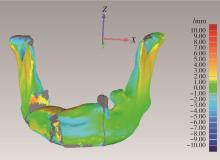
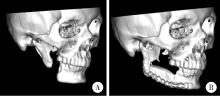
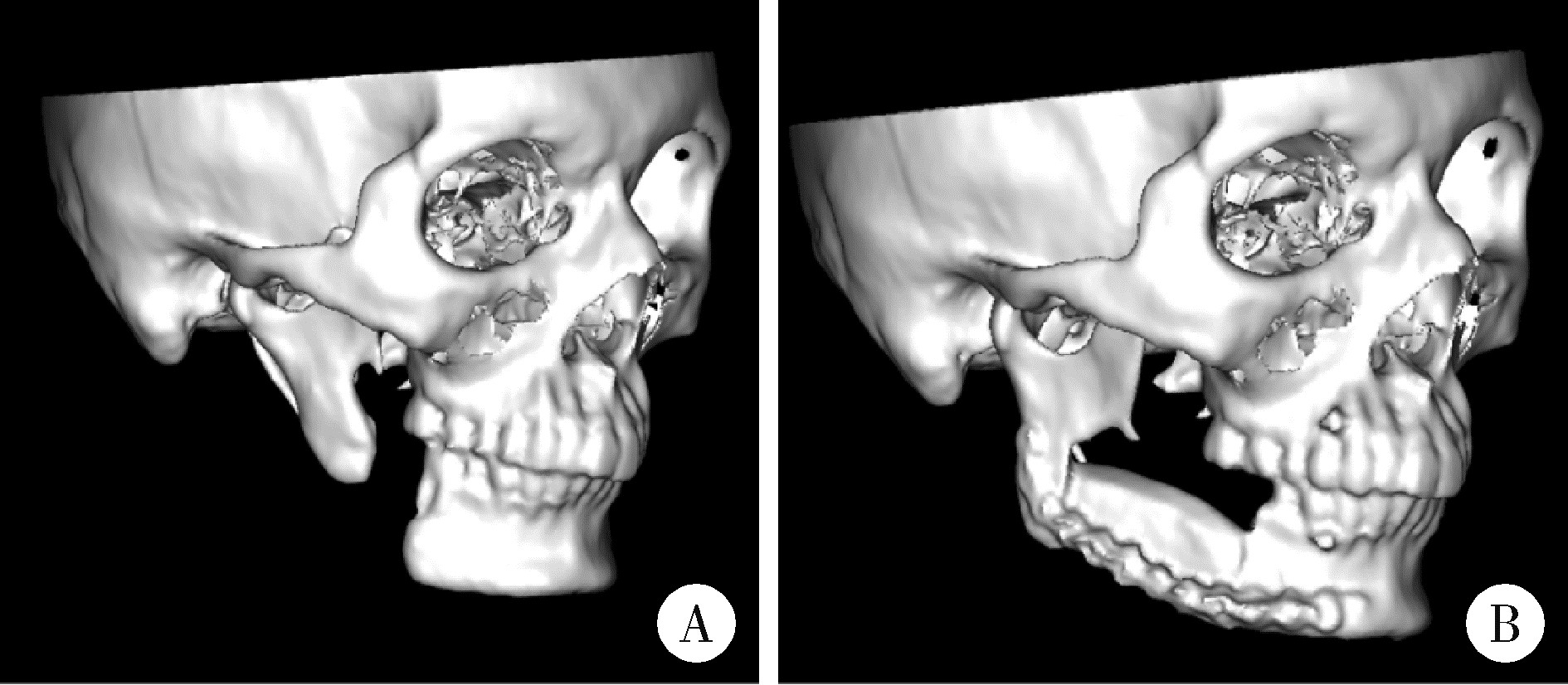
目的: 提出基于下颌骨数据库和全连接神经网络(fully connected neural network,FCNN) 的三维检索模型辅助下的下颌骨个性化重建方案,并验证该方案的临床可行性。方法: 建立一个300例正常中国北方汉族人下颌骨数据库,在头影测量的基础上,进一步筛选稳定性较好的下颌骨标志点,制定下颌骨标志点方案,提取下颌骨几何特征。开发三维检索算法,该算法能从上述数据库中检索出与待匹配下颌骨最相似的下颌骨。搭建FCNN训练上述算法以提高三维检索精度,使用Geomagic Control 2014软件评价基于上述下颌骨数据库和算法的三维检索模型匹配精度。从2019年12月到2021年3月,共有5例患者在北京大学口腔医院颌面外科接受了基于下颌骨数据库和FCNN的三维检索模型辅助下的下颌骨个性化重建手术。通过三维检索算法从上述下颌骨数据库中检索获得最相似下颌骨,使用最相似下颌骨恢复缺损区病变前形态和指导下颌骨重建。5例患者的下颌骨缺损均由髂骨瓣修复,使用个性化手术导板实现术前手术设计的转化和实施。结果: 通过筛选,可重复性和稳定性较高的下颌骨标志点被确定并组成下颌骨标志点方案。经过训练后,基于FCNN的三维检索模型在300例下颌骨数据库中检索获得的最相似下颌骨与待匹配下颌骨的平均偏差为(1.77±0.44) mm,均方根偏差为(2.58±0.86) mm。5例患者的下颌骨重建手术均成功,面部对称性和咬合功能得以恢复,所有患者都对术后外观恢复感到满意。三维比较显示,术后下颌骨与术前设计之间的平均偏差为(0.98±0.17) mm,偏差≤1 mm区域占比61.34%±14.13%,≤2 mm区域占比83.82%±7.35%,≤3 mm区域占比93.94%±2.87%。结论: 基于下颌骨数据库和FCNN的三维检索模型辅助下的下颌骨个性化重建具有临床可行性。
中图分类号:
- R782.1
| 1 |
Kakarala K , Shnayder Y , Tsue TT , et al. Mandibular reconstruction[J]. Oral Oncol, 2018, 77, 111- 117.
doi: 10.1016/j.oraloncology.2017.12.020 |
| 2 |
Hanasono MM , Skoracki RJ . Computer-assisted design and rapid prototype modeling in microvascular mandible reconstruction[J]. Laryngoscope, 2013, 123 (3): 597- 604.
doi: 10.1002/lary.23717 |
| 3 |
Zhang L , Liu Z , Li B , et al. Evaluation of computer-assisted mandibular reconstruction with vascularized fibular flap compared to conventional surgery[J]. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol, 2016, 121 (2): 139- 148.
doi: 10.1016/j.oooo.2015.10.005 |
| 4 | Ren W , Gao L , Li S , et al. Virtual planning and 3D printing modeling for mandibular reconstruction with fibula free flap[J]. Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal, 2018, 98 (33): 2666- 2670. |
| 5 |
Moiduddin K , Al-Ahmari A , Nasr ES , et al. A comparison study on the design of mirror and anatomy reconstruction technique in maxillofacial region[J]. Tech Health Care, 2016, 24 (3): 377- 389.
doi: 10.3233/THC-161136 |
| 6 |
陈全, 蔡志刚, 彭歆, 等. 下颌骨大范围缺损修复重建设计可变形模型的建立[J]. 中华口腔医学杂志, 2014, 49 (7): 414- 419.
doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1002-0098.2014.07.008 |
| 7 | Wang E , Tran KL , D'heygere E , et al. Predicting the premorbid shape of a diseased mandible[J]. Laryngoscope, 2021, 131 (3): E781- E786. |
| 8 | 周子疌, 朱向阳, 韩婧, 等. 基于机器学习的颌骨特征点还原法辅助跨中线颌骨缺损重建[J]. 中国口腔颌面外科杂志, 2020, 18 (4): 323- 327. |
| 9 |
Yao BC , He Y , Jie BM , et al. Reconstruction of bilateral post-traumatic midfacial defects assisted by three-dimensional craniomaxillofacial data in normal chinese people: A preliminary study[J]. J Oral Maxillofac Surg, 2019, 77 (11): 2302. e1- 2302. e13.
doi: 10.1016/j.joms.2019.04.030 |
| 10 | 傅民魁, 林久祥, 周彦恒, 等. 口腔正畸学[M]. 2版 北京: 北京大学医学出版社, 2014: 63- 78. |
| 11 |
Shnayder Y , Lin D , Desai SC , et al. Reconstruction of the lateral mandibular defect: A review and treatment algorithm[J]. JAMA Facial Plast Surg, 2015, 17 (5): 367- 373.
doi: 10.1001/jamafacial.2015.0825 |
| 12 | Cannon TY , Strub GM , Yawn RJ , et al. Oromandibular reconstruction[J]. Clin Anat, 2011, 25 (1): 108- 119. |
| 13 |
Mazzola F , Smithers F , Cheng K , et al. Time and cost-analysis of virtual surgical planning for head and neck reconstruction: A matched pair analysis[J]. Oral Oncol, 2020, 100, 104491.
doi: 10.1016/j.oraloncology.2019.104491 |
| 14 |
Tarsitano A , Mazzoni S , Cipriani R , et al. The CAD/CAM technique for mandibular reconstruction: An 18 patients oncological case-series[J]. J Craniomaxillofac Surg, 2014, 42 (7): 1460- 1464.
doi: 10.1016/j.jcms.2014.04.011 |
| 15 |
Chang EI , Boukovalas S , Liu J , et al. Reconstruction of posterior mandibulectomy defects in the modern era of virtual planning and three-dimensional modeling[J]. Plast Reconstr Surg, 2019, 144 (3): 453- 462.
doi: 10.1097/PRS.0000000000005954 |
| 16 | 蔡志刚. 数字化外科技术在下颌骨缺损修复重建中的应用[J]. 中华口腔医学杂志, 2012, 47 (8): 474- 478. |
| 17 |
Yu HB , Shen GF , Wang XD , et al. The indication and application of computer-assisted navigation in oral and maxillofacial surgery: Shanghai' s experience based on 104 cases[J]. J Craniomaxillofac Surg, 2013, 41 (8): 770- 774.
doi: 10.1016/j.jcms.2013.01.016 |
| 18 |
Davies JC , Chan HH , Jozaghi Y , et al. Analysis of simulated mandibular reconstruction using a segmental mirroring technique[J]. J Craniomaxillofac Surg, 2019, 47 (3): 468- 472.
doi: 10.1016/j.jcms.2018.12.016 |
| [1] | 康一帆, 葛严军, 吕晓鸣, 谢尚, 单小峰, 蔡志刚. 即刻种植体支持式义齿修复的血管化髂骨瓣重建下颌骨缺损[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2025, 57(1): 78-84. |
| [2] | 王聪伟,高敏,于尧,章文博,彭歆. 游离腓骨瓣修复下颌骨缺损术后义齿修复的临床分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(1): 66-73. |
|
||