北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2025, Vol. 57 ›› Issue (4): 748-752. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2025.04.019
腹腔镜下改良经胆囊管胆管引流术在胆石症治疗及胆道疾病诊断中的应用
张铃福*, 王港*, 侯纯升*( ), 崔龙, 王立新, 凌晓锋, 徐智
), 崔龙, 王立新, 凌晓锋, 徐智
- 北京大学第三医院普通外科,北京 100191
Laparoscopic modified transcystic biliary drainage for the treatment of biliary stones and diagnosis of biliary disease
Lingfu ZHANG, Gang WANG, Chunsheng HOU*( ), Long CUI, Lixin WANG, Xiaofeng LING, Zhi XU
), Long CUI, Lixin WANG, Xiaofeng LING, Zhi XU
- Department of General Surgery, Peking University Third Hospital, Beijing 100191, China
摘要:
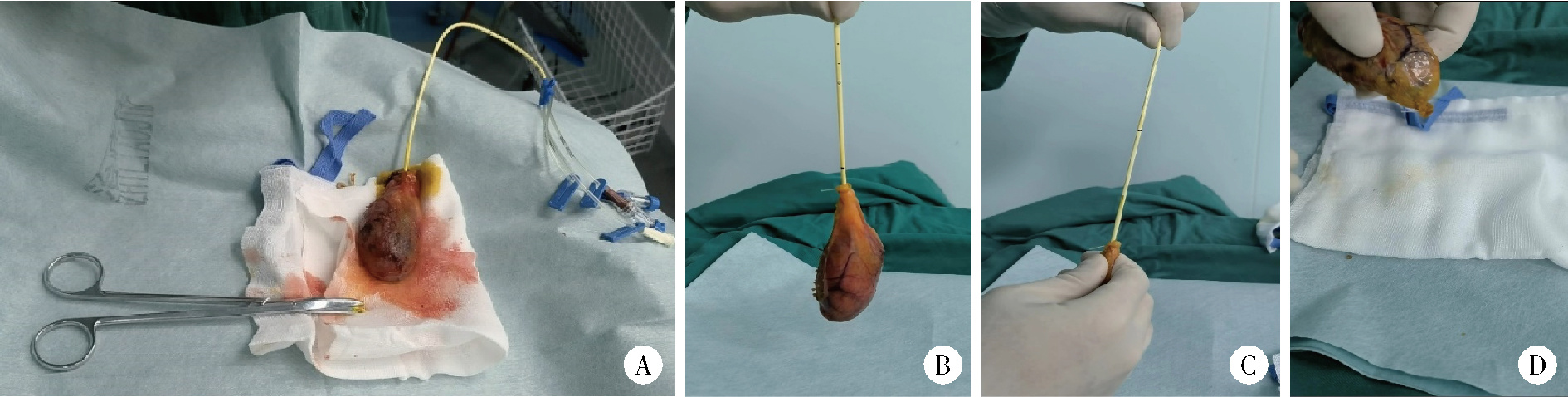
目的: 探讨腹腔镜下改良经胆囊管胆管引流术(改良C管技术)治疗胆石症的安全性及其在胆道疾病诊断中的应用。方法: 连续选择2021年8月至2023年12月于北京大学第三医院成功采用腹腔镜下改良C管技术治疗的所有胆石症患者的病例资料进行回顾性分析,共收集到患者68例,分析手术安全性、有效性及其应用领域。采用离体胆囊验证改良固定方法原理的可靠性。结果: 3例离体胆囊验证试验表明改良固定方法的固定强度可靠,即刻拔出C管后缝合形成的组织窦道可错位闭合,抵抗胆囊重量所致的胆汁流出。68例患者中,42例为复杂胆管结石,6例为可疑胆总管结石,5例为肝外胆管结石合并肝内胆管结石;其中48例行胆道镜辅助下胆总管切开取石,10例行胆道镜辅助下经胆囊管取石,6例行经胆囊管网篮探查取石(5例术后C管造影无结石残余;1例可疑结石残余,该患者无症状拒绝进一步检查和治疗),4例仅行经胆囊管胆道引流。2例腹腔镜手术后经C管药物辅助排石成功,7例腹腔镜手术后行C管辅助下内镜取石,效果良好。手术时间(131±44) min(76~279 min),C管单日最大引流量(401±235) mL(10~1150 mL),住院时间(8.6±3.6) d (2~19 d),C管拔管时间(11±6.9) d (5~46 d)。围手术期总体并发症14例,除2例残余结石,其余C管相关并发症12例(包括Ⅲa级1例,Ⅱ级2例,Ⅰ级9例)。未造成并发症的C管相关不良事件9例(包括早期脱落3例,移位2例,置入过深4例)。术后中位随访时间21(2~30)个月,5例患者再发结石,其中4例存在造影过程中造影剂流出缓慢,1例存在明显胰胆反流。55例患者行C管淀粉酶测定,意外发现9例胆汁淀粉酶明显升高(349~44 936 U/L),考虑存在胰胆反流。结论: 腹腔镜下改良C管技术可以有效应用于胆石症的治疗过程中,相对安全,也可尝试在胆道疾病的诊断中进行应用。
中图分类号:
- R657.4
| 1 |
管辉球, 景岚, 徐锁青. 胆总管一期缝合经胆囊管胆管引流与鼻胆管引流的对比研究[J]. 中华外科杂志, 2018, 56 (2): 130- 134.
|
| 2 |
|
| 3 |
张铃福, 侯纯升, 徐智, 等. 腹腔镜下经胆囊管胆管引流联合胆总管探查取石术治疗复杂胆管结石的临床效果[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54 (6): 1185- 1189.
doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2022.06.021 |
| 4 |
张铃福, 辛春艳, 王立新, 等. 腹腔镜改进C管技术联合术后十二指肠镜下取石治疗急诊胆囊结石合并胆总管结石[J]. 中国微创外科杂志, 2023, 23 (4): 294- 297.
|
| 5 |
|
| 6 |
|
| 7 |
|
| 8 |
|
| [1] | 黄万伟, 沙显燊, 张艺宝, 伍国豪, 骆峰, 陈智慧, 叶东明, 李学松, 赖彩永. 完全3D腹腔镜回肠代双侧输尿管联合膀胱扩大术修复放射治疗后双侧输尿管狭窄并膀胱挛缩[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2025, 57(4): 789-795. |
| [2] | 毛海,张帆,张展奕,颜野,郝一昌,黄毅,马潞林,褚红玲,张树栋. 基于MRI前列腺腺体相关参数构建腹腔镜前列腺癌术后尿失禁的预测模型[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(5): 818-824. |
| [3] | 张铃福,侯纯升,徐智,王立新,凌晓锋,王港,崔龙,修典荣. 腹腔镜下经胆囊管胆管引流联合胆总管探查取石术治疗复杂胆管结石的临床效果[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(6): 1185-1189. |
| [4] | 马闰卓,夏海缀,陆敏,张智荧,张启鸣,卢剑,王国良,马潞林. 输尿管镜活体组织检查对上尿路尿路上皮癌根治性手术的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2019, 51(4): 665-672. |
| [5] | 张铃福,侯纯升,黄永辉,徐智,王立新,凌晓锋,王港,崔龙,修典荣. 胃空肠吻合术后胆总管结石腹腔镜手术取石和内镜取石的比较[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2019, 51(2): 345-348. |
| [6] | 叶雄俊,刘军,阿不都克依木·阿不力米提,熊六林,刘士军,徐涛,黄晓波. 后腹腔镜联合经腰小切口“杂交”手术在复杂肾肿瘤保留肾单位手术中的应用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2017, 49(4): 613-616. |
| [7] | 李学松, 周利群, 唐琦, 张争. 联合后腹腔及经腹入路腹腔镜技术在肾癌伴下腔静脉瘤栓患者中的应用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2015, 47(4): 569-570. |
|
||