北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2025, Vol. 57 ›› Issue (6): 1042-1050. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2025.06.005
非靶向代谢组学揭示原发性干燥综合征血小板减少患者血清差异代谢物及代谢通路
- 1. 达州市中心医院风湿免疫科,四川达州 625000
2. 绵阳市中心医院风湿免疫科,四川绵阳 621000
Untargeted metabolomics reveals differential serum metabolites and metabolic pathways in patients with primary Sjögren syndrome and thrombocytopenia
Zhao XIANG1, Li YANG2, Jing YANG2,*( )
)
- 1. Department of Rheumatology and Immunology, Dazhou Central Hospital, Dazhou 625000, Sichuan, China
2. Department of Rheumatology and Immunology, Mianyang Central Hospital, Mianyang 621000, Sichuan, China
摘要:
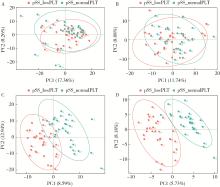
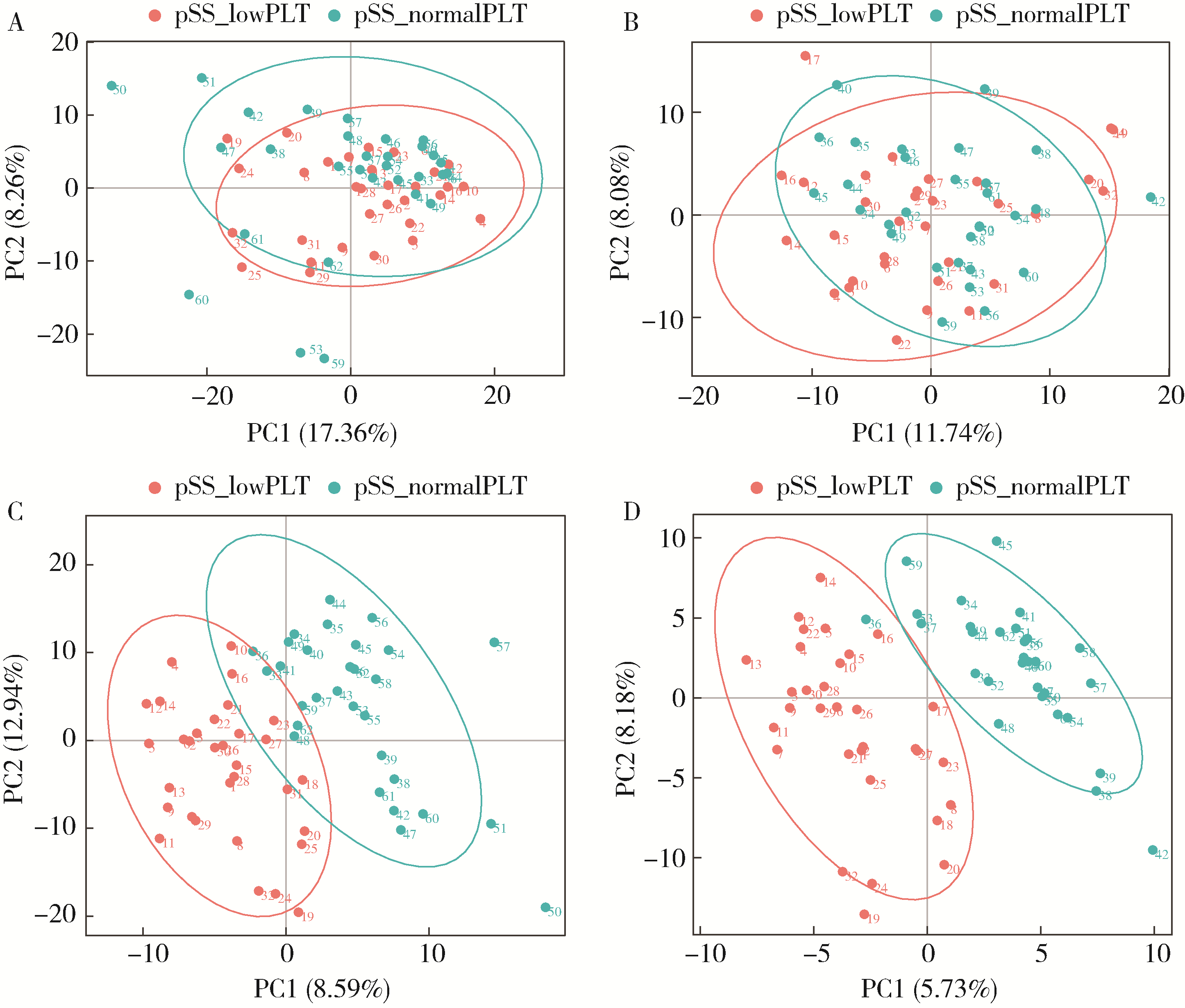
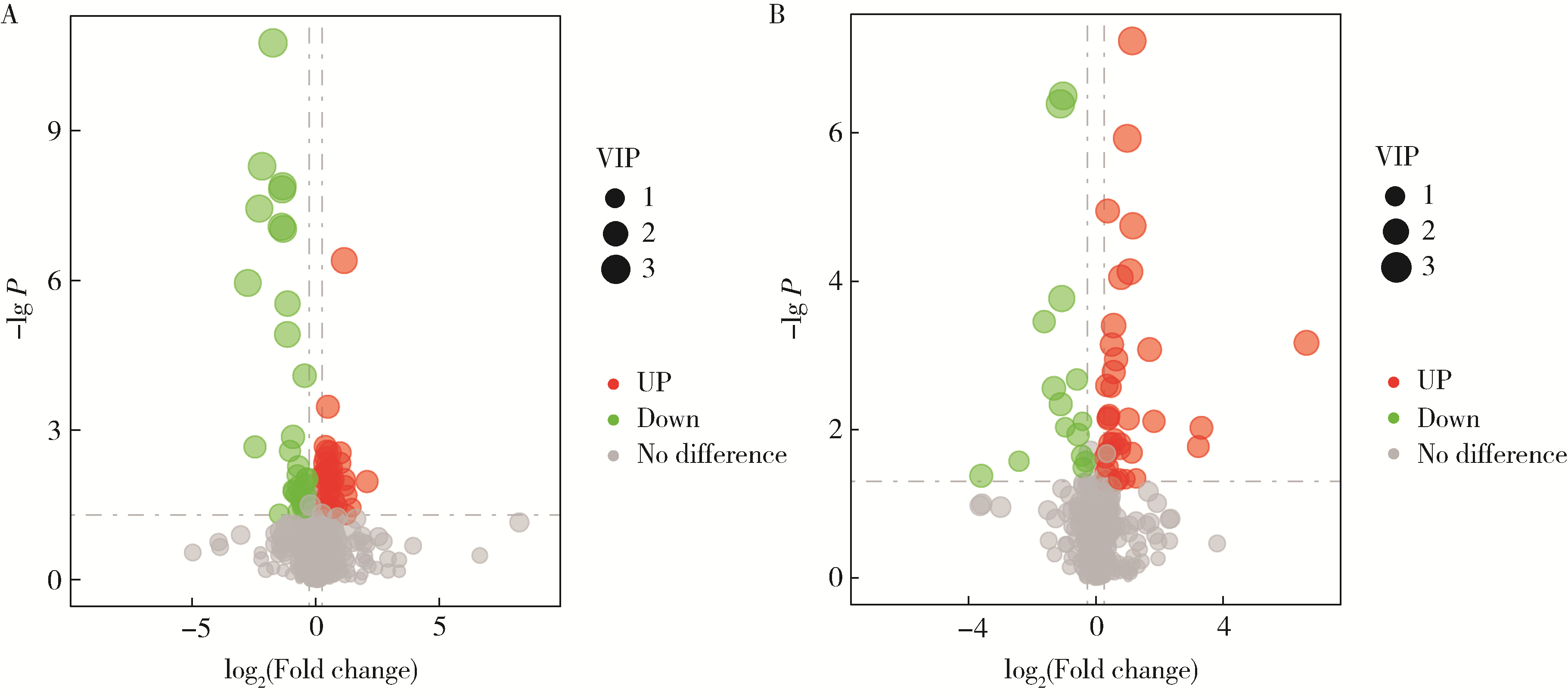
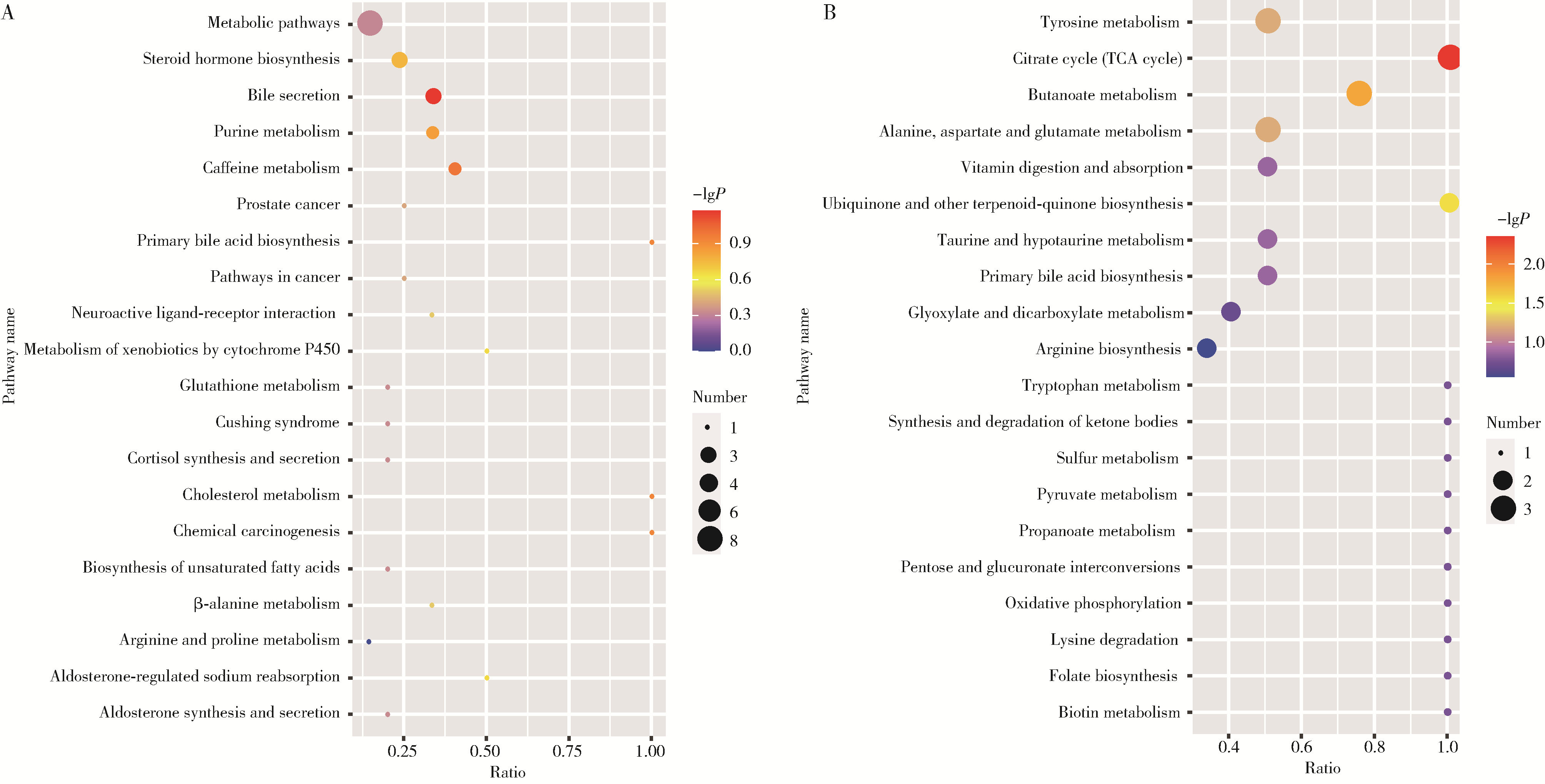
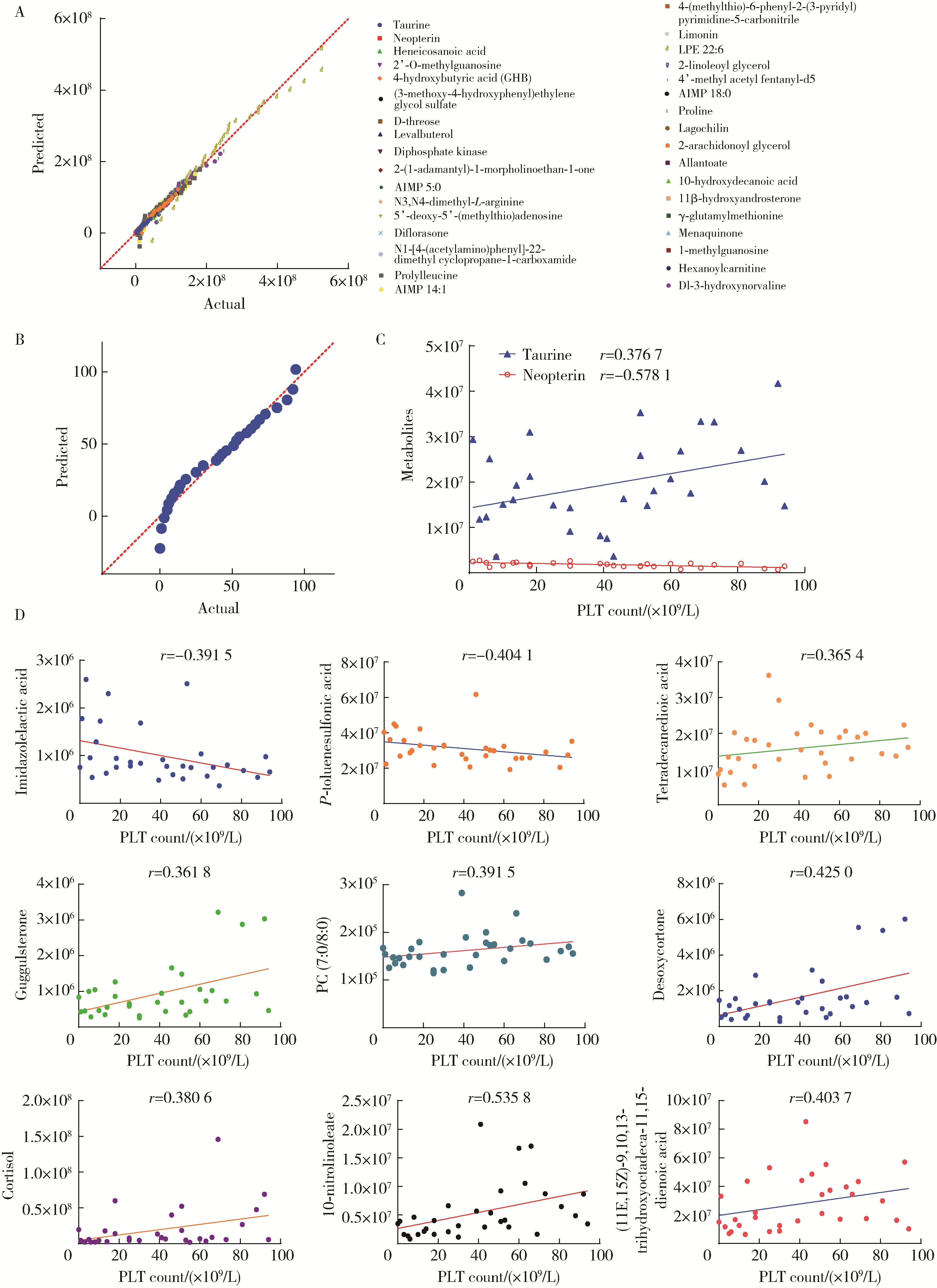
目的: 通过非靶向代谢组学技术,系统比较原发性干燥综合征(primary Sjögren syndrome,pSS)血小板减少与血小板正常患者的血清代谢谱差异,鉴定出差异代谢物,分析差异代谢物的相对定量与血小板数量之间的关系,筛选出与pSS血小板减少患者的血小板数量相关的代谢途径。方法: 将pSS患者根据有无血小板减少分组,收集患者血清样本,采用液相色谱-质谱联用(liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry,LC-MS)技术对样品进行分析。通过人类代谢组学数据库(human metabolome database,HMDB)、脂质代谢途径研究计划(lipid metabolites and pathways strategy,LIPID MAPS)等数据库进行分类注释;采用主成分分析(principal component analysis,PCA)和偏最小二乘判别分析(partial least squares discriminant analysis,PLS-DA)进行多元统计分析,筛选出组间差异代谢物。基于京都基因和基因组百科全书(Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes,KEGG)进行富集分析,研究代谢物的功能和代谢途径。对pSS伴血小板减少患者的血清差异代谢物的表达量与血小板计数进行相关性分析。结果: 共纳入62例pSS患者,其中32例伴有血小板减少,30例血小板正常。与pSS不伴血小板减少患者相比,pSS伴有血小板减少患者血清中一共有137种差异表达的代谢物,分别富集于54条代谢途径。其中,去氧皮质酮、氢化可的松、牛磺酸的表达量与血小板计数呈正相关,新蝶呤的表达量与血小板计数呈负相关。富集分析显示,去氧皮质酮和氢化可的松富集于类固醇激素生物合成途径,牛磺酸富集于牛磺酸和亚牛磺酸的代谢途径,新蝶呤富集于叶酸生物合成途径。结论: pSS患者血小板减少可能与类固醇激素生物合成途径、牛磺酸和亚牛磺酸代谢途径活性减弱以及叶酸生物合成途径活性增强有关。
中图分类号:
- R593.2
| 1 |
doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-23472-7 |
| 2 |
doi: 10.1056/NEJMcp1702514 |
| 3 |
|
| 4 |
doi: 10.1002/acr.21610 |
| 5 |
王英, 蓝晶莹, 石桂秀. 原发性干燥综合征重度血小板减少患者的临床及免疫学特点分析[J]. 内科急危重症杂志, 2022, 28(2): 103- 107.
|
| 6 |
秦伟, 李四强. 自身免疫性疾病介导的血小板减少机制研究进展[J]. 中国基层医药, 2019, 26(23): 2941- 2944.
|
| 7 |
doi: 10.1002/rth2.12691 |
| 8 |
|
| 9 |
doi: 10.1177/0961203314547796 |
| 10 |
薛媛, 徐东, 李梦涛, 等. 原发性干燥综合征合并严重血小板减少症患者的治疗反应预测[J]. 中华内科杂志, 2019, 58(4): 282- 287.
|
| 11 |
doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2019-216114 |
| 12 |
doi: 10.1007/s00296-010-1395-4 |
| 13 |
doi: 10.1080/09537104.2019.1678121 |
| 14 |
|
| 15 |
doi: 10.1038/nbt.4101 |
| 16 |
doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2019.11.009 |
| 17 |
doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/keaa456 |
| 18 |
doi: 10.3390/ijms22168997 |
| 19 |
doi: 10.1021/acs.jproteome.0c00179 |
| 20 |
张紫妍. 基于GC-MS的ITP患者的血浆代谢组学研究[D]. 苏州: 苏州大学, 2021.
|
| 21 |
doi: 10.3390/ijms23147978 |
| 22 |
doi: 10.1002/art.39859 |
| 23 |
doi: 10.1080/17512433.2021.1903315 |
| 24 |
doi: 10.1038/srep31424 |
| 25 |
doi: 10.1038/ncomms5753 |
| 26 |
doi: 10.1038/nature07762 |
| 27 |
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0159384 |
| 28 |
doi: 10.1007/s10067-018-4021-6 |
| 29 |
|
| 30 |
doi: 10.1101/gad.1128003 |
| 31 |
|
| 32 |
|
| 33 |
doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1974.tb09707.x |
| 34 |
doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2017.06.079 |
| 35 |
doi: 10.1016/j.pathophys.2018.04.001 |
| 36 |
doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.586527 |
| 37 |
doi: 10.1053/j.sult.2013.12.001 |
| 38 |
|
| [1] | 刘源, 石桂秀. 干燥综合征到干燥病的命名变迁[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2025, 57(6): 1015-1017. |
| [2] | 林文灏, 谢阳, 王芳晴, 王淑盈, 刘香君, 胡凡磊, 贾园. 基于B细胞单细胞转录组测序的干燥综合征分子分型[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2025, 57(6): 1032-1041. |
| [3] | 赵亚云, 倪梦凡, 李雪, 王蓓, 程功, 何菁, 金月波. 利妥昔单抗治疗原发性干燥综合征肾损害的临床疗效和安全性[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2025, 57(6): 1051-1060. |
| [4] | 朱丽秀, 陈仁利, 周素娟, 林烨, 汤一榕, 叶桢. 水通道蛋白5对干燥综合征大鼠TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB信号的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2025, 57(5): 875-883. |
| [5] | 包振英, 王雅杰. 炎症指标和细胞因子联合检测在慢性牙周炎中的应用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2025, 57(4): 772-778. |
| [6] | 宁圆, 张晓盈, 李雪, 李原, 何菁, 金月波. 干燥综合征并发乳腺淋巴瘤1例[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2025, 57(4): 808-811. |
| [7] | 杨玉淑, 齐晅, 丁萌, 王炜, 郭惠芳, 高丽霞. 抗唾液腺蛋白1抗体联合抗腮腺分泌蛋白抗体对干燥综合征的诊断价值[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(5): 845-852. |
| [8] | 王鹏,杨子瑶,王萌,王巍,李爱芝. 2例罕见RhD变异型RHD*DEL37的分子生物学分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(2): 352-356. |
| [9] | 韩艺钧,李常虹,陈秀英,赵金霞. 抗SSB抗体阳性和阴性的原发性干燥综合征患者临床及免疫学特征的比较[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(6): 1000-1006. |
| [10] | 李建斌,吕梦娜,池强,彭一琳,刘鹏程,吴锐. 干燥综合征患者发生重症新型冠状病毒肺炎的早期预测[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(6): 1007-1012. |
| [11] | 孟彦宏,陈怡帆,周培茹. CENP-B抗体阳性的原发性干燥综合征患者的临床和免疫学特征[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(6): 1088-1096. |
| [12] | 吴洁,张雯,梁舒,秦艺璐,范文强. 妊娠期原发性干燥综合征合并视神经脊髓炎谱系疾病危重症1例[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(6): 1118-1124. |
| [13] | 王丽芳,石连杰,宁武,高乃姝,王宽婷. 干燥综合征合并冷凝集素病1例[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(6): 1130-1134. |
| [14] | 邢海霞,王琳,乔迪,刘畅,潘洁. 干燥综合征口腔疾病的治疗特点[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(5): 929-933. |
| [15] | 曹钟,岑红兵,赵建红,梅俊,秦灵芝,廖伟,敖启林. 胰腺神经内分泌肿瘤和实性假乳头状肿瘤中INSM1和SOX11的表达及意义[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(4): 575-581. |
|
||