1 病例资料
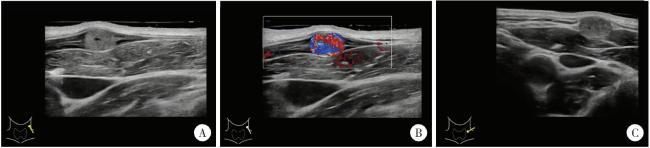
图1 IPEH患者的超声影像Figure 1 Ultrasound imaging of the patient with IPEH A, a hypoechoic nodule with clear, incompressible borders was seen in a local superficial vein; B, color doppler imageing shows rich blood flow signal; C, adjacency of the nodule to the surrounding neck vessels.IPEH, intravascular papillary endothelial hyperplasia. |
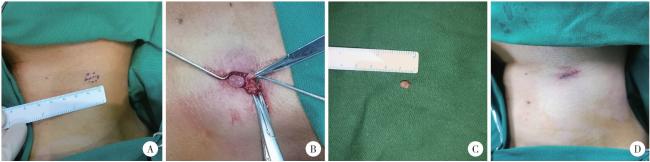
图2 IPEH患者术中情况Figure 2 Intraoperative situation of the patient with IPEH A, tumor range and incision design line; B, herniation of a mass after blunt separation of the left sternocleidomastoid muscle; C, isolated mass specimen; D, wound condition after suture. IPEH, intravascular papillary endothelial hyperplasia. |
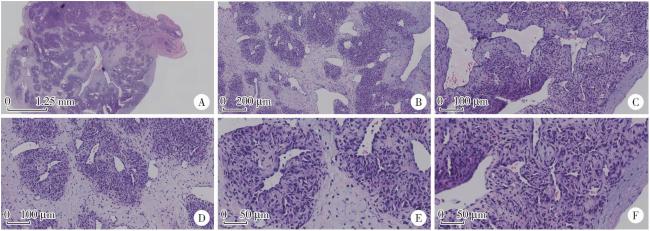
图3 IPEH的病理特点Figure 3 Pathological microscopic features of IPEH A, full view of intravascular tumor (20×); B, vascular endothelial hyperplasia, fibrous tissue hyperplasia, fibrous interstitial hyperplasia and recanalized vessels (40×); C, papillary structure (200×); D, endothelial lining fissures and papillary hyperplasia (200×); E, no obvious polymorphism of endothelial cells (400×); F, papillary structure (400×).IPEH, intravascular papillary endothelial hyperplasia. |