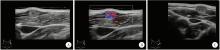
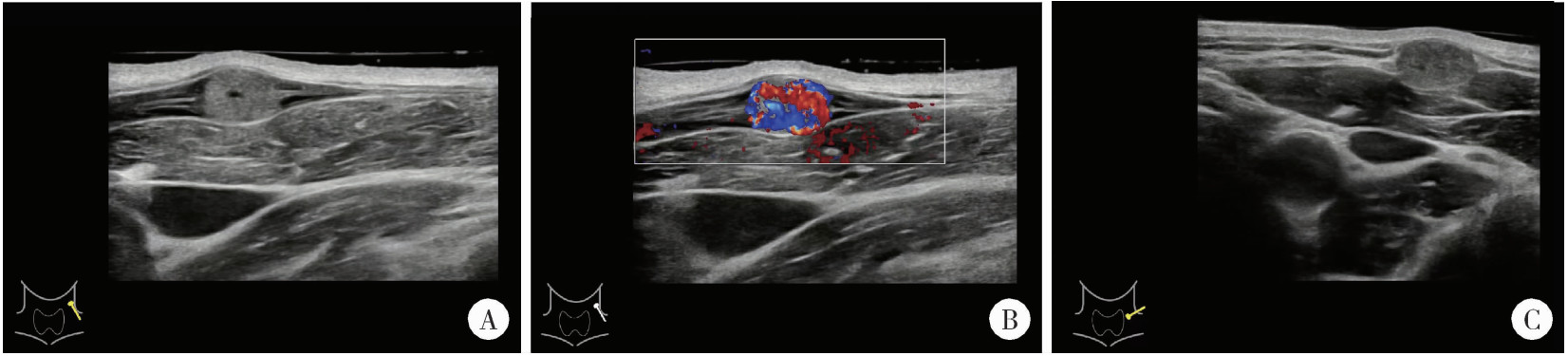
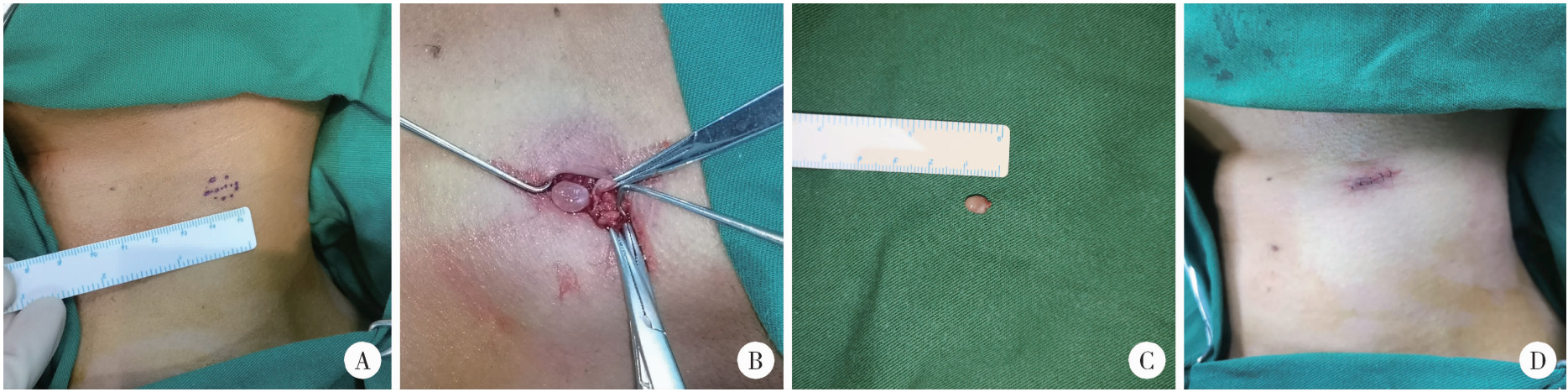
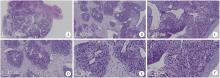
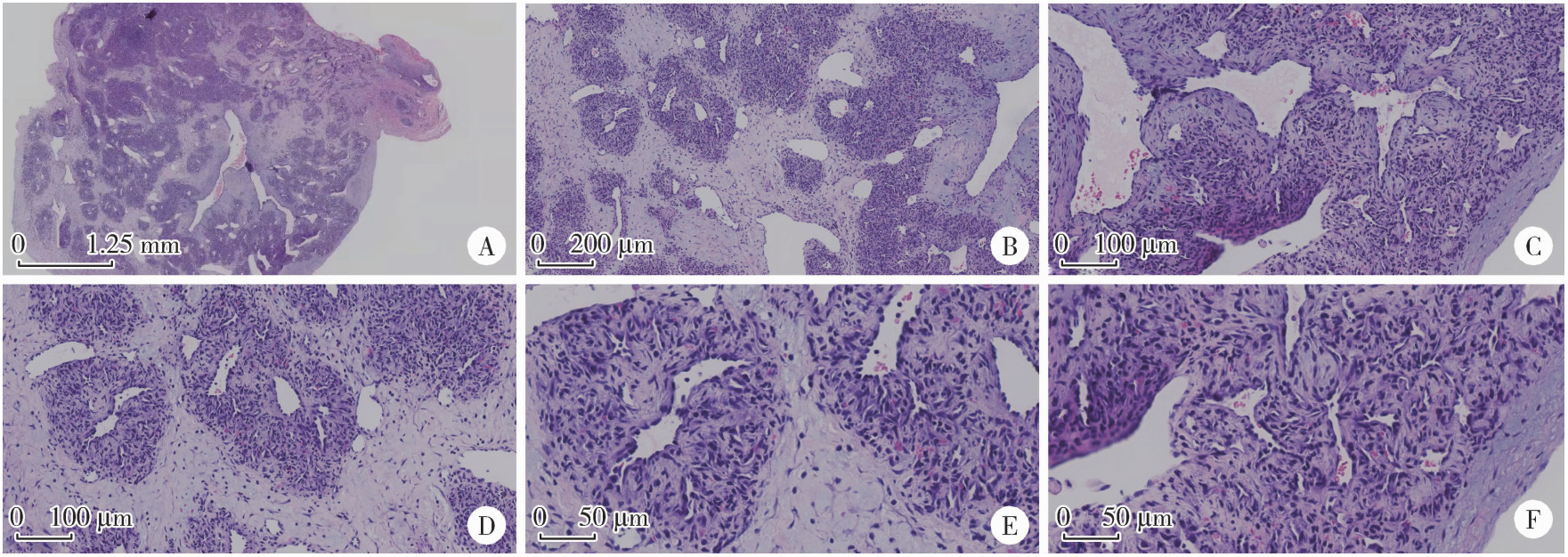
北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2025, Vol. 57 ›› Issue (5): 1002-1004. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2025.05.028
左侧胸锁乳突肌间血管内乳头状内皮增生1例
- 1. 北京大学第三医院成形外科, 北京 100191
2. 北京大学第三医院病理科, 北京 100191
3. 北京大学第三医院超声科, 北京 100191
Left sided sternocleidomastoid interosseous intravascular papillary endothelial hyperplasia: A case report
Xiaodi XIAO1, Youchen XIA1, Jianying LIU2, Peng FU3,*( )
)
- 1. Department of Plastic Surgery, Peking University Third Hospital, Beijing 100191, China
2. Department of Pathology, Peking University Third Hospital, Beijing 100191, China
3. Department of Ultrasound, Peking University Third Hospital, Beijing 100191, China
中图分类号:
- R730.262
| 1 |
doi: 10.7181/acfs.2018.02208 |
| 2 |
|
| 3 |
doi: 10.1055/s-0039-1688925 |
| 4 |
doi: 10.3892/mco.2016.1117 |
| 5 |
doi: 10.1016/j.tripleo.2008.08.011 |
| 6 |
doi: 10.1007/s00256-015-2281-7 |
| 7 |
|
| 8 |
doi: 10.1016/0363-5023(94)90256-9 |
| 9 |
doi: 10.1097/00000372-198312000-00004 |
| 10 |
doi: 10.1016/j.joms.2005.11.095 |
| [1] | 左超, 王国立, 杨昆霖, 车新艳, 孟一森, 张凯. 前列腺体积不同的患者经尿道光纤铥激光前列腺剜除术的有效性及安全性比较[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2025, 57(4): 711-716. |
| [2] | 朱慧, 闵赛南, 苏家增, 陈艳, 彭歆, 于尧, 俞光岩. 口腔黏膜嗜酸性溃疡的临床病理分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2025, 57(3): 620-625. |
| [3] | 刘宁, 满立波, 何峰, 黄广林, 翟建坡. 良性前列腺增生患者排尿中断症状与尿动力学指标的相关性[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2025, 57(2): 328-333. |
| [4] | 钟华, 李原, 徐丽玲, 白明欣, 苏茵. 18F-FDG PET/CT在风湿免疫病中的应用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(5): 853-859. |
| [5] | 刘菊梅,梁丽,张继新,戎龙,张梓怡,吴悠,赵旭东,李挺. 411例早期胃癌及癌前病变内镜黏膜下剥离术标本的病理学评估[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(2): 299-307. |
| [6] | 哈雪梅,姚永正,孙莉华,辛春杨,熊焰. 实性肺胎盘样变形1例及文献复习[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(2): 357-361. |
| [7] | 森本智惠子,王益勤,周蓉,王建六. 子宫内膜非典型增生及子宫内膜癌患者保留生育功能治疗的临床研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(5): 936-942. |
| [8] | 翟莉,邱楠,宋惠. 多中心网状组织细胞增生症1例[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(6): 1183-1187. |
| [9] | 刘可,张帆,肖春雷,夏海缀,郝一昌,毕海,赵磊,刘余庆,卢剑,马潞林. 低功率钬激光“七步两叶法”前列腺剜除术治疗良性前列腺增生[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2019, 51(6): 1159-1164. |
| [10] | 卢昕,张立宁. 肌活检在特发性炎性肌病诊断和临床分型中的价值[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2018, 50(6): 949-951. |
| [11] | 孙佳鹏,卢新天,赵卫红,华瑛. 自身免疫性淋巴细胞增生综合征1例并文献复习[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2015, 47(6): 1022-1027. |
| [12] | 刘宁, 黄广林, 满立波, 何峰, 王海东, 王海, 李贵忠, 王建伟. 缩短钬激光前列腺剜除术学习曲线的方法[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2015, 47(4): 720-723. |
| [13] | 胡浩, 许克新, 张晓鹏, 方志伟, 陈京文, 霍飞, 王栋, 王晓峰. 伴有膀胱过度活动症症状的良性前列腺增生患者尿液中脑源性神经营养因子的表达[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2014, 46(4): 519-523. |
| [14] | 张峰波, 邵强, 田野. 二极管激光与铥激光经尿道前列腺剜除术治疗良性前列腺增生的应用比较[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2013, 45(4): 592-. |
| [15] | 翟国君, 姚伟娟, 贾子昌, 韩金涛, 赵军, 李选, 董国祥. 静脉人工血管桥内膜增生的形态学特征及洛伐他汀的干预作用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2012, 44(5): 783-787. |
|
||