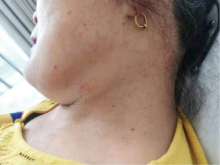
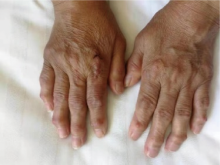
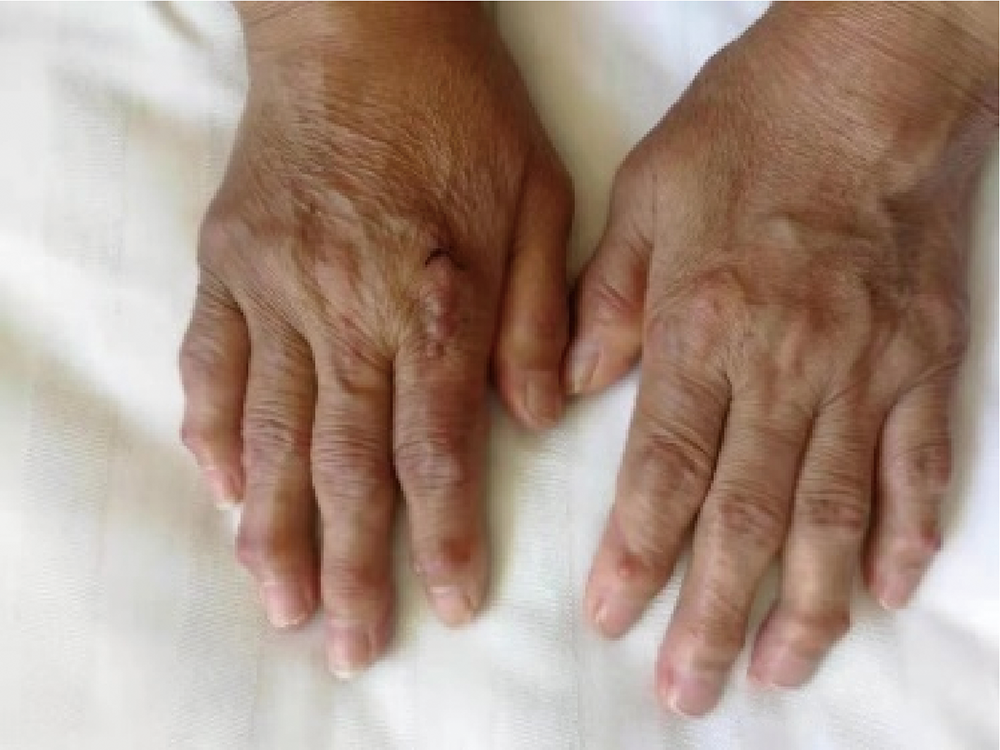
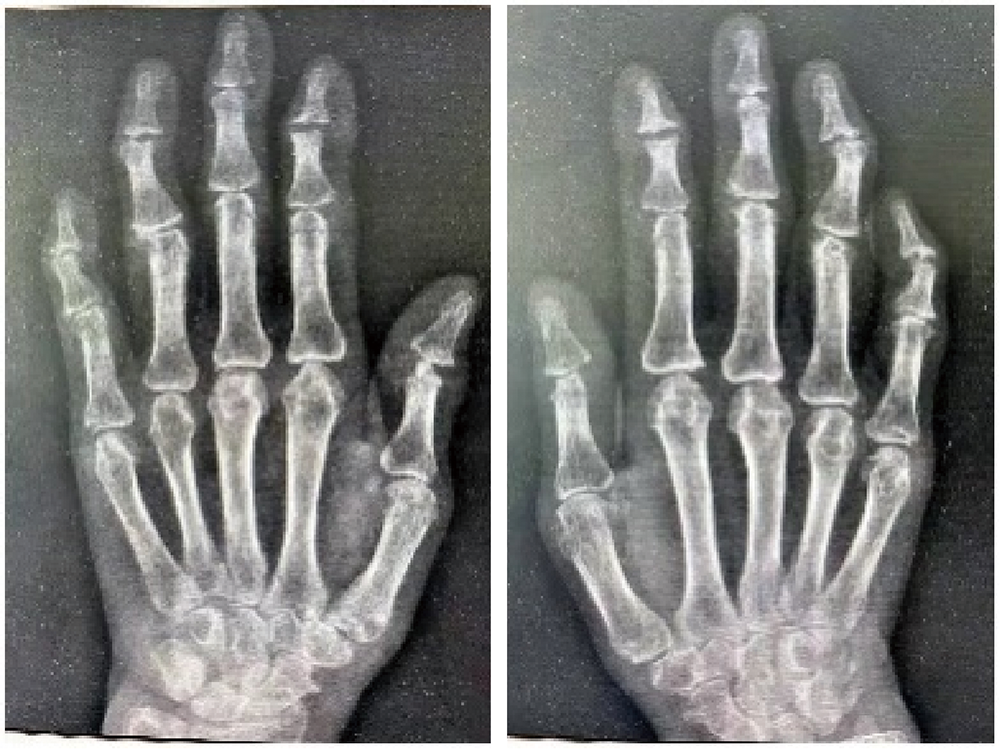
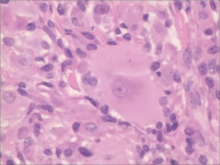
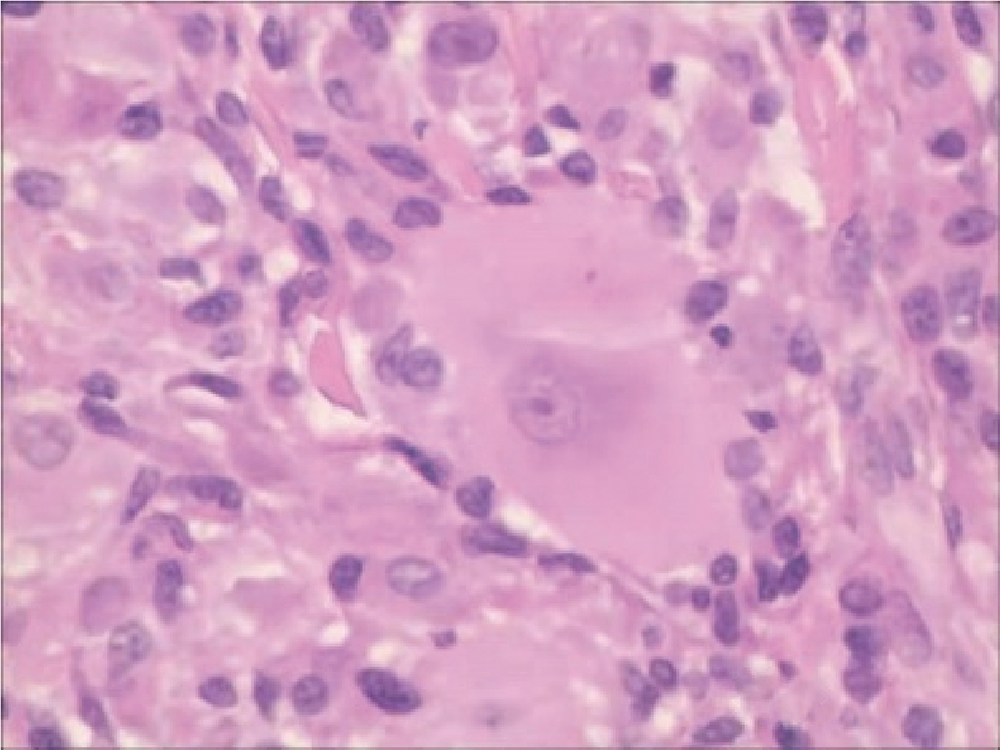
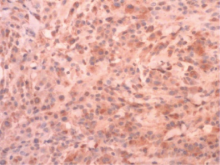
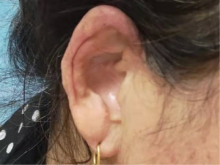
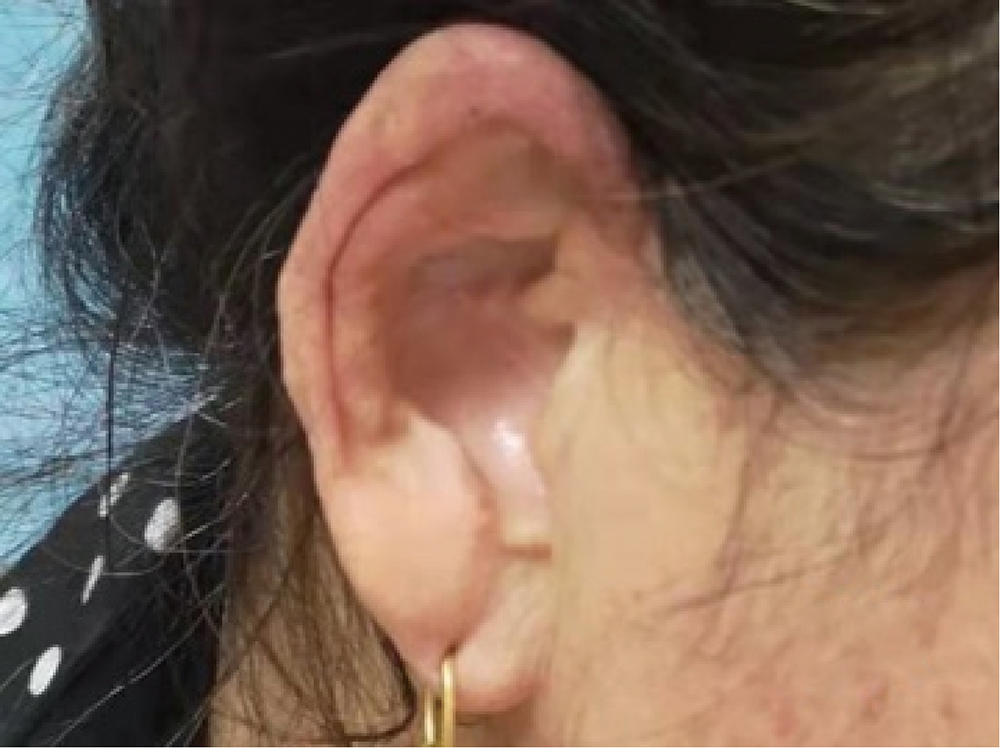
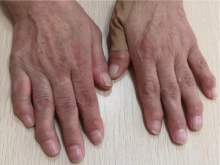
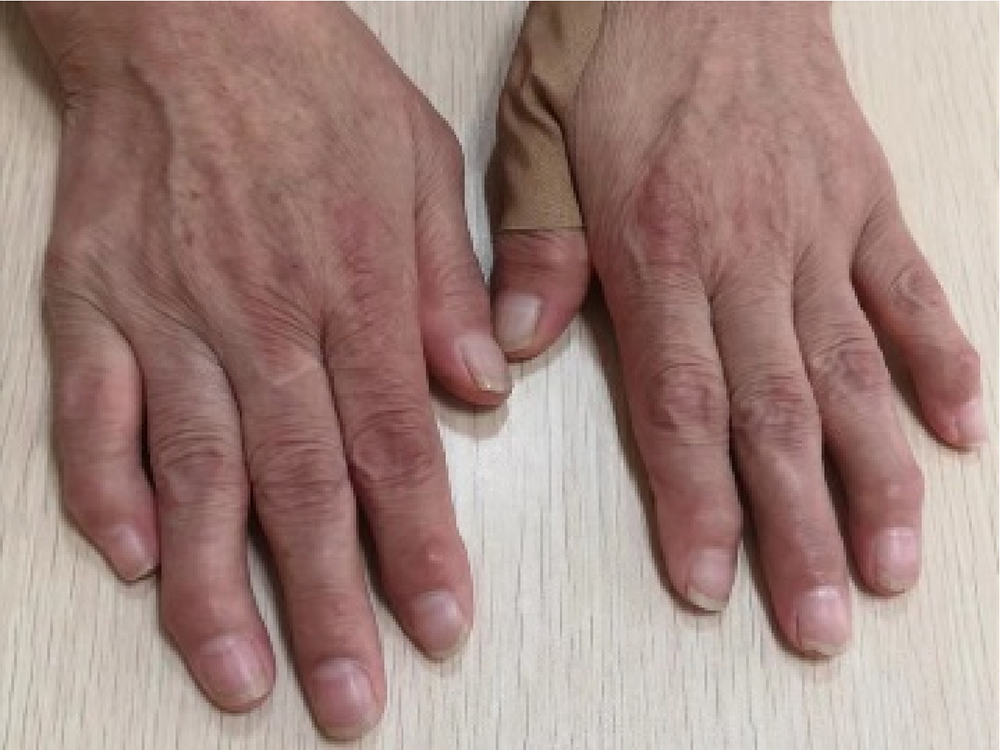
北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2021, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (6): 1183-1187. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2021.06.029
多中心网状组织细胞增生症1例
- 1.中国人民解放军联勤保障部队第960医院,山东泰安 271000
2.泰安市中心医院中医科,山东泰安 271000
Multicentric reticulohistiocytosis: A case report
ZHAI Li1,QIU Nan1,SONG Hui2,△( )
)
- 1. Department of Rheumatology and Immunology, The 960th Hospital of the PLA Joint Logistics Support Force, Tai’an 271000, Shandong, China
2. Department of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Taian City Central Hospital, Tai’an 271000, Shandong, China
中图分类号:
- R59
| [1] | 王白鹤, 惠云, 苑春雨, 等. 多中心网状组织细胞增生症一例[J]. 中国麻风皮肤病杂志, 2018, 34(9):550-552. |
| [2] |
Luz FB, Gaspar TAP, Kalil-Gaspar N, et al. Multicentric reticulohistiocytosis[J]. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol, 2001, 15(6):524-531.
pmid: 11843211 |
| [3] |
Tajirian AL, Malik MK, Robinson-Bostom L, et al. Multicentric reticulohistiocytosis[J]. Clin Dermatol, 2006, 24(6):486-492.
pmid: 17113966 |
| [4] |
Tariq S, Hugenberg ST, Hirano-Ali SA, et al. Multicentric reticulohistiocytosis (MRH): Case report with review of literature between 1991 and 2014 with in depth analysis of various treatment regimens and outcomes[J]. Springerplus, 2016, 5(1):180.
doi: 10.1186/s40064-016-1874-5 |
| [5] |
Sanchez-Alvarez C, Sandhu AS, Crowson CS, et al. Multicentric reticulohistiocytosis: The Mayo clinic experience (1980-2017)[J]. Rheumatology(Oxford), 2020, 59(8):1898-1905.
doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/kez555 |
| [6] | 李慧娟, 王立, 侯勇, 等. 多中心网状组织细胞增生症8例临床特征[J]. 中华临床免疫和变态反应杂志, 2015, 9(3):213-217. |
| [7] |
Lu YY, Lu CC, Wu CH. Leonine facies in the cutaneous form of multicentric reticulohistiocytosis[J]. Intern Med, 2012, 51(15):2069-2070.
doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.51.8119 |
| [8] |
Islam AD, Naguwa SM, Cheema GS, et al. Multicentric reticulohistiocytosis: A rare yet challenging disease[J]. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol, 2013, 45(2):281-289.
doi: 10.1007/s12016-013-8362-2 |
| [9] |
Gorman JD, Danning C, Schumacher HR, et al. Multicentric reticulohistiocytosis: Case report with immunohistochemical analysis and literature review[J]. Arthritis Rheum, 2000, 43(4):930-938.
doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(200004)43:4<930::AID-ANR27>3.0.CO;2-A |
| [10] | Yamamoto T. Skin manifestation associated with multicentric reticulohistiocytosis[J/OL]. J Clin Rheumatol, 2020(2020-12-15)[2021-08-01]. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33337805/. |
| [11] |
El-Haddad B, Hammoud D, Shaver T, et al. Malignancy-associated multicentric reticulohistiocytosis[J]. Rheumatol Int, 2011, 31(9):1235-1238.
doi: 10.1007/s00296-009-1287-7 pmid: 20012625 |
| [12] | 白丽杰, 李鸿斌, 徐晓艳. 多中心网状组织细胞增多症1例并文献复习[J]. 临床荟萃, 2015, 30(7):831-832. |
| [13] |
Zhao H, Wu C, Wu M, et al. Tumor necrosis factor antagonists in the treatment of multicentric reticulohistiocytosis: Current clinical evidence[J]. Mol Med Rep, 2016, 14(1):209-217.
doi: 10.3892/mmr.2016.5253 |
| [14] | Lim K, D’Souza J, Vasquez JB, et al. Looks can be deceiving: A case report on multicentric reticulohistiocytosis successfully treated with rituximab[J]. Cureus, 2017, 9(5):e1220. |
| [15] |
Pacheco-Tena C, Reyes-Cordero G, Ochoa-Albíztegui R, et al. Treatment of multicentric reticulohistiocytosis with tocilizumab[J]. J Clin Rheumatol, 2013, 19(5):272-276.
doi: 10.1097/RHU.0b013e31829cf32b pmid: 23872542 |
| [16] |
Aouba A, Leclerc-Mercier S, Fraitag S, et al. Assessment and effective targeting of Interleukin-1 in multicentric reticulohistyo-cytosis[J]. Joint Bone Spine, 2015, 82(4):280-283.
doi: 10.1016/j.jbspin.2015.02.003 |
| [1] | 陈心心, 唐哲, 乔艳春, 荣文笙. 北京市密云区4岁儿童患龋状况及其与龋活跃性检测的相关性[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(5): 833-838. |
| [2] | 钟华, 李原, 徐丽玲, 白明欣, 苏茵. 18F-FDG PET/CT在风湿免疫病中的应用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(5): 853-859. |
| [3] | 刘家骏, 刘国康, 朱玉虎. 免疫相关性重症肺炎1例[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(5): 932-937. |
| [4] | 黄教悌,胡菁,韩博. 治疗相关神经内分泌前列腺癌机制研究与靶向治疗新进展[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 557-561. |
| [5] | 李正芳,罗采南,武丽君,吴雪,孟新艳,陈晓梅,石亚妹,钟岩. 抗氨基甲酰化蛋白抗体在诊断类风湿关节炎中的应用价值[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 729-734. |
| [6] | 侯婉音,董捷. 腹膜透析患者获得性肾囊肿出血3例[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(3): 546-550. |
| [7] | 李文菁,张保宙,李恒,赖良鹏,杜辉,孙宁,龚晓峰,李莹,王岩,武勇. 胫距跟融合治疗终末期踝和后足病变的中短期临床结果[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(2): 299-306. |
| [8] | 冯琦琛,盖铄,王昌明,李选. 经同侧大隐静脉入路髂静脉成型及支架植入术在日间治疗模式中的应用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(2): 322-325. |
| [9] | 彭圣嘉,祁雨,孙丽杰,李丹,王新宇,韩江莉,陈宝霞,张媛. 传入压力反射衰竭合并低钠血症1例[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(2): 357-361. |
| [10] | 陈晨,梁宇红. 复杂根管上颌磨牙的根管治疗3例[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(1): 190-195. |
| [11] | 任晓萌,李凯一,李春蕾. 基于转录组测序探索口腔扁平苔藓局部激素治疗敏感性相关分子特征[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(1): 32-38. |
| [12] | 张晗,秦亦瑄,韦帝远,韩劼. 牙周炎患者种植修复维护治疗依从性的影响因素[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(1): 39-44. |
| [13] | 周颖,赵宁,黄竑远,李庆祥,郭传瑸,郭玉兴. 双层软组织缝合封闭技术在下颌骨中早期药物相关性颌骨骨坏死患者手术治疗中的应用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(1): 51-56. |
| [14] | 邹雪,白小娟,张丽卿. 艾拉莫德联合托法替布治疗难治性中重度类风湿关节炎的疗效[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(6): 1013-1021. |
| [15] | 姚海红,杨帆,唐素玫,张霞,何菁,贾园. 系统性红斑狼疮及成人Still病合并巨噬细胞活化综合征的临床特点及诊断指标[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(6): 966-974. |
|
||